血漿APC和DCC基因啟動子甲基化測定在肺癌早期診斷中的應用
朱宇敏,李堅,俞立超,朱立歡,陳萍(江蘇大學附屬醫院.呼吸科,.胸外科,江蘇鎮江 00)
血漿APC和DCC基因啟動子甲基化測定在肺癌早期診斷中的應用
朱宇敏1,李堅1,俞立超2,朱立歡1,陳萍1
(江蘇大學附屬醫院1.呼吸科,2.胸外科,江蘇鎮江 212001)
目的:檢測肺癌患者血漿游離 DNA中腺瘤樣結腸息肉易感基因(adenomatous polyposis coli,APC)和結直腸癌缺失基因(deleted in colorectal carcinoma,DCC)啟動子甲基化狀態并分析其在肺癌診斷中的意義。方法:應用甲基化特異性 PCR(methylation specific PCR,MSP)法,檢測70例肺癌患者、40例肺良性病變患者和30例健康志愿者血漿APC和DCC兩個基因啟動子區甲基化狀態。同時測定血清癌胚抗原,并與血漿 APC和DCC基因甲基化測定結果進行比較。結果:(1)肺癌患者血漿標本中 APC、DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性檢出率分別為25.71%(18/70)、35.71% (25/70),接近于血清癌胚抗原的陽性率(37.14%);肺良性病變患者血漿中 APC、DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性率分別為2.50%(1/40)、7.50%(3/40);健康志愿者血漿中這兩個基因未檢測出甲基化;3組間兩基因甲基化陽性率間的差異有統計學意義(P均<0.05);(2)APC和 DCC兩個基因甲基化聯合檢測診斷肺癌的靈敏度為51.43%,特異度為90.00%;血漿APC、DCC基因甲基化和血清癌胚抗原三項聯合檢測可明顯提高肺癌診斷的靈敏度(68.57%),但特異度輕微下降(82.50%);(3)APC和DCC基因啟動子甲基化與肺癌患者年齡、性別、吸煙指數、組織學類型、分化程度、臨床分期及淋巴結轉移無明顯相關性(P>0.05)。結論:外周血漿中 APC、DCC基因甲基化有望成為診斷肺癌的腫瘤標志物,在肺癌早期診斷中具有潛在的應用價值。
肺癌;血漿DNA;甲基化特異性 PCR;腺瘤樣結腸息肉易感基因;結直腸癌缺失基因
[Abstract]Objective:To evaluate clinical utility of the genes promoter hypermethylation of adenomatous polyposis coli(APC)and deleted in colorectal carcinoma(DCC)in plasma for the early diagnosis of lung cancer.Methods:A methylation specific PCR(MSP)was used to detect the status of APC and DCC promoter hypermethylation in plasma DNA from 70 lung cancer patients,40 benign lung disease patients and 30 healthy volunteers.Serum carcinoembryonic antigen(CEA)was detected simultaneously and compared with the plasma APC and DCC genes methylation.Results:(1)The positive rates of plasma APC and DCC genes promoter methylation in lung cancer patients were 25.71% (18/70)and 35.71% (25/70),respectively,which were similar to the positive rate of serum CEA(37.14%).Whereas the positive rates of APC and DCC genes methylation in plasma of benign lung disease patients were 2.50% (1/40)and 7.50% (3/40),respectively.The two genes methylation in plasma was not found in healthy volunteers.There was a significant difference between patients with lung cancer and patients with benign lung disease in plasma APC and DCC genes promoter methylation(P<0.05);(2)Combination of plasma APC and DCC genes methylation raised sensitivity to 51.43%,with 90.00%specificity for the diagnosis of lung cancer.Com-bined use of APC,DCC and CEA achieved sensitivity of 68.57%,with slight decrease of specificity (82.50%);(3)APC and DCC genes promoter methylation in lung cancer patients were not associated with the age,sex,smoking index,pathological types,the degree of tumor differentiation,clinical staging and lymph metastasis of patients with lung cancer.Conclusion:Plasma APC and DCC genes methylation might be two potential candidates as tumor markers of lung cancer.The detections of the two genes methylation may be a complementary tool for the early diagnosis of lung cancer.
[Key words]lung cancer;plasma DNA;methylation specific PCR;adenomatous polyposis coli;deleted in colorectal carcinoma
肺癌是全球公認的癌癥相關致死的首要原因,且致死率呈逐年上升趨勢,即便可手術治療,其預后仍不盡人意,難點在于早期診斷[1]。肺癌患者的總體長期生存率較低,5年生存率低于15%,但Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期患者的 5年生存率分別為 57%~67%和38%~55%[2],提示早期診斷和治療可明顯提高 5年生存率。眾所周知,血液中檢測腫瘤細胞的分子遺傳標志物可以用于癌癥的診斷、治療效果評估及監測病情進展[3]。研究表明,血漿中循環 DNA與腫瘤的發病機制有關聯[4-9],可作為腫瘤診斷和預后評估的工具。因此,篩選出有價值的腫瘤標志物成為肺癌早期診斷的一個重要研究方向。近年來,表觀遺傳學成為分子腫瘤學研究的熱點,DNA甲基化是其中頗為重要的一種表現形式,大量研究證實DNA甲基化在胚胎發育、基因表達、細胞增殖等方面起重要作用,并與腫瘤的發生發展密切相關。抑癌基因甲基化失活是腫瘤發生的表觀遺傳學調控機制,而啟動子 CpG島甲基化是抑癌基因失活的重要方式。本實驗中,我們采用甲基化特異性 PCR (methylation specific PCR,MSP)檢測肺癌患者外周血血漿中腺瘤樣結腸息肉易感基因(adenomatous polyposis coli,APC)和結直腸癌缺失基因(deleted in colorectal carcinoma,DCC)甲基化狀態,探討其在肺癌早期診斷中的應用價值。
1 對象與方法
1.1 研究對象
選擇2013年 5月至 2014年10月期間在本院就診,經病理組織學確診為肺癌的患者70例為研究對象,其中男58例,女12例,年齡38~81歲,中位年齡63.96歲。根據 WHO肺癌組織學分類,鱗癌30例,腺癌 29例,小細胞肺癌 9例,未分型 2例;中、高分化19例,低分化、未分化 51例。按國際抗癌聯盟2009年修訂的肺癌TNM分期標準,符合Ⅰ期 +Ⅱ期 24例,Ⅲ期 +Ⅳ期 46例。所有患者均排除其他惡性腫瘤病史。選擇我院呼吸內科同期住院治療的40例肺部良性疾病患者作為對照,其中男29例,女11例,年齡18~85歲,中位年齡59.08歲。該組所有病例均無肺部或其他器官的惡性腫瘤,其中肺炎15例,慢性阻塞性肺病10例,肺結核 5例,支氣管擴張4例,間質性肺病、哮喘、肺囊腫、炎性假瘤、支氣管炎及肺門淋巴結炎性增生各1例。另選擇30例健康志愿者為健康組,其中男13例,女17例,年齡51~67歲,中位年齡60.37歲。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 標本采集 所有受試者均于治療前抽取清晨空腹外周靜脈血 2 mL,EDTA抗凝,2 500 r/min離心10 min分離血漿,再以12 000 r/min離心10 min,獲得無血細胞成分的血漿,以1.5 mL EP管分裝,于 -80℃保存待檢測。同時抽取靜脈血標本檢測血清癌胚抗原,根據試劑盒說明書標示,癌胚抗原的正常上限為5 μg/L。
1.2.2 血漿 DNA提取 采用 QIAamp DNA Mini Kit(QIAGEN公司,德國)提取血漿 DNA。每份標本使用1 mL血漿,按照說明成比例地增大所需的反應試劑用量,多次過離心柱,最后以 50 μL AE緩沖液洗脫DNA,-20℃保存。
1.2.3 亞硫酸氫鈉修飾 按說明以 EZ DNA Methylation-Gold Kit(Zymo Research,美國)對所提取的血漿 DNA進行亞硫酸氫鈉修飾,將 DNA序列中未甲基化的胞嘧啶(C)轉變為尿嘧啶(U)。最終以20 μL M-洗脫緩沖液洗脫修飾后的 DNA,-20℃保存。
1.2.4 MSP 參照文獻設計 APC基因[10]和 DCC基因[11]引物,分別識別甲基化特異性序列(M)和非甲基化特異性序列(U),由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成。引物序列及MSP反應條件見表1。
MSP反應體系20 μL,其中 DreamTaq Green PCR Master Mix(2×)10 μL(Thermo Scientific,美國),上下游引物各0.5 μL(10 pmol),修飾后的DNA模板4μL,去離子水 5 μL,充分混勻后置于DNA擴增儀中擴增。反應條件為95℃預變性3 min,95℃變性30 s、60℃或62℃退火30 s、72℃延伸30 s,共38個循環,最后72℃延伸10 min。以人甲基化/非甲基化 DNA標準品(北京天恩澤公司)作為甲基化陽性和陰性對照,水空白代替 DNA作為空白對照。
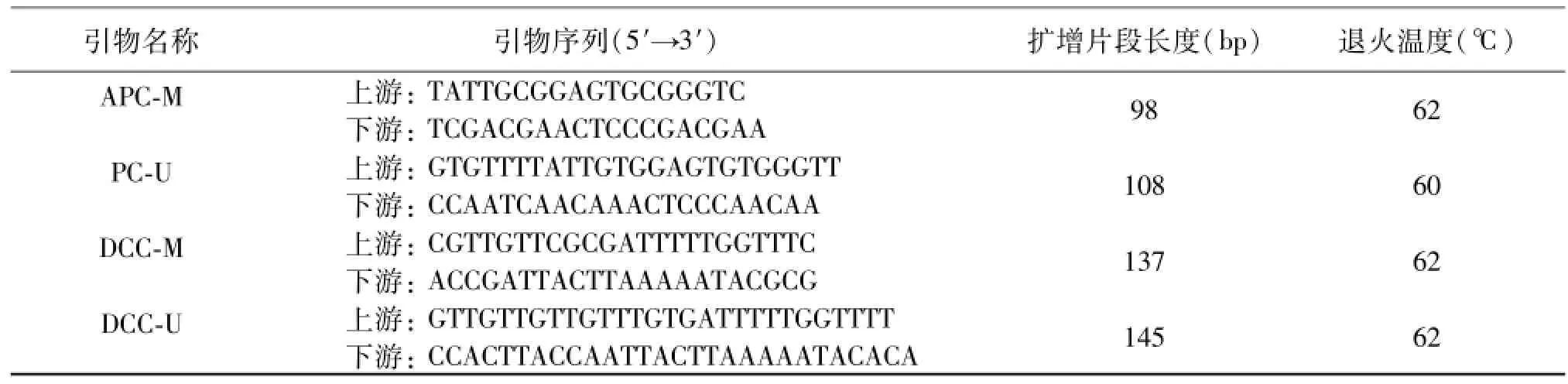
表1 引物序列及其擴增片段長度
1.2.5 瓊脂糖凝膠電泳 MSP結束后,取擴增產物10 μL行2%~2.5%瓊脂糖凝膠電泳(10 V/cm,45 min)鑒定,電泳緩沖液為1×TB緩沖液,500 bp標準參照物作標記,溴化乙啶染色后凝膠成像系統拍照。甲基化結果判定:甲基化引物擴增后出現陽性條帶,不論非甲基化引物擴增結果如何均視為基因甲基化;非甲基化引物擴增后出現陽性條帶,而不出現甲基化條帶的樣品視為基因未甲基化。
1.3 統計學方法
采用SPSS 16.0軟件進行統計學處理。靈敏度=真陽性例數/(真陽性例數 +假陰性例數);特異度=真陰性例數/(真陰性例數 +假陽性例數);陽性預測值 =真陽性例數/(真陽性例數+假陽性例數);陰性預測值=真陰性例數/(真陰性例數+假陰性例數)。計數資料采用 χ2檢驗或 Fisher精確檢驗法,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 血漿APC和 DCC基因甲基化檢測結果
肺癌患者血漿標本中 APC、DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性檢出率分別為25.71%(18/70)、35.71% (25/70);良性肺病患者血漿標本中 APC、DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性率分別為2.50%(1/40)、7.50% (3/40);健康志愿者外周血漿中未檢出這兩個基因啟動子甲基化。3組間 APC基因和 DCC基因甲基化檢測結果比較,差異均有統計學意義(χ2= 18.015,23.732,P均 <0.001)。MSP電泳結果見圖1。
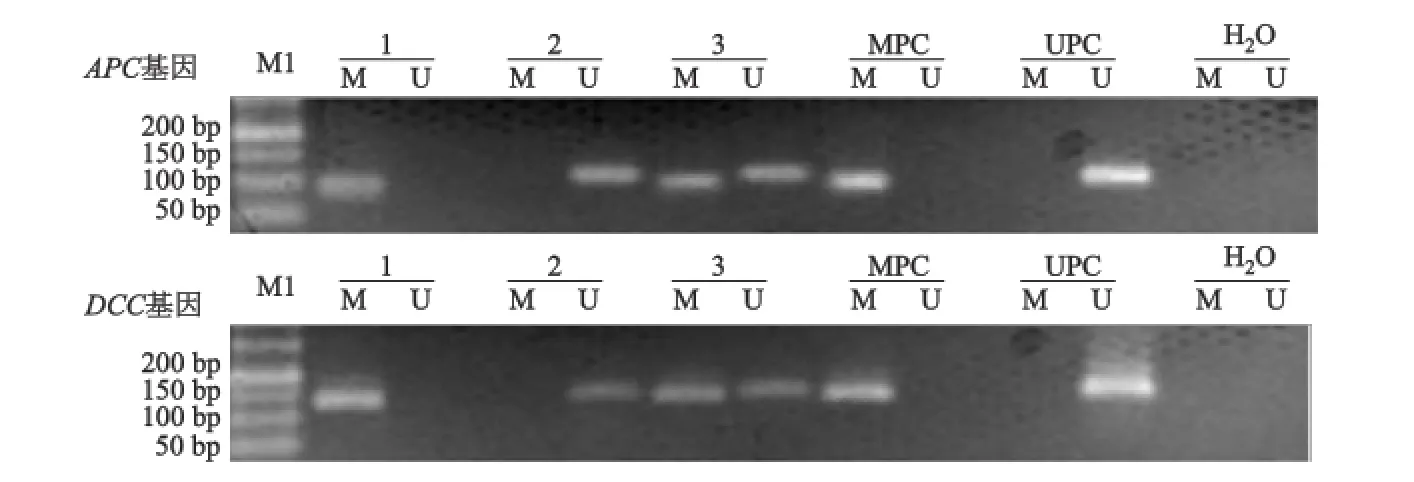
圖1 肺癌患者血漿中 APC、DCC基因的甲基化狀態
2.2 兩類基因甲基化測定對肺癌的診斷效果
我們將肺癌患者血漿 APC和DCC基因甲基化的測定結果與血清癌胚抗原測定結果進行比較。由表2可見,血漿APC和 DCC基因甲基化檢測診斷肺癌的靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值和陰性預測值與血清癌胚抗原檢測結果相似,雖然靈敏度略低于血清癌胚抗原,但特異度要高于血清癌胚抗原。APC和DCC基因甲基化聯合檢測可提高診斷的靈敏度(51.43%),并有較高的特異度(90.00%)。APC、DCC基因甲基化和血清癌胚抗原 3項聯合檢測用于肺癌診斷可進一步提高靈敏度(68.57%),但特異度有所下降(82.50%)。
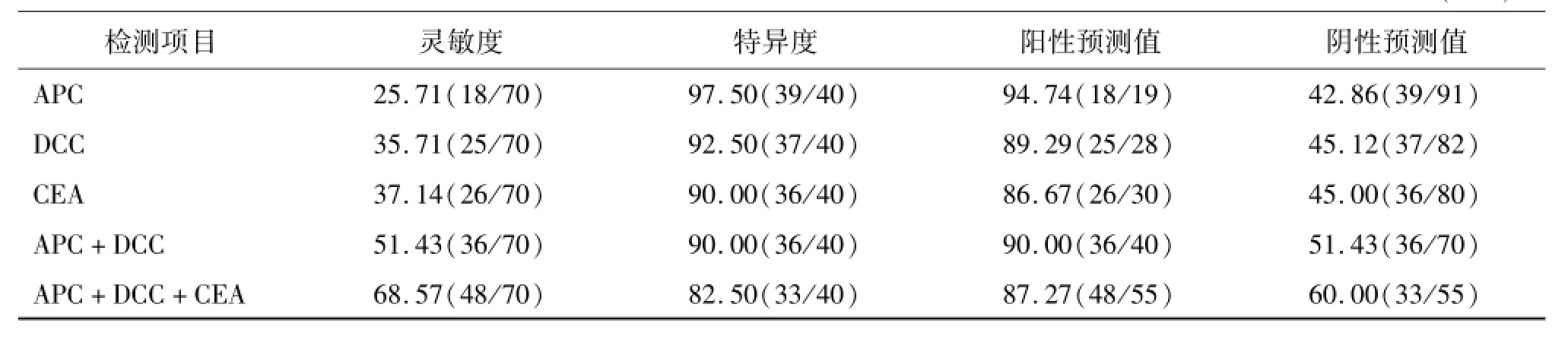
表2 血漿 APC、DCC基因甲基化及血清癌胚抗原檢測診斷肺癌的靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值和陰性預測值%(n/n)
2.3 肺癌患者血漿 APC和 DCC基因甲基化狀態與臨床病理特征間的關系
兩類基因甲基化測定結果與肺癌患者臨床病理特征的相關性分析顯示,血漿APC和DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性與肺癌患者的性別、年齡、吸煙指數、組織學類型、分化程度、TNM分期及淋巴結轉移均無明顯相關性(P均>0.05),見表3。

表3 肺癌患者血漿 APC、DCC基因甲基化狀態與臨床病理特征間的關系
3 討論
肺癌發病率居我國惡性腫瘤首位,大部分肺癌患者確診時已處于中晚期,失去了最佳治療時機,因此,早期診斷是臨床亟須解決的問題之一。早在1977年,Leon等[12]報道健康者的血清或血漿中僅含有極少量游離的DNA,約(13±3)ng/mL,而腫瘤患者外周循環血中DNA的含量明顯增加,約(180± 38)ng/mL。近來研究也顯示,在肺癌患者血液DNA中可檢測到與原發腫瘤細胞一致的分子遺傳學特征[3]。故可通過留取肺癌患者的外周血標本,從基因水平檢測出與肺癌相關的腫瘤標志物,以診斷肺癌的存在。APC基因是 Wnt信號傳導通路中重要的抑癌基因[13],位于人類染色體5q21,長度為8 535 bp,含 21個外顯子。該基因啟動子區高甲基化使之失活,呈不表達或低表達,而基因表達缺失可使 Wnt信號傳導通路異常而導致腫瘤發生[14-16]。據報道,APC基因啟動子高甲基化導致基因轉錄缺失,可見于結直腸癌、食管癌、胃癌、胰腺癌、肺癌、乳腺癌、宮頸癌、子宮內膜癌等多種腫瘤[14]。Laird[17[18]得出的靈敏度(24.36%)和特異度(100.00%)的結果基本一致。
DCC基因是 Fearon等[19]研究結直腸腫瘤時發現的一種抑癌基因,位于人類染色體18q21.1,長度為1.4M bp,含 29個外顯子。Llambi等[20]發現,在結直腸癌中,啟動子甲基化和基因缺失是導致 DCC基因表達顯著下降的主要機制。Begum等[2]用熒光定量MSP法檢測出肺癌患者血漿中 DCC基因的靈敏度為 35.50%,特異度為100.00%;Ostrow等[21]檢測出27.14%(19/70)肺癌患者血漿中DCC基因啟動子區發生了甲基化。本研究顯示,肺癌患者血漿中DCC基因檢測的靈敏度為35.71%,特異度為 92.50%,結果與上述研究基本一致。本研究還表明,血漿APC、DCC基因甲基化與患者性別、年齡、吸煙指數、組織學類型、分化程度、TNM分期及有無淋巴結轉移均不相關。
癌胚抗原是一種廣譜性的腫瘤標志物,臨床上已用于包括肺癌在內多種腫瘤的診斷,具有一定的診斷價值,但其特異性不高。研究表明,血清癌胚抗原水平與肺癌的分期相關,分期越晚,血清癌胚抗原水平越高,故對肺癌早期診斷的作用并不明顯。本研究發現,APC和DCC基因啟動子甲基化陽性檢測結果與肺癌的臨床分期無相關性,Ⅰ-Ⅱ期患者血漿中這兩個基因甲基化陽性率與Ⅲ-Ⅳ期肺癌患者間的差異無統計學意義,表明 APC、DCC基因啟動子甲基化可能是肺癌發生的早期分子事件,早期肺癌患者仍可在血漿標本檢測到與中晚期肺癌患者相似的陽性率。這一結果提示檢測血漿APC和DCC基因甲基化在早期肺癌診斷中的潛在應用價值。在本研究中,兩個基因甲基化的陽性檢出率與淋巴結轉移亦無相關性,其在肺癌診斷中的臨床意義與上述相同。
眾多實驗證實,單個基因出現甲基化狀態在腫瘤的發生發展中并不起決定性作用,腫瘤的發生及病情進展是多基因、多步驟異常變化的結果,包括出現多個基因的甲基化;因此,多個基因甲基化聯合檢測可能對腫瘤的診斷更具意義。Esteller等[22]測定非小細胞肺癌患者血漿中多個與腫瘤相關的 DNA甲基化狀態,結果表明多個基因甲基化聯合檢測的靈敏度為33%~80%。Begum等[2]研究表明,聯合檢測肺癌患者血漿中多個基因可將靈敏度由35.5%提高到75.0%。本實驗中聯合檢測APC、DCC基因甲基化及血清癌胚抗原 3個腫瘤標志物,雖特異度有所下降(82.50%),但靈敏度增高到68.57%,說明多個指標的聯合檢測可明顯提高診斷的靈敏度,有利于肺癌的早期診斷。
研究表明,巢式PCR或實時熒光定量PCR更能提 高 基 因 甲 基 化 的 檢 測 率[23-24]。有 報 道 指 出TaqMan方法的靈敏度是傳統定量MSP法的10倍,但高靈敏度的方法易降低其特異度[25]。故在甲基化分析的眾多方法中,我們選用了 MSP法,其對血清、血漿樣本和石蠟包埋組織中微量的DNA模板均可進行甲基化檢測,且不受內切酶的限制,簡便、準確、高效的特點使其更易在實驗室中廣泛開展。
綜上,APC和DCC基因的甲基化與肺癌的發生、發展密切相關,可作為肺癌診斷的標志物。采用MSP法對APC和DCC基因進行甲基化檢測,結合其他腫瘤標志物測定,有望成為肺癌早期診斷的重要輔助手段。今后,我們還可將腫瘤患者血漿中抑癌基因甲基化檢測用于腫瘤的治療效果、預后、復發等多方面的研究。
[1]Brzeziańska E,Dutkowska A,Antczak A.The significance of epigenetic alterations in lung carcinogenesis [J].Mol Biol Rep,2013,40(1):309-325.
[2]Begum S,Brait M,Dasgupta S,et al.An epigenetic marker panel for detection of lung cancer using cell-free serum DNA[J].Clin Cancer Res,2011,17(13):4494-4503.
[3]Ponomaryova AA,Rykova EY,Cherdyntseva NV,et al. Potentialities of aberrantly methylated circulating DNA for diagnostics and post-treatment follow-up of lung cancer patients[J].Lung Cancer,2013,81(3):397-403.
[4]Kumar S,Guleria R,Singh V,et al.Plasma DNA level in predicting therapeutic efficacy in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer[J].Eur Respir J,2010,36(4):885-892.
[5]van der Drift MA,Hol BE,Klaassen CH,et al.Circulating DNA is a non-invasive prognostic factor for survival in non-small cell lung cancer[J].Lung Cancer,2010,68(2):283-287.
[6]Ponomaryova AA,Rykova EY,Cherdyntseva NV,et al. RARβ2 gene methylation level in the circulating DNA from blood of patients with lung cancer[J].Eur J Cancer Prev,2011,20(6):453-455.
[7]Ponomaryova AA,Rykova Elu,Cherdyntseva NV,et
al.Assay of methylated gene RARβ2 in circulating DNAof blood from patients with lung cancer as a potential prognostic marker[J].Vopr Onkol,2011,57(3):302-307.
[8]Cooke S,Campbell P.Circulating DNA and next-generation sequencing[J].Recent Results Cancer Res,2012,195:143-149.
[9]Gahan PB.Biology of circulating nucleic acids and possible roles in diagnosis and treatment in diabetes and cancer[J].Infect Dis Drug Targets,2012,12(5):360 -370.
[10]Esteller M,Sparks A,Toyota M,et al.Analysis of adenomatous polyposis coli promoter hypermethylation in human cancer[J].Cancer Res,2000,60(16):4366-4371.
[11]Sato K,Tamura G,Tsuchiya T,et al.Frequent loss of expression without sequence mutations of the DCC gene in primary gastric cancer[J].Br J Cancer,2001,85 (2):199-203.
[12]Leon SA,Shapiro B,Sklaroff DM,et al.Free DNA in the serum of cancer patients and the effect of therapy [J].Cancer Res,1977,37(3):646-650.
[13]Schneikert J,Behrens J.The canonical Wnt signaling pathway and its APC partner in colon cancer development[J].Gut,2007,56(3):417-425.
[14]Zysman M,Saka A,Millar A,et al.Me thylation of adenomatous polyposis coli in endometrial cancer occurs more frequently in tumors with microsatellite instability phenotype[J].Cancer Res,2002,62(13):3663-3666.
[15]Radpour R,Barekati Z,Kohler C,et al.Hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes involved in critical regulatory pathways for developing a blood-based test in breast cancer[J].PLoS One,2011,6(1):e16080.
[16]Van der Auwera I,Bovie C,Svensson C,et al.Quantitative methylation profiling in tumor and matched morphologically normal tissues from breast cancer patients[J].BMC Cancer,2010,10:97.
[17]Laird PW.The power and the promise of DNA methylation markers[J].Nat Rev Cancer,2003,3(4):253-266.
[18]潘世揚,謝而付,束永前,等.肺癌患者血漿中 APC基因啟動子甲基化定量檢測研究[J].癌癥,2009,28 (4):384-389.
[19]Fearon ER,Cho KR,Nigro JM,et al.Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers[J].Science,1990,247(4938):49-56.
[20]Llambi F,Causeret F,Bloch-Gallego E,et al.Netrin-1 acts as a survival factor via its receptors UNC5H and DCC[J].EMBO J,2001,20(11):2715-2722.
[21]Ostrow KL,Hoque MO,Loyo M,et al.Molecular analysis of plasma DNA for the early detection of lung cancer by quantitative methylation-specific PCR[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2010,16(13):3463-3472.
[22]Esteller M,Sanchez-Cespedes M,Rosell R,et al.Detection of aberrant promoter hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes in serum DNA from non-small cell lung cancer patients[J].Cancer Res,1999,59(1):67-70.
[23]An Q,Liu Y,Gao Y,et al.Detection of p16 hypermethylation in circulating plasma DNA of non-small cell lung cancer patients[J].Cancer Lett,2002,188(1/ 2):109-114.
[24]Harden SV,Tokumaru Y,Westra WH,et al.Gene promoter hypermethylation in tumors and lymph nodes of stageⅠ lung cancer patients[J].Clin Cancer Res,2003,9(4):1370-1375.
[25]Eads CA,Danenberg KD,Kawakami K,et al.MethyLight:a high-throughput assay to measure DNA methylation[J].Nucleic Acids Res,2000,28(8):E32.
Clinical utility of plasma APC and DCC genes promoter hypermethylation in the early diagnosis of lung cancer
ZHU Yu-Min1,LI Jian1,YU Li-Chao2,ZHU Li-Huan1,CHEN Ping1
(1.Department of Respiratory Medicine,2.Department of Thorax Surgery,the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University,Zhenjiang Jiangsu 212001,China)
R734.2
A
1671-7783(2015)01-0062-06
10.13312/j.issn.1671-7783.y140290
朱宇敏(1987—),女,碩士研究生;李堅(通訊作者),教授,主任醫師,博士生導師,E-mail:lijian541226@163.com
2014-11-10 [編輯]劉星星

