層級護理對肺癌PICC置管血流感染的影響
馮紅喜 劉晨晨 唐穎

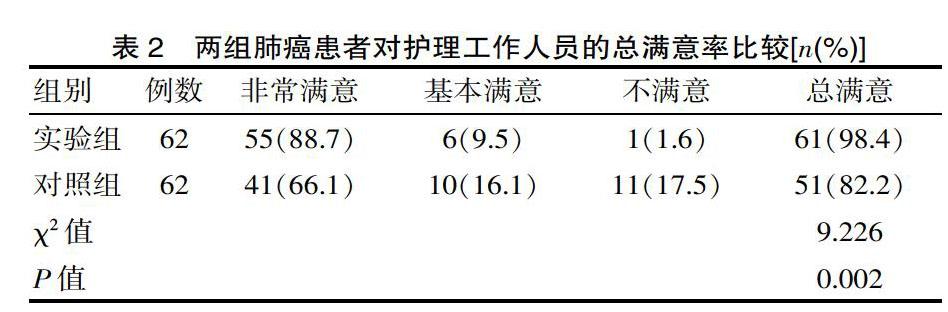
[摘要] 目的 觀察分析層級護理對肺癌PICC置管血流感染的影響。方法 方便選取2018年2月—2019年2月124例肺癌患者,分為實驗組(應用層級護理方法)和對照組(應用常規護理方法),比較兩組干預效果。結果 實驗組平均置管時間、導管相關血流感染發生率分別為(116.3±42.5)d、1.6%,對照組分別為(82.1±34.4)d、14.5%,實驗組導管相關血流感染發生率低于對照組(χ2=15.543,P<0.05);實驗組護理工作人員對相關知識掌握度評分為(95.6±1.5)分,對照組護理工作人員對相關知識掌握度評分為(80.8±1.1)分;實驗組非常滿意率、基本滿意率、不滿意率分別為88.7%、9.7%、1.6%,對照組分別為66.1%、16.1%、17.8%;實驗組平均置管時間、相關知識掌握度評分、護理總滿意率高于對照組(t=3.454、5.365,χ2=9.226,P=0.000、0.000、0.002)。結論 層級護理可顯著降低肺癌外周中心靜脈置管血流感染發生率,延長置管時間。
[關鍵詞] 層級護理;肺癌;外周中心靜脈置管;血流感染;總滿意率
[中圖分類號] R473.73? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1674-0742(2020)06(c)-0102-03
Effect of Hierarchical Nursing on Bloodstream Infection of PICC Catheterization of Lung Cancer
FENG Hong-xi, LIU Chen-chen, TANG Ying
Department of Oncology, Liaocheng Infectious Disease Hospital, Liaocheng, Shandong Province, 252000 China
[Abstract] Objective To observe and analyze the effect of hierarchical nursing on blood flow infection of lung cancer PICC catheterization. Methods 124 patients with lung cancer from February 2018 to February 2019 were convenienty selected and divided into experimental group (application level nursing method) and control group (application conventional nursing method) Compare the effects afthe two groups. Results The average catheter insertion time and the incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections in the experimental group were (116.3±42.5) d and 1.6%, and the control group were (82.1±34.4) d and 14.5%, respectively. The incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infection in the experimental group, lower than the control group (χ2=15.543,P<0.05); the nursing staff of the experimental group scored (95.6±1.5) points of relevant knowledge, and the nursing staff of the control group scored (80.8±1.1) points; very satisfied rate, basic satisfied rate, unsatisfied rate in the experimental group were 88.7%, 9.7%, 1.6%,and the control group were 66.1%, 16.1%, 17.8%; The average tube placement time, relevant knowledge mastery score, and overall nursing satisfaction rate of the experimental group were higher than those of the control group (t = 3.454, 5.365,χ2=9.226,P=0.000, 0.000, 0.002). Conclusion Hierarchical nursing can significantly reduce the incidence of bloodstream infections in peripheral central venous catheterization of lung cancer and prolong the catheterization time.
[Key words] Level nursing; Lung cancer; Peripheral central venous catheterization; Bloodstream infection; Total satisfaction rate; Routine care
外周中心靜脈置管具有以下優勢而被廣泛應用在臨床之中:其一,易于維護;其二,操作便捷;其三,可長時間留置;其四,安全性高等[1]。外周中心靜脈置管尤其能夠被廣泛應用于癌癥患者的治療過程中,隨著外周中心靜脈置管的廣泛應用,臨床發現由外周中心靜脈置管所致的血流感染并發癥也逐漸受到醫患人員的高度重視[2]。血流感染一旦形成,勢必會加重患者的身心負擔,與此同時降低患者的主動性和積極性,最終在很大程度上影響到預后效果。相關研究資料顯示,外周中心靜脈置管所致的血流感染病死率約11.6%~24.5%[3]。為了提高臨床治療效果,必須有效控制外周中心靜脈置管血流感染發生率,采取有效的護理措施。有關研究資料顯示,層級護理方法有效避免護理不合理所致的護患糾紛,與此同時提高患者的總滿意率[4]。該文方便選取該院在2018年2月—2019年2月收治的124例肺癌患者作為研究對象,分析不同護理方法所致效果。……

