基于N-EKF的非合作低軌目標雙星無源定位跟蹤算法


摘 要:
針對兩顆天基光學衛星對低軌非合作目標進行無源定位跟蹤的問題,提出了一種基于Newton迭代與擴展卡爾曼濾波(Newton iteration and extended Kalman filter, N-EKF)的定位跟蹤算法。首先,將基于角度測量信息的雙星觀測模型轉化為雙直線公垂線中點問題,并進一步轉化為非線性方程問題,使用Newton迭代算法得到非合作目標的初始定位信息。然后,采用擴展卡爾曼濾波(extended Kalman filter, EKF)方法,在初始定位信息基礎上,結合近地軌道動力學模型,實現對非合作在軌目標的精確跟蹤濾波。最后,通過仿真驗證了所提方法的可行性及優勢。
關鍵詞:
雙星; 無源定位; 非合作低軌目標; 跟蹤濾波
中圖分類號:
V 212
文獻標志碼: A""" DOI:10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.05.30
Double satellite borderless location and tracking algorithm for
non-cooperative low orbit target based on N-EKF
LI Luogang*, LU Ying, CHAO Lujing, REN Jinlei
(China Academy Aerospace Science and Innovation, Beijing 100088, China)
Abstract:
Aiming at the problem of location and tracking non-cooperative low orbit target in two satellites case, an location and tracking algorithm based on the Newton iteration and extended Kalman filter (N-EKF) is proposed. Firstly, the double satellite observation model based on angle measurement information is transformed into two straight lines perpendicular midpoint problem, which is further transformed into non-linear equations problem. The Newton iterative algorithm is used to calculate the initial location information of the non-cooperative target. Then, based on initial positioning information, extended Kalman filter (EKF) and the near-earth orbit dynamic model are used to achieve the precise tracking filter of the non-cooperative in-orbit target. Finally, simulation result verifies the feasibility and advantages of the proposed method.
Keywords:
double satellite; borderless location; non-cooperative low orbit target; tracking
0 引 言
近年來,以美國新一代預警監視衛星為代表的低軌光學跟蹤監視衛星發展迅速。其不僅能用于彈道導彈的預警[1],還可以對包括彈道導彈、臨近高超飛行器、大型飛機在內的多種時敏目標進行可靠定位和跟蹤,為反導、反臨、反空中目標提供可靠的目標信息[2-4]。另外,新一代預警跟蹤監視衛星系統未來還可以為民航飛機提供導航服務[5-6]。
由于新一代低軌光學預警跟蹤監視衛星系統的廣泛用途與巨大戰略優勢,世界主要航天大國近年來都在該領域投入巨資。除美國外,俄羅斯等國近年來也在努力發展其預警跟蹤監視衛星[7-8]。
天基預警跟蹤監視衛星系統的發展,首要目的就是要實現對彈道導彈、高超飛行器、大型飛機等多種時敏目標的無源定位、跟蹤濾波、動態監視,國內外已涌現出大量的研究成果[9-13]。
文獻[14]和文獻[15]對彈道導彈目標助推段運動方程進行了合理簡化,并建立天基預警跟蹤監視衛星量化噪聲模型,提出一種基于量化降噪條件的協同目標跟蹤方法,實現光學預警衛星協同跟蹤助推段導彈目標跟蹤。文獻[16]針對彈道導彈突防中對方攔截點及攔截時間預測問題,提出一種基于監督學習算法的在線預測方法。文獻[17]和文獻[18]面對臨近空間高超聲速目標多星協同定位跟蹤問題,提出一種總體最小二乘與卡爾曼濾波算法結合的跟蹤濾波方法,考慮星上計算能力限制,通過總體最小二乘算法降低了迭代計算量,但也犧牲了部分定位精度。
在相關研究成果的基礎上,針對新一代光學跟蹤監視衛星系統多星協同的特點,進行了系統的無源定位及跟蹤濾波算法研究,考慮到近年來星上計算能力迭代提高,進一步提出了一種基于Newton迭代及擴展卡爾曼濾波(Newton iteration and extended Kalman filter, N-EKF)的無源定位跟蹤算法,進一步提高了雙星無源定位及跟蹤濾波的精度。
1 相關模型及觀測方程
本文中,所用到的坐標系包括:地固系、衛星觀測系。其中,衛星觀測系原點位于衛星質心,oz軸沿地心-衛星方向,ox軸垂直于oz軸指向北極,oy軸、oz軸、ox軸構成右手系,如圖1所示。
衛星的觀測信息,包括視線高低角α和視線方位角β,衛星對目標的觀測模型如圖2所示。
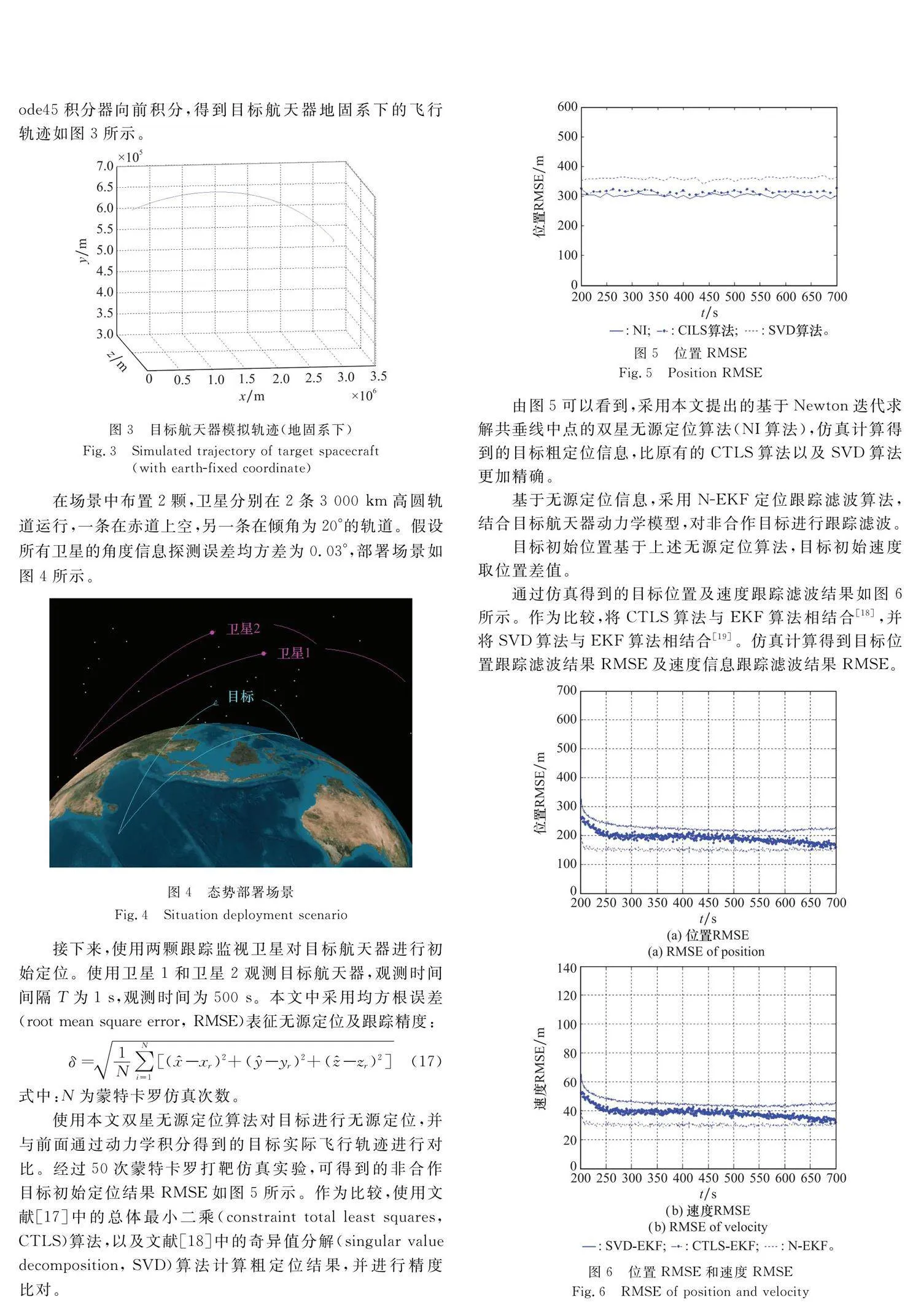
使用本文雙星無源定位算法對目標進行無源定位,并與前面通過動力學積分得到的目標實際飛行軌跡進行對比。經過50次蒙特卡羅打靶仿真實驗,可得到的非合作目標初始定位結果RMSE如圖5所示。作為比較,使用文獻[17]中的總體最小二乘(constraint total least squares, CTLS)算法,以及文獻[18]中的奇異值分解(singular value decomposition, SVD)算法計算粗定位結果,并進行精度比對。
由圖5可以看到,采用本文提出的基于Newton迭代求 解共垂線中點的雙星無源定位算法(NI算法),仿真計算得到的目標粗定位信息,比原有的CTLS算法以及SVD算法更加精確。
基于無源定位信息,采用N-EKF定位跟蹤濾波算法,結合目標航天器動力學模型,對非合作目標進行跟蹤濾波。
目標初始位置基于上述無源定位算法,目標初始速度取位置差值。
通過仿真得到的目標位置及速度跟蹤濾波結果如圖6所示。作為比較,將CTLS算法與EKF算法相結合[18],并將SVD算法與EKF算法相結合[19]。仿真計算得到目標位置跟蹤濾波結果RMSE及速度信息跟蹤濾波結果RMSE。
由圖6可以看到,使用本文N-EKF算法,兩顆衛星對目標航天器的跟蹤濾波誤差快速收斂,由此證明了N-EKF算法的可行性。通過比較可以看到,采用N-EKF算法得到的跟蹤濾波信息,比過去采用的CTLS-EKF跟蹤濾波算法以及SVD-EKF跟蹤濾波算法更加精確。
5 結束語
本文提出一種基于N-EKF的雙衛星定位跟蹤算法。該算法具有以下主要特點:使用2顆光學衛星探測非合作目標;使用Newton迭代求解共垂線中點算法對目標航天器進行粗定位,獲取粗位置信息;在粗位置信息基礎上對目標航天器進行精確跟蹤濾波。
仿真實驗證明N-EKF算法可對非合作近地軌道目標進行定位跟蹤,定位跟蹤精度取得了進一步提高。
然而,本文中所使用的雙星定位跟蹤監視算法,僅局限于兩顆衛星的情況。未來天基衛星要向網絡化、星座化方向發展。如何在3顆以上預警跟蹤監視衛星情況下,實現更加理想的定位及跟蹤濾波效果,需要進一步進行研究。
參考文獻
[1] MAURO P, PAOLO T. Satellite constellations for continuous and early warning observation: a correlation-based approach[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamic, 2007, 30(4): 910-920.
[2] 葉慶, 孫曉泉, 邵立. 紅外預警衛星最佳探測波段分析[J]. 紅外與激光工程, 2010, 39(3): 389-393.
YE Q, SUN X Q, SHAO L. Analysis of optimum detective wavebands for infrared early-warning satellite[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2010, 39(3):389-393.
[3] 李小將, 金山, 廖海玲, 等. 美軍SBIRS GEO-1預警衛星探測預警能力分析[J]. 激光與紅外, 2013, 43(1):3-8.
LI X J, JIN S, LIAO H L, et al. Analysis on infrared detecting and early warning capabilities of America’s SBIRS GEO-1 sate-llite[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2013, 43(1): 3-8.
[4] 張慧. 天基紅外傳感器對中段目標群跟蹤技術研究[D]. 長沙: 國防科技大學, 2014.
ZHANG H. Tracking techniques for midcourse target complex via space-based infrared sensors[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014.
[5] MEIKE R, PIETER V, NAN H. Satellite monitoring of volcanic sulfur dioxide emissions for early warning of volcanic hazards[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2009, 2(3): 196-206.
[6] JEAN-FRANOIS P, PIETRO C, CHRISTELLE V. Development and application of multi-temporal colorimetric transformation to monitor vegetation in the desert locust habitat[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2011, 4(2): 318-326.
[7] 代科學, 馮占林, 萬歆睿. 俄羅斯空間態勢感知體系發展綜述[J].中國電子科學研究院學報, 2016,11(3): 233-238.
DAI K X, FENG Z L, WAN X R, Study on developments of space situation awareness system in Russia[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2016, 11(3): 233-238.
[8] PALEOLOGUE A. Early warning satellites in Russia what past, what state today, what future?[C]∥Proc.of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2005: 146-157.
[9] RAMESH G, MIKE A, GEORGE G. High field HTS Ramp;D solenoid for muon collider[J]. IEEE Trans.on Applied Superconductivity, 2011, 21(3): 1884-1887.
[10] ANDREAS N S. Space-based infrared system (SBIRS) system of systems[C]∥Proc.of IEEE Aerospace Conference, 1997: 429-438.
[11] DAVIS T M, TOMLINSON B J. AFRL cryogenic technology development programs[J] IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2008, 23(3): 18-27.
[12] 申鎮, 強勝, 張寅生. 單星無源探測彈道導彈射向估計新方法[J]. 宇航學報, 2011, 32(7): 1451-1456.
SHEN Z, QIANG S, ZHANG Y S. New method on course heading estimation with single satellite’s passive detection[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2011, 32(7): 1451-1456.
[13] 陳磊, 王海麗. 基于預警衛星觀測數據的彈道重構算法研究[J]. 宇航學報, 2003, 24(2): 203-205.
CHEN L, WANG H L. The research on trajectory estimation algorithm based on observation data of geostationary early-warning satellite[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2003, 24(2): 203-205.
[14] 王宇, 馬成, 彭博, 等.天基紅外預警衛星高精度協同目標跟蹤方法[J]. 中國慣性技術學報, 2022, 30(2): 257-263.
WANG Y, MA C, PENG B, et al. High precision cooperation target tracking method for space-based infrared early-warning satellite[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2022, 30(2): 257-263.
[15] 王宇. 助推—滑翔飛行器高精度軌跡跟蹤方法研究[D]. 哈爾濱: 哈爾濱工業大學, 2021.
WANG Y. Research on the high precision trajectory tracking of boost-glide vehicle[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021.
[16] 楊子成, 鮮勇, 李少朋, 等. 基于學習的中段反導攔截時間和攔截點預測方法[J]. 北京航空航天大學學報, 2021, 47(11): 2368-2378.
YANG Z C, XIAN Y, LI S P, et al. Prediction method of intercept time and intercept point based on learning mid-course antimissile[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(11): 2368-2378.
[17] 李羅鋼, 荊武興, 高長生. 基于預警衛星系統的臨近空間飛行器跟蹤[J]. 航空學報, 2014, 35(1): 105-115.
LI L G, JING W X, GAO C S. Tracking near space vehicle using early-warning satellite[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(1): 105-115.
[18] 李羅鋼. 臨近空間飛行器定位跟蹤及攔截彈制導問題研究[D]. 哈爾濱: 哈爾濱工業大學, 2014.
LI L G. Research on the location and tracking of near space aircraft and the guidance of interceptor[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014.
[19] 吳軍彪, 陳進, 鐘平. 基于總體最小二乘算法的平穩聲信號二階盲分離方法[J]. 聲學學報, 2004, 29(3): 221-225.
WU J B, CHEN J, ZHONG P. Second-order statistics method based on total least-squares for blind separation of stationary sound signals[J]. Acta Acustica, 2004, 29(3): 221-225.
作者簡介
李羅鋼(1984—),男,高級工程師,博士,主要研究方向為飛行器攻防對抗技術。
路 鷹(1982—),男,研究員,博士,主要研究方向為飛行器智能化技術。
晁魯靜(1985—),男,高級工程師,博士,主要研究方向為飛行器仿真技術。
任金磊(1989—),男,高級工程師,博士,主要研究方向為體系仿真技術。

