動葉片葉根強度數值仿真研究
曾瑜
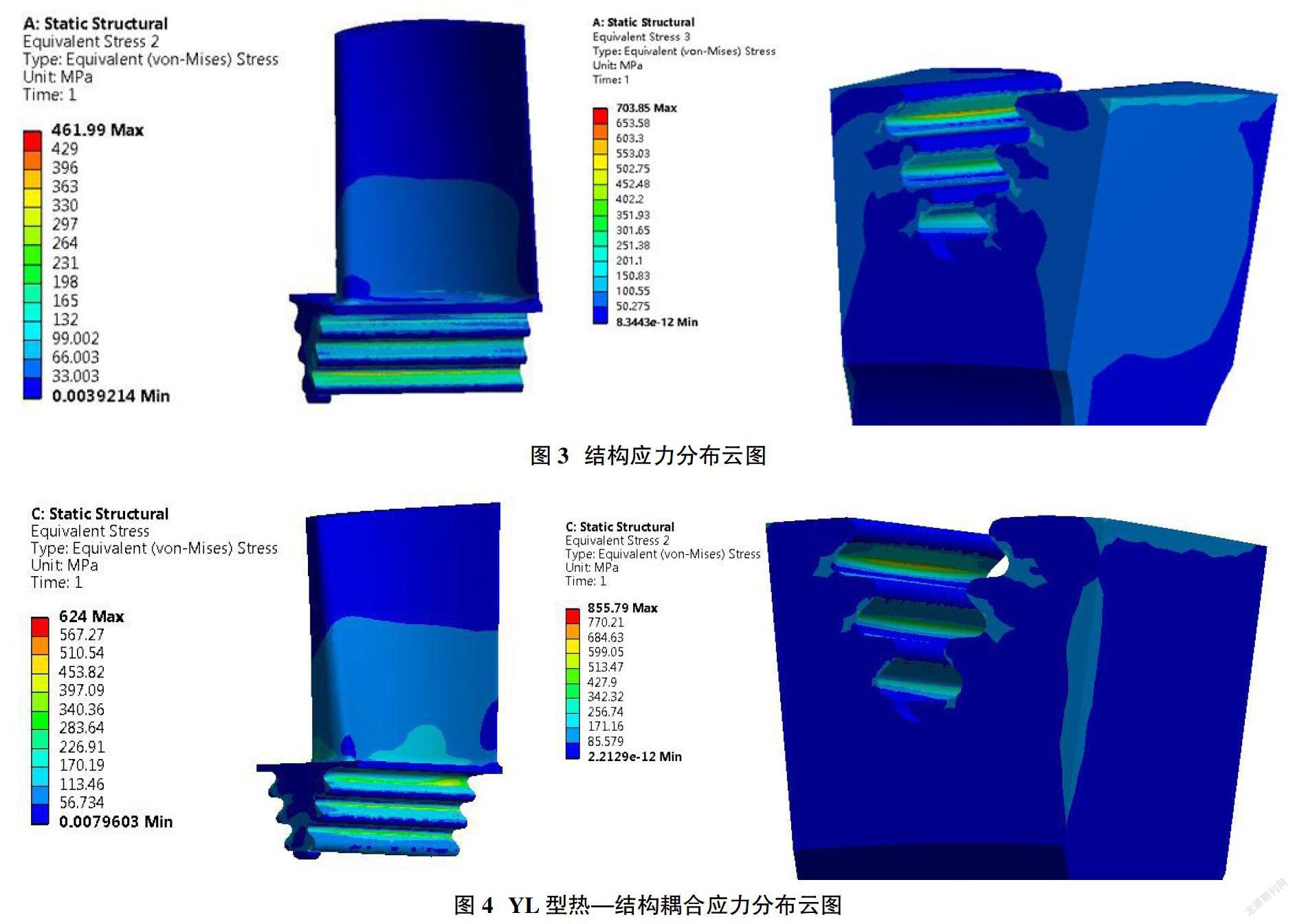
摘要:動葉片旋轉做功時,葉根局部會產生應力集中現象,當最大應力超過材料最大屈服強度時,會導致動葉片斷裂。本文運用ANSYS軟件對動葉片分別進行數值仿真研究,研究結果表明,溫度和轉速是葉根產生應力的重要因素,最大應力位置會因熱載荷的影響而改變。
Abstract: When the rotating blade works, the stress concentration will occur at the root of the blade. When the maximum stress exceeds the maximum yield strength of the material, it will lead to the fracture of the moving blade. In this paper, ANSYS software is used to study the numerical simulation of the moving blade. The results show that temperature and rotation speed are important factors for the stress of the blade root, and the position of the maximum stress will change due to the influence of thermal load.
關鍵詞:動葉片;熱分析;熱-結構耦合分析
Key words: moving blade;thermal analysis;thermal structure coupling analysis
0 ?引言
動葉片是煙氣輪機的核心部件,目前在葉根的經驗設計中僅考慮結構載荷對葉根的影響,但在實際工況下,入口的煙氣溫度很高,會將大量熱傳遞給動葉片,葉根由于受熱膨脹發生變形,這會間接降低葉根結構設計的安全系數, 因此設計葉根結構時要充分考慮熱載荷的影響,通過數值仿真熱-結構耦合作用下葉根的應力集中情況給葉根的結構設計提供理論依據[1]。
1 ?前處理
1.1 模型的建立
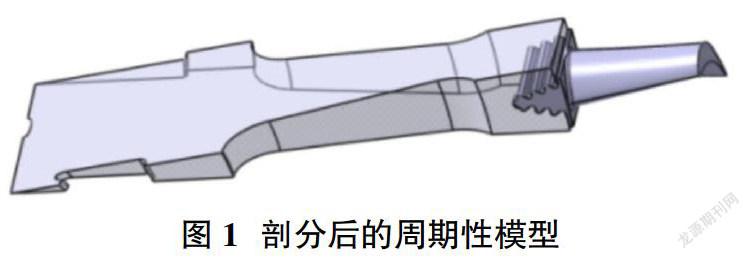
在對煙氣輪機的動葉片進行結構分析時,通常使用NURBS方法進行三維建模[2]。動葉片葉根共由三對齒組成,齒形為縱樹型結構。總裝配模型是由1個輪盤和52片動葉組成,為減少計算量,在仿真模擬前,將模型進行剖分,取其一個周期性模型進行分析,如圖1所示。
1.2 網格的劃分
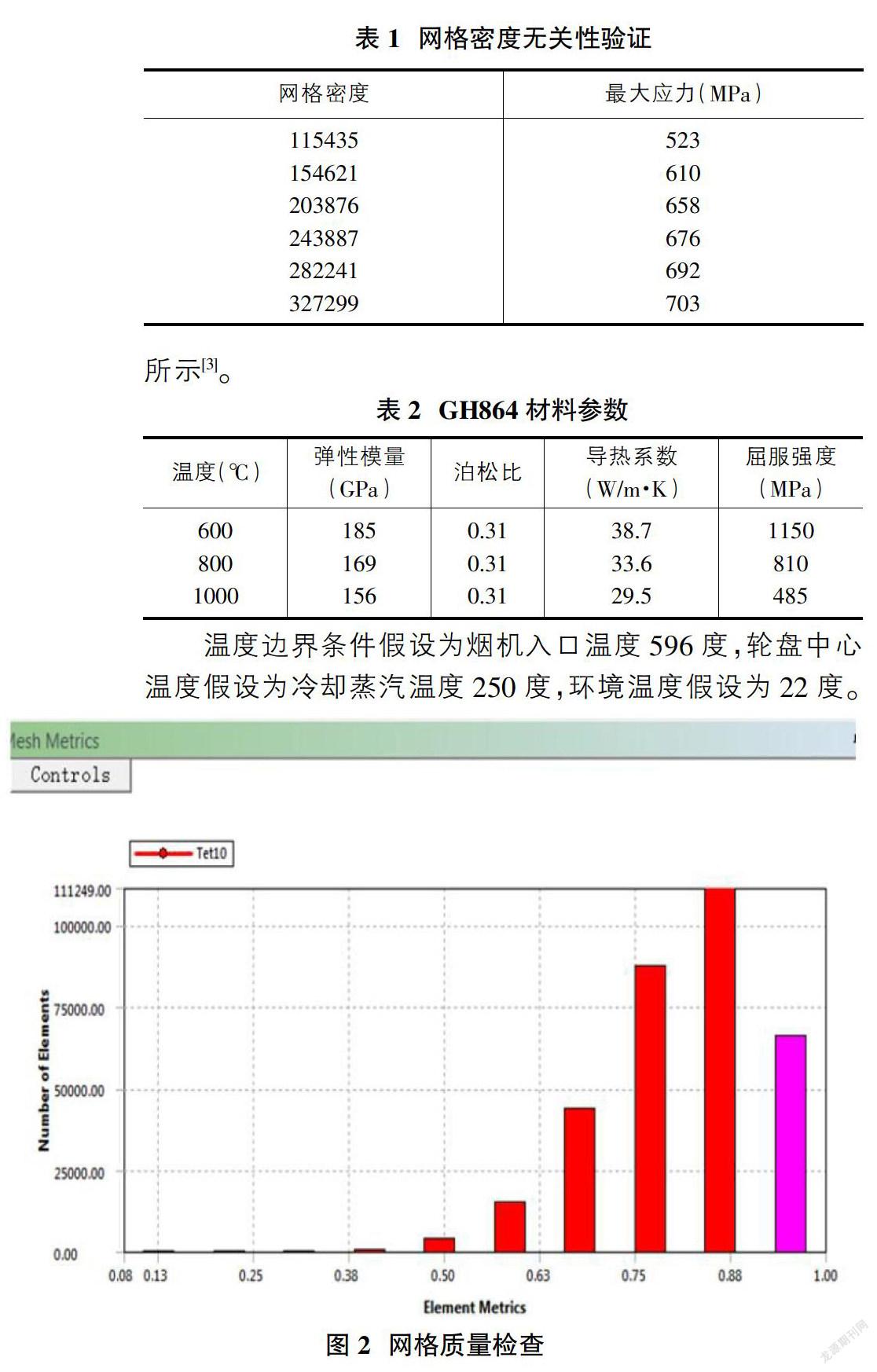
網格劃分時,對模型進行四面體非結構網格劃分。通過網格無關性驗證,如表1所示,當網格數量為327299時,計算結果已基本收斂,因此將該網格數量定為最終的網格密度,網格劃分后進行網格質量檢查,如圖2所示,網格平均質量為0.8,一般網格質量需達到0.6以上,此網格能夠滿足計算精度要求。……

