基于多元統(tǒng)計(jì)分析的冬小麥干旱綜合指標(biāo)構(gòu)建及監(jiān)測(cè)研究
謝永凱 馮美臣 秦明星 楊武德 劉敏 孟萬忠
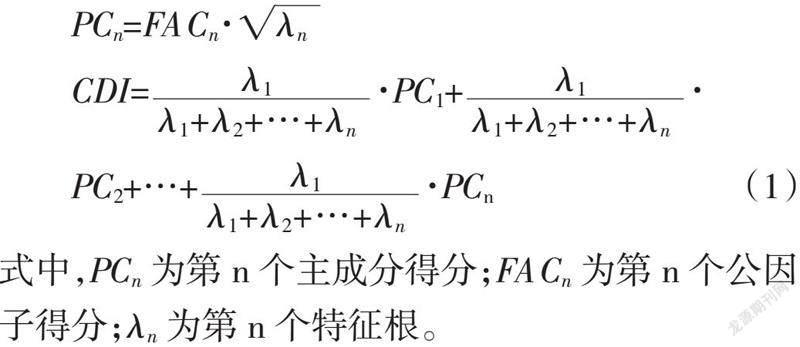
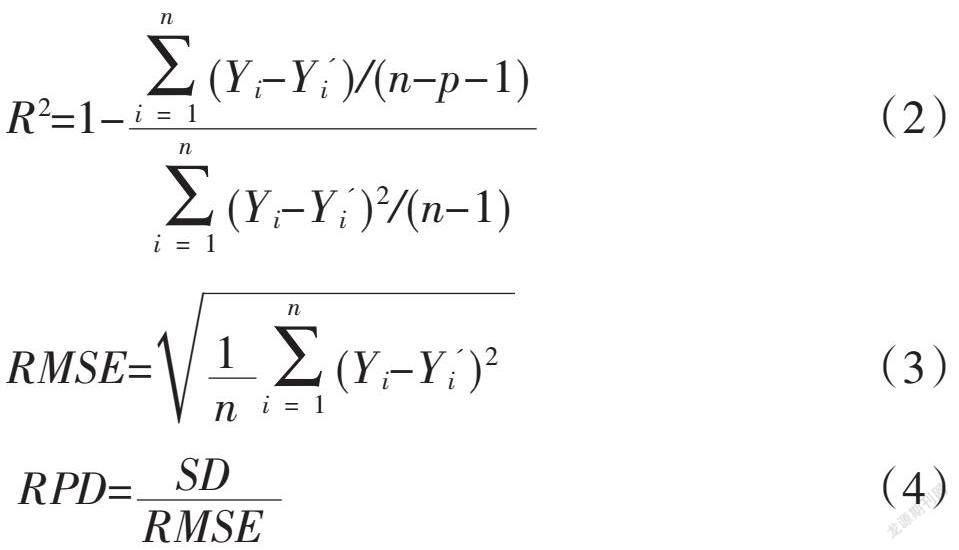
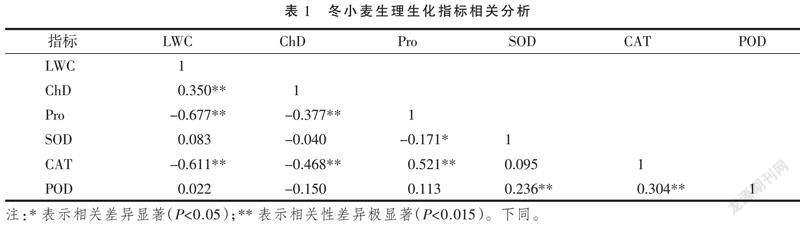
摘? ? 要:為了實(shí)現(xiàn)水分脅迫后冬小麥干旱指標(biāo)綜合表現(xiàn)的定量監(jiān)測(cè),以2017—2018、2018—2019年的冬小麥水分脅迫試驗(yàn)為基礎(chǔ),選擇冬小麥葉片含水量(LWC)、葉綠素密度(ChD)、游離脯氨酸含量(Pro)以及抗氧化物酶中的超氧化物歧化(SOD)、過氧化氫酶(CAT)和過氧化物酶(POD)活性等生理參數(shù)作為研究對(duì)象,利用主成分分析方法(PCA)構(gòu)建了冬小麥干旱綜合指標(biāo)(Comprehensive drought index,CDI)。結(jié)合相關(guān)分析法和逐步多元線性回歸(CA+SMLR)、偏最小二乘法和逐步多元線性回歸(PLS+SMLR)及連續(xù)投影算法(SPA)對(duì)光譜反射率進(jìn)行了特征波段提取,綜合利用化學(xué)計(jì)量學(xué)方法,對(duì)冬小麥生理生化及CDI指標(biāo)監(jiān)測(cè)展開了研究。結(jié)果表明:通過CA+SMLR提取的特征波段個(gè)數(shù)較少,并且所構(gòu)建的SMLR模型表現(xiàn)一般;利用SPA構(gòu)建的監(jiān)測(cè)模型表現(xiàn)優(yōu)于CA+SMLR和PLS+SMLR 2種方法,可以實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)冬小麥CDI指標(biāo)優(yōu)化目的。利用多元回歸分析方法構(gòu)建的模型對(duì)比,發(fā)現(xiàn)基于全譜建立的PLSR模型表現(xiàn)(R2=0.885,RMSEC=0.221,RPD=2.772;R2=0.631,RMSEP=0.441,RPD=1.625),其預(yù)測(cè)效果最好;SPA方法提取特征波段建立的MLR模型表現(xiàn)(R2=0.647,RMSEC=0.387,RPD=1.355;R2=0.672,RMSEP=0.376,RPD=1.500)次之。綜上,通過CDI模型的構(gòu)建,為實(shí)現(xiàn)水分脅迫后冬小麥生理參數(shù)綜合表現(xiàn)的高光譜監(jiān)測(cè)提供了參考。
關(guān)鍵詞:主成分分析;干旱綜合指標(biāo);特征波段;模型表現(xiàn)
中圖分類號(hào):S512.1+1? ? ? ?文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A? ? ? DOI 編碼:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6500.2023.05.004
Abstract:The study was based on tests of winter wheat after water stress that from 2017—2018 and 2018— 2019 to realize the quantitative monitoring of drought index. By selecting physiological parameters such as leaf water content (LWC), chlorophyll density (ChD), free proline content (Pro) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) activities of antioxidant enzymes of winter wheat as a comprehensive drought index (CDI) for winter wheat was constructed using principal component analysis (PCA). Combined with correlation analysis and stepwise multiple linear regression(CA+SMLR), partial least square method and stepwise multiple linear regression(PLS+SMLR) and successive projections algorithm (SPA), the important band extraction was carried out, comprehensive use of stoichiometry methods, physiological and biochemical and CDI? monitoring of winter wheat were studied. The results showed that the number of important bands extracted by CA+SMLR was low and the performance of the SMLR model was average. The model constructed using SPA outperformed both CA+SMLR and PLS+SMLR, and could achieve the purpose of optimizing the CDI indicators for winter wheat. Comparing the models constructed using multiple regression analysis methods, it was found that the performance of the PLSR model built based on the full spectrum (R2=0.885, RMSEC=0.221, RPD=2.772; R2=0.631,RMSEP=0.441, RPD=1.625) was best performance, and the performance of the MLR model built by the SPA method of extracting the important bands (R2=0.647, RMSEC=0.387, RPD=1.355; R2=0.672, RMSEP=0.376, RPD=1.500) was the second performance. The construction of the CDI model provides a reference for achieving hyperspectral monitoring of the integrated performance of physiological parameters of winter wheat after water stress.
Key words: principal component analysis; comprehensive drought index; important bands; performance of model
干旱是影響農(nóng)業(yè)生產(chǎn)最具破壞性的災(zāi)害之一,是影響糧食產(chǎn)量穩(wěn)定性的重要非生物因子。干旱災(zāi)害發(fā)生后,作物產(chǎn)量會(huì)發(fā)生不同程度的下降[1-2]。干旱災(zāi)害造成的產(chǎn)量損失,并不是單一指標(biāo)的影響,而是多參數(shù)共同作用導(dǎo)致的。……

