洞庭湖湖體溶解氧的變化特征及其對水稻覆蓋程度變化的影響
彭美齡 金琳 姚一飛 李婉雪 代秦
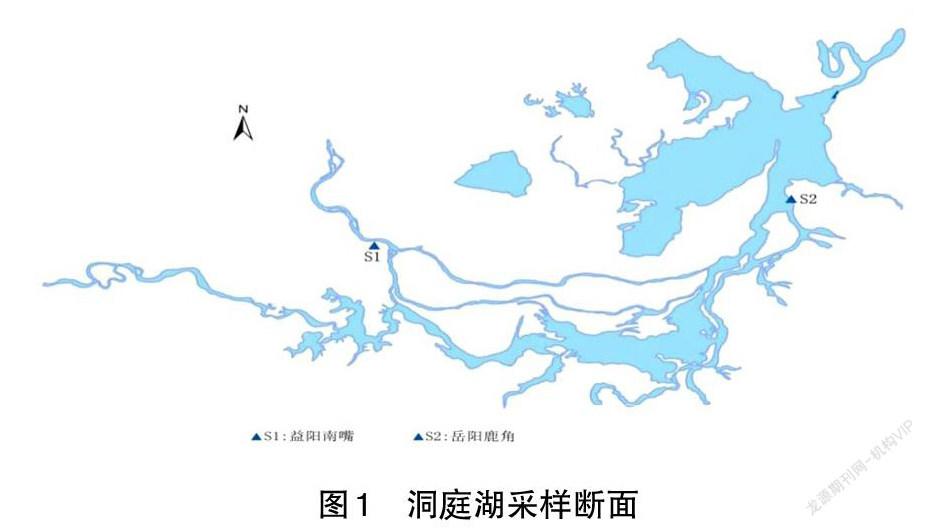
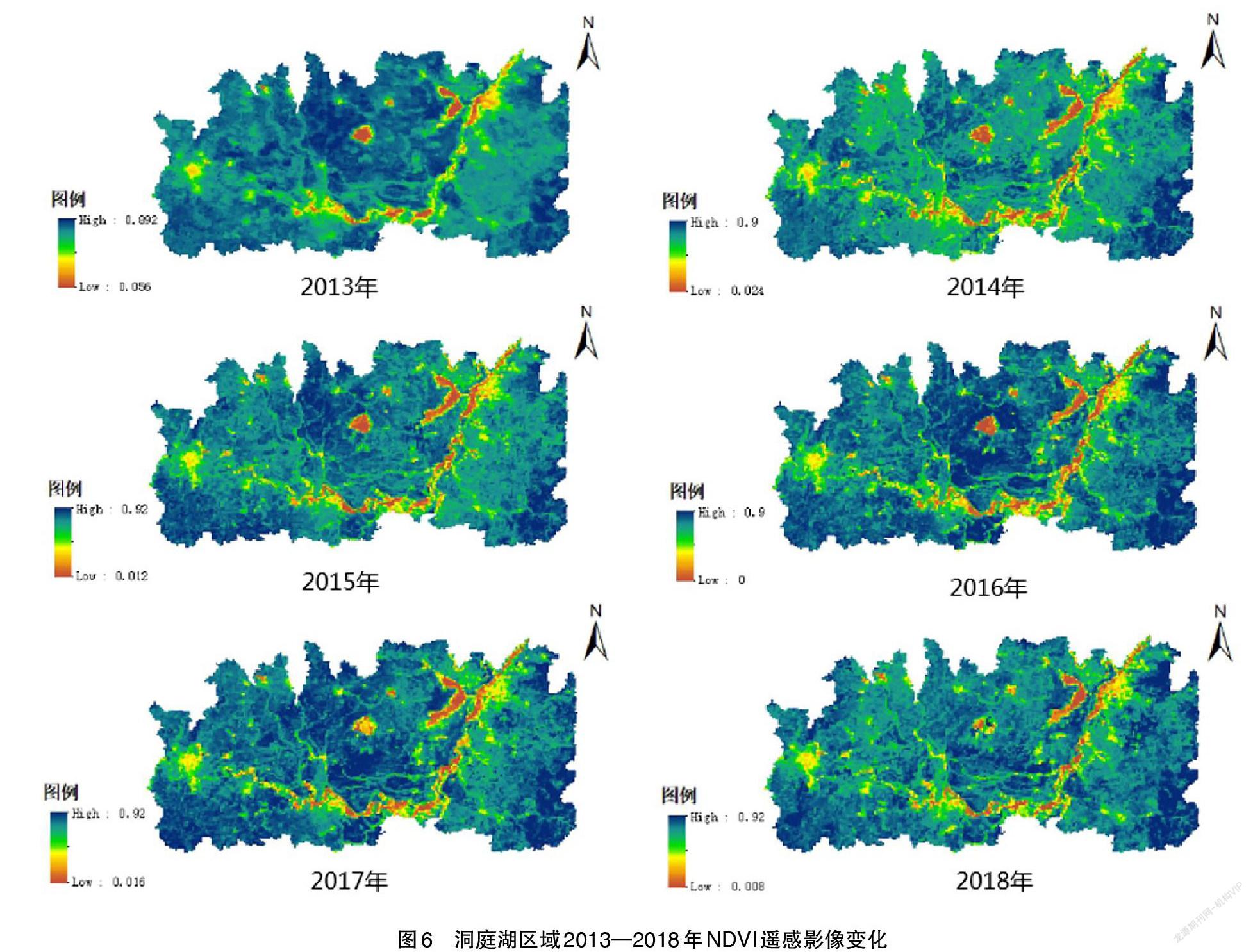

摘 要:2013—2018年,每周對洞庭湖的2個湖體斷面進行水質監測,采集酸堿度(pH)、溶解氧(DO)、高錳酸鉀指數(CODMn)、氨氮含量指標(NH3-N)等4個水環境質量指標,進行相關性和回歸分析,得出DO與其他3個水質指標之間的相關關系。并通過GIS繪制洞庭湖植被覆蓋特征的遙感圖像,研究洞庭湖水體DO值水平與附近植被覆蓋度之間的關系。結果表明:(1)洞庭湖湖體溶解氧(DO)夏季(6—8月份)含量低,冬季(11月至次年1月份)含量高,季節性變化十分明顯;(2)從空間上來看,西洞庭湖溶解氧含量整體上大于東洞庭湖,不同地域溶解氧的水平差異較大;(3)洞庭湖水體中的溶解氧含量在一定范圍內與pH值正相關,與氨氮含量呈明顯正相關,與高錳酸鉀指數無相關關系;(4)水體中的溶解氧對水稻生產有影響且兩者之間不是單一的正相關關系,當溶解氧為9.8mg/L左右時,稻田覆蓋率是最高的。
關鍵詞:溶解氧;洞庭湖;水污染;植被覆蓋度;遙感
中圖分類號 X171? 文獻標識碼 A文章編號 1007-7731(2021)20-0134-06
Variation Characteristics of Dissolved Oxygen in Dongting Lake and Its Effect on Rice Coverage
PENG Meiling1 et al.
(1Northwest A & F University, Yangling 712100, China)
Abstract: From 2013 to 2018, the water quality of two lake sections in Dongting Lake was monitored weekly. The correlation and regression analysis of four water environmental quality indexes:pH, DO, CODMn and NH3-N were carried out, and the correlation between DO and the other three water quality indexes was obtained. The remote sensing images of vegetation coverage characteristics of Dongting Lake were drawn by GIS to study the coupling law between DO value level of Dongting Lake water body and nearby vegetation coverage rate. The result showed that:(1) The content of dissolved oxygen in Dongting Lake is low in summer (June–August) and high in winter (November–January of the next year), and the seasonal variation is very obvious. (2) In terms of space, the dissolved oxygen content in West Dongting Lake is generally higher than that in East Dongting Lake, and the dissolved oxygen levels in different regions are quite different. (3) The dissolved oxygen content in Dongting Lake water was positively correlated with pH value in a certain range, and was significantly positively correlated with ammonia nitrogen content, and had no correlation with potassium permanganate index. (4) Dissolved oxygen in water has an impact on rice production and there is not a single positive correlation between them. When dissolved oxygen is about 9.8mg/L, the rice field coverage is the highest.
Key words: Dissolved oxygen; Dongting Lake;Water pollution;Vegetation coverage; Remote sensing
1 研究背景
洞庭湖是長江中游很重要的一個吞吐湖泊。作為中國第二大淡水湖,其湖區橫跨湖南、湖北2省,位于荊江南岸,地理坐標為27°39′N~29°51′N、111°19′E~113°34′E,北連長江、南接湘江、資江、沅江、酆水四水,是一個過水性季節型湖泊。近年來,洞庭湖流域人口迅速增加,周邊工農業、水產養殖業與時俱進的發展,長江上游大型水利工程不斷地興建,洞庭湖生態環境遭到了嚴重的破壞[1-4],洞庭湖水體水質整體呈現惡化的趨勢[5],湖水污染愈發嚴重,水中DO值整體含量也隨之產生變化。
溶解氧是水體通過和空氣中的氧(O2)交換或者經過各種化學反應后溶解于水中的氧氣[6]。DO值是洞庭湖水體中的主要水質指標之一,也是水體中動植物賴以生存的氧的來源。當溶解氧含量低于一定數值,就不再符合人類健康飲用水的標準,甚至會造成水中魚類窒息死亡。當水中有各種還原性質的污染物時,DO含量就會降低[7],而溫度、含鹽量和水深的增加也會導致DO的減少[8]。游健永[9]在葉綠素a與水質因子的多元分析中得出,溶解氧與水溫有顯著負相關關系;溶解氧與水中浮游生物的生長繁殖有著緊密關系[10]。已有研究[1]指出,在洪水期間,水中DO含量較低的原因主要是:許多動植物殘骸隨著洪水的沖刷留在了水中,然后通過氧化分解消耗大量的溶解氧,但人們對于洞庭湖溶解氧與水中其他成分之間的關系還有待探索。韓沁哲[11]等在洞庭湖區植被覆蓋度下降的成因分析指出,近年來洞庭湖植被覆蓋下降區集中在水田、人口密集區和濕地。洞庭湖流域盛產水稻,利用遙感數據得到洞庭湖水稻的分布規律,并將DO與洞庭湖中其他水質因子含量的時空變化規律進行相關性分析,從而能夠得到DO變化的主要影響因素及其變化對洞庭湖植被覆蓋度的影響。

