右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠血清及外周血單個核細胞HMGB1表達的影響
王珊珊,楊曉明,王 濤
(中國人民解放軍空軍總醫院麻醉科,北京 100142)
?
右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠血清及外周血單個核細胞HMGB1表達的影響
王珊珊,楊曉明△,王濤
(中國人民解放軍空軍總醫院麻醉科,北京 100142)
[摘要]目的研究右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠血清及外周血單個核細胞(PBMCs)中高遷移率族蛋白1(HMGB1)表達的影響及其可能機制。 方法32只SD大鼠分為對照組(C組)、模型組(H組)、右美托咪定組(D組)和育亨賓組(Y組)。麻醉后將大鼠置于(40.0±0.5)℃環境,直至體溫達到42 ℃,建立熱射病模型。于熱應激終點后1 h采血,酶聯免疫吸附試驗(ELISA)試劑盒測定血清HMGB1濃度,淋巴細胞分離液提取PMBCs,Western blot法測定PBMCs中HMGB1的水平。結果與C組相比,H組大鼠血清HMGB1濃度明顯增加,而PBMCs中HMGB1水平明顯降低(P<0.05);與H組相比,D組大鼠血清HMGB1濃度降低,而PBMCs中HMGB1水平增加(P<0.05);與D組相比,Y組大鼠血清HMGB1濃度增加,而PBMCs中HMGB1水平降低(P<0.05)。結論右美托咪定降低熱射病大鼠血清HMGB1水平,其機制可能與作用于PBMCs表面α2受體,減少其HMGB1的釋放有關。
[關鍵詞]右美托咪定;熱射病;高遷移率族蛋白1; PBMCs
熱射病(heat stroke,HS)是一種由中心體溫極度升高引起的威脅生命的疾病[1-2]。熱射病常是致命的,至今尚缺乏特異性和有效的治療。高遷移率族蛋白1(HMGB1)是一種核非組蛋白DNA結合蛋白,近年研究認為HMGB1是無菌損傷炎癥和器官損傷的早期介質[3-4],由壞死的組織細胞釋放或由單核巨噬細胞等炎癥細胞分泌。研究表明,HMGB1參與熱射病的發生與發展,阻斷HMGB1通路可能改善熱射病預后[5-6]。右美托咪定是一種α2腎上腺素受體激動劑,能夠降低膿毒血癥及缺血再灌注模型大鼠的血清細胞因子及HMGB1水平,改善其預后[7-9]。因此,本研究推測右美托咪定可能通過調節HMGB1水平,從而影響熱射病預后。本實驗通過測定熱射病模型大鼠血清及血單個核細胞中的HMGB1水平來研究右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠HMGB1水平的影響及其可能作用機制。
1材料與方法
1.1材料成年雄性240~280 g SD大鼠32只(中國人民解放軍第304醫院實驗動物中心)。實驗開始前,動物飼養在24 ℃環境中,12/12 h晝夜節律,自由攝食飲水,適應環境1周。
1.2方法
1.2.1熱射病模型建立方法3%戊巴比妥鈉(45 mg/kg)麻醉大鼠,置于預熱至(40.0±0.5)℃的熱艙中,每隔5 min監測記錄肛溫(代表中心體溫),以中心體溫達42.0 ℃為熱應激終點[10]。
1.2.2分組與處理所有大鼠麻醉后分為4組,每組8只。對照組(C組):麻醉后直接放入24 ℃室溫環境中。其余組大鼠麻醉后放于(40.0±0.5)℃的熱艙中,達熱應激終點后,模型組(H組):腹腔注射1 mL生理鹽水;右美托咪定組(D組):腹腔注射含右美托咪定(25 μg/kg)的生理鹽水1 mL(批號為14010632,江蘇恒瑞有限公司);育亨賓組(Y組):熱應激終點即刻腹腔注射育亨賓0.25 mg/kg(0.25 mg/mL,批號為101144729,sigma公司),5 min后腹腔注射右美托咪定(25 μg/kg),然后全部大鼠置于24 ℃常溫環境中。
1.2.3酶聯免疫吸附試驗(ELISA)測HMGB1各組大鼠于給藥后1 h采血,取2 mL放入促凝管,3 000 r/min離心10 min,取上清液,用ELISA試劑盒(上海西塘生物科技有限公司)測定血清HMGB1水平。
1.2.4外周血單個核細胞(PBMCs)的分離每只大鼠各取2 mL血放入枸櫞酸鈉抗凝管,參照說明用淋巴細胞分離液(天津市灝洋生物制品科技有限責任公司)分離單個核細胞(PBMCs):加同體積生理鹽水稀釋后,沿試管壁輕輕加入2 mL淋巴細胞分離液 (外周血∶淋巴細胞分層液=1∶1),3 000 r/min離心20 min,收集環狀乳白色的淋巴細胞層的細胞放入含8 mL生理鹽水的試管內,充分混勻,2 000 r/min離心10 min,沉淀反復洗滌2次,棄上清液,加l mL生理鹽水重懸細胞,將細胞懸液轉移至1.5 mL EP管中,2 000 r/min離心10 min,棄凈上清液,-80 ℃冷藏,備用。
1.2.5PBMCs中HMGB1的Western blot檢測提取PBMCs中HMGB1蛋白,用BCA蛋白濃度測定試劑盒(上海西唐生物科技有限公司的產品)測定蛋白濃度。進行十二烷基硫酸鈉-聚丙烯酰胺凝膠(SDS-PAGE)電泳,用濕轉膜法轉到聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上,300 mA恒流轉膜甘油醛-3-磷酸脫氫酶(GAPDH)60 min、 HMGB1 55 min;5%牛血清清蛋白(BSA)室溫封閉2 h;TBST洗膜后加入TBST稀釋的相應一抗(GAPDH 1∶20 000,上海海肽生物科技有限公司;HMGB1 1∶500,美國CST公司)4 ℃孵育過夜;洗膜,加入辣根過氧化物酶(HRP)標記的相應二抗(1∶10 000,上海前塵生物科技有限公司),室溫孵育2 h;ECL法顯色,暗室中用X膠片感光、顯影、定影。采用 Quantity-One軟件分析蛋白條帶平均光密度值。以GAPDH為內參照,目標蛋白與內參照平均光密度的比值代表目標蛋白的相對表達量 。
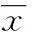
2結果
2.1各組大鼠血清HMGB1變化與C組相比,H、D及Y組大鼠血清HMGB1水平增加(P<0.05);與H組相比,D組大鼠血清HMGB1降低(P<0.05),而Y組大鼠血清HMGB1水平差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);與D組相比,Y組大鼠血清HMGB1水平升高(P<0.05),見圖1。

圖1 各組大鼠血清中HMGB1水平的比較

A:Western blot檢測;B:PBMCs中HMGB1表達。
圖2各組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1表達的比較
2.2各組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1水平的比較與C組相比,H、D和Y組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1水平降低(P<0.05);與H組相比,D組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1水平升高(P<0.05),而Y組大鼠血清HMGB1水平則差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);與D組相比,Y組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1水平降低(P<0.05),見圖2。
3討論
熱射病常以全身炎癥反應(SIRS)及多器官功能障礙為特點,其許多后果是由于中性粒細胞和巨噬細胞產生過量細胞因子所致。HMGB1存在于幾乎所有真核細胞內,在免疫炎癥細胞內含量更多,在細胞內發揮多種生物學作用。在細胞外環境中HMGB1可以激活免疫系統,介導炎性反應,參與感染和非感染炎癥[11]。細胞外的HMGB1來源于壞死細胞的釋放及活化炎癥細胞的分泌,HMGB1可以作用于炎癥細胞表面的糖基化終產物受體(RAGE)、Toll樣受體2(TLR2)、Toll樣受體4(TLR4)、Toll樣受體9(TLR9)等,令多種細胞的核因子κB(NF-κB)的移位,從而引起促炎細胞因子的分泌,引起炎性器官損傷[12-13]。Tong 等[5]研究表明,熱射病患者在入院時血清HMGB1水平是健康志愿者的25倍,HMGB1可能在早期階段釋放入循環。PBMCs中包含單核細胞、淋巴細胞等免疫炎癥細胞,本研究測定PBMCs中HMGB1來反應循環中炎癥細胞內HMGB1改變。結果表明,熱射病發生1 h后PBMCs中HMGB1水平降低,血清中HMGB1水平升高,這可能是由于熱應激引起PBMCs中HMGB1釋放至胞外,而自身HMGB1 mRNA及蛋白表達還沒有相應增加所致。
多項研究表明,在動物膿毒血癥、缺血再灌注及熱射病模型中,抑制HMGB1可有效抑制炎癥發展,阻斷SIRS進展[14-17]。Gu等[8]研究表明,腹腔注射25 μg/kg右美托咪定可以降低腎臟缺血再灌注大鼠血清HMGB1水平,改善腎缺血再灌注損傷及遠隔肺損傷。有體外研究表明臨床相關劑量的右美托咪定可以抑制脂多糖誘導的巨噬細胞HMGB1的表達,其機制可能是通過NF-κB和α2受體途徑[18]。此外,Kawasaki等[19]研究表明,右美托咪定在體外能夠抑制脂多糖誘導的人全血細胞促炎介質的釋放。本實驗結果表明,熱應激結束即刻給予右美托咪定能夠降低熱射病大鼠血清HMGB1水平,且D組大鼠PBMCs中HMGB1水平高于H病組。因此,右美托咪定能夠降低血清HMGB1水平,改善炎性反應,這可能與其減少PBMCs釋放 HMGB1相關,其具體作用機制并不清楚。
右美托咪定是一種高選擇性α2受體激動劑,α2受體廣泛存在于全身各組織器官,淋巴細胞和單核細胞等免疫炎癥細胞也有α2受體表達,且α2受體參與抑制淋巴細胞細胞因子產生的調節[20-21]。育亨賓是一種α2受體阻滯劑,本實驗予育亨賓拮抗右美托咪定的α2受體激動作用,以研究右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠HMGB1影響是否通過α2受體介導。本研究表明,右美托咪定作為α2受體激動劑能夠降低熱射病大鼠血清HMGB1水平,抑制PBMCs中HMGB1由胞內至胞外的釋放,而α2受體抑制劑育亨賓可以拮抗右美托咪定對熱射病大鼠血清及PBMCs中HMGB1水平的影響。因此,右美托咪定降低熱射病大鼠血清HMGB1水平,可能與其作用于PBMCs表面α2受體,抑制HMGB1的釋放有關,但右美托咪定是否也通過作用于其他組織器官α2受體而抑制HMGB1釋放有待進一步研究。
研究表明,低分子肝素鈉[16]和高劑量抗凝血酶Ⅲ(ATⅢ)[17]提高熱應激模型大鼠生存率,可能與多種炎性介質的調節相關,如腫瘤壞死因子α(TNF-α)、白細胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、白細胞介素6 (IL-6)和HMGB1,但DA和ATⅢ可能活化抗凝系統,臨床應用有很大風險。丁酸鈉、氯喹抑制HMGB1信號通路,對膿毒癥相關的多器官功能損害可能有保護效應,但對這些藥物改善炎性反應方面的研究仍處于實驗室階段,臨床效果并不清楚,且有多種不良反應。右美托咪定是一種臨床常用鎮靜鎮痛藥,對呼吸及循環影響較小,且具有抗交感效應,本研究表明右美托咪定在鎮靜鎮痛的同時還可降低血清HMGB1,改善炎性反應。因此,右美托咪定有鎮靜及抗炎雙重作用,但其是否能夠有效改善臨床熱射病患者的預后有待進一步研究。
綜上所述,右美托咪定能夠降低熱射病大鼠血清HMGB1水平,其可能機制之一是激動PBMCs表面α2受體減少HMGB1的釋放。因此,本研究認為右美托咪定可以通過減少炎癥細胞HMGB1釋放,改善熱射病大鼠的炎性反應,可能對熱射病有潛在的治療效應,為右美托咪定更安全有效地應用于熱射病患者的鎮靜、抗炎提供重要依據。
參考文獻
[1]Leon LR,Bouchama A.Heat stroke[J].Compr Physiol,2015,5(2):611-647.
[2]Leon LR,Helwig BG.Heat stroke:role of the systemic inflammatory response[J].J Appl Physiol,2010,109(6):1980-1988.
[3]Andersson U,Tracey KJ.HMGB1 is a therapeutic target for sterile inflammation and infection[J].Annu Rev Immunol,2011,29:139-162.
[4]Dehbi M,Uzzaman T,Baturcam E,et al.Toll-like receptor 4 and high-mobility group box 1 are critical mediators of tissue injury and survival in a mouse model for heatstroke[J].PLoS One,2012,7(9):e44100.
[5]Tong HS,Tang YQ,Chen Y,et al.Early elevated HMGB1 level predicting the outcome in exertional heatstroke[J].J Trauma,2011,71(4):808-814.
[6]Hagiwara S,Iwasaka H,Goto K,et al.Recombinant thrombomodulin prevents heatstroke by inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 protein in sera of rats[J].Shock,2010,34(4):402-406.
[7]Pandharipande PP,Sanders RD,Girard TD,et al.Effect of dexmedetomidine versus lorazepam on outcome in patients with sepsis:an a priori-designed analysis of the MENDS randomized controlled trial[J].Crit Care,2010,14(2):R38.
[8]Gu J,Sun P,Zhao H,et al.Dexmedetomidine provides renoprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice[J].Crit Care,2011,15(3):R153.
[9]Xu L,Bao H,Si Y,et al.Effects of dexmedetomidine on early and late cytokines during polymicrobial sepsis in mice[J].Inflamm Res,2013,62(5):507-514.
[10]Chen GM,Xu HN,Gao LF,et al.Effects of continuous haemofiltration on serum enzyme concentrations,endotoxemia,homeostasis and survival in dogs with severe heat stroke[J].Resuscitation,2012,83(5):657-662.
[11]Klune JR,Dhupar R,Cardinal J,et al.HMGB1:endogenous danger signaling[J].Mol Med,2008,14(7/8):476-484.
[12]Bianchi ME,Manfredi AA.Immunology dangers in and out[J].Science,2009,323(5922):1683-1684.
[13]Mollnes TE.High mobility group box-1 protein:one step closer to the clinic?[J].Crit Care,2008,12(4):168.
[14]Gentile LF,Moldawer LL.HMGB1 as a therapeutic target for sepsis:it′s all in the timing! [J]Expert Opin Ther Targets,2014,18(3):243-245.
[15]Liu YT,Yang LQ,Tao KM,et al.Protective effects of Hydrogen enriched saline on liver ischemia reperfusion injury by reducing oxidative stress and HMGB1 release[J].BMC Gastroenterol,2014,14:12.
[16]Hagiwara S,Iwasaka H,Shingu C,et al.Danaparoid Sodium attenuates the effects of heat stress[J].J Surg Res,2011,171(2):762-768.
[17]Hagiwara S,Iwasaka H,Shingu C,et al.High-dose antithrombin Ⅲ prevents heat stroke by attenuating systemic inflammation in rats[J].Inflamm Res,2010,59(7):511-518.
[18]Chang Y,Huang X,Liu Z,et al.Dexmedetomidine inhibits the secretion of high mobility group box 1 from lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages in vitro[J].J Surg Res,2013,181(2):308-314.
[19]Kawasaki T,Kawasaki C,Ueki M,et al.Dexmedetomidine suppresses proinflammatory mediator production in human whole blood in vitro[J].J Trauma Acute Care Surg,2013,74(5):1370-1375.
[20]Xiao J,Huang HW,Peng YP,et al.Modulation of natural killer cell function by alpha-adrenoreceptor-coupled signalling[J].Neuro Endocrinol Lett,2010,31(5):635-644.
[21]Bao JY,Huang Y,Wang F,et al.Expression of alpha-AR subtypes in T lymphocytes and role of the alpha-ARs in mediating modulation of T cell function[J].Neuroimmunomodulation,2007,14(6):344-353.
作者簡介:王珊珊(1989-),住院醫師,碩士,主要從事重要臟器損傷的保護研究。 △通訊作者,E-mail:yangxiaom2@hotmail.com。
doi:論著·基礎研究10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2016.15.009
[中圖分類號]R594.1+1
[文獻標識碼]A
[文章編號]1671-8348(2016)15-2058-03
(收稿日期:2015-11-08修回日期:2016-01-15)
The impact of dexmedetomidine on the expression level of HMGB1 in the serum and PBMCs of heat stroke rats
Wang Shanshan,Yang Xiaoming△,Wang Tao
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,ChinesePLAAirForceGeneralHospital,Beijing100142,China)
[Abstract]ObjectiveTo investigate the impact of dexmedetomidine on the levels of HMGB1 in the serum and PBMCs of heat stroke rats and explore the possible mechanism.MethodsThirty-two rats were divided into four groups (n=8):control group (group C),heat stroke model group (group H),dexmedetomidine group (group D) and yohimbine group (group Y).Anesthetized rats were subjected to heat stress(40.0±0.5) ℃ until the core temperature of the rats reached 42 ℃to induce heat stroke.The concentration of HMGB1 in the serum was measured by using ELISA kit at 1 h after the heat stress ending.Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were extracted by using lymphocyte separation medium.The level of HMGB1 in the PBMCs was determined by western blot analysis.ResultsCompared with group C,the concentration of HMGB1 in the serum of rats in group H was increased significantly (P<0.05),and the level of HMGB1 in PBMCs was decreased (P<0.05);compared with group H,the concentration of HMGB1 in the serum of rats in group H was decreased significantly (P<0.05),and the level of HMGB1 in PBMCs was increased (P<0.05);compared with group D,the concentration of HMGB1 in the serum of rats in group Y was increased significantly (P<0.05),and the level of HMGB1 in PBMCs was decreased (P<0.05).ConclusionDexmedetomidine could decrease the level of HMGB1 in the serum of heat stroke rats,and the mechanism might be associated with interacting with the α2 receptor in the surface of PBMCs and reduced the release of HMGB1 from PBMCs.
[Key words]dexmedetomidine;heat stroke;HMGB1;PBMCs

