無創正壓通氣在急性左心衰中的應用
陶麗
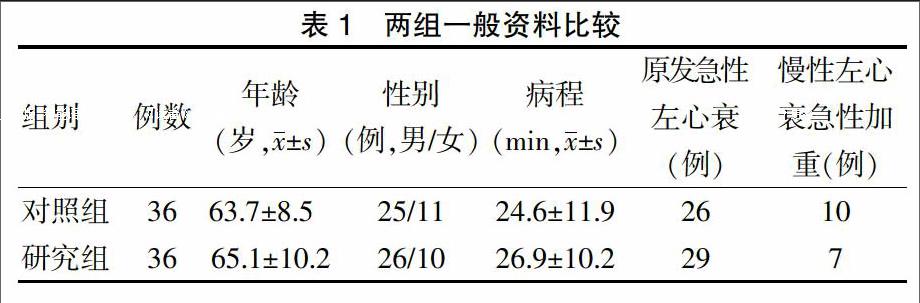
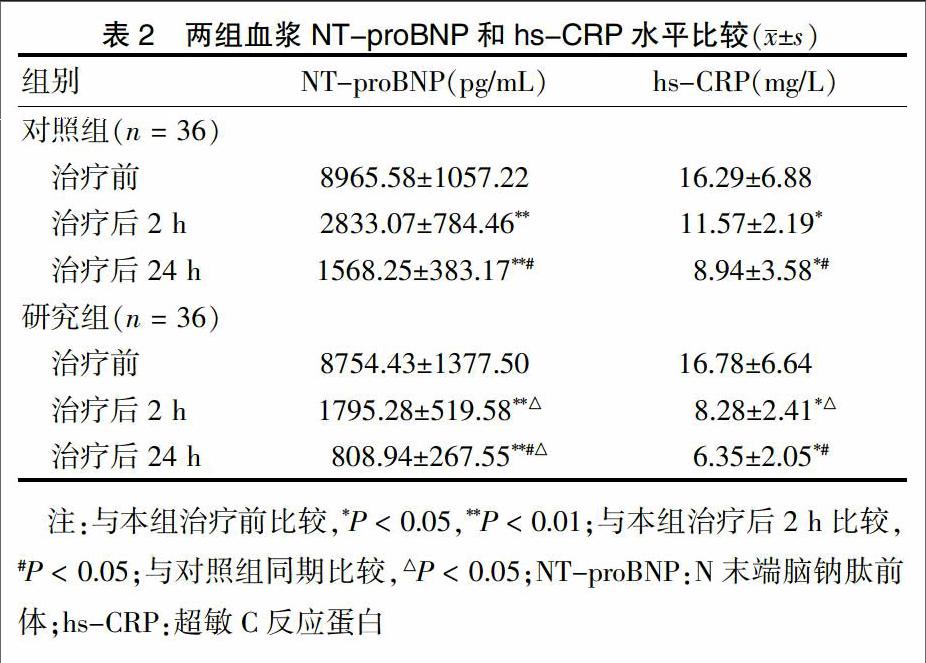
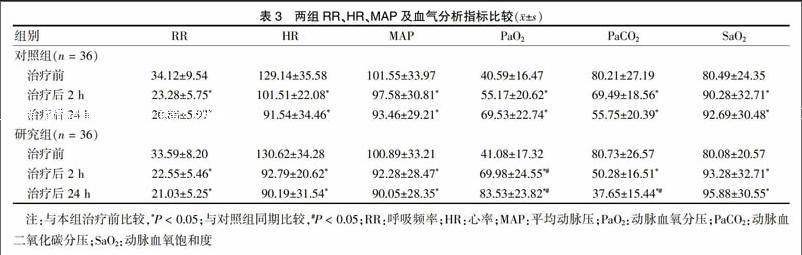
[摘要] 目的 探討無創正壓通氣在急性左心衰中的應用效果。 方法 選取2015年1月~2016年6月于重慶涪陵中心醫院住院治療的72例急性左心衰患者為研究對象,根據治療方法的不同將其分為研究組和對照組,每組各36例。兩組患者均給予吸氧、鎮靜、強心、利尿、擴張血管等對癥治療,研究組在此治療的基礎上給予無創正壓通氣。觀察兩組患者治療前、治療后2 h、治療后24 h的血漿N末端腦鈉肽前體(NT-proBNP)、超敏C反應蛋白(hs-CRP)的含量,以及呼吸頻率(RR)、心率(HR)、平均動脈壓(MAP)和動脈血氧分壓(PaO2)、動脈血二氧化碳分壓(PaCO2)、動脈血氧飽和度(SaO2)等血氣分析指標。 結果 治療后2、24 h,兩組患者NT-proBNP、hs-CRP均較治療前顯著降低,且治療后24 h低于治療后2 h,差異均有統計學意義(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。治療后2、24 h,研究組NT-proBNP水平均顯著低于對照組,治療后2 h研究組hs-CRP低于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05)。治療后2、24 h,兩組患者RR、HR、MAP、PaCO2均較治療前明顯降低,PaO2和SaO2較治療前明顯升高,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05);治療后2、24 h,研究組PaO2均高于對照組,治療后24 h PaCO2低于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(均P < 0.05)。研究組總有效率顯著高于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P < 0.05)。 結論 無創正壓通氣可迅速緩解急性左心衰患者的臨床癥狀,提高治療效果,值得臨床推廣應用。
[關鍵詞] 急性左心衰;無創正壓通氣;血氣分析;療效
[中圖分類號] R541.61 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1673-7210(2016)11(b)-0121-04
[Abstract] Objective To study the application effect of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation for the acute left heart failure. Methods Seventy-two patients with breast cancer in Chongqing Fuling Central Hospital from January 2015 to June 2016 were selected as the study objects, they were divided into research group and the control group according to the different treatments, with 36 cases in each group. Patients of the two groups were given symptomatic treatment, such as oxygen inhalation, sedative, strong heart, diuresis, dilate blood vessels. The patients of the research group were given the treatment of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation in addition. Precursor plasma N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), respiratory rate (RR), heart rate (HR), mean arterial pressure (MAP) and blood gas analysis, such as arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2), arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) and so on, in the two groups before treatment and 2, 24 hours after treatment were observed. Results After treatment for 2, 24 hours, the levels of NT-proBNP and hs-CRP in the two groups were all significantly reduced compared with those before treatment, and those after treatment for 24 hours were lower than those after treatment for 2 hours, the differences were all statistically significant (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). After treatment for 2, 24 hours, the levels of NT-proBNP in the research group were all significantly lower than those of control group, 2 hours after treatment, the level of hs-CRP in the research group was lower than that of control group, the differences were all statistically significant (all P < 0.05). After treatment for 2, 24 hours, RR, HR, MAP, PaCO2 in the two groups were significantly lower than those before treatment, PaO2 and SaO2 were obviously higher than those before treatment, the differences were all statistically significant (all P < 0.05); 2, 24 hours after treatment, PaO2 of research group was higher than that of control group, 24 hours after treatment, PaCO2 of research group was lower than that of control group, the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The total effective rate of research group was significantly higher than that of control group, the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation can rapidly alleviate the clinical symptoms of patients with acute left heart failure, improve the curative effect, which is worthy of clinical popularization and application.
[Key words] Acute left heart failure; Noninvasive positive pressure ventilation; Blood gas analysis; Curative effect
急性心力衰竭(acute heart failure)是指急性發作或加重的左心功能異常所致的心肌收縮力降低、心臟負荷加重,造成急性心排血量驟降、肺循環壓力升高、周圍循環阻力增加,引起肺循環充血而出現急性肺瘀血、肺水腫并可伴組織、器官灌注不足和心源性休克的臨床綜合征,是臨床常見的急危重癥。隨著我國老年人口的逐漸增多,急性重癥心力衰竭的發病率也逐年增高。臨床上常以面罩或鼻導管吸氧、利尿、擴容、強心等治療方式改善患者的缺氧癥狀,但效果并不顯著[1-2]。無創正壓通氣治療是在自主呼吸的吸氣相和呼氣相施加不同壓力干預的通氣方式,吸氣時增加患者的肺通氣量,呼氣時減少患者的殘氣量,提高肺氧合能力[3-4]。……

