氣相色譜法測定水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的方法研究
姜建彪,李治國,常 青
(石家莊市環境監測中心,河北石家莊 050022)
?
氣相色譜法測定水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的方法研究
姜建彪,李治國,常 青
(石家莊市環境監測中心,河北石家莊 050022)
百菌清和溴氰菊酯的前處理工藝中鮮有對2種組分同時進行測定的方法,為優化萃取方法,研究建立了液液萃取-氣相色譜法同時測定水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯,針對影響回收率的因素進行了試驗,確定了氯化鈉、正己烷用量及萃取時間。百菌清和溴氰菊酯的最低方法檢出限分別為0.05 μg/L和0.40 μg/L,精密度分別為2.3%~13.2%和3.8%~9.1%。結果表明,該方法的靈敏度、重現性、準確性均滿足水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的測定要求。
水體環境學;氣相色譜法;水;百菌清;溴氰菊酯
百菌清是一種非內吸性、廣譜性、保護性殺蟲劑,對糧食、蔬菜、果樹等作物的真菌病害具有預防作用,藥效穩定,殘效期長。有文獻報道,百菌清在一定劑量下對動物的胃、腎等重要臟器及皮膚黏膜有影響[1-3]。溴氰菊酯是20世紀80年代研制成功的擬除蟲菊酯類殺蟲劑,殺蟲活性高、殺蟲譜廣、藥效迅速,被作為農藥廣泛使用[4],近年來人們常在水產養殖中利用溴氰菊酯來殺死水體中的錨頭鳋、魚怪等[5-8]。《地表水環境質量標準》(GB 3838—2002)中指出,集中式生活飲用水地表水源地特定項目標準限值中百菌清的質量濃度為0.01 mg/L,溴氰菊酯的質量濃度為0.02 mg/L[9]。百菌清和溴氰菊酯的前處理方法有液液萃取法[10]、固相萃取法[11]等,分析方法有氣相色譜法[12]、氣相色譜-質譜法[13]、三維熒光光譜法[14]、高效液相色譜法[15]等,但對2種組分同時測定的文獻并不多。本文采用液液萃取-氣相色譜法同時測定水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯,優化萃取方法。
1 實驗過程
1.1 儀器與試劑
儀器:Agilent 6890N氣相色譜儀,電子捕獲檢測器。
標準樣品:百菌清(百靈威科技有限公司提供,批號為214101163-01,質量濃度為100 μg/mL);溴氰菊酯標準溶液(百靈威科技有限公司提供,批號為214101500-01,質量濃度為100 μg/mL);正己烷,農殘級;無水硫酸鈉,優級純;氯化鈉,優級純。
1.2 方法原理
用正己烷萃取樣品中的百菌清和溴氰菊酯,萃取液經無水硫酸鈉脫水、濃縮、定容后,用氣相色譜儀-電子捕獲檢測器(ECD)分離、檢測,根據保留時間定性,外標法定量。
1.3 色譜條件
色譜柱:HP-5毛細管柱(30 m×320 μm×0.25 μm);載氣(N2) 流速:2.0 mL/min;尾吹:60 mL/min;汽化室溫度:250 ℃;檢測器溫度:300 ℃;程序升溫:100 ℃,保留1.0 min,以30 ℃/ min升至200 ℃,保留8.0 min,以30 ℃/ min升至290 ℃,保留10.0 min;分流比:10∶1。
1.4 樣品處理
取100.0 mL樣品,置于250 mL分液漏斗中,加入40 g氯化鈉,溶解后加入20 mL正己烷,振搖放氣后置于振蕩器上劇烈振蕩6 min,靜置10 min分層,將萃取液除水,濃縮至1 mL測定。
2 結果與分析
2.1 前處理方法的優化
2.1.1 氯化鈉加入量的確定
在水樣中加入氯化鈉是為了提高百菌清和溴氰菊酯的萃取效率,氯化鈉加入量的不同會影響兩者的萃取效果。用純水配制5份100 mL質量濃度分別為0.2 μg/L和1.0 μg/L的百菌清和溴氰菊酯水溶液,分別加入30,35,40,45,50 g的氯化鈉,然后加入10 mL正己烷,經萃取、干燥、濃縮,反應一段時間后測定百菌清和溴氰菊酯的響應,確定最佳加入量。對比結果見圖1。
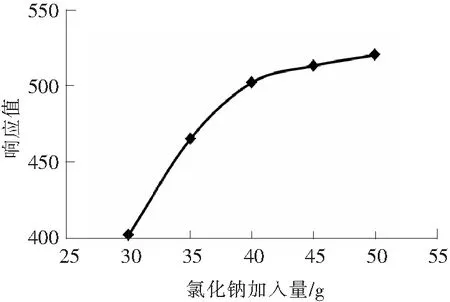
圖1 氯化鈉加入量對反應的影響Fig.1 Effect of NaCl amount on the reaction
由圖1可知,隨著氯化鈉加入量的增加,響應值變大。當加入量為40,45,50 g時,響應值變化不明顯。加入量為40 g時,既取得了較好的萃取效果,又節省了氯化鈉的使用量,從而確定氯化鈉的加入量為40 g。
2.1.2 正己烷用量的確定
隨著正己烷用量的變化,百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率會有所變化。同樣用純水配制3份100 mL質量濃度分別為0.2 μg/L和1.0 μg/L的百菌清和溴氰菊酯水溶液,加入40 g氯化鈉,再分別加入10,20,30 mL的正己烷萃取,然后干燥、濃縮。百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率見表1。
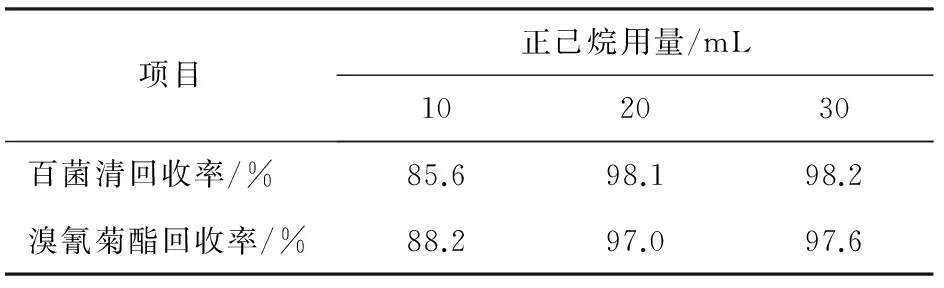
表1 正己烷用量對百菌清和溴氰菊酯回收率的影響Tab.1 Effect ofn-hexane amount on recovery rates ofchlorothalonil and deltamethrin
從表1可以看出,隨著正己烷用量的增加,百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率有所提高。當正己烷用量為20 mL時,百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率分別為98.1%和97.0%。再增加正己烷的用量,回收率并無明顯提高。從滿足實驗要求和節約試劑、利于環保的角度考慮,確定正己烷的用量為20 mL。
2.1.3 萃取時間的確定
隨著萃取時間的變化,百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率會有所變化。同樣用純水配制4份100 mL質量濃度分別為0.2 μg/L和1.0 μg/L的百菌清和溴氰菊酯水溶液,加入40 g氯化鈉,再加入20 mL正己烷,分別萃取2,4,6 min,然后干燥、濃縮。百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率見表2。
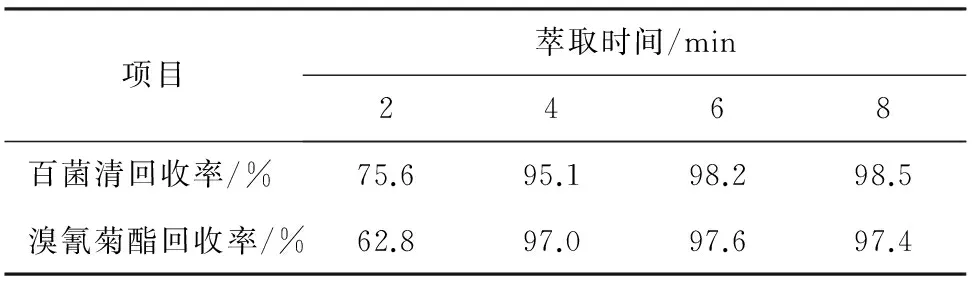
表2 萃取時間對百菌清和溴氰菊酯回收率的影響Tab.2 Effect of extraction time on recovery rates ofchlorothalonil and deltamethrin
從表2可以看出,隨著萃取時間的延長,百菌清和溴氰菊酯的回收率有所提高。當萃取時間達到6 min后,回收率提高并不明顯。綜合考慮后,確定萃取時間為6 min。
2.2 標準曲線
配制百菌清和溴氰菊酯的系列標準溶液,繪制標準曲線,見表3。

表3 質量濃度及標準曲線Tab.3 Mass concentration and standard curve
2.3 方法精密度、準確度和檢出限
配制低、中、高3種質量濃度的百菌清和溴氰菊酯水溶液,每個濃度處理6份,經計算得到的精密度和回收率見表4。純水中測定結果為未檢出。
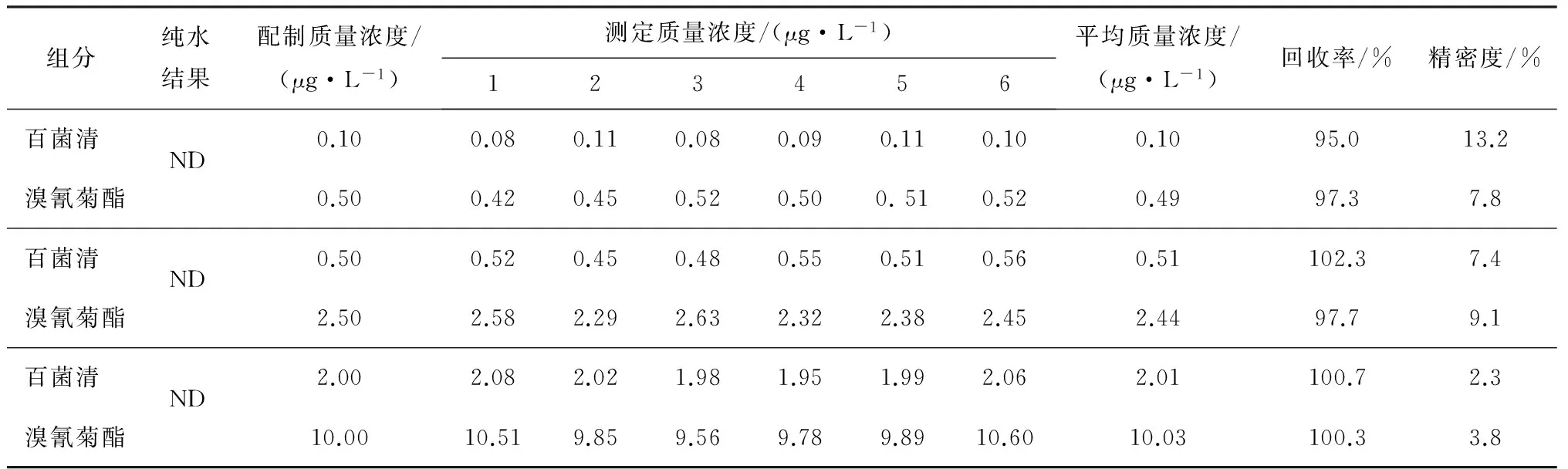
表4 百菌清和溴氰菊酯的精密度、準確度Tab.4 Accuracy and recovery rates of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin
配制100 mL質量濃度分別為0.02 μg/L和0.10 μg/L的百菌清和溴氰菊酯水溶液,重復測定7次,計算方法的檢出限。百菌清的檢出限為0.05 μg/L,溴氰菊酯的檢出限為0.40 μg/L,滿足地表水中對百菌清和溴氰菊酯的測定要求。
2.4 色譜圖和計算結果
百菌清和溴氰菊酯的氣相色譜圖見圖2。

圖2 百菌清、溴氰菊酯的色譜圖Fig.2 Chromatograms of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin
根據工作曲線,按照式(1)進行計算,可得到樣品中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的含量(μg/L)。

(1)
式中:σ為樣品中百菌清、溴氰菊酯的質量濃度,μg/L;σ1為由校準曲線計算得到的萃取液中百菌清、溴氰菊酯的質量濃度,mg/L;V1為水樣的體積,mL;V2為濃縮液的體積,mL。
3 結 論
1)樣品的前處理直接關系著待測物的回收率。為了達到最佳的實驗效果,氯化鈉的加入量需控制
在40 g,正己烷加入量控制為20 mL,萃取時間控制為6 min。
2)前處理采用液液萃取的方法,對儀器要求不高,適用性廣。
3)利用液液萃取-氣相色譜法同時測定水中的百菌清和溴氰菊酯,減少了重復萃取,提高了工作效率。
4)該方法操作簡便,具有較高的靈敏度,線性良好,精密度高,回收率高,可滿足對水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的測定要求。
[1] 仲來福,王維民,方耀明.長期喂飼百菌清純品對大鼠前胃和腎臟的毒效應[J].遵義醫學院學報,1984,7(1) : 13-15. ZHONG Laifu,WANG Weimin,FANG Yaoming.Toxic effects of long term feeding of bacteria on the stomach and kidney of rats[J]. Acta Academiae Medicinae Zunyi,1984,7(1) : 13-15.
[2] 彭運卿.農藥百菌清引起皮膚黏膜損害8例報告[J].職業醫學,1998,25(1) : 31. PENG Yunqing. Report of 8 cases of skin and mucous membrane damage caused by pesticide[J]. China Occupational Medicine,1998, 25(1) : 31.
[3] 郝乙杰,向月琴,方華,等.百菌清在土壤中的降解和對土壤微生物多樣性的影響[J].農業環境科學學報,2007,26(5):1672-1676. HAO Yijie, XIANG Yueqin, FANG Hua,et al. Degradation of chlor othalonil in soil and its effect on soil microbial diversity[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2007,26(5):1672-1676.
[4] 陸旸,徐娜,宋洋,等.溴氰菊酯檢測方法的研究與開發[J].食品與機械,2009,25(5):137-141. LU Yang ,XU Na, SONG Yang.et al. Research and development of detection methods of deltamethrin[J].Food & Machinery, 2009,25(5):137-141.
[5] 遲恒,李健,王吉橋,等.水環境中低濃度溴氰菊酯的降解規律及其動力學研究[J].農業環境科學學報,2007,26(5):1725-1728. CHI Heng, LI Jian, WANG Jiqiao, et al. Residual elimination and kinetics of low concentration of deltamethr in in water[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2007,26(5):1725-1728.
[6] 梁鴻唐,程沃明.用溴氰菊酯防治孔雀虱的試驗[J].廣西畜牧獸醫,2000,16(2):34-35. LIANG Hongtang,CHENG Woming. Test for deltamethrin against peacock lice[J]. Guangxi Journal of Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2000,16(2):34-35.
[7] 涂澇,俞澤溪.溴氰菊酯防治魚類甲殼動物寄生蟲病的探討[J].江西水產科技,2000,98(2):22-26. TU Lao,YU Zexi. Study of deltamethrin animal parasitic disease prevention and treatment of fish[J].Jiangxi Fishery Sciences and Technology,2000,98(2):22-26.
[8] 賀順連.三種常用魚藥對寬體金線蛭的急性毒性作用[J].湖南農業大學學報(自然科學版),2001,27(3):190-192. HE Shunlian. Acute toxic effect of three pesticides onWhitmaniapigra[J].Journal of Hunan Agricultural University(Natural Sciences), 2001,27(3):190-192.
[9] GB 3838—2002,地表水環境質量標準[S].
[10]李雪春,林野.飲用水中百菌清、溴氰菊酯測定前處理方法探討[J].環境衛生學雜志,2015,5(4):385-388. LI Xuechun,LIN Ye. Pre-processing method for detecting chlorothalonil and deltamethrin in drinking water[J]. Journal of Environmental Hygiene, 2015,5(4):385-388.
[11]江蓮.固相萃取-氣相色譜法測定水中溴氰菊酯和百菌清方法的研究[J].科技信息,2012(35):86-87. JIANG Lian. Study on the determination of deltamethrin in water by solid phase extraction gas chromatography and chlorothalonil method [J].Science & Technology Information,2012(35):86-87.
[12]劉寧.固相萃取-氣相色譜法測定水中百菌清-七氯-環氧七氯的含量[J].分析測試,2012,18(3):104-106. LIU Ning.Determination of chlorothalonil, heptachlor and heptachlor epoxide in water by solid phase extraction-gas chromatography[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2012,18(3):104-106.
[13]陳劍剛,朱克先,張亦庸,等.固相萃取-氣質聯用法測定水中三氯殺螨醇及百菌清[J].中國衛生檢驗雜志,2005,15(4):418-421. CHEN Jiangang,ZHU Kexian,ZHANG Yiyong, et al. Deter-mination of dicofol and chlorothalonile pesticide residues in water by gas chromatography-mass spectro metry with solid phase extract ion[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology, 2005,15(4):418-421.
[14]劉小靜,吳曉燕,齊彩亞,等.三維熒光光譜分析技術的應用研究進展[J].河北工業科技,2012,19(6):422-424. LIU Xiaojing,WU Xiaoyan,QI Caiya, et al. Applications of three-dimensional fluorescent spectroscopy analysis technology[J].Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2012,19(6):422-424.
[15]余彥海,鐘新林,陳軍,等.在線固相萃取-雙梯度高效液相色譜測定環境水體中痕量甲萘威和百菌清[J].中國環境監測,2013,29(4):138-141. YU Yanhai,ZHONG Xinlin,CHEN Jun, et al.Determination of carbaryl and chlorothalonil in environmental water using on-line SPE and HPLC[J].Environmental Monitoring in China, 2013,29(4):138-141.
Study on the determination method of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin in water by GC
JIANG Jianbiao, LI Zhiguo, CHANG Qing
(Shijiazhuang Environmental Monitoring Center, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050022, China)
There are few methods for simultaneous determination of the two components in the chlorothalonil and deltamethril pretreatment processes. In order to optimize the extraction method, liquid-liquid extraction combined with gas chromatography is established for the determination of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin in water. The factors influencing the recovery rate are tested. The added amount of sodium chloride and hexane and the extraction time are determined, and the extraction method is optimized. The detective limits of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin are 0.05 μg/L and 0.40 μg/L, respectively, and the peak area repeatability of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin are 2.3%~13.2% and 3.8%~9.1%. The results show that the sensitivity, reproducibility and accuracy of the method can meet the determination of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin in water.
water environment science; gas chromatography; water; chlorothalonil; deltamethrin
1008-1534(2016)06-0515-04
2016-06-30;
2016-08-16;責任編輯:張士瑩
河北省科技計劃重點項目(15273604D)
姜建彪(1980—),男,河北泊頭人,工程師,主要從事環境監測方面的研究。
E-mail:kdjjb@126.com
A
10.7535/hbgykj.2016yx06013
姜建彪,李治國,常 青.氣相色譜法測定水中百菌清和溴氰菊酯的方法研究[J].河北工業科技,2016,33(6):515-518. JIANG Jianbiao,LI Zhiguo,CHANG Qing.Study on the determination method of chlorothalonil and deltamethrin in water by GC[J].Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2016,33(6):515-518.

