微污染源水的混凝處理及絮體粒徑研究
夏瑋 張蕊 吳根宇 馬江雅
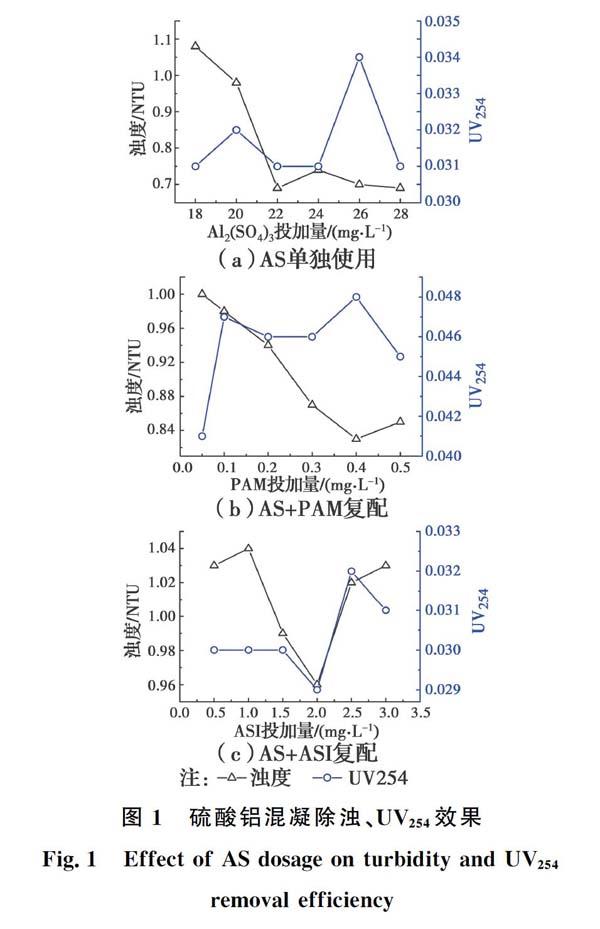


摘要:微污染源水的處理已經成為一個重要課題并在全世界范圍內引起廣泛關注,其中的濁度、腐殖質等影響到了飲用水水質。混凝是一種安全、實用、高效的水處理技術,而混凝劑是混凝技術的核心,選擇一種合適的混凝劑至關重要。以硫酸鋁(AS)、聚合氯化鋁(PAC)、氯化鐵、聚合氯化鐵(PFC)等4種混凝劑處理微污染源水,再分別與助凝劑PAM、活化硅酸(ASI)復配使用,PAM與ASI具有較好的吸附架橋能力,大大提高了絮凝效率。通過檢測濁度、UV254、絮體粒徑3個指標,得出這4種混凝劑單獨使用時的最佳投加量分別為22、18、16、8 mg/L;與PAM復配使用時PAM的最佳投加量分別為0.1、0.1、0.05、0.2 mg/L;與ASI復配使用時ASI的最佳投加量分別為0.5、1.5、1.0、1.0 mg/L。另外,自然水體中有機物的降解會產生腐殖酸,從而污染水質。分別使用聚丙烯酰胺(PAM)、PAC以及兩者復配,通過檢測混凝后的UV254以及絮體粒徑指標,得出PAM、PAC單獨使用時的最佳投加量分別為8、100 mg/L,PAM與PAC復配時PAM的最佳投加量為0.8 mg/L,證明復配可在低投加量下有效增強混凝效果。
關鍵詞:混凝;微污染源水;腐殖酸廢水;絮體粒徑
中圖分類號:X703.5;TU991.22 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:20966717(2020)04018509
收稿日期:20191101
基金項目:國家自然科學基金(51878001、51408004);安徽省高校自然科學研究項目(KJ2018A0044)
作者簡介:夏瑋(1995 ),女,主要從事混凝水處理研究,Email:xwvampire@163.com。
馬江雅(通信作者),男,副教授,Email:majiang_ya@126.com。
Received:20191101
Foundation items:National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51878001, 51408004); Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Province (No. KJ2018A0044)
Author brief:Xia Wei (1995 ), main research interest: coagulation water treatment, Email: xwvampire@163.com.
Ma Jiangya (corresponding author), associate professor, Email: majiang_ya@126.com.
Coagulation treatment of micropolluted water and study of floc size
Xia Wei, Zhang Rui, Wu Genyu, Ma Jiangya
(College of Civil Engineering and Architecture; Engineering Research Center of Water Purification and Utilization Technology, Ministry of Education, Anhui University of Technology, Maanshan 243032, Anhui, P.R. China)
Abstract: Treatment of micropolluted water is considered to be a vital issue and has attracted more and more attentions around the world. The turbidity and humus affect the quality of drinking water. As a widely used type of water treatment technology, coagulation is known for safety, practical and highefficiency, and has been considered as a prospective technology for micropolluted water. Coagulants are the core of coagulation technology and choosing a suitable coagulant to achieve high coagulation efficiency in the treatment process is crucial. Different kinds of coagulants, coagulants containing aluminum such as aluminum sulfate (AS) and polyaluminum chloride (PAC), coagulants containing ferric such as ferric chloride and polyferric chloride (PFC) were applied, and then followed by compound of coagulant aid polyacrylamide (PAM) and activated silicic acid (ASI) respectively. These coagulant aid possess good adsorption bridging ability and can improve the flocculation efficiency greatly to a certain extent. And in this work, turbidity, UV254 and floc size were investigated to indicate the coagulation efficiency. The optimum coagulation conditions are determined as follows: AS dosage of 22 mg/L, PAC dosage of 18 mg/L, FeCl3 dosage of 16 mg/L, and PFC dosage of 8 mg/L when used alone. PAM dosage of 0.1, 0.1, 0.05, 0.2 mg/L respectively when compounded with PAM. ASI dosage of 0.5, 1.5, 1.0, 1.0 mg/L respectively when compounded with ASI. In general, large amounts of humic acid are produced by the degradation of organic matter for aquatic organisms, and as a result, the water quality are seriously endangered. Thus, the removal of humic acid from wastewater has become imperative. In the passage, two common coagulants, PAC and PAM were applied in the treatment of humic acid wastewater, and PAC compounded with PAM was explored too. Same as before, the coagulation effect was determined by the measure of turbidity and floc size. The result shows that the optimal coagulation efficiency is achieved with PAM dosage of 8 mg/L, PAC dosage of 100 mg/L respectively when used alone. PAM dosage of 0.8 mg/L when compounded with PAC. The result shows that the compound can effectively enhance the coagulation effect at low dosage.
Keywords:coagulation; micropolluted water; humic acid wastewater; floc size
地球上水占70%的面積,其中海水占97.3%,可用淡水只占2.7%,淡水中77.2%存在于雪山冰川中,22.4%存在于土壤中和地下水(降水與地表水滲入),只有0.4%為地表水[1]。隨著社會與工業的快速發展,用水量和排水量大大增加,大量的工業廢水和生活污水未達標便排入水體中,嚴重污染了水生環境[2]。……

