基于加權(quán)最小二乘法的供水管網(wǎng)節(jié)點(diǎn)流量校核
范江 杜坤 周明 徐冰峰 龍?zhí)煊?/p>

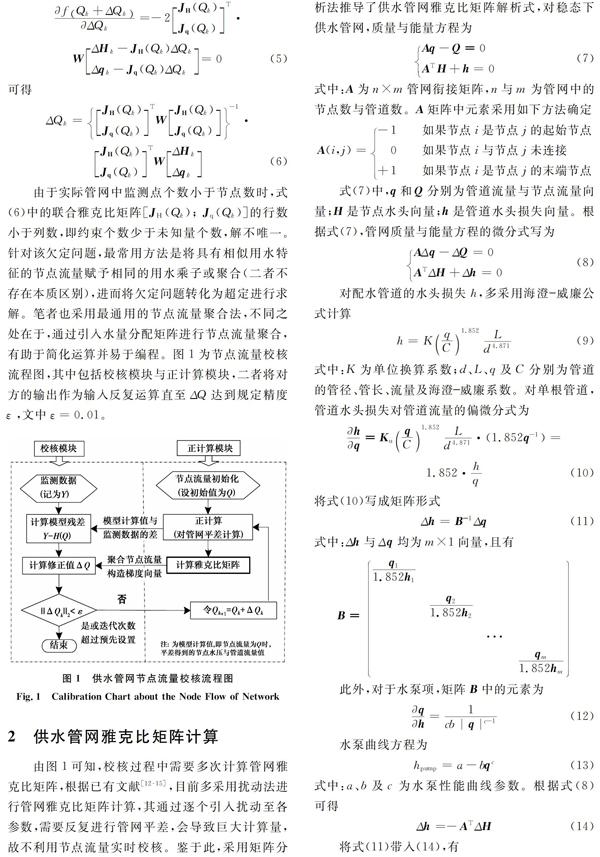

摘要:管網(wǎng)水力模型是實(shí)現(xiàn)供水系統(tǒng)現(xiàn)代化管理的重要工具,要使水力模型能比較準(zhǔn)確地反映管網(wǎng)真實(shí)運(yùn)行狀態(tài),達(dá)到預(yù)期使用目的,其中的參數(shù)需要校核。將管網(wǎng)節(jié)點(diǎn)流量校核作為優(yōu)化問題,采用加權(quán)最小二乘法逐步迭代求解,與已有研究相比,采用矩陣分析法推導(dǎo)供水管網(wǎng)雅克比矩陣解析式,引入水量分配矩陣聚合節(jié)點(diǎn)流量,將欠定問題轉(zhuǎn)化為超定,提高了校核的計(jì)算效率和結(jié)果的可靠性。采用簡(jiǎn)單管網(wǎng)闡明了雅克比矩陣的計(jì)算、節(jié)點(diǎn)流量的聚合及梯度向量的構(gòu)造,利用實(shí)際管網(wǎng)驗(yàn)證了方法的實(shí)用性。
關(guān)鍵詞:供水管網(wǎng);節(jié)點(diǎn)流量校核;加權(quán)最小二乘法;雅克比矩陣;解析式
中圖分類號(hào):TU 991.32
文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼:A 文章編號(hào):1674-4764(2016)03-0073-07
Abstract:Hydraulic model of water distribution systems (WDSs) is an essential tool to realize modernization management of WDSs. To make the model capable of reflecting the systems behavior with reasonable accuracy and achieving intended purposes, the parameters in it should be calibrated. The nodal demand calibration of WDS models is formulated as a nonlinear optimization problem, which is then solved iteratively using weighted least squares method. Comparing to previous studies, the proposed method deduces the analytical solution of Jacobian matrix of WDSs based on matrix analysis method, and translates the under-determined problem to over-determined by aggregating the nodal demand using demand allocation matrix, such that the computational efficiency and the reliability of calibration results were improved. A simple network is used to illustrate the computation of Jacobian matrix, the construction of gradient vectors and the aggregation of nodal demand. The practicability of the method is further validated by a real network.
Keywords:water distribution system; nodal demand calibration; weighted least squares algorithm; jacobian matrix; analytical solution
管網(wǎng)水力模型不僅能用于指導(dǎo)供水調(diào)度、優(yōu)化運(yùn)營管理,還是開展其他相關(guān)研究的基礎(chǔ),如管網(wǎng)水質(zhì)模擬、突發(fā)性水質(zhì)污染事件預(yù)警與定位等。隨著社會(huì)經(jīng)濟(jì)發(fā)展,各地自來水廠開始投入大量人力與財(cái)力構(gòu)建或完善管網(wǎng)水力模型。管網(wǎng)水力模型校核,或稱管網(wǎng)參數(shù)校正,是指通過調(diào)整模型中預(yù)先設(shè)置的水力參數(shù),使模型計(jì)算值與監(jiān)測(cè)值匹配的過程,其目的在于使構(gòu)建的水力模型能比較準(zhǔn)確地反映管網(wǎng)的真實(shí)運(yùn)行狀態(tài),達(dá)到預(yù)期使用目的。在構(gòu)建的管網(wǎng)水力模型中,由于節(jié)點(diǎn)流量隨時(shí)間不斷發(fā)生變化,為時(shí)間“常變量”,需要進(jìn)行實(shí)時(shí)校核[1]。
針對(duì)管網(wǎng)節(jié)點(diǎn)流量校核,吳學(xué)偉等[2]嘗試以節(jié)點(diǎn)水壓為已知量計(jì)算節(jié)點(diǎn)流量,并采用實(shí)驗(yàn)室管網(wǎng)進(jìn)行驗(yàn)證,結(jié)果表明,對(duì)實(shí)驗(yàn)室小型管網(wǎng)狀態(tài)估計(jì)精度較高,但對(duì)于實(shí)際大型管網(wǎng)的工況分析有待進(jìn)一步研究。……

