基于神經網絡的大數據云平臺DDoS攻擊檢測方法研究
葛菁 趙巍 徐亦丹

摘 ?要: 針對基于OpenFlow協議的云平臺的安全性問題,文中對分布式拒絕服務攻擊(DDoS)檢測方法進行研究。通過引入自組織映射(SOM)神經網絡,利用網絡流量的包數、速率、生存周期等特征建立網絡的輸入特征向量對SOM中的輸入層、競爭層進行合理的優化,借助Stacheldraht工具生成網絡的訓練和測試數據。在實驗時,文中基于不同的流量數據集訓練得到3個不同的SOM網絡。測試結果表明,所提方法對于惡意流量的識別準確率可達98%以上,誤判率可降低至0.5%以下,證明了神經網絡在DDoS攻擊檢測中的可用性。
關鍵詞: 云平臺; DDoS攻擊監測; 自組織映射; 神經網絡; 特征優化; 流量檢測; 實驗測試
中圖分類號: TN911.7?34; TP311 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼: A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文章編號: 1004?373X(2020)24?0102?03
Research on neural network based DDoS attack detection method for
big data cloud platform
GE Jing, ZHAO Wei, XU Yidan
(Institute of Technology, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang 330100, China)
Abstract: In allusion to the security problem of cloud platform based on OpenFlow protocol, the detection method of distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack is researched. With the introduction of the self?organizing mapping (SOM) neural network, the input eigenvector of the network is established by means of the characteristics of the number of packet, rate and life cycle of network traffic to reasonably optimize the input layer and competition layer in the SOM neural network. The training and testing data of the network are generated with Stacheldraht. In the experiment, three different SOM networks were obtained on the basis of training of different traffic datasets. The testing results show that the recognition accuracy of this method for malicious traffic can reach more than 98%, and its misjudgment rate can reduce less than 0.5%, which proves the availability of neural network in DDoS attack detection.
Keywords: cloud platform; DDoS attack detection; SOM; neural network; characteristic optimization; traffic detection; experimental testing
隨著計算機技術的發展,大數據時代的來臨,對于數據中心云平臺的建設需求越來越大。為了提升數據中心的建設效率,降低維護難度,數據中心通常基于集中式的控制器和標準化接口對各種網絡設備進行管理。這種架構的云平臺需要借助負載均衡設備平衡各路流量,協調網絡服務。云平臺的網絡安全性是大數據平臺建設中需要面對的嚴峻挑戰之一。在上述的云平臺架構中,會面臨分布式拒絕服務(DDoS)、Web、操作系統等攻擊。云平臺被攻擊會造成大量的隱私數據泄露,給用戶帶來嚴重的安全和財產損失[1?3]。
基于上述分析,本文對基于OpenFlow協議的數據云平臺的安全性進行了研究。針對DDoS攻擊,建立流量檢測模型,可以及時發現惡意流量,從而保證云平臺的安全。
1 ?算法研究
1.1 ?DDoS攻擊
在大數據平臺的數據中心,其網絡結構大多基于SDN(Software Defined Network),運行OpenFlow協議。在該模式下,數據中心在邏輯上可以劃分為3個部分:端口、流表和安全通道。各主機通過端口和數據中心連接,安全通道和流表運行在OpenFlow交換機上,OpenFlow交換機與控制器之間通過OpenFlow、TCP、SSL協議連接。圖1給出了這種結構的拓撲圖[4?7]。
正常狀態下,數百萬的用戶共享了上述架構的數據設施。但當用戶中存在惡意主機,其向基礎數據設施不斷發送惡意流量。此時,控制器與交換機間就會存在大量的數據流量交互,影響其他合法用戶獲取數據服務。這種攻擊方式即為分布式拒絕服務攻擊(DDos)[8?10]。
DDoS攻擊會造成嚴重的后果:首先是數據中心計算資源的無端消耗,甚至耗盡計算資源;其次,惡意主機在攻擊過程中會偽裝成合法的Web流量,從而創建出更多代理,泄露數據隱私,給云平臺的正常用戶帶來不良影響[11?13]。
為了防止DDoS攻擊給云平臺帶來的傷害,需建立高效的DDoS攻擊檢測機制,因此需要快速的流量識別技術。本文使用自組織映射(Solf Orgnanizing Maps,SOM)神經網絡進行異常流量的識別。
1.2 ?SOM神經網絡
圖2給出SOM神經網絡結構,其包括輸入層x和競爭層l。輸入層的n維向量通過競爭層映射為一維向量,是一種無監督的機器學習算法,其基本步驟如下:
1) 初始化。給網絡中所有的神經元隨機賦予權值,維護輸入層的神經元數和特征向量的維度相等。
2) 采樣。隨機選取入口模式空間內的樣本,反饋至神經網絡。
3) 依據歐幾里得距離,利用l個神經元,篩選神經元:
[i(x)=argminjx-wj] ?(1)
式中,j=1,2,…,l。
4) 調整權重。利用競爭勝利的神經元調整其載體的權重:
[wj(t+1)=wj(t)+η(t)θj(t)(x(t)-Wj(t))] (2)
5) 迭代。重復步驟2)~步驟4),直至網絡收斂。
SOM網絡只對入口模式進行學習。根據訓練樣本對自身進行重新組織并調整權重,對于網絡流量的識別具有較好的甄別能力。
2 ?算法仿真
2.1 ?仿真實驗設計
為了識別惡意流量,需要合理選擇流量的特征。本文選取的流量特征有:流的平均包數(Average of Packets per Flow,APF)、流的平均比特數(Average of Bytes per Flow,ABF)、流的平均生存周期(Averge of Duration per Flow,ADF)、流內的成對數據比例(Percentage of Pair?Flows,PPF)、流量增長速率(Growth of Single?Flows,GSF)及偽造端口增長率(Growth of Different Ports,GDP)。其中,GSF和GDP的定義如下:
[GSF=Num_Flows-(2×Num_PairFlows)interval ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?GDP=Num_Portsinterval] (3)
SOM神經網絡的相關參數設置如表1所示。
在訓練數據的選擇上,本文使用的網絡流量組成如下:TCP流量占85%、UDP流量占10%、ICMP流量占5%。DDoS攻擊流量由Stacheldraht產生。攻擊流量和正常流量組成相同,如表2所示。
在訓練數據和測試數據的生成上,按照上述比例與表2的數量生成3組不同的Swich,3組數據可以訓練3個不同的SOM網絡。為了衡量測試、訓練數據數量對模型性能的影響,Swich1與Swich2的數據量相等,Swich3的數量大于Swich1和Swich2。因此,訓練數據與測試數據的比例為1∶10。
2.2 ?仿真結果
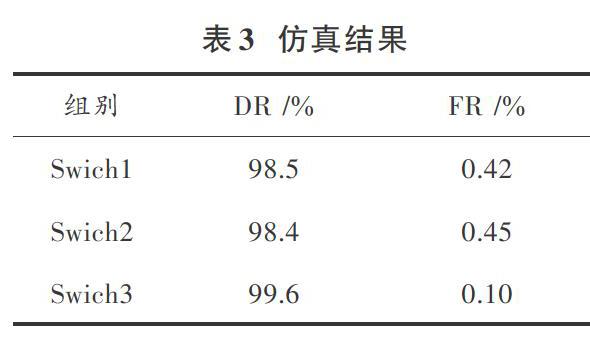
為了合理評價本文模型的效果,在網絡性能指標的評價上,選取檢測率(DR)和誤報率(FR)作為網絡指標。測試結果如表3所示。
從表3中可以看出,本文建立的DDoS攻擊檢測模型有較高的識別準確率。經過3次訓練后得到的模型,其識別準確率均達到了98%以上;模型的誤報率也較小,均在0.5%以下。此外,模型的訓練效果會受到數據流大小的影響,在數據流的大小上有:Swich1=Swich2 3 ?結 ?語 針對OpenFlow協議下的云平臺安全問題,本文設計了基于SOM神經網絡的DDoS攻擊檢測方法。本文方法從惡意主機中發送的流量入手,通過識別惡意流量,阻止DDoS攻擊的發生。實驗結果表明,該方法具有較高的識別精度、極低的誤判率以及較強的實用價值。 參考文獻 [1] DANESHGADEH S, KEMMERICH T, AHMED T, et al. A hybrid approach to detect DDoS attacks using KOAD and the mahalanobis distance [C]// IEEE 17th International Symposium on Network Computing and Applications. Cheyenne: IEEE, 2018: 17?23. [2] PRASAD K M, REDDY A R M, RAO K V. Ensemble classifiers with drift detection (ECDD) in traffic flow streams to detect DDoS attacks [J]. Wireless personal communications, 2018, 39(5): 1?21. [3] ZHANG J, LIU P, HE J B, et al. A hadoop based analysis and detection model for IP spoofing typed DDoS attack [C]// IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications. Xian: IEEE, 2017: 231?236. [4] REZAEI H, MOTLAGHA N G, FARJAMIB Y, et al. A novel framework for DDoS detection in huge scale networks, thanks to QoS features [J]. IEEE transactions on communications, 2018, 33(7): 633?642. [5] BREMLER?BARR A, BROSH E, SIDES M. DDoS attack on cloud auto?scaling mechanisms [C]// IEEE INFOCOM 2017?IEEE Conference on Computer Communications. Detroit: IEEE, 2017: 56?62. [6] LIU J, LAI Y X, ZHANG S X. FL?GUARD: a detection and defense system for DDoS attack in SDN [C]// International Conference on Computer Science. Beijing: IEEE, 2017: 32?46. [7] TORJESEN A, ISTFAN R, ROBLYER D. Ultrafast wavelength multiplexed broad bandwidth digital diffuse optical spectroscopy for in vivo extraction of tissue optical properties [J]. Journal of biomedical optics, 2017, 22(3): 36?49. [8] AGRAWAL N, TAPASWI S. A lightweight approach to detect the low/high rate IP spoofed cloud DDoS attacks [C]// 7th International Symposium on Cloud and Service Computing. Frankfort: IEEE, 2017: 106?115. [9] REBECCHI F, BOITE J, NARDIN P A, et al. Traffic monitoring and DDoS detection using stateful SDN [C]// Conference on Network Softwarization. Harrisburg: IEEE, 2017: 421?426. [10] LIU Z Y, YANG X, ZHANG Y L, et al. Application?layer DDoS defense model based on Web behavior trajectory [J]. Journal of computer applications, 2017, 38(4): 233?239. [11] YUAN X Y, LI C H, LI X L. Deep defense: identifying DDoS attack via deep learning [C]// 2017 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing. Wuhan: IEEE, 2017: 101?106. [12] KO I, CHAMBERS D, BARRETT E. Feature dynamic deep learning approach for DDoS mitigation within the ISP domain [J]. International journal of information security, 2019(7): 79?83. [13] LI C H, WU Y, YUAN X Y, et al. Detection and defense of DDoS attack?based on deep learning in OpenFlow?based SDN [J]. International journal of communication systems, 2018(11): 3497?3508. 作者簡介:葛 ?菁(1982—),女,江西南昌人,碩士,講師,研究方向為計算機科學。

