不同術式白內障術后屈光狀態變化規律及穩定性研究
謝南明,呂旭菁
?
·臨床研究·
不同術式白內障術后屈光狀態變化規律及穩定性研究
謝南明,呂旭菁
Department of Ophthalmology,Changzhou First People’s Hospital,Changzhou 213000,Jiangsu Province,China
Abstract
?AIM: To compare and contrast different operation after cataract patients with refractive change rules.To analyze the patients with refractive stability after cataract surgery,and to provide a reference for cataract patients with clinical surgery after visual quality.
?METHODS: Retrospective study.A total of 126 cases (150 eyes) were selected from Jan.2014 to Dec.2015 in Changzhou First People’s Hospital of cataract extraction combined with foldable intraocular lens implantation for cataract patients as the research samples.According to the different operation for three groups,the first group of 42 patients (50 eyes) underwent above 3 mm clear corneal incision; 52 cases in group 2 (60 eyes) underwent temporal side 3 mm clear corneal incision.The third group,32 cases (40 eyes) underwent 3 corner above the scleral tunnel incision.All the cases were measured at different time point in patients with naked eyes far visual acuity,best corrected visual acuity,spherical degree,the degree of astigmatism and astigmatic axial,comparative analysis of after cataract surgery in patients with refractive change regularity and stability of refraction.
?RESULTS: The uncorrected distance visual comparison within the group,and each time point after preoperative differences were significant (P<0.01),and the early postoperative period after 1,3mo significantly different (P<0.05).Three groups of patients after surgery compared with preoperative uncorrected distance visual acuity improved significantly,and were stable after 1mo.Compare the best corrected distance vision within the group,and each time point after preoperative differences were significant (P<0.01),postoperative 1wk and after 1,3d significantly different (P<0.05),after 1wk and after 1,3mo was not significantly different (P>0.05),three groups of patients were compared with the preoperative best corrected distance visual acuity were increased significantly,and were in stable after 1wk; relatively spherical degree within the array,after 1d and 3d was not significantly different (P>0.05),hyperopia drift,after 1wk and 1,3d was significantly different (P<0.05),after 1wk and 1,3mo was not significantly different (P>0.05).Three groups of patients’ spherical degrees after 1wk were stabilized.Comparative degree of astigmatism within the array,postoperative compared with preoperative corneal astigmatism were increased 1d after surgery.Corneal astigmatism in each group reached the maximum,and then decreases 1wk and 1d after surgery,compared with postoperative 3d was significantly different (P<0.05).After 1wk and 1,3mo was not significantly different (P>0.05).Three groups of patients were compared with preoperative astigmatism were significantly increased,and in operation after 1wk were stabilized; astigmatic axis were three groups in the preoperative astigmatism against the rule,the first and third group after 1d,three Tianshun rule astigmatism proportional were increased,and then decreased.Group 2 the-rule astigmatism proportion,after 1wk,1 and 3mo,the first and third group gradually reduced the proportion of cis regulatory astigmatism,and compared with preoperative increased,increasing the-rule astigmatism group 2 ratio,and increased compared with preoperative.
?CONCLUSION: Above 3 mm the transparent corneal incision,temporal clear corneal incision and above the scleral tunnel incision different surgical postoperative visual acuity are good.It can be used as a routine surgical procedure in treatment of cataract; phacoemulsification in cataract patients with former majority against the rule astigmatism.After cataract surgery,early refractive state is a state of mild hyperopia and stabilized about 1wk,combined with clinical guide glasses.
目的:研究不同術式白內障術后患者的屈光狀態變化規律,分析白內障術后患者屈光穩定性,為白內障患者術后視覺質量獲得提供參考。
方法:回顧性研究。選取2014-01/2015-12常州市第一人民醫院行白內障摘除聯合人工晶狀體植入術的患者126例150眼作為研究對象,按照手術方式不同分為3組,第1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口42例50眼;第2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口52例60眼,第3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口32例40眼。分別測量患者不同時間點的裸眼遠視力、最佳矯正遠視力、球鏡度數及散光度數,對比分析術后患者的屈光狀態變化規律及屈光穩定性。
結果:裸眼遠視力組內比較,術前與術后各時間點均差異具有統計學意義 (P<0.01),術后早期(術后1、3d)與術后1、3mo差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05),三組患者術后裸眼遠視力較術前均提高明顯,且均在術后1mo趨于穩定;最佳矯正遠視力組內比較,術前與術后各時間點均差異具有統計學意義(P<0.01),術后1wk與術后1、3d差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),三組患者最佳矯正遠視力術后較術前均提高明顯,且均在術后1wk趨于穩定;球鏡度數組內比較,術后1、3d差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),出現遠視漂移,術后1wk與術后1、3d比較差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),三組患者球鏡度數在術后1wk趨于穩定;散光度數組內比較,術后較術前角膜散光度數均增加,術后1d,各組術后角膜散光達到最大,隨后逐漸減小;術后1wk與術后1、3d比較差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),三組患者術后較術前散光度數均增加明顯,且均在術后1wk趨于穩定。
結論:白內障手術中3mm左右上方透明角膜切口、顳側透明角膜切口及上方鞏膜隧道切口不同術式術后視力恢復均良好,均可作治療白內障的常規手術術式;白內障術后早期屈光狀態呈輕度遠視狀態,且在術后1wk左右穩定,結合臨床可指導配鏡。
白內障;屈光狀態;屈光穩定性
引用:謝南明,呂旭菁.不同術式白內障術后屈光狀態變化規律及穩定性研究.國際眼科雜志2016;16(10):1865-1868
0 引言
目前,白內障是我國視力損害主要疾病,嚴重時可致盲,每年世界上視力喪失患者有一半左右是由白內障導致的,但目前沒有藥物可有效預防或延緩白內障,以手術治療為主[1]。美國Stephen Brint在1994年率先提出“屈光性白內障手術”的概念,經過20a的不斷演變與改進,小切口白內障超聲乳化聯合人工晶狀體植入術不僅能防盲復明,術后還能有效改善視覺質量[2]。球鏡度數和散光度數反映了白內障術后的屈光狀態,術后球鏡度數常受術前測量、術后囊膜改變等因素影響,探討術后屈光狀態的變化規律,對臨床術后屈光誤差提供參考[3]。目前對于術后1wk,1、3mo的研究較多,術后1d與術后3d定義為術后早期,而對于術后1、3d的早期屈光狀態的研究較少[4]。本研究通過比較不同術式白內障術后患者的屈光狀態變化規律,分析白內障術后患者屈光穩定性,以期為白內障患者臨床術后視覺質量獲得提供參考。
1 對象和方法
1.1對象回顧性研究。選取2014-01/2015-12常州市第一人民醫院行白內障摘除聯合人工晶狀體植入術的患者126例150眼,其中男61例72眼、女65例78眼,年齡51~85(平均62.74±6.89)歲。根據不同手術方式分為3組,第1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口42例50眼;第2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口52例60眼,第3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口32例40眼。入選標準:手術前后隨訪資料完整;排除患有基礎疾病、其他眼部疾病及術后發生并發癥的患者。術前各組間的年齡、性別構成比差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),各組間具有可比性。
1.2方法所有患者術前1d,給予鹽酸左氧氟沙星滴眼液點術眼,3次/d,預防感染;于術前30min,予鹽酸奧布卡因滴眼液行表面麻醉點術眼。第1組:在11∶00~12∶00位角膜緣內約1mm做一寬約3mm三平面透明角膜切口,注入適量透明質酸鈉穩定前房,然后行直徑約5mm連續環形撕囊,采用單純劈核技術吸出晶狀體核,再然后注入適量透明質酸鈉至囊袋內,植入人工晶狀體,抽吸剩余黏彈劑,術畢涂妥布霉素地塞米松眼膏,包扎術眼。第2組:在顳側角膜緣內約1mm做一寬約3mm三平面透明角膜切口,注入適量透明質酸鈉穩定前房,然后行直徑約5mm連續環形撕囊,采用單純劈核技術吸出晶狀體核,再然后注入適量透明質酸鈉至囊袋內,植入人工晶狀體,抽吸剩余黏彈劑,術畢涂妥布霉素地塞米松眼膏,包扎術眼。第3組:在11∶00~12∶00位角膜緣后約1mm做一寬約3mm帶結膜瓣的角鞏膜隧道式切口,注入適量透明質酸鈉穩定前房,然后行直徑約5mm連續環形撕囊,撥動晶狀體核至前房,在其表面注入適量透明質酸鈉,將晶狀體手法碎核乳化后取出,再然后注入適量透明質酸鈉至囊袋內,植入人工晶狀體,抽吸剩余黏彈劑,術畢涂涂妥布霉素地塞米松眼膏,包扎術眼。術后隨訪3mo。手術前后采用標準視力對數表測定裸眼遠視力;先用經綜合驗光儀測量,再經主覺驗光測定,同時記錄球鏡度數;采用ZeissATLAS9000角膜地形圖儀進行不少于5次的測量散光度數,取其中一次最好的測量作為測定結果[5-6]。
統計學分析:采用SPSS 20.0軟件,計量資料用t檢驗,計數資料采用χ2檢驗,重復測量數據采用方差分析,組間均數兩兩比較采用LSD-t法。以P<0.05為差異具有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1手術前后裸眼遠視力情況三組患者術后較術前裸眼遠視力均提高明顯,且均在術后1mo趨于穩定。不同組間各相同時間點兩兩之間差異均無統計學意義(F=1.17,P>0.05);組內比較,三組均術后1d與術后3d差異無統計學意義 (P>0.05),術后1mo與術后3mo差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),但術后早期(1、3d)與術后1、3mo均差異有統計學意義(F=19.02,P<0.05),術前與術后各時間點均差異有統計學意義(P<0.01),見表1。
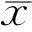
表1 三組患者手術前后裸眼遠視力比較 ±s
注:1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口;2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口;3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口。
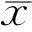
表2 三組患者手術前后最佳矯正遠視力比較 ±s
注:1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口;2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口;3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口。

表3 三組患者手術前后球鏡度數比較 ,D)
注:1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口;2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口;3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口。

表4 三組患者手術前后散光度數比較 ,D)
注:1組行上方3mm透明角膜切口;2組行顳側3mm透明角膜切口;3組行3mm上方角鞏膜隧道切口。
2.2手術前后最佳矯正遠視力情況三組患者術后較術前最佳矯正遠視力均提高明顯,且均在術后1wk趨于穩定。不同組間各相同時間點兩兩之間差異均無統計學意義(F=1.22,P>0.05);組內比較,三組均術后1d與術后3d差異均無統計學意義(F=19.11,P>0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3d差異有統計學意義 (P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),術前與術后各時間點均差異有統計學意義(P<0.01),見表2。
2.3手術前后球鏡度數情況三組患者球鏡度數在術后1wk趨于穩定。 不同組間各相同時間點兩兩之間差異均無統計學意義(F=1.75,P>0.05);組內比較,三組均術后1d與術后3d差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),出現遠視漂移,術后1wk與術后1、3d差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo差異無統計學意義 (P>0.05),見表3。
2.4手術前后散光度數情況三組患者術后較術前散光度數均增加明顯,且均在術后1wk趨于穩定。不同組間各相同時間點兩兩之間差異均無統計學意義(F=1.66,P>0.05);組內比較,三組均術后較術前角膜散光度數均增加,術后1d,各組術后角膜散光達到最大,隨后逐漸減小;術后1d與術后3d差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3d差異有統計學意義 (P<0.05),術后1wk與術后1、3mo差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),表4。
3 討論
白內障術后裸眼視力及最佳矯正視力的恢復在臨床上往往存在波動,有研究報道,術后早期與前房深度的變化、角膜水腫及角膜散光有一定關系[7]。在視力穩定的術后晚期波動與后發性白內障關系密切,受術前狀況、手術方式、人工晶狀體、術后炎癥等因素影響,術中連續環形撕囊、術后抗炎藥物應用對降低后發性白內障有積極作用[8]。本研究中,測量并記錄患者術后1、3d,1wk,1、3mo的裸眼視力及最佳矯正視力,探究白內障術后的視力變化。術前與術后比較,三組的視力較術前均有明顯提高,術后早期視力的恢復與前房深度的變化、前房炎癥反應有關,術后1wk以后,視力逐漸上升;組間進行比較,三組之間無明顯差異,不同手術方式對術后視力的恢復無明顯影響,表明三種手術方式均可作為常規治療方法。
白內障術后球鏡度數是衡量術后改善視覺質量的重要參數,它受術中撕囊口的直徑、術后人工晶狀體的位置偏差等因素影響[9]。術后屈光狀態受術中撕囊的大小的影響,撕囊直徑剛好覆蓋光學部邊緣約0.5mm為宜,過大或過小均會導致屈光改變[10];白內障術后人工晶狀體的位置偏差也會導致患者術后的屈光誤差,嚴重可能要置換人工晶狀體[11]。本研究中,三組間比較,各相同時間點兩兩之間差異均無統計學意義(P>0.05),表明不同術式對白內障術后的球鏡度數無明顯影響。組內比較,早期術后1d與術后3d差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),出現遠視漂移,可能是患者術后房角組織水腫損傷以致眼壓升高,人工晶狀體后移,出現遠視;術后1wk與術后1、3d差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),與術后1、3mo差異均無統計學意義 (P>0.05),表明三組患者球鏡度數在術后1wk趨于穩定,可能隨著房角功能的恢復,人工晶狀體前移,遠視消失[12]。白內障術后球鏡度數受多因素影響,根據臨床情況,把握好術前、術中及術后各個環節,最大限度降低術后屈光偏差[13]。
白內障術后散光是術后改善視覺質量的另一重要方面。本研究中,大部分患者術前低度散光,且隨年齡增加而增大,可能與老年人眼球張力變化有關[14]。術后早期三組角膜散光度數最大,可能與角膜水腫有關,約術后1wk穩定[15]。另外,顳側切口出現了由逆規向順規的漂移,而其他兩個術式切口的散光軸向均出現了由順規向逆規的漂移。可能是由于切口處角膜水腫,增加了切口散光,而后,隨著切口的愈合,又降低了切口散光[16]。白內障術后屈光狀態的穩定與切口愈合密切相關。本研究中,屈光穩定時間為1wk。有研究報道,術后1wk屈光己穩定,但眼內各部分并未穩固,約術后3mo才達到充分穩定,所以,建議術后3mo后配鏡[17]。
綜上所述,3mm左右上方透明角膜切口、顳側透明角膜切口及上方鞏膜隧道切口不同術式術后視力恢復均良好,均可作為治療白內障的常規手術術式;白內障術后早期屈光狀態呈輕度遠視狀態,且在1wk左右穩定,結合臨床可指導配鏡。
1Bench RPG.Mark standards for reffactive out comes after NHS cataract surgery.Eye(Lond) 2009;23(1):149-152
2陳冬芳,楊麗紅,馬伊.透明角膜切口位置對老年性白內障患者術后角膜散光的影響.山東醫藥2013;53(45):56-59
3樊頌雅,解傳奇,張蕊.對比白內障超聲乳化術中兩種角膜切IA方向對角膜屈光的影響.中華眼外傷職業眼病雜志2013;35(12):427-429
4蘇定旺,鐘丘,岑志敏,等.白內障超聲乳化術3.2mm透明角膜切口術源性散光的分析.國際眼科雜志2010;10(5):58-60
5Seitz BL,Langenbucher A.Intraocular lens calculations status after corneal refractive surgery.Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2010;11(1):35-46
6Rosa N,De Bernardo M,Borrelli M,et al.New factor to improve reliability of the clinical history method for intraocular lens power calculation after refractive surgery.J Cataract Refract Surg 2010;36(12):2123-2128
7Aramberri J.Intraocular lens power calculation after corneal reffactive surgery: double-K method.J Cataract Refract Surg 2013;29(11):2063-2068
8羅靜.白內障術后屈光狀態及其變化的臨床研究.四川醫科大學2015
9Saiki M,Negishi K,Kato N,et al.Modified double-K method for intraocular lens power calculation after excimer laser corneal refractive surgery.J Cataract Refract Surg 2013;39(4):556-562
10Saiki M,Negishi K,Kato N,et al.A new central-peripheral corneal curvature method for intraocular lens power calculation after excimet laser refiactive surgery.Acta Ophthalmol 2013;91(2):133-139
11Jin H,Holzer MR,Rabsilber T,et al.Intraocular lens power calculation after laser refractive surgery: corrective algorithm for corneal power estimation.J Cataract Refract Surg 2010;36(1):87-96
12Jin H,Auffalth GU,Guo H,et al.Corneal power estimation for intraocular lens power calculation after corneal laser refractive surgery in Chinese eyes.J Cataract Refract Surg 2012;38(10):1749-1757
13Frings A,Hold V,Steinwender G,et al.Use of true net power in intraocular lens power calculations in eyes with prior myopic laser rcfractive surgery.Int Ophthalmol 2014;34(5):1091-1096
14Xu K,Hao Y,Qi H.Intraocular lens power calculations using a Scheimpflug camera to measure corneal power.Bio His 2014;89(5):348-354
15Tang M,Wang L,Koch DD,et al.Intraocular lens power calculation after previous myopic laser’vision correction based on corneal Power measured by Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography.J Cataract Refract Surg 2012;38(4):589-594
16Tang M,Wang L.Intraocular lens power calculation after myopicand hyperopic laser vision correction using optical cohelence tomography.Saudi J Ophthalmol 2012;26(1):19-24
17Huang D,Tang M,Wang L,et al.Optical coherence tomography-based corneal power measurement and intraocular lens power calculation following laser vision correction(An American Ophthalmological Society Thesis).Trans Am Ophthalmol Soci 2013;111(34):125-128
Retrospective study on the changes of refractive state and stability after cataract surgery
Nan-Ming Xie,Xu-Jing Lü
Nan-Ming Xie.Department of Ophthalmology,Changzhou First People’s Hospital,Changzhou 213000,Jiangsu Province,China.3483017010@qq.com
2016-06-17Accepted:2016-09-06
cataract; refraction; refractive stability
(213000)中國江蘇省常州市第一人民醫院眼科
謝南明,副主任醫師,眼科副主任,研究方向:白內障及視網膜病。
謝南明.3483017010@qq.com
2016-06-17
2016-09-06
Xie NM,Lü XJ.Retrospective study on the changes of refractive state and stability after cataract surgery.Guoji Yanke Zazhi(Int Eye Sci) 2016;16(10):1865-1868
10.3980/j.issn.1672-5123.2016.10.19

