與有限熱浴耦合的布朗粒子的演化行為研究

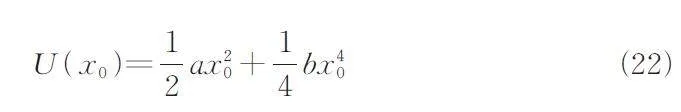

摘要: 本文重點考查與有限熱浴耦合的布朗粒子的非各態歷經和非平衡性. 在廣義朗之萬方程框架下,基于拉普拉斯變換理論推導得出粒子演化的精確解,并進一步探究粒子的漸進行為. 研究發現即使在非線性勢束縛作用下,粒子的穩態行為依賴于初始坐標,而與初始速度無關,呈現非各態歷經性. 數值模擬結果表明,只初始坐標分布取Gibbs-Boltzmann 分布時,粒子才有可能達到平衡態.
關鍵詞: 布朗運動; 非各態歷經; 非線性勢
中圖分類號: O414 文獻標志碼: A DOI: 10. 19907/j. 0490-6756. 2024. 044001
Abstract: Non-equilibrium dynamics and stochastic thermodynamics have emerged as prominent areas of researchin recent years,particularly focusing on small systems. These systems often exhibit unique properties due tomemory effects and finite-scale considerations,which present challenges within the traditional theoreticalframework. The system-plus-heat bath model has been utilized as a phenomenological and intuitive approach forinvestigating complex multi-body problems. However,there is currently a dearth of research on the dynamics ofa particle coupled to a finite-size reservoir. This study aims to fill this gap by investigating the nonergodic andnonequilibrium behaviors of a particle. Specifically,the particle is in contact with one end of a finite coupled oscillatorchain through a harmonic potential. The dynamics of the particle,confined to an external potential,areprecisely analyzed using a Hamiltonian microscopic map within the framework of the generalized Langevin equation.It is important to note that an additional harmonic force with a certain frequency only exists in a finite-size heat bathchain and can be disregarded for a sufficiently large number of coupled oscillators. The second moments of theparticle's coordinates and velocities are obtained through the inversion of the Laplace transform and the utilizationof the fluctuation-dissipation theorem. Furthermore,the long-time asymptotic behaviors of the particle are examinedusing the final-value theorem. The movement of the particle confined to a nonlinear potential is also simulatedthrough the implementation of the fourth-order stochastic Runge-Kutta algorithm. Notably,it is observed that thesteady variance of the particle's coordinate depends on its initial coordinate rather than its initial velocity, dem?onstrating a kind of nonergodic motion. Additionally,the study reveals that nonergodicity and nonequilibrium aredistinct concepts,indicating that nonequilibrium does not necessarily imply nonergodicity. The behavioral evolutionand establishment of stationary production are contingent upon the particle's initial coordinate rather than its initialvelocity. Moreover,the shapes of the stationary probability density function solely depend on the particle's initialcoordinate,specifically the first and second moments. Equilibrium is solely attained when the initial distributionof the particle adheres to a Gibbs-Boltzmann distribution. If the particle is not initially thermally equilibrated,itwill never reach an equilibrium state due to its inherent nonergodicity. These findings, along with future researchin this area,are expected to enhance our understanding of the intricate relationships between nonergodicity andnonequilibrium phenomena.
Keywords: Brownian motion; Nonergodicity; Nonlinear potential
1 Introduction
The stochastic dynamics of open systems is animportant fundamental problem in nonequilibrium statisticalphysics,especially in the study of target particlesin different media environments. Its theoreticalresults greatly promote biophysics,material physics,chemical physics,plasma physics,nuclear physics,and optoelectronic information science[1-6]. The couplingbetween target particles and media environmentsis a complex and difficult problem to handle. Inorder to describe the dissipation and stochastic processesof target particle and explore their inherentphysical essence, various microscopic theoreticalphysical essence, various microscopic theoreticalmodels have been established[7,8]. Among them,Rubin’smodel where the medium environment is thesemi-infinite coupled harmonic oscillator chain(CHO) is widely used to solve practical problemssuch as lattice vibration,thermal conduction,phononoptics,electron transport,condensed phase chemicalreactions,and protein adsorption[9-11].
To the best of our knowledge,the dynamics of aparticle coupled to a reservoir have not been studiedto a great extent. Based on the method of recurrencerelations,Florencio and Lee investigated the dynamicalbehavior of CHO with periodic and fixed-endboundary conditions[12]. Recently,some authors havediscussed its properties and corrected Lee’s results[13]. Plyukhin and Schofield observed the interestingphenomenon that an additional harmonic force ispresent in the generalized Langevin equation( GLE)for a terminal particle in a finite-size reservoir. This force is absent from an equation of motion for a semiinfinitechain. However,the time evolution of a particleof interest,especially the memory effects on therelaxation processes of coordinate and velocity variables,have not been studied for this case. It should beof interest that the localization phenomenon,which isa special kind of nonergodicity,was found for CHOand anharmonic oscillator chains due to the absenceof a zero-frequency mode of collective oscillation[14].On the other hand,the ergodicity of an isothermalsystem without external influences,which approachesa Gibbs-Boltzmann distribution,is a fundamental requirementfor equilibrium statistical mechanics. Atpresent,the relation between ergodicity and equilibriumhas attracted great attention[15-19],particularly thenecessary conditions for a particle to thermalize withthe CHO bath[20-22] and the root of non-stationarity associatedwith nonergodicity[23-26]. From this viewpoint,analysis and discussion of the ergodicity andequilibrium properties of a particle coupled to a finitesizereservoir are in demand and may reveal interestingfindings.
In this work,we intend to consider a particle incontact with a finite heat bath,whose time evolutionand asymptotic behavior will be deduced and analyzedin the framework of GLE. In particular,the nonergodicbehavior of a particle bounded by a nonlinearpotential is discussed in detail. Finally,the concludingremarks are given in the end part.
2 Brownian particle coupled to afinite-size reservoir
We model the system such that the zeroth par?ticle of mass M is coupled to the reservoir comprisinga finite number of CHOs. The particle only interactswith the free-end oscillator through a harmonic potentialV ( x0 - x1 )= Mω2 ( x0 - x1 )2 /2 and is assumedto be confined to an external potential U(x0). Thenthe total Hamiltonian is written as[27,28]
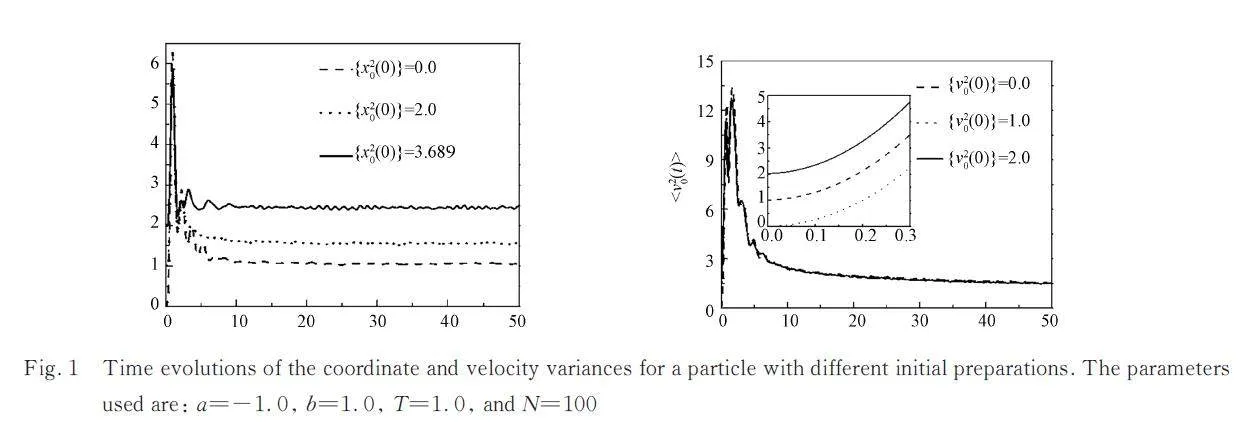
In a recent work,Dhar et al.[17] pointed out that in anonlinear potential,a single oscillator system coupledto an infinite bath of harmonic oscillators does notequilibrate for arbitrary initial conditions due to the localizedmodes. We searched for further discussions ofthe nonergodicity and equilibrium properties of a particlein a bounded potential U(x0). The fourth-orderstochastic Runge-Kutta algorithm is used with asmall time step Δt=0. 01 and 104 calculated trajectoriesto numerically simulate the equations of motioncorresponding to the Hamiltonian in Eq.(1). We considera coupled oscillator-bath with N=100 oscillators,the initial coordinates and velocity of which aresampled from Boltzmann distributions. The particleis chosen with different initial preparations {x02(0),v02(0)} selected from a Gaussian distribution. Weverified that the results do not change as the numberof oscillators in the chain increases. In Fig. 1,we plotthe coordinate and velocity variances of the particle in a double well potential( alt;0 and bgt;0) for differentinitial conditions. Upon inspection,we find that thesteady variance of the coordinate for a particle dependson its initial coordinate,whereas in the longtimelimit,the steady variance of the velocity remainsconstant,regardless of the initial conditions. This,indeed,implies that the coordinate of the particle is anonergodic variable,and the velocity is ergodic[31,32].This situation definitely falls among the second-classnonergodic systems,the nonergodic behavior ofwhich cannot be removed by a potential,even a nonlinearone[33]. Here,we attempt to give a reasonableexplanation that traces back to intrinsic requirements.In this case,there exists an additional potential,i. e. ,Ω2x02/2,which induces divergence of the effectivedamped kernel friction at zero frequency[34]. This potentialimplies that a damping trapping well is addedto the initial region of the particle,which is exactlythe intrinsic reason of the nonergodic behavior of theparticle.
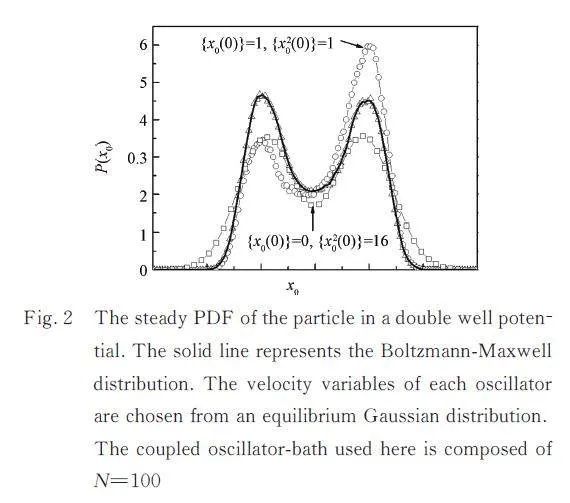
To further clarify the relationship between thenonergodicity and the nonequilibrium state,we investigatethe stationary probability density function(PDF) of a particle for various initial conditions. Theresults are shown in Fig. 2. In particular,the triangleis the numerical result obtained by using the canonicalinitial distribution of the particle in the external potentialU(x0),i. e. ,{x02(t=0)}=3. 689,and thesolid line denotes the theoretical Gibbs-Boltzmanndistribution( GBD). The PDF of the particle departsfrom the GBD if the initial coordinate distribution isnot in an equilibrium state. In particular,the PDFpeak position depends strongly on the initial averageposition of the particle,and the width of the PDF increaseswith increasing {x02(t=0)}. However,thePDF is independent of its initial velocity preparation.As a consequence,if the particle is not initially thermalequilibrated,it will never reach an equilibriumstate. In fact,this is due to the nonergodicity of theparticle. The evolution of the behavior and stationaryproduction depend on the particle’s initial coordinaterather than the initial velocity. The shapes of the stationaryPDF are only determined by the initial coordinateof the particle,namely,its first and second mo?ments. Only if the initial preparation of the particle isGBD can it approach equilibrium. In other words,equality between nonergodicity and nonequilibriumdoes not exist.
4 Conclusions
The nonergodicity and nonequilibrium propertiesof a particle in contact with a finite coupledoscillator-bath have been investigated. Inspection ofthe numerical and analytical calculations elucidatesthe time evolution of the particle in contact with thefinite CHO bath. We have found two crucial andprominent results for a nonlinear particle coupled to afinite CHO bath.(1) The steady variance of the particlecoordinate depends on its initial coordinaterather than its initial velocity,which is indeed nonergodicmotion of a kind.(2) Nonergodicity and nonequilibriumare not equivalent. The equilibrium stateof a particle can be ensured only if its initial distributionis a Gibbs-Boltzmann distribution. We are confidentthat our present results and future studies willcontribute to a deeper understanding of the relationsbetween nonergodicity and nonequilibrium.
References:
[1] Fogelmark K, Lomholt M A, Irb?ck A, et al. Fittinga function to time-dependent ensemble averageddata[ J]. Sci Rep-UK, 2018, 8: 6984.
[2] Huang K,Szlufarska I. Effect of interfaces in the nearbyBrownian motion[ J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 8558.
[3] Kheifets S, Simha A, Melin K, Li T, et al. Observationof Brownian motion in liquids at short times: Instantaneousvelocity and memory loss [J]. Science,2014, 343: 1493.
[4] Zheng Y, Serdukova L, Duan J, et al. Transitions ina genetic transcriptional regulatory system under Lévymotion[ J]. Sci Rep-UK, 2016, 6: 29274.
[5] Huang R, Chavez I, Taute K M, et al. Direct observationof the full transition from ballistic to diffusive Brownianmotion in a liquid[ J]. Nat Phys, 2011, 7: 576.
[6] Metzler R, Klafter J. The random walk’s guide toanomalous diffusion: A fractional dynamics approach[ J]. Phys Rep, 2000, 1: 339.
[7] Zwanzig R. Nonequilibrium statistical mechanics [M].New York: Oxford University Press, 2001.
[8] Weiss U. Quantum dissipative systems [M]. 3rd ed.Singapore: World Scientific, 2008.
[9] Kim J, Sawada I. Dynamics of a harmonic oscillatoron the Bethe lattice [J]. Phys Rev E, 2000, 61:R2172.
[10] Plyukhin A V,Schofield J. Trapping, reflection, andfragmentation in a classical model of atom-lattice collisions[ J]. Phys Rev E, 2002, 65: 026603.
[11] Gendelman O V, Savin A V. Normal heat conductivityof the one-dimensional lattice with periodic potentialof nearest-neighbor interaction[ J]. Phys Rev Lett,2000, 84: 2381.
[12] Florencio Jr J, Lee M H. Exact time evolution of aclassical harmonic-oscillator chain [J]. Phys Rev A,1985, 31: 3231.
[13] Plyukhin A V,Schofield J. Stochastic dynamics with amesoscopic bath[ J]. Phys Rev E, 2001, 64: 041103.
[14] Lee M H. Phys. Ergodic theory,infinite products,andlong time behavior in hermitian models [J]. Rev Lett,2001, 87: 250601.
[15] Lapas L C,Morgado R,Vainstein M H,et al. Khinchintheorem and anomalous diffusion [J]. Phys RevLett, 2008, 101: 230602.
[16] Lee M H. Why irreversibility is not a sufficient conditionfor ergodicity [J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2007, 98:190601.
[17] Dhar A,Wagh K. Equilibration problem for the generalizedLangevin equation [J]. Europhys Lett, 2007,79: 60003.
[18] Plyukhin A V. Nonergodic solutions of the generalizedLangevin equation[ J]. Phys Rev E, 2011, 83: 062102.
[19] Plyukhin A V. Nonergodic Brownian oscillator [J].Phys Rev E, 2022, 105: 014121.
[20] Lee M H. Birkhoff’s theorem,many-body responsefunctions,and the ergodic condition [J]. Phys RevLett, 2007, 98: 110403.
[21] Lapas L C,Morgado R,Vainstein M H,et al. Khinchintheorem and anomalous diffusion [J]. Phys RevE, 2008, 101: 230602.
[22] Wei Q,Smith S T,Onofrio R. Equilibrium states of atest particle coupled to finite-size heat baths [J]. PhysRev E, 2009, 79: 031128.
[23] Siegle P,Goychuk I,Talkner P,et al. Markovian embeddingof non-Markovian superdiffusion [J]. PhysRev E, 2010, 81: 011136.
[24] Ishikawa F, Todo S. Localized mode and nonergodicityof a harmonic oscillator chain [J]. Phys Rev E,2018, 98: 062140.
[25] Bao J D. Disentangling roots of ergodicity breakdown byspectral analyses[ J]. Eur Phys J B, 2020, 93: 184.
[26] Bao J D,Wang X R,Liu W M. Ergodic timescale andtransitive dynamics in single-particle tracking [J].Phys Rev E, 2021, 103: 032136.
[27] Weiss U. Quantum dissipative systems [M]. 2nd ed.Singapore: World Scientific, 1999.
[28] Lu H,Bao J D. Nonergodic Brownian motion in a collinearparticle-coupled harmonic chain model [J]. ChinPhys Lett, 2013, 30: 010502.
[29] Pottier N. Aging properties of an anomalously diffusingparticle[ J]. Physica A, 2003, 317: 061101.
[30] Mai T,Dhar A. Nonequilibrium work fluctuations foroscillators in non-Markovian baths [J]. Phys Rev E,2007, 75: 061101.
[31] Bao J D,H?nggi P,Zhuo Y Z. Non-markovian Browniandynamics and nonergodicity [J]. Phys Rev E,2005, 72: 061107.
[32] Bao J D,Zhuo Y Z,Oliveira F A,et al. NonergodicBrownian dynamics and the fluctuation-dissipationtheorem[ J]. Phys Rev E, 2006, 74: 061111.
[33] Lu H,Qin L,Bao J D. Nonergodicity of Brownian motionin a periodic potential [J]. Acta Phys Sin, 2009,58: 8127.[盧宏, 覃莉, 包景東. 周期場中非各態歷經布朗運動[J]. 物理學報, 2009, 58: 8127.]
[34] Lu H,Lü Y,Bao J D. Studies of nonergodic criterionbased on the fractinal heat bath model [J]. Acta PhysSin, 2015, 64: 170502.[盧宏, 呂艷, 包景東. 基于分數階環境熱浴的非各態歷經判據研究[J]. 物理學報, 2015, 64: 170502.]
(責任編輯: 于白茹)
基金項目: 教育部春暉計劃項目(RZ1900010925); 貴州省教育廳青年科技人才成長項目(黔教合KY 字[2018]407); 畢節市聯合基金項目(畢科聯合字G[2019]14); 貴州工程應用技術學院高級人才啟動基金(院科合字G2018005)

