血小板平均體積與膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的相關性研究
蘇柯,李龍杰,王軍
(河北省滄州市中心醫(yī)院關節(jié)外科治療中心,河北 滄州 061001)
?
血小板平均體積與膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的相關性研究
蘇柯,李龍杰,王軍
(河北省滄州市中心醫(yī)院關節(jié)外科治療中心,河北 滄州061001)
目的研究血小板平均體積(mean platelet volume,MPV)與膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的相關性。方法2011年7月至2014年6月收治539 例患者,其中男212 例,女327 例;年齡34~59 歲,平均50 歲。根據骨關節(jié)炎K-L分級和Ayral滑膜炎評分分為膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎(synovitis associated with osteoarthritis,SOA)173 例,膝骨關節(jié)炎(osteoarthritis,OA)189 例,不符合膝骨關節(jié)炎診斷(對照組)177 例。測量患者MPV、紅細胞沉降率(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR)、C-反應蛋白(C-reactive protein,CRP),數據采用方差分析、雙變量相關與回歸分析進行統(tǒng)計檢驗。結果膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組與膝骨關節(jié)炎組MPV差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組與對照組MPV差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(P<0.05);膝骨關節(jié)炎組與對照組MPV差異無統(tǒng)計學意義(P=0.939)。膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組MVP與CRP呈負相關(r=-0.263,P<0.01),MPV與ESR呈負相關(r=-0.246,P<0.01)。膝骨關節(jié)炎組MPV與CRP無相關(P=0.310),MPV與ESR無相關(P=0.598)。對照組MPV與CRP、MPV與ESR無相關。結論MPV可反映膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的病變程度,滑膜炎癥反應與MPV的變化有關。
骨關節(jié)炎;滑膜炎;血小板平均體積;C-反應蛋白;紅細胞沉降
膝骨關節(jié)炎是臨床常見疾病,以軟骨病變、骨贅形成、關節(jié)間隙變窄為特征,且多伴有滑膜增生、充血水腫[1]。有報道證實類風濕性關節(jié)炎患者血小板平均體積(mean platelet volume,MPV)與關節(jié)滑膜病變的嚴重程度相關,而經關節(jié)鏡探查的膝骨關節(jié)炎患者,約50%伴有滑膜炎癥改變[2],滑膜病變的嚴重程度也可反映膝骨關節(jié)炎的病變進展[3]。目前國內關于膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎與MPV的相關性未見報道,大量文獻表明MPV可輔助其他化驗指標如白細胞計數(white blood cell count,WBC)、C反應蛋白(-reactive protein,CRP)、血沉(erythrocyte sedimentation rate,ESR)、血小板(platelet,PLT)反映炎癥程度[4-5]。因此,我們研究MPV與膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的關系,現報道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料選擇2011年7月至2014年6月就診治療的膝關節(jié)疾病患者539 例,男212 例,女327 例;年齡34~59 歲,平均50 歲。術前根據Kellgren-Lawrence(K-L)分級將患者分為骨關節(jié)炎組362 例,非骨關節(jié)炎組177 例。其中骨關節(jié)炎組均行膝關節(jié)鏡手術,術中根據Ayral滑膜評分[6]分為膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組173 例,膝骨關節(jié)炎組189 例;膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組男59 例,女114 例,平均年齡(53.87±3.01) 歲;膝骨關節(jié)炎組男67 例,女122 例,平均年齡(47.22±4.51) 歲。非骨關節(jié)炎組男86 例,女91 例,平均年齡(51.40±5.41) 歲,無手術指證且未經手術治療。各組一般資料見表1。

表1 539 例患者性別、年齡分布及骨關節(jié)炎分級
1.2分組標準膝骨關節(jié)炎組的入選標準(K-L分級)0級:膝正側位X線無改變;1級:關節(jié)間隙可疑狹窄,可能有骨贅;2級:明確骨贅,關節(jié)間隙正常或可疑狹窄;3級:中度骨贅,關節(jié)間隙明確狹窄,軟骨下骨部分硬化;4級:巨大骨贅,關節(jié)間隙明顯狹窄,軟骨下骨嚴重硬化,明顯畸形。
Ayral滑膜評分,0分:正常滑膜,半透明細絨毛狀;0.5分:增生滑膜,不透明肥大絨毛,血管網不可見;1分:炎癥滑膜,嚴重增生肥大絨毛,血管增生。關節(jié)腔內區(qū)域按比例劃分髕上囊:后壁(X1)占20%,前內側壁(X2)占10%,前外側壁(X3)占10%,髕下脂肪墊(X4)占25%;股骨內側溝(X5)占10%,外側溝(X6)占10%;半月板周圍:內側(X7)占5%,外側(X8)占5%;髁間切跡(X9)占5%。Ayral滑膜評分=20X1+10X2+10X3+25X4+10X5+10X6+5X7+5X8+5X9。
關節(jié)鏡下Outerbridge分級,Ⅰ度:表面輕度的水皰(軟化和腫脹);Ⅱ度:直徑小于1 cm的毛糙和淺表潰瘍、纖維化;Ⅲ度:損傷直徑大于1 cm深潰瘍,無軟骨下骨暴露;Ⅳ度:全厚撕裂合并軟骨下骨暴露。
根據以上標準分為三組,膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組:符合膝骨關節(jié)炎診斷且Ayral評分大于等于60分;膝骨關節(jié)炎組:符合膝骨關節(jié)炎診斷且Ayral評分小于60分;對照組:不符合膝骨關節(jié)炎診斷,未經手術治療患者。排除標準:排除影響PLT及MPV的血液系統(tǒng)疾病、腫瘤、免疫系統(tǒng)疾病、糖尿病、心血管疾病、外周血管疾病以及外傷感染。1.3數據采集采集空腹靜脈血1 mL,Sysmex XE5000血細胞分析儀測量各組MPV,日立7 600生化儀測量CRP、ESR。
1.4統(tǒng)計分析使用SPSS 13.0統(tǒng)計軟件進行統(tǒng)計描述、正態(tài)性檢驗。多樣本均數比較采用方差分析,統(tǒng)計學標準選用P<0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計學意義。兩因素相關性采用Pearson相關分析,統(tǒng)計學標準選用P<0.01為差異有統(tǒng)計學意義。
2 結 果
膝骨關節(jié)炎組與對照組MPV、ESR、CRP分別比較,P=0.000;膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組與膝骨關節(jié)炎組MPV、ESR、CRP分別比較,P=0.000,差異有統(tǒng)計學意義(見表2)。兩因素相關分析結果為:膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組中MPV與CRP呈負相關(r=-0.263,P<0.01),MPV與ESR呈負相關(r=-0.246,P<0.01)(見圖1~2);而膝骨關節(jié)炎組中MPV與CRP無相關(P=0.310),MPV與ESR也無相關(P=0.598)(見圖3~4);對照組中MPV與CRP、ESR均無相關。
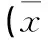
表2 膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組、膝骨關節(jié)炎組與對照組MPV、ESR、CRP比較±s)
3 討 論
膝骨關節(jié)炎是老年人群中的一種常見疾病[7],以關節(jié)軟骨變性、關節(jié)邊緣和軟骨下骨再生為特征,可累及關節(jié)滑膜并使滑膜增生出現炎癥反應。Ayral等報道,關節(jié)內滑膜炎癥反應會加劇軟骨病變,導致軟骨缺失。
以往描述滑膜增生程度常采用Ayral滑膜炎評分,但這種評分需要手術,是一種有創(chuàng)評估。術前提示滑膜炎癥程度的血液指標常采用ESR和CRP,在急性炎癥反應時,CRP與炎癥反應有良好的相關性。我們查閱以往文獻發(fā)現MPV與心血管疾病的危險因素(肥胖、糖尿病、高血壓、動脈硬化)相關[8-10]。而且已有研究表明,MPV與類風濕性關節(jié)炎、強直性脊柱炎、腹腔內感染呈負相關[11-12],其治療效果可通過MPV水平進行監(jiān)測[11,13]。Yazici等[14]通過研究97 例類風濕性關節(jié)炎患者的血小板特性,發(fā)現MPV與類風濕疾病的嚴重程度相關。Kisacik等[15]比較類風濕性關節(jié)炎、強直性脊柱炎和骨關節(jié)炎患者MPV水平,結果顯示類風濕性關節(jié)炎患者的MPV水平明顯低于骨關節(jié)炎患者,經過確切的抗風濕治療,MPV水平明顯提高,在強直性脊柱炎患者中,MPV的變化特性同樣存在。因此,Gasparyan等[16]建議將MPV作為炎癥反應指標,通過檢測MPV水平評價抗類風濕治療的療效。而MPV水平與骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎是否具有相關性目前尚未見報道,我們通過采集臨床資料觀察MPV與膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎的相關性,滑膜炎在膝骨關節(jié)炎患者中普遍存在,滑膜炎癥反應表現為滑膜細胞增生,其中乳頭樣增生多見,滑膜間質有淋巴細胞浸潤。滑膜炎癥反應使關節(jié)內滑液產生增多,體積大的血小板更易形成血栓,從而影響關節(jié)滑液微循環(huán),導致滑膜積液[17],因此通過MPV檢測可間接反應滑膜的炎癥程度。在臨床化驗中MPV是血常規(guī)檢查中的一項指標,具有采集方便、費用低廉等優(yōu)點,便于臨床觀察。

圖1 膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組MPV與CRP相關性比較

圖2 膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組MPV與ESR相關性比較

圖3 膝骨關節(jié)炎組MPV與CRP相關性比較

圖4 膝骨關節(jié)炎組MPV與ESR相關性比較
血小板是從骨髓成熟的巨核細胞胞質裂解脫落下來的具有生物活性的小塊胞質,可參與炎癥反應的發(fā)生、發(fā)展,并同時具有免疫調節(jié)作用[18]。促血小板生成素和大量炎癥因子可調節(jié)血小板形成,其中白介素6(interleukin-6,IL-6)可影響巨核細胞的成熟過程,調控巨核細胞凋亡,增強白介素3(interleukin-3,IL-3)對巨核細胞集落生長的刺激作用。炎癥反應促使白介素1(interleukin-1,IL-1),IL-6,腫瘤壞死因子α(tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α)增多,Bath等研究發(fā)現,過多的炎癥介質抑制巨核細胞生成,限制了大體積血小板形成,從骨髓中生成更多體積小的血小板,所以MPV會下降。Gasparyan等[19]研究表明通過抑制血小板活性使血小板致炎作用減弱,可以控制骨關節(jié)炎的進展。
通過我們的研究發(fā)現,測量并記錄膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組、膝骨關節(jié)炎組、對照組間的MPV、ESR、CRP水平,發(fā)現三組間MPV差異有統(tǒng)計學意義,且膝骨關節(jié)炎伴滑膜炎組MVP與CRP、ESR與MPV均呈負相關;膝骨關節(jié)炎組、對照組無明顯相關性。此結論仍需大量前瞻性研究予以支持,在今后的研究中我們將繼續(xù)進行。
[1]Benito MJ,Veale DJ,FitzGerald O,etal.Synovial tissur inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2005,64(9):1263-1267.
[2]Rollin R,Marco F,Jover JA,etal.Early lymphocyte activation in the synocial microenvironment in patients with osteoarthritis:Comparison with rheumatoid arthritis patients and healthy controls[J].
Rheumatol Int,2008,28(8):757-764.
[3]Da RR,Qin Y,Baeten D,etal.B cell clonal expansion and somatic hypermutation of Ig variable heavy chain genes in the synovial membrane of patients with osteoarthritis[J].J Immunol,2007,178(1):557-565.
[4]Kim DH,Kang SH,Jeong WS,etal.Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in young adults can be used to discriminate between inflammatory and non-inflammatory diarrhea[J].Dig Dis Sci,2013,58(2):504-508.
[5]Zareifar S,Farahmand Far MR,Golfeshan F,etal.Changes in platelet count and mean platelet volume during infectious and inflammatory disease and their correlation with ESR and CRP[J].J Clin Lab Anal,2014,28(3):245-248.
[6]Ayral X,Mayoux-Benhamou A,Dougados M.Propose scoring system for assessing synovial membrane abnormalities at arthroscopy in knee osteoarthritis[J].Br J Rheumatol,1996,35(suppl 3):14-17.
[7]喻飛,王振中,楊波,等.關節(jié)鏡手術治療膝骨關節(jié)炎的隨機對照研究[J].實用骨科雜志,2014,20(9):801-802.
[8]Icli A,Tayyar S,Varol E,etal.Reply:the relationship between mean platelet volume,inflammatory markers and clinical outcomes in infective endocarditis[J].Med Princ Pract,2014,23(4):391-392.
[9]李莎,王椿,鐘曉衛(wèi),等.2型糖尿病患者平均血小板體積變化及其與下肢動脈病變的相關關系[J].中華醫(yī)學雜志,2012,92(4):232-235.
[10]Tasolar H,Cetin M,Balli M.Relationship between mean platelet volume and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy[J].Angiology,2014,65(9):851 .
[11]Gasparyan AY,Ayvazyan L,Mikhailidis DM,etal.Mean platelet volume:A link between thrombosis and inflammation?[J].Curr Pharm Des,2011,17(1):47-58.
[12]Pauling D,O′Donnell VB,Mchugh NJ.The contribution of platelets to the pathogenesis of Raynaud′s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis[J].Platelets,2013,24(7):503-515.
[13]Sert A,Aypar E,Odabas D.Mean platelet volume in acute rheumatic fever[J].Platelets,2013,24(5):378-382.
[14]Yazici S,Yazici M,Erer B,etal.The platelet indices in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:Mean platelet volume reflects disease activity[J].Platelets,2010,21(2):122-125.
[15]Kisacik B,Tufan A,Kalyoncu U,etal.Mean platelet volume(MPV) as an inflammatory marker in ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis[J].Joint Bone Spine,2008,75(3):291-294.
[16]Gasparyan AY,Sandoo A,Kalinoglou AS,etal.Mean platelet volume in patients with rheumatoid arthritis:The effect of anti-TNF-α therapy[J].Rheumatol Int,2010,30(8):1125-1129.
[17]Schmitt-Sody M,Metz P,Klose A,etal.In vivo interactions of platelets and leucocytes with the endothelium in murine antigen-induced arthritis:The roll of P-selectin[J].Scand J Rheumatol,2007,36(4):311-319.
[18]彭茜,楊永宗.免疫炎癥中血小板的作用[J].中華臨床醫(yī)學衛(wèi)生雜志,2007,5(3):38-41.
[19]Gasparyan AY,Stavropoulos A,Kalinoglou KMJ,etal.Platelet function in rheumatoid arthritis:Arthritic and cardiovascular implications[J].Rheumatol Int,2011,31(2):153-164.
Correlation between mMean Platelet Volume and Synovitis Associated with Knee Osteoarthritis
Su Ke,Li Longjie,Wang Jun
(Department of Orthopedics,Cangzhou Central Hospital,Cangzhou 061001,China)
ObjectiveTo investigate the levels of mean platelet volume(MPV) in patients with synovitis associated with knee osteoarthritis.MethodsFrom July 2011 to June 2014,173 patients diagnosed with synovitis associated to osteoarthritis,189 patients with knee osteoarthritis and 177 patients between the same age range who did not have joint complaints(control group),totally 539 participants,were included in our study.MPV,sedimentation(ESR),CRP values were evaluated accorded to the Kellgren-Lawrence scoring and Ayral synovitis scoring.The normal distribution and homogeneity of each parameter was tested and analysis of variance was used to determine differences in all groups.Pearson correlation coefficient was used for binary correlations.ResultsWe found a significant difference between the patient group with synovitis associated with osteoarthritis of knee and patients with knee osteoarthritis in MPV blood level(P<0.05),similarly a significant difference was found between the patient group with synovitis associated with osteoarthritis of knee and the control group(P<0.05).There was no significant difference between the knee osteoarthritis patient group and the control group(P=0.939).According to the Pearson correlation,it was found that there was a negative relationship between MPV and CRP variables in those of patients with synovitis associated with osteoarthritis of knee(r=-0.263,P<0.01),similarly the negative relationship between MPV and ESR in those patients(r=-0.246,P<0.01).Significant relationship was not found between MPV and CRP(P=0.310),MPV and ESR(P=0.598) in patients with the osteoarthritis group.In the control group no correlation was found between MPV-CRP and MPV-ESR.ConclusionMPV levels may be beneficial in osteoarthritis with synovitis patients.MPV levels may be considered as a marker of inflammation but further comprehensive prospective trials are needed in osteoarthritis associated with synovitis patients.
osteoarthritis;synovitis;mean platelet volume;C-reactive protein;erythrocyte sedimentation rate
1008-5572(2016)08-0701-04
R684.3
B
2015-12-15
蘇柯(1985- ),男,主治醫(yī)師,河北省滄州市中心醫(yī)院關節(jié)外科治療中心,061001。

