右胸導聯在運動試驗中對冠狀動脈再狹窄檢測的作用
周序鋒,居艷娟,謝東明,陽貽紅,鐘文婷
(贛南醫學院第一附屬醫院 1.心內二科;2.風濕免疫科,江西 贛州 341000)
?
右胸導聯在運動試驗中對冠狀動脈再狹窄檢測的作用
周序鋒1,居艷娟2,謝東明1,陽貽紅1,鐘文婷1
(贛南醫學院第一附屬醫院 1.心內二科;2.風濕免疫科,江西贛州341000)
目的:評估附加V3R~V5R導聯在運動試驗中對檢測右冠狀動脈(RCA)和/或回旋支動脈(LCX)接受經皮冠狀動脈介入治療(PCI)無癥狀患者再狹窄診斷能力的作用。方法:129例在RCA和/或LCX接受PCI的患者,術前進行運動試驗,6個月后,所有患者為檢測再狹窄導致的無癥狀心肌缺血均接受第二次平板運動試驗和冠脈造影,并記錄運動中標準12導聯和V3R~V5R導聯的數據。結果:129例患者中,其中右冠狀動脈狹窄80例,回旋支狹窄26例,雙支血管狹窄23例。6個月后,分別有6例(RCA)、2例(LCX)及3例(雙支血管)出現再狹窄。PCI術后使用V3R~V5R導聯運動試驗的靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值,陰性預測值及準確率均有改善(分別為73% VS 55%,97% VS 80%,73% VS 21%,97% VS 95%,95% VS 78%,除了陰性預測值外,P均<0.05)。PCI術后運動試驗導致最大ST段下移值(毫米)在12導聯中無變化(1.4±0.3 vs 1.5±0.3,P>0.05),而在V3R~V5R導聯中有下降(0.2±0.2 vs 1.2±0.2,P<0.01)。結論:對右冠狀動脈(RCA)和/或回旋支動脈(LCX)接受經皮冠狀動脈介入治療(PCI)患者,使用附加V3R~V5R導聯可以提高標準運動試驗檢測再狹窄導致的無癥狀性心肌缺血的診斷能力。
右胸導聯;運動試驗;再狹窄
支架置入經皮冠脈介入治療(PCI)已經成為冠心病(CAD)患者心肌再血管化的一項非常成熟的技術。但是,支架植入6個月內支架內再狹窄依然存在,其中金屬裸支架者再狹窄約20%~30%,藥物洗脫支架再狹窄約<10%[1]。然而冠脈造影證實明顯再狹窄患者并非總會導致心絞痛的反復發作,其中有相當一部分再狹窄患者屬于無癥狀類型[2]。目前已經有研究報道[3-4]無癥狀心肌缺血對于冠心病患者是一項預測死亡和心血管事件的指標,因此對于無癥狀患者尋找一種后續評估及非侵入預測再狹窄的方法是一項重要的臨床課題。
目前廣為接受的評估再狹窄的風險及預警方法為PCI術后運動心電描述法[5],但是,其用來預測再狹窄缺乏靈敏性,靈敏度范圍為33%~58%,顯著劣于單光子發射計算機斷層掃描(SPECT)[6],并且運動試驗不利于回旋支區域病變的反映。而運動心電圖導聯數目和類型變化范圍大,2項研究[7-8]的初步結果顯示右胸導聯ST段偏移的不一致也許可以提高運動試驗的靈敏度(特異度無明顯下降),原因主要可能是增加了檢測右冠狀動脈和回旋支動脈顯著狹窄的靈敏度。
本研究目的在于探討對于右冠和/或回旋支接受PCI患者,使用附加右胸導聯的運動試驗(ET)是否有助于提高檢測無癥狀患者再狹窄的診斷能力。
1 資料和方法
1.1研究對象入選2011年8月至2015年9月在贛南醫學院第一附屬醫院右冠狀動脈和/或回旋支動脈成功接受PCI的患者129例,所有患者同意參加此項研究并無排除標準。PCI前均接受最大跑步運動試驗,成功接受PCI術后6個月,為了證實再狹窄導致的可能存在的無癥狀心肌缺血,所有患者盡管沒有癥狀均常規接受第二次跑步試驗及第二次冠脈造影。所有患者均給予心臟病藥物治療:抗血小板藥物(阿司匹林或氯吡咯雷或兩者同時服用),血管緊張素轉換酶抑制劑(ACEI)或血管緊張素受體阻滯劑(ARB),β-受體阻滯劑,鈣通道阻滯劑,和/或他汀類藥物。
排除標準:左束支或右束支傳導阻滯患者、左室或右室肥大患者、室性早搏患者、既往心肌梗死患者、瓣膜病或先天性心臟病患者以及接受冠狀動脈旁路移植術或既往冠脈血管成形術及正在服用地高辛患者。β-受體阻滯劑、二氫吡啶類及硝酸酯類藥物運動試驗前至少中斷5個半衰期。
1.2跑步運動試驗所有患者在美國TMX425平板運動試驗系統接受最大運動試驗。每一位患者使用標準12導聯加3個附加右胸導聯(V3R、V4R、V5R導聯)心電圖記錄。標準導聯及右胸導聯的位置與既往描述一致。運動終止標準及陽性結果判定參照診斷標準[9],如涉及V3R~V5R導聯,ST段偏移≥1 mm認為是陽性結果。同時當血壓下降至少20 mmHg,或者如果嚴重室性心律失常導致典型胸痛出現也認為是運動試驗陽性結果。心電圖測量由兩位不知曉冠脈造影結果的研究者使用放大鏡進行測量。觀察者自身及各觀察者之間對ST段偏移的變異度分別為(0.07±0.05) mm和(0.08±0.04) mm(相關系數分別為0.98和0.99)。
1.3冠狀動脈造影和經皮冠狀動脈介入治療所有患者使用經皮Judkins技術行選擇性冠脈造影術。左冠狀動脈選擇正位+頭位25°、左前斜45°+頭位/足位25°、右前斜30°+頭位/足位25°進行投影,右冠狀動脈選擇左前斜45°、右前斜30°進行投影。右冠狀動脈和回旋支動脈管腔直徑≥50%被看作是冠脈再狹窄。結果由兩位不知曉運動試驗結果的研究者評估。
2 結 果
2.1研究患者運動參數見表1,PCI成功6個月后大多數運動參數有改善:運動持續時間;最大心率;ST段壓低1 mm出現的時間;右胸導聯ST段壓低最大幅度;心絞痛發生率。
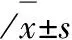
表1 研究患者的運動試驗參數
2.2接受PCI治療129例患者中,右冠明顯狹窄80例,回旋支明顯狹窄26例,右冠與回旋支均有狹窄23例。成功PCI術后6個月,11例患者通過冠脈造影證實再狹窄,其中右冠狹窄為6例,回旋支狹窄為2例,右冠和回旋支均有狹窄為3例。
2.3129例患者運動試驗結果見表2,依據結果,可以計算出PCI前后標準12導聯運動試驗和右胸導聯(V3R~V5R)運動試驗的靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值、陰性預測值及診斷準確率(圖1)。應用V3R~V5R導聯后運動試驗結果中各項指標均有改善。

表2 研究患者的運動試驗陽性結果
注:單支血管病變=右冠狀動脈或回旋支動脈病變,雙支血管病變=右冠狀動脈和回旋支動脈病變,任何一支血管病變=右冠狀動脈和/或回旋支動脈病變,ET=運動試驗。

注:各組之間比較,P值均﹤0.05,除了陰性預測值。
3 討 論
本研究顯示標準12導聯運動試驗對于檢測右冠病變是一項非常不敏感的診斷工具,尤其對于右冠和/或回旋支接受成功PCI后涉及右冠和/或回旋支再狹窄,靈敏度分別為53%和57%。這些比例與以往報道[10]一致,并且明顯差于其他非侵入性技術如SPECT(分別為87%[11]和87%[6])或壓力超聲心動圖(分別為86%[12]和63%[6])。根據我們研究結果,在標準導聯基礎上附加V3R~V5R導聯,提高了運動試驗在預測部分冠心病及再狹窄的靈敏度,同時也提高了運動試驗在預測右冠和/或回旋支患者成功實施PCI后6個月的再狹窄的特異度、預測值及準確率。因此, PCI術后6個月15導聯(標準12導聯和V3R~V5R)運動試驗陽性結果判定再狹窄可能性大,而陰性結果可以實際排除右冠狀動脈和/或回旋支的嚴重狹窄。
12導聯運動試驗對接受PCI患者晚期隨訪的價值不大,本研究結果(PCI術后6個月12導聯運動試驗預測無癥狀冠脈再狹窄靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值、陰性預測值及準確率分別為57%、80%、21%、95%及78%)與其它一些非侵入性技術預測再狹窄研究結果一致[10-12]。既往沒有關于15導聯運動試驗檢測冠脈再狹窄數據研究。依據我們研究結果,右胸導聯提高技術的可靠性(靈敏度、特異度、陽性預測值、陰性預測值及準確率分別上升為79%、97%、69%、98%及95%),與單光子發射計算機斷層掃描成像和壓力超聲心動圖相似甚至更高[6,12-13]。
本研究認為右胸導聯可以提高運動試驗對檢測冠心病和右冠狀動脈及回旋支動脈再狹窄的能力,其可能原因為V3R~V5R導聯(它位于對稱的右側胸部V3R~V5R)投影在心臟的下側壁,而該部位主要由右冠狀動脈和回旋支動脈提供血供。
[1]Mercado N,Boersma E,Wijns W,et al.Clinical and quantitative coronary angiographic predictors of coronary restenosis: a comparative analysis from the balloon-to-stent era[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2001,38:645-652.
[2]Ruygrok PN,Webster MWI,de Valk V,et al.Clinical and angiographic factors associated with asymptomatic restenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention[J].Circulation,2001,104:2289-2294.
[3]Davies RF,Goldberg AD,Forman S,et al.Asymptomatic Cardiac Ischemia Pilot (ACIP) study two-year follow-up:outcomes of patients randomized to initial strategies of medical therapy versus revascularization[J].Circulation,1997,95:2037-2043.
[4]Stone PH,Chaitman BR,Forman S,et al.Prognostic significance of myocardial ischemia detected by ambulatory electrocardiography,exercise treadmill testing and electrocardiogram at rest to predict cardiac events by one year[J].Am J Cardiol,1997,80:1395-1401.
[5]Laarman G,Luitjen HE,van Zeyl LG,et al.Assessment of silent restenosis and long-term follow-up after successful angioplasty in single vessel coronary artery disease:the value of quantitative exercise electrocardiography and quantitative coronary angiography[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,1990,16:578-585.
[6]Garzon P,Eisenberg MJ.Functional testing for the detection of restenosis after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty:a meta-analysis[J].Can J Cardiol,2001,17:41-48.
[7]Michaelides AP,Psomadaki ZD,Dilaveris PE,et al.Improved detection of coronary artery disease by exercise electrocardiography with the use of right chest leads[J].N Engl J Med,1999,340:340-345.
[8]Michaelides AP,Fourlas CA,Andrikopoulos GK,et al.Role of right-sided chest leads in the detection of multivessel coronary artery disease in patients with extended Q-wave anterior myocardial infarction[J].Coron Artery Dis,2006,17:165-171.
[9]Lai HM,Aronow WS,Mercando AD,et al.Risk factor reduction in progression of angiographic coronary artery disease[J].Arch Med Sci,2012,8(3):444-448.
[10]Gibbons RJ,Balady GJ,Bricker JT,et al.ACC/AHA 2002 guideline update for exercise testing: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines (committee to update the 1997 exercise testing guidelines)[J].Circulation,2002,106:1883-1892.
[11]Klocke FJ,BairdMG,Lorell BH,et al.ACC/AHA/ASNC guidelines for the clinical use of cardiac radionuclide imagingexecutive summary:a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASNC Committee to Revise the 1995 Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Cardiac Radionuclide Imaging)[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2003,42:1318-1333.
[12]Cheitlin MD,Armstrong WF,Aurigemma GP,et al.ACC/AHA/ASE 2003 guideline update for the clinical application of echocardiography-summary article:a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/ASE Committee to Update the 1997 Guidelines for the Clinical Application of Echocardiography)[J].J Am Coll Cardiol,2003,42:954-970.
[13]Isaaz K,Afif Z,Prévot N,et al. The value of stress single photon emission computed tomography imaging performed routinely at 6 months in asymptomatic patients for predicting angiographic restenosis after successful direct percutaneous intervention for acute ST elevation myocardial infarction[J].Coron Artery Dis,2008,19:89-97.
The Role of Right-sided Chest Leads in Exercise Testing for Detection of Coronary Restenosis
ZHOUXu-feng1,JUYan-juan2,XIEDong-yang1,YANGYi-hong1,ZHONGWen-ting1
(1.Dept.ofCardiovascularMedicineII;2.Dept.ofRheumatismImmunity,theFirstAffiliatedHospitalofGannanMedicalUniversity,GanzhouJiangxi341000)
Objective:To evaluate the role of additional V3R through V5 R leads in exercise testing to detect restenosis in asymptomatic patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in the right coronary artery (RCA) or/and left circumflex (LCX). Methods:We studied 129 consecutive patients (54 ± 7 years old, 80 males) undergoing PCI in RCA or/and LCX. A treadmill test had been performed before PCI. Six months later, all patients underwent a second treadmill test and arteriography in order to detect silent ischemia due to restenosis. Recordings during exercise were obtained with the standard 12-leads plus V3R through V5R. Results:Out of 129 patients, 80 had stenosis in RCA, 26 in LCX, and 23 in both vessels while 6 months later, restenosis was detected in 6 (for RCA), 2 (for LCX), and 3(for both vessels) patients respectively. Sensitivity, specificity, positive prognostic value, negative prognostic value, and accuracy of exercise testing performed post PCI were ameliorated using V3R through V5R (73% VS 55%,97%VS 80%,73%VS 21%,97%VS 95%,95% VS 78%respectively,P<0.05 for all except negative prognostic value). Maximal exercise-induced ST-segment deviation (in mm) was not changed post PCI in 12 leads (1.4± 0.3 vs 1.5 ± 0.3,P=NS) while it decreased in V3R through V5R (0.2 ± 0.2 vs 1.2 ± 0.2,P<0.01). Conclusion:The addition of V3R through V5R improves the diagnostic ability of standard exercise testing in detecting silent ischemia due to restenosis in patients undergoing PCI in RCA or/and LCX.
Right-sided chest leads;Exercise testing;Restenosis
R541.4
A
1001-5779(2016)03-0388-04
10.3969/j.issn.1001-5779.2016.03.016
2015-11-05)(責任編輯:敖慧斌)

