早產兒早期凝血功能與胎齡的關系
霍樂潁
(珠海市婦幼保健院新生兒科,廣東 珠海 519000)
早產兒早期凝血功能與胎齡的關系
霍樂潁
(珠海市婦幼保健院新生兒科,廣東 珠海 519000)
目的 探討不同胎齡早產兒早期凝血功能的變化及其臨床意義。方法 將141例早產兒按不同的胎齡分為早期早產兒組(胎齡27~31+6周,44例)、中期早產兒組(胎齡32~33+6周,39例)和晚期早產兒組(胎齡34~36+6周,58例)。各組出生后2 h內抽取靜脈血,檢測凝血酶原時間(prothrombin time,PT)、活化部分凝血酶原時間(activated partial thromboplastin time,APTT)、凝血酶時間(thrombin time,TT)及纖維蛋白原(fibrinogen,FIB)的水平,并對各檢測指標與胎齡的相關性進行分析。結果 中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組PT、APTT、TT均較早期早產兒組短,FIB水平均較早期早產兒組升高(均P<0.05)。早期早產兒組、中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組的PT、APTT、TT與胎齡呈負相關(r=-0.67、-0.31、-0.33,均P<0.05),早期早產兒組、中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組的FIB與胎齡呈正相關(r=0.34,P<0.05)。結論 早產兒早期凝血功能與胎齡有密切關聯,在早期早產兒組尤為明顯。當PT、APTT延長及FIB降低時,應引起足夠重視,注意復查凝血功能,必要時進行干預治療。
早產兒; 凝血功能; 胎齡
隨著圍產醫學和新生兒重癥監護水平的不斷提高,早產兒問題越來越受到人們重視。由于早產兒各器官發育不成熟,尤其是肝臟發育不成熟,肝功能相對較差,生后易患出血性疾病[1]。本研究通過對不同胎齡早產兒生后2 h內凝血功能的檢測,探討其臨床意義。
1 對象與方法
1.1 研究對象
選擇2015年1—12月在珠海市婦幼保健院新生兒科住院的早產兒141例,均為生后24 h的早產兒。患兒母親肝、腎功能正常,無血液病和自身免疫性疾病,無妊娠合并癥,無胎盤早剝、胎膜早破史,產前、產時均未使用抗凝藥物、抗驚厥藥物及抗結核藥物。患兒無窒息、宮內缺氧等病史。將141例早產兒按不同的胎齡分為3組:早期早產兒組44例,男24例,女20例,胎齡27~31+6(30.42±1.45)周,出生體質量980~2060(1 365.68±288.94)g。其中剖宮產術16例,自然分娩28例。中期早產兒組39例,男19例,女20例,胎齡32~33+6(32.95±0.88)周,出生體質量1420~2410(1 932.82±344.96)g。其中剖宮產術17例,自然分娩22例。晚期早產兒組58例,男31例,女27例,胎齡34~36+6(35.92±1.46)周,出生體質量1530~3050(2 172.31±386.06)g。其中剖宮產術33例,自然分娩26例。3組性別、胎齡及出生體質量比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。
1.2 檢測方法
對3組早產兒于生后2 h內抽取肘靜脈血1.8 mL,采用日本東亞公司生產的Sysmex 1500型全自動血凝分析儀(凝固法)檢測凝血酶原時間(prothrombin time,PT)、活化部分凝血酶原時間(activated partial thromboplastin time,APTT)、凝血酶時間(thrombin time,TT)及纖維蛋白原(fibrinogen,FIB)的水平。具體操作根據儀器標準化操作程序進行。
1.3 統計學方法
2 結果
中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組PT、APTT、TT均較早期早產兒組短,FIB水平均較早期早產兒組升高,均P<0.05;晚期早產兒組PT、APTT、TT均較中期早產兒組短,FIB水平均較中期早產兒組升高,均P<0.05。見表1。
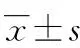
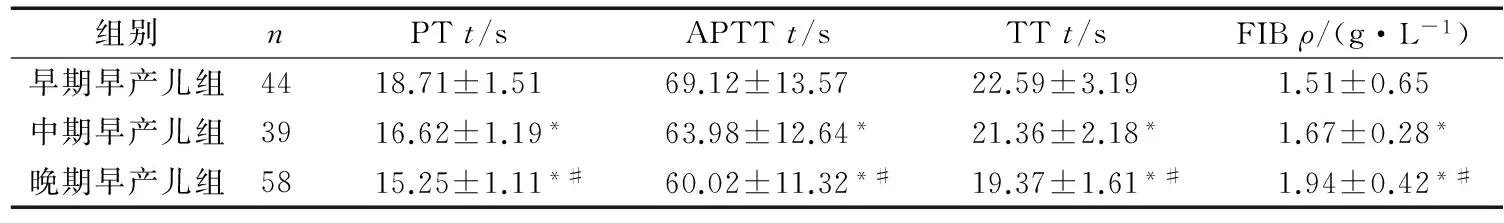
組別nPTt/sAPTTt/sTTt/sFIBρ/(g·L-1)早期早產兒組4418.71±1.5169.12±13.5722.59±3.191.51±0.65中期早產兒組3916.62±1.19*63.98±12.64*21.36±2.18*1.67±0.28*晚期早產兒組5815.25±1.11*#60.02±11.32*#19.37±1.61*#1.94±0.42*#
*P<0.05與早期早產兒組比較,#P<0.05與中期早產兒組比較。
相關性分析結果顯示:早期早產兒組、中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組的PT、APTT、TT與胎齡呈負相關(r=-0.67、-0.31、-0.33,均P<0.05),早期早產兒組、中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組的FIB與胎齡呈正相關(r=0.34,P<0.05)。
3 討論
早產兒出生后肝臟發育不成熟,腸道菌群未建立,消化吸收功能低下,維生素K通過胎盤的能力較差,早產兒腸道定植產維生素K的細菌少,使早產兒出生后維生素K缺乏,導致維生素K依賴因子Ⅱ、Ⅶ、Ⅸ、X功能低下,且是無功能的蛋白質,不能參與凝血過程。機體內凝血因子活性低下,凝血酶原缺乏,易患出血性疾病[2-3]。
PT是外源性凝血系統較為敏感和最為常用的篩選指標,主要由肝臟合成的凝血因子Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ、Ⅶ、Ⅹ的水平決定。APTT是檢測內源性凝血途徑較為敏感和最為常用的篩選指標,是由凝血因子Ⅰ、Ⅱ、Ⅴ、Ⅷ、Ⅸ、Ⅹ、Ⅺ、Ⅻ的水平決定。Andrew等[4]研究認為,凝血系統是一個動態、演變的系統,凝血蛋白水平隨著胎齡增加而逐漸提高。本研究通過比較不同胎齡早產兒凝血指標,結果顯示,中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組PT、APTT、TT均較早期早產兒組短,晚期早產兒組PT、APTT、TT均較中期早產兒組短(均P<0.05),且早期早產兒組、中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組的PT、APTT、TT與胎齡呈負相關(r=-0.67、-0.31、-0.33,均P<0.05),其與徐發林等[5]研究的結果一致,并提示胎齡越小的早產兒凝血功能越差,越容易發生出血性疾病。 FIB是一種由肝臟合成的、具有凝血功能的蛋白質,是纖維蛋白的前體,它不能通過胎盤從母體獲得,而需要自身合成。本研究結果顯示,中期早產兒組、晚期早產兒組FIB水平均較早期早產兒組升高,晚期早產兒組FIB水平較中期早產兒組升高(均P<0.05),其與Ignjatovic等[6]研究的結果一致,并提示早產兒血液處于一種低凝和纖溶亢進的狀態,這也解釋了早產兒為什么容易并發肺出血、顱內出血、消化道出血、彌漫性血管內凝血等出凝血障礙疾病的原因。
綜上所述,早產兒血液處于低凝和繼發性纖溶亢進的狀態,胎齡越小,越容易出現凝血功能障礙[7-8]。早期評估PT、APTT、TT、FIB水平,可以早期發現凝血功能異常,早期干預,為臨床正確使用凝血功能的藥物提供參考,對防治早產兒出血性疾病的發生具有重要的意義。
[1] 李麗蓮.早產兒凝血功能與出生體質量的關系研究[J].當代醫學,2015,21(13):33-34.
[2] 李寧俠,何雨峰,劉芳,等.新生兒凝血指標及部分生化指標檢測參考區間調查[J].現代生物醫學進展,2016,16(17):3295-3298.
[3] Kuzmenko G N,Nazarov S B,Popova I G,et al.The functional characteristics of hemostasis of full-term and premature newborn according results of thromboflexography[J].Klin Lab Diagn,2013(5):14-17.
[4] Andrew M,Vegh P,Johnston M,et al.Maturation of the hemostatic system during childhood[J].Blood,1992,80(8):1998-2005.
[5] 徐發林,程慧清,高亮,等.早產兒早期凝血功能與胎齡的關系[J].臨床兒科雜志,2016,34(1):25-28.
[6] Ignjatovic V,Lai C,Summerhayes R,et al.Age-related differences in plasma proteins:how plasma proteins change from neonates to adults[J].PLoS One,2011,6(2):e17213.
[7] 林薇.早產兒凝血酶時間、凝血酶原時間、部分凝血酶時間及纖維蛋白原的監測及臨床意義[J].中國醫藥指南,2014,12(14):118-119.
[8] 李霞.早產兒凝血功能指標變化及凝血時間監測的臨床意義分析[J].現代診斷與治療,2014,25(16):3620-3621.
(責任編輯:胡煒華)
Relationship between Early Coagulation Function and Gestational Age in Preterm Infants
HUO Le-ying
(DepartmentofNeonatology,ZhuhaiMaternalandChildHealthHospital,Zhuhai519000,China)
Objective To investigate the changes in early coagulation function and its clinical significance in preterm infants of different gestational ages.Methods A total of 141 preterm infants were divided into three groups:early preterm group(gestational age ranged from 27 to 31+6weeks,44 cases),moderate preterm group(gestational age ranged from 32 to 33+6weeks,39 cases),and late preterm group(gestational age ranged from 34 to 36+6weeks,58 cases).Venous blood samples were collected within 2 hours after birth to detect prothrombin time(PT),activated partial thromboplastin time(APTT),thrombin time(TT) and fibrinogen(FIB) levels.The relationships of these indicators to gestational age were analyzed.Results Compared with early preterm group,the PT,APTT and TT were shortened and the FIB levels were increased in both moderate preterm group and late preterm group(P<0.05).In addition,PT,APTT and TT were negatively correlated with gestational age but FIB was positively correlated with gestational age in all the three groups(r=-0.67,-0.31,-0.33 and 0.34,respectively;P<0.05).Conclusion The early coagulation function is closely associated with the gestational age in preterm infants,especially in early preterm infants.When PT and APTT are prolonged and FIB is decreased,enough attention should be paid to the coagulation function and the necessary intervention.
preterm infants; coagulation function; gestational age
2016-08-22
霍樂潁(1983—),女,碩士,主治醫師,主要從事免疫性疾病的診治研究。
R72; R71; R446.1
A
1009-8194(2016)11-0057-03
10.13764/j.cnki.lcsy.2016.11.023

