中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚減輕小兒注射痛的效果觀察
彭文勇 上官王寧 杜光生 連慶泉
中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚減輕小兒注射痛的效果觀察
彭文勇 上官王寧 杜光生 連慶泉
目的 觀察中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚是否能減輕小兒靜脈麻醉誘導注射痛。方法對擇期兒科手術的160例患兒采用隨機數字表法分成S組、L組、L+P組和M組,每組各40例。S組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液);L組:靜脈注射利多卡因0.5mg/kg(稀釋成2ml),30s后注射丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液);L+P組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射利多卡因混合丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%丙泊酚18ml+2%利多卡因2ml);M組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液)。丙泊酚注射期間使用VRS四分法對患兒進行注射痛評分;并記錄丙泊酚注射前和注射時心率,觀察注射過程和注射后的不良反應,評價各組疼痛發生率及程度。結果4組患兒注射痛發生率分別是:S組38例(95%),L組32例(80%),L+P組20例(50%),M組19例(47.5%),L組、L+P組、M組注射痛發生率均低于S組38例(均P<0.05),L+P組、M組注射痛發生率低于L組(P<0.05),其余各組間比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);各組丙泊酚注射時心率均增快(P<0.05);與S組比較,丙泊酚注射時L+P組、M組心率低于S組(P<0.05),與L組比較,丙泊酚注射時L+P組心率低于L組(P<0.05);其余各組患兒丙泊酚注射時心率比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);各組間不良反應的差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚能減輕小兒靜脈麻醉誘導注射痛,與利多卡因混合丙泊酚注射效果相當。
中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚 注射痛 利多卡因 丙泊酚
丙泊酚臨床使用廣泛,其主要不良反應為丙泊酚引起的注射痛,且從外周靜脈注射時更明顯,在臨床令人關注的33大問題中,丙泊酚注射痛排在第7位[1],發生率28%~90%[2]。丙泊酚注射痛的發生率如此之高,限制了其在小兒麻醉誘導中的使用。中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚是采用中-長鏈脂肪酸作為丙泊酚的溶劑,增加了脂溶性,降低了丙泊酚水相濃度,從而降低注射痛發生率[3]。國內中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚上市不久,這方面的研究很少,特別是在小兒注射痛的研究尚未見報道,因此,筆者在小兒麻醉誘導過程中采用中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚,觀察其是否能減輕注射痛,現報道如下。
1 對象和方法
1.1 對象 經醫院倫理委員會批準及患者家屬同意,選擇金華市中心醫院2013年3月至2014年6月小兒門診擇期短小手術患兒160例,其中男113例,女47例,年齡5~12(6.8±1.7)歲;體重13.5~52.0(22.8±5.9)kg,ASAⅠ~Ⅱ級。排除標準:對局麻藥、脂類、丙泊酚過敏,哮喘、神經系統功能不全或精神紊亂者,肝、腎功能不全或胰腺功能不全者,靜脈炎患兒,靜脈穿刺失敗2次以上者,入手術室后哭鬧不合作者。按隨機數字表法分為S組、L組、L+P組、M組4組,每組各40例。4組患兒的性別、年齡、體重、身高和ASA分級比較差異均無統計學意義(均P>0.05),詳見表1。
表1 4組患兒性別、年齡、身高、體重和ASA分級的比較
1.2 方法 所有患兒術前均未用藥,術前常規禁飲、禁食。進入準備室后,由準備室護士穿刺手背撓側最粗靜脈,置入24G靜脈留置針,連接三通管并用乳酸鈉林格液沖洗。待觀察液體輸入通暢,患兒無哭鬧后再進行分組。5min后送入手術間,常規監測心電圖、無創血壓、脈搏血氧飽和度。在三通管一端連接2ml注射器,內裝2ml試驗預注藥物,在三通管另一端接上丙泊酚誘導計量,由微泵控制注藥速度。S組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(北京費森尤斯卡比醫藥有限公司,批號:0808055,200mg/20ml)(1%丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液);L組:靜脈注射利多卡因0.5mg/kg(稀釋成2ml),30s后注射丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液);L+P組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射利多卡因混合丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(1%丙泊酚18ml+2%利多卡因2ml);M組:靜脈注射0.9%氯化鈉溶液2ml,30s后注射中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚2.5mg/kg(北京費森尤斯卡比醫藥有限公司,批號:0811002)(1%中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚18ml+2ml氯化鈉溶液)。給藥者和疼痛評估記錄觀察指標者均不知道分組情況。待患兒平靜后打開連有注射器端的三通管,以1ml/6s的速度注射試驗預注藥物,待藥物進入靜脈后關閉輸液通路,30s后使用恒速泵以1ml/6s,將丙泊酚注入靜脈進行麻醉誘導。當患兒意識消失后立即予面罩100%氧氣輔助通氣,然后依次注射2μg/kg的芬太尼和順式阿曲庫胺0.2mg/kg,完成氣管插管;或2%~3%七氟醚、氧氣/空氣1∶1(新鮮氧流量2L/min)進行吸入麻醉,置入喉罩,術中保持自主呼吸。
1.3 疼痛評估及觀察指標 麻醉助手從開始輸注丙泊酚到輸注完畢,嚴密觀察患兒的面部表情、語言反應、肢體運動和手臂回抽動作、口述及流淚現象,并使用McCririck和Hunter[4]使用的VRS四分法評估患兒的疼痛情況(表2);注射期間記錄各組患兒注射前和注射時的心率、心律失常、皮疹,并觀察麻醉蘇醒期丙泊酚的不良反應:煩躁不安、惡心、嘔吐、視物不清等。術后隨訪患者靜脈穿刺點及靜脈沿路的疼痛及皮膚情況,是否有紅、腫等靜脈炎表現。
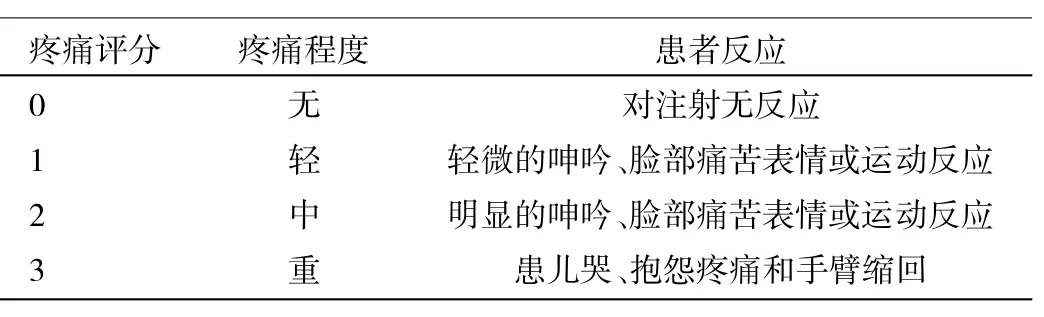
表2 VRS四分法疼痛分級評定
1.4 統計學處理 采用SPSS16.0統計軟件。計量資料以表示,組間比較采用ANOVA單因素方差分析,組內比較采用重復測量數據的方差分析,兩兩比較采用LSD檢驗;計數資料組間比較采用χ2檢驗,等級資料的比較采用秩和檢驗。各組疼痛發生程度的比較采用秩和檢驗。
2 結果
2.1 4組患兒疼痛評分比較 L組、L+P組、M組患兒注射痛發生率均低于S組(均P<0.05),L+P、M組注射痛發生率低于L組(P<0.05),其余各組間比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),詳見表3。
2.2 4組患兒丙泊酚注射前后心率的比較 4組患兒丙泊酚注射時心率均較注射前增快(均P<0.05);與S組比較,丙泊酚注射時L+P、M組心率較低(P<0.05),與L組比較,丙泊酚注射時L+P組心率較低(P<0.05);其余各組丙泊酚注射前后心率比較差異均無統計學意義(均P>0.05),詳見表4。
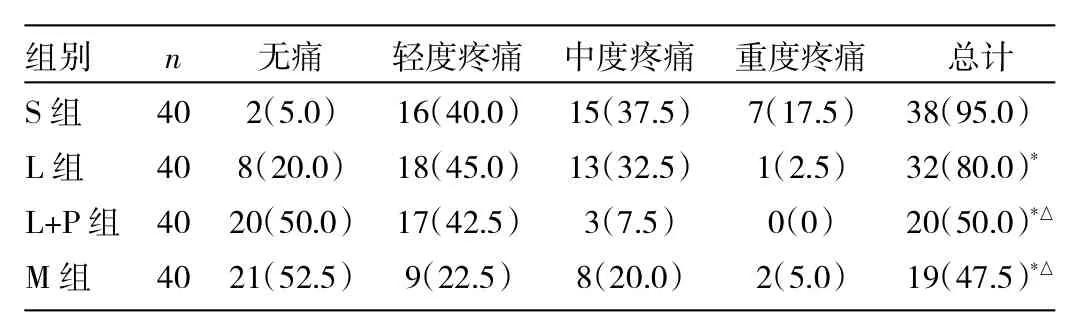
表3 VRS四分法評價丙泊酚注射痛程度[例(%)]
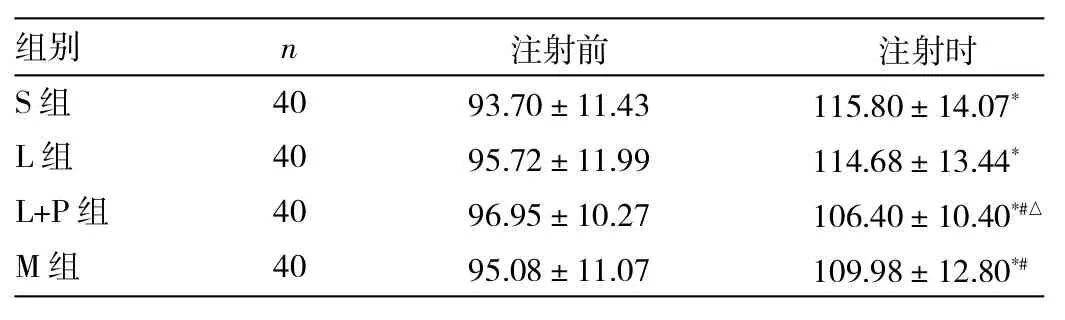
表4 4組患兒丙泊酚注射前后心率的比較(次/min)
2.3 4組患兒不良反應的比較 S組和M組中各2例患兒出現惡心、嘔吐,L組和L+P組中各出現3例,L+P組中1例患兒靜脈穿刺部位出現微紅,拔除靜脈留置針后消除。4組間不良反應發生率的差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),詳見表5。
表5 4組患兒不良反應的比較(例)
3 討論
目前,已有多種方法可以預防其注射痛的發生,包括藥物與非藥物方法。非藥物方法主要通過選用粗大靜脈、前臂結扎止血帶、減慢注射速度甚至給藥時停止輸液、改變制劑成分、改變藥物濃度和溫度、使用濾器、改變藥物pH值等;藥物方法主要使用有全身或局部鎮痛藥物:如利多卡因[5]、阿片類[6-7]、硫噴妥鈉[8]、解熱鎮痛藥、吸入麻醉藥、氯胺酮[9]和其他藥如麻黃堿、硫酸鎂[10]、止吐藥等。即使采用了各種方法,仍不能完全預防丙泊酚的注射痛,其注射痛的發生率仍在32%~48%[11]。臨床上預防丙泊酚注射痛最常用的方法仍是在丙泊酚中混合利多卡因,混合利多卡因改變了丙泊酚的pH值,并可能穩定由于水相丙泊酚[12]引起的激肽系統的瀑布式級聯反應[1]。而混合利多卡因會使丙泊酚注射液變得不穩定,使其產生脂滴,有發生肺栓塞的危險[13]。
雖然已經提出了大量丙泊酚注射痛的機制,但其真正的機制仍不清楚,可能包括以下兩個方面的作用:丙泊酚乳劑中的水相與游離神經末梢接觸而產生的直接致痛效應;游離丙泊酚引發前列腺素釋放誘導產生注射痛,通過激活激肽級聯系統生成緩激肽而產生的延遲作用。緩激肽可以使局部靜脈擴張,血管壁通透性增加,這樣異丙酚就可以透過血管壁接觸到更多的血管外游離神經末梢,從而加重疼痛[14]。
中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚是一種丙泊酚溶于10%的中鏈和長鏈甘油三酯的新型制劑,其不同于傳統的單獨溶于長鏈脂肪酸的制劑,由于其能降低丙泊酚的游離水相濃度而能降低注射痛[15]。研究表明中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚能明顯減輕成人和小兒的丙泊酚注射痛,且與丙泊酚混合0.1%利多卡因效果一致,均能減少丙泊酚注射痛至24%~38%[2,16]。但Nyman等[17]發現中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚減少小兒注射痛的程度不如丙泊酚混合0.1%利多卡因。本研究中中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚注射痛的發生率(47.5%)明顯低于S組(95.0%),與L+P組(50.0%)的發生率接近。
在本研究中,S組及L組丙泊酚注射痛發生率均較高,可能系所有患兒均未使用術前藥,穿刺靜脈及穿刺針較細等緣故。在臨床上很多成人及小兒的預防丙泊酚注射痛研究中,采用了在注射近端結扎止血帶法。止血帶加壓對小兒是一種不良刺激,降低患兒的配合度,并可能影響患兒的心率,故本研究未使用止血帶加壓,或許是造成利多卡因0.5mg/kg預注組注射痛發生率較其他處理組較高的緣故,但仍低于S組(P<0.05)。各組患兒丙泊酚注射時心率均較注射前有所上升,組內比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),而M組、L+P組注射時心率低于L組(P<0.05),可能與注射痛程度較輕有關。
已知影響丙泊酚注射痛的因素有很多,本研究對各項影響因素作了充分的考慮,包括限定靜脈粗細及留置針大小,藥物使用恒定輸液泵恒速輸注,室溫下配置試驗用藥,丙泊酚輸注時停止輸液。
本研究比較了中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚減輕丙泊酚注射痛的效果,發現其作用顯著,與S組比較差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),且減輕丙泊酚注射痛作用優于利多卡因0.5mg/kg預注(P<0.05),與利多卡因40mg預混相比,減輕注射痛程度相同(P>0.05),說明中長鏈脂肪酸丙泊酚是一種有效的預防丙泊酚注射痛的制劑,值得臨床推廣應用。
[1]Macario A,Weinger M,Truong P,et al.Which clinical anesthesia outcomes are both common and important to avoid?The perspective of a panel of expert anesthe-siologists[J].Anesth Analg, 1999,88(5):1085-1091.
[2]Picard P,Tramer M R.Prevention of pain on injection with propofol:a quantitative systematic review[J].Anesth Analg,2000, 90(4):963-969.
[3]錢玉芳.丙泊酚中長鏈脂肪乳全麻誘導對全子宮切除術注射痛的影響[J].浙江醫學,2012,34(11):949-950.
[4]Mccrirrick A,Hunter S.Pain on injection of propofol:the effect of injectate temperature[J].Anaesthesia,1990,45(6):443-444.
[5]Walker B J,Neal J M,Mulroy M F,et al.Lidocaine pretreatment with tourniquet versus lidocaine-propofol admixture for attenuating propofol injection pain:a randomized controlled trial[J].Reg Anesth Pain Med,2011,36(1):41-45.
[6]Zhang L,Bao Y,Shi D.Comparing the pain of propofol via different combinations of fentanyl,sufentanil or remifentanil in gastrointestinal endoscopy[J].Acta Cir Bras,2014,29(10):675-680.
[7]Chae Y J,Min S K,Park S K,et al.Reduction of microemulsion propofol-induced injection pain via target-controlled remifentanil infusion[J].J Int Med Res,2011,39(6):2151-2157.
[8]Saadawy I,Ertok E,Boker A.Painless injection of propofol:pretreatment with ketamine vs thiopental,meperidine,and lidocaine [J].Middle East J Anesthesiol,2007,19(3):631-644.
[9]Wang M,Wang Q,Yu Y Y,et al.An effective dose of ketamine for eliminating pain during injection of propofol:a dose response study[J].Ann Fr Anesth Reanim,2013,32(9):103-106.
[10]Memis D,Turan A,Karamanlioglu B,et al.The use of magnesium sulfate to prevent pain on injection of propofol[J].Anesth Analg,2002,95(3):606-608.
[11]King S Y,Davis F M,Wells J E,et al.Lidocaine for the prevention of pain due to injection of propofol[J].Anesth Analg,1992, 74(2):246-249.
[12]Dubey P K,Kumar A.Pain on injection of lipid-free propofol and propofol emulsion containing medium-chain triglyceride:a comparative study[J].Anesth Analg,2005,101(4):1060-1062.
[13]Davies A F,Vadodaria B,Hopwood B,et al.Efficacy of microfiltration in decreasing propofol-induced pain[J].Anaesthesia, 2002,57(6):557-561.
[14]Nishiyama T.How to decrease pain at rapid injection of propofol:effectiveness of flurbiprofen[J].J Anesth,2005,19(4):273-276.
[15]Larsen B,Beerhalter U,Biedler A,et al.Less pain on injection by a new formulation of propofol?A comparison with propofol LCT[J].Anaesthesist,2001,50(11):842-845.
[16]Yew W S,Chong S Y,Tan K H,et al.The effects of intravenous lidocaine on pain during injection of medium-and long-chain triglyceride propofol emulsions[J].Anesth Analg,2005,100(6): 1693-1695.
[17]Nyman Y,Von Hofsten K,Georgiadi A,et al.Propofol injection pain in children:a prospective randomized double-blind trial of a new propofol formulation versus propofol with added lidocaine[J].Br J Anaesth,2005,95(2):222-225.
ObjectiveTo investigate the effect of medium-and long-chain triglycerides propofol(propofol M/LCT)in reducing injection pain during intravenous anesthesia induction in pediatric surgery.MethodsOne hundred and sixty pediatric patients who were scheduled for elective operation under general anesthesia were randomly divided into four groups(n=40 in each group):group S,group L,group L+P and group M.During anesthesia induction patents in group S,L+P and M were given 2ml normal saline(NS),group L was given lidocaine 0.5mg/kg in 2ml NS,followed by injection of 2.5mg/kg propofol(groups S and L),propofol mixed lidocaine(group L+P)or 2.5mg/kg propofol M/LCT(group M),respectively.Pain was assessed by the four-point scores of verbal rating scale at the time of propofol injection.The heart rate was recorded before and during injecting,adverse reaction of injection was observed and the incidence and severity of injection pain was evaluated.ResultsThe incidence of injection pain occurred ingroups L,L+P and Mwere lowerthan that in group S(80%,50%and 47.5%,97%,P<0.05),the incidence in groups L+P and M was lower than that in group L(P<0.05).The heart rate during the injection was higher than that before injection in all groups(P<0.05),the heart rate during the injection in groups L+P and M was lower than that in group S(P<0.05),in L+P was lower than that in group L(P<0.05).There was no difference in adverse reaction of injection among all groups(P>0.05).ConclusionMedium-and long-chain triglycerides propofol can reduce the injection pain during intravenous anesthesia induction with propofol in pediatric surgery,and effect is same to the propofol mixed lidocaine.
Medium-and long-chain triglycerides propofolInjection pain Lidocaine Propofol

2014-03-19)
(本文編輯:嚴瑋雯)
321000 金華市中心醫院麻醉科(彭文勇、杜光生);溫州醫科大學附屬第二醫院麻醉科(上官王寧、連慶泉)
連慶泉,E-mail:lianqingquan@yahoo.com.cn

