幽門螺桿菌感染對社區2型糖尿病患者的血糖和血脂的影響
王萬敏 尹相風 胡承偉 鄒凡

摘 要 目的:本研究旨在探討幽門螺桿菌(Helicobacter pylori,Hp)感染對社區2型糖尿病患者血糖、血脂等指標的影響,為更好的控制2型糖尿病患者血糖水平尋找更多思路。方法:納入104例2型糖尿病門診患者,其中男性48名,女性56名,年齡為45~82歲,平均年齡為69.95歲。根據Hp感染情況分為Hp陽性和Hp陰性兩組。比較兩組患者的年齡、性別、體重指數、血糖、糖化血紅蛋白(HbA1c)、血脂。結果:在2型糖尿病患者中檢出Hp陽性者64例,檢出率為61.5%。Hp陽性組患者的年齡低于陰性組[(67.5±7.29)歲比(69.95.00±4.05)歲,P<0.05]。陽性組平均HbA1c水平和三酰甘油水平高于陰性組[(7.69±1.40)%比(7.12±1.36)%,P<0.05和(1.64±0.65)mmol/L比(1.36±0.55)mmol/L,P<0.05],陰性組患者的HbA1c達標率高于陽性組(57.5%比32.8%,P<0.05)。結論:Hp感染影響2型糖尿病患者的血糖控制,有可能促進糖尿病的發展。
關鍵詞 幽門螺桿菌感染;2型糖尿病;血糖;糖化血紅蛋白;血脂
中圖分類號:R58 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:1006-1533(2021)18-0053-03
Influence of helicobacter pylori infection on blood glucose and blood lipids of type 2 diabetic patients in the community
WANG Wannmin, YIN Xiangfeng, HU Chengwei, ZOU Fan
(General Practice Department of Changzheng Community Health Service Center of Putuo District, Shanghai 200333, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the influence of helicobacter pylori(HP) infection on blood glucose, blood lipids and other indicators of type 2 diabetic patients in the community to find more ideas for better control of blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Methods: One hundred and four patients with type 2 diabetes were included in the study, there were 48 males and 56 females, and the age ranged from 45 to 82 years old, with an average age of 69.95 years old. According to HP infection, they were divided into the HP positive group and HP negative group. The age, gender, body mass index, blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin(HbA1c) and blood lipid of the two groups were compared. Results: In type 2 diabetes patients, 64 cases of HP positive were detected, and the detection rate was 61.5%. The age of the patients in the HP positive group was lower than that in the negative group[(67.5±7.29) years to (69.95.00±4.05) years, P<0.05]. The average HbA1c and triacylglycerol levels in the positive group were higher than those in the negative group[(7.69±1.40)% to (7.12±1.36)%, P<0.05 and (1.64±0.65) mmol/L to (1.36±0.55) mmol/L, P<0.05], the HbA1c compliance rate in the negative group was higher than that in the positive group(57.5% vs. 32.8%, P<0.05). Conclusion: HP infection affects blood glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients, and may promote the development of diabetes.
KEY WORDS helicobacter pylori infection; type 2 diabetes; plasma glucose; glycosylated hemoglobin; blood lipids
目前幽門螺桿菌(Helicobacter pylori,Hp)的全球感染率超過50%[1],我國普通人群中Hp感染的檢出率達56.22%[2]。糖尿病是一組以高血糖水平為特征的代謝性疾病,其中2型糖尿病最常見,約占全部糖尿病的90%。在我國成年中,糖尿病患病率估計約10.9%[3]。近年越來越多的研究發現,Hp感染不僅是明確的人類致癌因子[4-5],還與糖尿病、心血管疾病的發生和發展相關[6]。但目前對于社區合并Hp感染的2型糖尿病患者研究較少,對該類患者的管理還不完善,本研究旨在分析Hp感染的2型糖尿病患者的臨床特征、血糖水平,為更好的控制2型糖尿病患者血糖水平尋找更多思路。
1 對象和方法
1.1 對象
連續收集2019年1月-2020年12月社區衛生服務中心中符合入選標準的2型糖尿病患者共104名,其中男性48名,女性56名,年齡為45~82歲,平均年齡為69.95歲。所有入組患者均行碳14尿素酶呼氣試驗(14C-urea breath test,14C-UBT)檢測Hp感染。排除標準:(1)年齡<35歲;(2)拒絕參與研究的患者或無相關實驗結果的患者;(3)在最近3個月內接受過潰瘍治療患者;(4)目前使用質子泵抑制劑或最近4周內服用抗生素的患者;(5)有胃癌或其他惡性腫瘤病史的患者。(6)孕婦和哺乳期婦女。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 生化指標檢測
所有入組患者均有近期檢查(1月內)的生化指標結果,包括空腹血糖、糖化血紅蛋白(glycosylated hemoglobin,HbA1c)、血清總膽固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、三酰甘油(triglyceride,TG)、高密度脂蛋白膽固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL-C)和低密度脂蛋白膽固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)等。
1.2.2 14 C–UBT檢測
所有研究對象均采用14 C-UBT檢查Hp感染情況,受檢者空腹漱口后服用1粒碳-14(14C)膠囊,靜坐20 min后通過專用呼氣瓶收集研究對象呼出的氣體,然后往瓶子內加入4.5 mL閃爍液,最后經由專業液閃儀檢測14C放射性活度并記錄。14C放射性活度≥100 dpm/ mmol/L為陽性,<100 dpm/mmol/L為陰性。
1.3 統計學處理
2 結果
2.1 Hp檢出情況
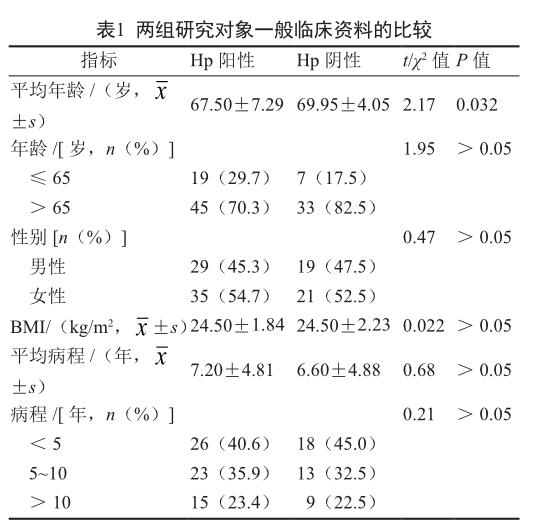
在104例調查對象中,40例2型糖尿病患者Hp感染檢測為陰性,64例2型糖尿病患者Hp感染檢測為陽性。除Hp陽性組2型糖尿病患者的平均年齡明顯低于陰性組外,其余指標兩組的差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05,表1)。
2.2 兩組研究對象血糖、血脂比較
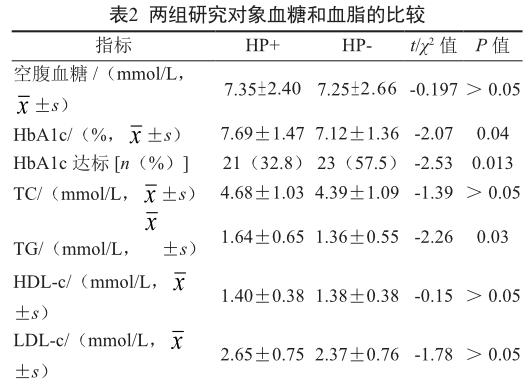
Hp陽性組HbA1c和TG平均值高于陰性組,HbA1c達標率高于陽性組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05,表2)。Logistic回歸分析顯示,調整了年齡、性別、病程等因素后,HbA1c水平仍與Hp相關(OR =2.77,95%CI為1.2~6.26;P=0.014)。
3 討論
近年來越來越多的研究發現Hp感染與2型糖尿病存在相關性。一項Meta分析指出2型糖尿病患者中Hp的患病率是健康人群的1.33倍[7]。喀麥隆一項橫斷面研究顯示糖尿病患者中Hp感染率為73.11%,非糖尿病患者中為58.05%,差異有統計學意義(OR=1.472,P=0.0279)[8]。本研究中2型糖尿病患者Hp陽性檢出率達61.5%,低于上述的研究結果。
本研究結果顯示,HbA1c水平與Hp感染存在相關性,在調整了年齡、性別等因素后差異仍有統計學意義(OR=2.77,95%CI為1.2~6.26,P=0.014)。目前有研究認為,Hp感染可能引起身體慢性炎癥反應,并通過炎癥影響某些調節胰島素的胃腸激素水平而增加胰島素抵抗[9]。于俊霞等[10]研究也證實Hp持續感染的2型糖尿病患者C反應蛋白水平明顯高于非感染患者。有研究發現,Hp感染導致胃泌素濃度增加和血清生長抑素濃度降低,從而影響胰島素分泌;同時Hp感染還會損害生長素釋放肽的產生,增強瘦素的產生[11]。上述研究結果提示,Hp感染一方面導致慢性全身炎癥反應,刺激機體大量炎癥因子的表達,影響胰島素的作用和胰腺β細胞的分泌。另一方面,Hp誘發的胃炎可能會影響胃激素的分泌和胰島素敏感性及葡萄糖穩態。
除上述結果外,本研究還發現Hp陽性組的平均年齡明顯低于陰性組。既往有研究發現Hp的感染率在18~30歲最高(55.7%),隨著年齡增長而逐年下降[12]。結合我國社區實際情況,其原因可能為社區中老年隨著年齡升高,包括聚餐等社交活動逐漸減少,很大程度減少Hp的感染機會。但考慮本研究為非隨機對照實驗研究,該結論需進一步研究證實。
參考文獻
[1] Gobert AP, Wilson KT. The Immune Hattle against Helicobacter pylori infection: NO Offense[J]. Trends Microbiol, 2016, 24(5): 366-376.
[2] 張萬岱, 胡伏蓮, 蕭樹東, 等. 中國自然人群幽門螺桿菌感染流行病學調查[J]. 現代消化及介入診療, 2010, 15(5): 265-270
[3] Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and pre-diabetes in China in 2013[J]. JAMA, 2017, 317: 2515-2523.
[4] de Souza CR, de Oliveira KS, Ferraz JJ, et al. Occurrence of Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus infection in endoscopic and gastric cancer patients from Northern Brazil[J] BMC Gastroen-terol, 2014, 14(1) : 179.
[5] Leja M, Axon A, Brenner H. Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection[J]. Helicobacter, 2016, 21(Suppl 1): 3-7.
[6] Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: systematic review and metaanalysis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2017, 153(2): 420-429.
[7] Zhou X, Zhang C, Wu J, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and diabetes mellitus: a metaanalysis of observational studies[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2013, 99(2): 200-208.
[8] Kouitcheu Mabeku LB, Noundjeu Ngamga ML, Leundji H. Helicobacter pylori infection, a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based cross-sectional study among dyspeptic patients in Douala-Cameroon[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12141.
[9] Guo X, Zhao BH, Zhang MX. Risk factors of Helicobacter pylori infection among adults in northern China[J]. HepatoGastroenterology. 2011, 58(106): 306-310.
[10] 于俊霞, 田寧艷, 李秀麗, 等. 根除幽門螺桿菌治療對老年2型糖尿病病人血糖控制及炎癥指標的影響[J]. 實用老年醫學, 2020, 34(12): 1239-1242.
[11] Jeffery PL, McGuckin MA, LindenS K. Endocrine impact of Helicobacter pylori: focus on ghrelin and ghrelinoacyltransferase[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2011, 17: 1249-60.
[12] Negash M, Wondifraw Baynes H, Geremew D. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Its Risk Factors: a prospective crosssectional study in resource-limited settings of northwest Ethiopia[J]. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2018, 2018: 9463710.

