基于AHP的武漢地區樟科植物園林應用價值評價
徐文斌+萬佳+吳風璨
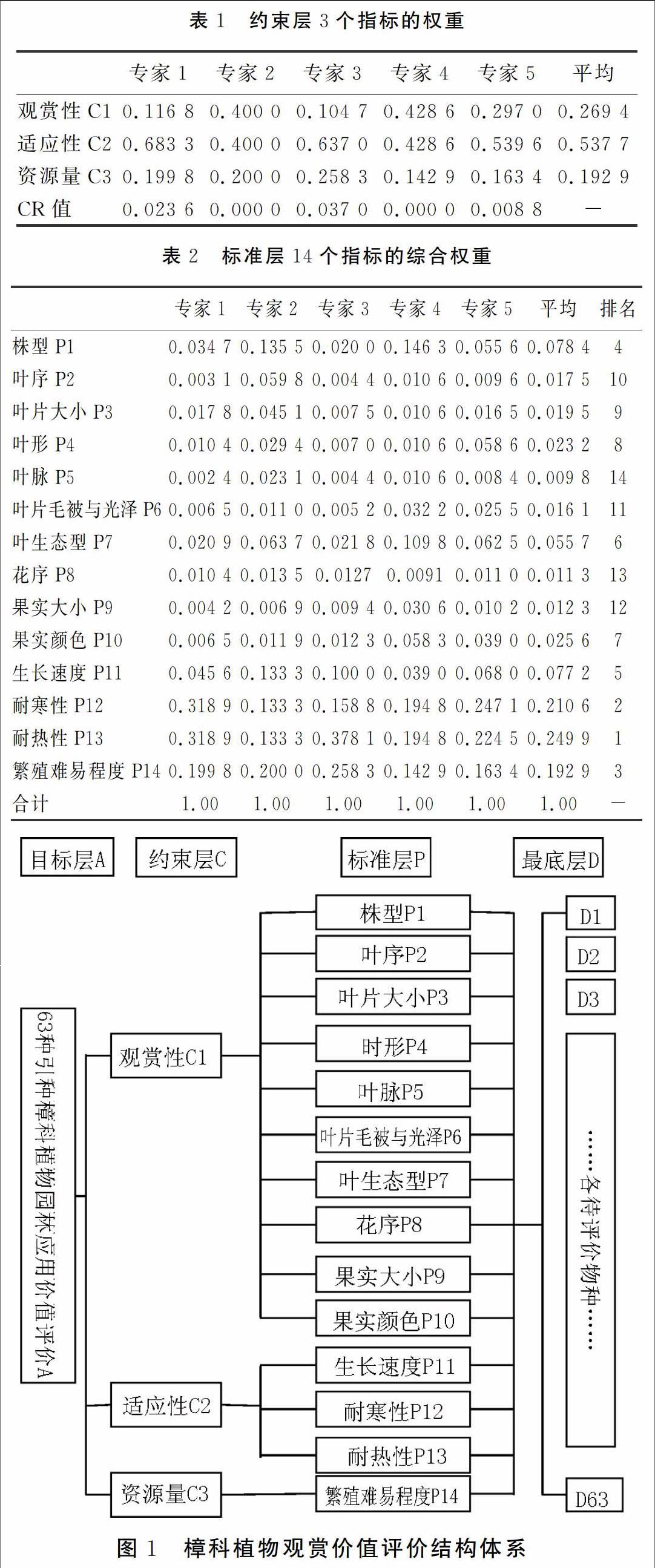

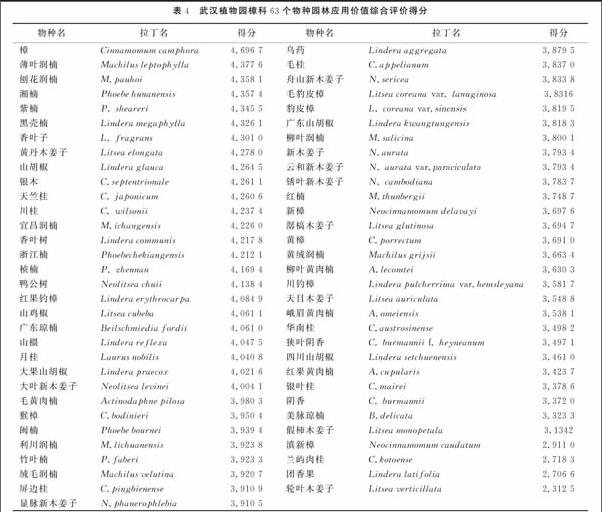
摘 要: 對武漢植物園引種成功的樟科植物進行了調查和統計,在此基礎上,運用層次分析法(AHP)對武漢植物園樟科物種進行了園林應用價值評價。確立了三個約束層(觀賞性C1、適應性C2、資源數量C3)、14個標準層的評價模型,并制定了標準層所有14個指標的5級評價標準,通過數據統計,從中篩選出24 種具有園林應用前景的種類,為武漢地區的樟科植物園林應用提供了科學的決策依據。
關鍵詞: AHP;樟科;園林應用;武漢
中圖分類號:S722.5 文獻標識碼:A 文章編號:1004-3020(2017)01-0030-05
Abstract: Based on a survey and statistics on the Lauraceae which were introduced successfully to Wuhan Botanical Garden, we used the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) to evaluate the landscape application value of Lauraceae species in this Garden. The evaluation model including three constraining layer (ornamental C1, adaptability C2, the amount of resources C3) and 14 standard layers was established, and a 5 levels evaluation criteria standard for all 14 indicators was developed; Through statistics, we screened out 24 kinds of species which had the landscape application prospect; In a word, it provided a scientific basis for decision making of the Lauraceaes landscape application in Wuhan area.
Key words: AHP;Lauraceae;landscape application;Wuhan
武漢市位于我國中部,屬北亞熱帶季風性濕潤氣候,年均氣溫15.8~17.5 ℃,雨量充沛、日照充足,武漢植物園坐落于武漢東湖之濱、磨山南麓,生態環境優越。特殊的地理環境使得武漢植物園成為良好的植物資源引種保育基地。
我國樟科植物約有24 屬, 423 種、43 變種和5變型[13],大多數物種都有良好的觀賞價值。通過調查統計,確認武漢植物園共引種保育63種樟科植物,但是縱觀武漢地區,常見的園林綠化物種僅有樟Cinnamomum camphora一種,絕大部分樟科植物資源都沒有得到應用。
層次分析法(AHP),是指將一個復雜的多目標決策問題作為一個系統,將目標分解為多個目標或準則,進而分解為多指標(或準則、約束)的若干層次,通過定性指標模糊量化方法算出層次單排序(權數)和總排序,以作為目標(多指標)、多方案優化決策的系統方法。該方法特別適合園林植物的評價及篩選,在園林綠化樹種的選擇上也有較多應用[48]。運用該方法,對武漢植物園引種成功的樟科物種進行園林應用價值綜合評價,從而為武漢市以及周邊地區的樟科植物推廣應用提供科學的決策依據。……

