調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)▽?duì)糖尿病胃輕癱患者腦腸肽的調(diào)節(jié)作用及療效觀察
俞建輝

[摘要] 目的 探討調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)▽?duì)糖尿病胃輕癱(DGP)患者腦腸肽的調(diào)節(jié)作用及療效。 方法 選擇72例DGP患者隨機(jī)分為聯(lián)合組和對(duì)照組。兩組患者均予控制飲食、適量運(yùn)動(dòng)和控制血糖等基礎(chǔ)治療。兩組患者均予莫沙比利片5 mg/次,3次/d,口服;聯(lián)合組患者配合調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)ㄡ槾讨委煟瑑山M均連用8周。比較兩組患者治療前與治療8周后血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)的變化情況,并進(jìn)行臨床療效評(píng)估。結(jié)果 治療8周后,兩組患者血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)與治療前比較明顯下降(P<0.05或P<0.01),且聯(lián)合組治療后VIP和NO指標(biāo)明顯低于對(duì)照組(P<0.05);同時(shí)聯(lián)合組和對(duì)照組治療的總有效率分別為94.44%和77.78%,聯(lián)合組明顯高于對(duì)照組(χ2=4.18,P<0.05)。 結(jié)論 調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)?lián)合西藥莫沙比利治療DGP療效確切,作用機(jī)制可能與其能降低血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平、糾正腦腸肽分泌紊亂、促進(jìn)胃腸動(dòng)力密切相關(guān)。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 糖尿病胃輕癱;調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)ǎ谎芑钚阅c肽;一氧化氮
[中圖分類號(hào)] R246.1 [文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼] B [文章編號(hào)] 1673-9701(2017)06-0123-03
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the regulation and curative effect of regulating spleen-stomach needling on brain-gut peptide in patients with diabetic gastroparesis(DGP). Methods 72 patients with DGP were randomly divided into combination group and control group. Both groups were given basic treatment including controlling diet, moderate exercise and controlling blood glucose.Two groups of patients were treated with moxabiride tablets 5 mg each time, 3 times/d, oral, and the combined group was also given treatment of regulating spleen-stomach needling. The treatment in the two groups both lasted for 8 weeks. The serum VIP and NO indexes were compared between the two groups before and after 8 weeks of treatment, and the clinical curative effect was evaluated. Results After 8 weeks of treatment, the levels of serum VIP and NO in the two groups significantly decreased compared with those before treatment(P<0.05 or P<0.01), and the VIP and NO indexes were significantly lower in the combined group than those in the control group(P<0.05). The total effective rates were 94.44% and 77.78% in the combined group and the control group, respectively, and the total effective rate in combined group was significantly higher than that in the control group(χ2=4.18, P<0.05). Conclusion Regulating spleen-stomach needling method combined with western medicine moxapril in the treatment of DGP is effective, and the mechanism may be closely related to its ability to reduce serum VIP and NO levels, correct brain-gut peptide secretion disorders, and promote gastrointestinal motility.
[Key words] Diabetic gastroparesis; Regulating spleen-stomach needling method; Vasoactive intestinal peptide; Nitric oxide
糖尿病胃輕癱(DGP)是糖尿病較常見(jiàn)的并發(fā)癥之一,主要表現(xiàn)為嘔吐、反復(fù)呃逆、食后飽脹等胃排空延緩下降相關(guān)癥狀,其病情易反復(fù)發(fā)作,治療處理頗困難[1]。近年來(lái)研究已發(fā)現(xiàn)血管活性腸肽(VIP)和一氧化氮(NO)等腦腸肽的分泌紊亂參與其整個(gè)發(fā)病過(guò)程,在DGP發(fā)病機(jī)制中有極其重要的地位[2,3]。近年來(lái)我院采用調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)ㄖ委烡GP,療效滿意,進(jìn)一步研究發(fā)現(xiàn)其對(duì)血清VIP和NO等腦腸肽具有明顯的調(diào)節(jié)作用,現(xiàn)報(bào)道如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 臨床資料
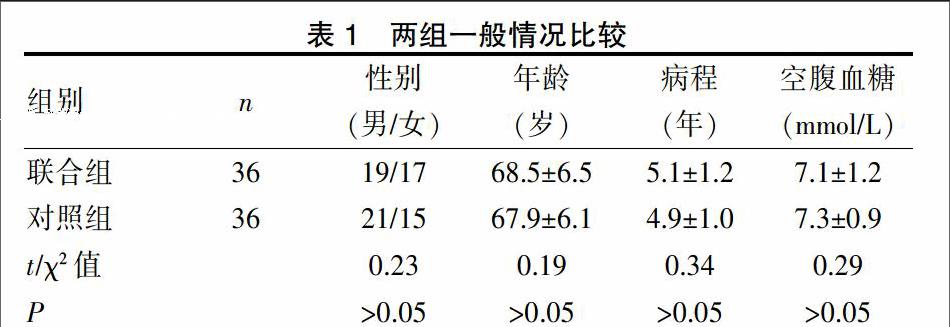
選取2014年1月~2016年5月我院針推康復(fù)科就診的72例DGP患者。納入標(biāo)準(zhǔn):(1)以《2型糖尿病防治指南(2007版)》中的診斷為準(zhǔn)[4],且病程時(shí)間>3年;(2)具有典型癥狀,鋇餐透視示吞鋇超過(guò)6 h仍有鋇條在胃內(nèi)殘留。排除標(biāo)準(zhǔn):(1)伴糖尿病的急性并發(fā)癥,如酮癥酸中毒、低血糖休克和高滲昏迷等;(2)原有肝膽消化道器質(zhì)性疾病或手術(shù)史。按照隨機(jī)數(shù)字表將患者分為聯(lián)合組和對(duì)照組。兩組性別、年齡、病程及空腹血糖等比較差異無(wú)統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。見(jiàn)表1。本方案經(jīng)醫(yī)院倫理委員會(huì)批準(zhǔn),納入前均簽署知情同意書(shū)。
1.2 治療方法
兩組患者予控制飲食、適量運(yùn)動(dòng)和控制血糖等基礎(chǔ)治療。兩組患者均予莫沙比利片(江西豪森藥業(yè)股份有限公司,規(guī)格:5 mg×24片,批號(hào)131005)5 mg/次,3次/d,口服;聯(lián)合組配合調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)ㄡ槾讨委煟⊙ǎ旱貦C(jī)、曲池、陰陵泉、三陰交、合谷、豐隆、太沖、足三里、血海、中脘。采用0.30 mm×50 mm和0.30 mm×60 mm針灸針。取仰臥位,穴位常規(guī)消毒,針刺深度以得氣為度,得氣后行補(bǔ)瀉手法,其中太沖、合谷、曲池、豐隆采用瀉法;三陰交、陰陵泉、足三里采用補(bǔ)法;中脘、血海、地機(jī)采用平補(bǔ)平瀉法;2次/d,每次留針30 min,連用5 d,休息2 d。兩組患者均連用8周。比較兩組患者治療前與治療8周后血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)的變化情況,并進(jìn)行臨床療效評(píng)估。
1.3 觀察指標(biāo)
1.3.1血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)測(cè)定 采集晨起空腹患者的靜脈血3 mL,常規(guī)低溫2500 r/min,離心10 min分離血清,將分離出上層血清提取,保存于-70℃冰箱。分別采用酶聯(lián)免疫吸附實(shí)驗(yàn)(ELISA)法與放射免疫法測(cè)定血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)。
1.3.2 療效評(píng)價(jià)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)[4] 顯效:癥狀較前明顯好轉(zhuǎn),鋇餐透視示胃蠕動(dòng)基本恢復(fù)正常;有效:癥狀較前有所好轉(zhuǎn),鋇餐透視示胃蠕動(dòng)較前加快;無(wú)效:癥狀較前無(wú)好轉(zhuǎn),鋇餐透視示胃蠕動(dòng)無(wú)好轉(zhuǎn)或加重。除無(wú)效均為總有效。
1.4 統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)處理
應(yīng)用SPSS18.0統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)軟件,計(jì)量資料與計(jì)數(shù)資料分別以均數(shù)±標(biāo)準(zhǔn)差(x±s)和率[n(%)]表示,采用t與χ2檢驗(yàn),檢驗(yàn)水準(zhǔn)α=0.05。P<0.05為差異有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義。
2 結(jié)果
2.1 兩組患者血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平比較
兩組患者治療前血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平比較差異無(wú)統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05)。治療8周后,兩組患者VIP和NO指標(biāo)與治療前比較明顯下降(t=3.27、2.89、2.19、2.31,P<0.05或P<0.01),且聯(lián)合組治療后VIP和NO指標(biāo)明顯低于對(duì)照組(t=2.29、2.21,P<0.05)。見(jiàn)表2。
2.2 兩組療效比較
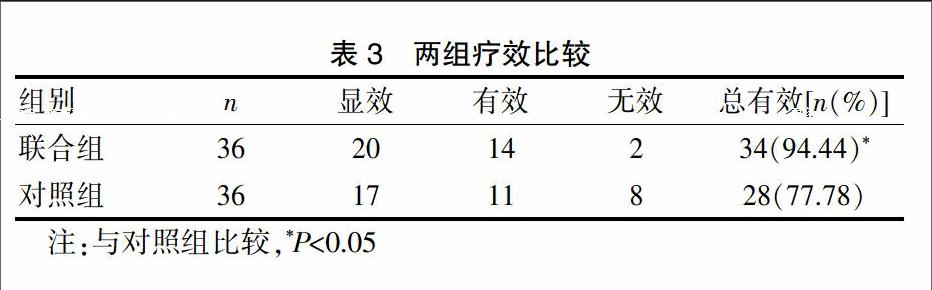
治療8周后,聯(lián)合組和對(duì)照組治療總有效率分別為94.44%和77.78%,聯(lián)合組明顯高于對(duì)照組(χ2=4.18,P<0.05)。見(jiàn)表3。
3討論
DGP是一種糖尿病并發(fā)癥,主要是由于胃排空顯著減慢,胃內(nèi)液體和固體食物潴留而出現(xiàn)的一系列臨床證候群,其發(fā)病率約1.5%~7.5%之間,臨床癥狀以胃運(yùn)動(dòng)障礙及胃排空延遲為主。DGP的發(fā)病機(jī)制十分復(fù)雜,至今國(guó)內(nèi)外尚未完全研究明確,隨著對(duì)DGP發(fā)病機(jī)制的深入研究,已發(fā)現(xiàn)高血糖毒性、間質(zhì)細(xì)胞數(shù)量或功能紊亂、幽門螺桿菌感染、腦腸肽分泌異常、氧化應(yīng)激、血管內(nèi)皮功能紊亂、鈉尿肽系統(tǒng)功能異常、神經(jīng)與微血管病變等因素參與DGP發(fā)病過(guò)程[5-8],其中VIP和NO等腦腸肽分泌異常在DGP的發(fā)病中發(fā)揮的作用逐漸引起臨床重視。VIP和NO均為胃腸道分泌的一種抑制性腦腸肽,可抑制胃腸道平滑肌運(yùn)動(dòng),減慢胃腸蠕動(dòng)和抑制胃排空作用,抑制胃腸動(dòng)力,抑制腸管對(duì)水電解質(zhì)的轉(zhuǎn)運(yùn),對(duì)胃腸運(yùn)動(dòng)起負(fù)性調(diào)節(jié)作用[9-16]。因此,抑制VIP和NO的分泌、促進(jìn)消化道運(yùn)動(dòng)有利于DGP的治療[17,18]。
中醫(yī)認(rèn)為DGP屬“消渴兼痞滿”范疇,其病機(jī)大多為消渴日久致脾失健運(yùn),內(nèi)生痰濁,痰郁日久,瘀阻脈絡(luò)引起,治療應(yīng)調(diào)理脾胃、降逆止嘔和運(yùn)化有常為主[19,20]。曲池與合谷和胃降逆,調(diào)理胃腸;中脘可健脾胃、助運(yùn)化;足三里,補(bǔ)之能健脾胃,升陽(yáng)舉陷,瀉之能引胃氣下行,助水谷之運(yùn)化;陰陵泉健脾升陽(yáng),化濕滯;三陰交健脾益氣,調(diào)補(bǔ)肝腎,與足三里、中脘相伍,振奮中焦,使清升濁降,與陰陵泉相配,健脾利濕,開(kāi)通水道;太沖平肝而調(diào)肝;豐隆和胃祛濕,潤(rùn)腸道;血海能引血理血,祛瘀通脈;地機(jī)善于活血化瘀。諸穴合用有調(diào)理脾胃、使升降有序、健運(yùn)有常、氣血得化之功效,切合DGP的病理與病機(jī)。本研究顯示治療8周后,聯(lián)合組血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)下降程度大于對(duì)照組,且總有效率高于對(duì)照組,提示調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)?lián)合西藥莫沙比利治療DGP療效確切,其作用機(jī)制與其降低血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平、促進(jìn)胃腸動(dòng)力密切相關(guān)。我們推測(cè)認(rèn)為調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)?lián)合西藥莫沙比利治療DGP可能通過(guò)糾正腦腸肽分泌異常、減少VIP和NO等抑制性腦腸肽的分泌,降低血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平,從而促進(jìn)胃腸蠕動(dòng)和胃排空,改善胃腸動(dòng)力,使得脾胃逐漸如常,升降有序,健運(yùn)有常,切合DGP的病理與病機(jī)達(dá)到治療目的。但本研究的病例數(shù)相對(duì)較少,研究時(shí)間相對(duì)較短,可能結(jié)果存在一定的偏差,必要時(shí)增加病例數(shù)及延長(zhǎng)研究時(shí)間深入研究探討。
綜上,調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)?lián)合西藥莫沙比利治療DGP療效確切,作用機(jī)制可能與其能降低血清VIP和NO指標(biāo)水平、糾正腦腸肽分泌紊亂、促進(jìn)胃腸動(dòng)力密切相關(guān)。
[參考文獻(xiàn)]
[1] Nicolas Intagliata BA,Kenneth L,Koch.Gastroparesis in type-diabetes mellitus:Prevalence,etiology,diagnosis,and treatment[J].Current Gastroenterology Reports,2007, 9(4):270-279.
[2] Anitha M,Gondha C,Sutliff R,et al.GDNF rescues hyperglycemia-in-duced diabetic enteric neuropathy through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. J Clin Invest,2006, 116(2):344-356.
[3] 吳波,韓萍,周卓.糖尿病胃腸病變與腦腸肽的相關(guān)性[J].廣東醫(yī)學(xué),2004,25(11):1297-1290.
[4] 中華醫(yī)學(xué)會(huì)糖尿病學(xué)分會(huì).中國(guó)2型糖尿病防治指南(2007年版)[J].中華醫(yī)學(xué)雜志,2008, 88(18):1227-1245.
[5] Larson JM,Tavakkoli A,Drane WE,et al.Advantages of azithromycin over erythromycin in improving the gastric emptying half-time in adult patients with gastroparesis[J].Journal of Neurogastroent Erology and Motility,2010,16(4):407-413.
[6] Borg J,Melander O,Johansson L,et al.Gastroparesis is associated with oxytocin deficiency, oesophageal dysmotility with hyper CCKemia,and autonomic neuropathy with hypergas trinemia[J]. BMC Gastroenterol,2009,9(2):17-19.
[7] James AN,Ryan JP,Crowell MD,et al.Regional gastric contractility alterations in a diabetic gastroparesis mouse model-eftects of cholinergic and serotoninergic stimulation[J].AmJ Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol,2004,287(3):612-619.
[8] Woerle HJ,Albrecht M,Linke R,et al.Impaired hyperglycemia-induced delay in gastric emptying in patients with type 1 diabetes deficient for iset amyloid polypeptide[J].Diabetes Care,2008,31(2):2325-2331.
[9] He CL,Soffer EE,F(xiàn)erris CD,et al.Loss of interstitial cells of cajal and inhibitory innervation in insulin-dependent diabetes[J].Gastroenterology,2001,121(2):427-434.
[10] 赫廣玉,劉玉佳,謝曉娜.糖尿病自主神經(jīng)病變胃輕癱發(fā)病機(jī)制及診治研究進(jìn)展[J].中國(guó)老年學(xué)雜志,2013, 33(6):2987-2990.
[11] 林琳,計(jì)敏,趙志泉,等.四種胃腸激素在糖尿病胃動(dòng)力障礙中的作用[J].現(xiàn)代消化及介入診療,2003,8(2):74-77.
[12] 劉曉娜,吳興全,王富春.胃腸激素與糖尿病胃輕癱發(fā)病機(jī)制的關(guān)系研究進(jìn)展[J].長(zhǎng)春中醫(yī)藥大學(xué)學(xué)報(bào),2016,31(1):209-212.
[13] Sanger GJ,Westaway SM,Barnes AA,et al.GSK962040:A small molecule,selective motilin receptor agonist,effective as a stimulant of human and rabbit gastrointestinal motility[J].Neurogastroenterol Motil,2009,21(6):657-664.
[14] Joseph IM,Kirschner D.A model for the study of helicobater pylori interaction with human gastric acid secretion[J].J Theor Biol,2004,228(1):55-80.
[15] Brzozowski T,Konturek PC,Mierzwa M,et al.Effect of probiotics and triple eradication therapy on the cyclooxygenase(COX)-2 expression,apoptosis,and functional gastric mucosal impairment in Helicobacter pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils[J].Helicobacter,2006,11(2):10-20.
[16] Czaja M,Szarszewski A,Kamińska B,et al.Serum gastrin concentration and changes in G and D cell densities in gastric antrum in children with chronic gastritis[J]. Int J Clin Practm, 2008,62(5):1044-1049.
[17] Wiedemann T,Loell E,Mueller S,et al.Helicobacter pylori cag-Pathogenicity island-dependent early immunological response triggers later precancerous gastric changes in Mongolian gerbils[J]. PLoS One,2009,4(1):e4754.
[18] 于豐彥,周福生,牛麗華,等.糖尿病胃輕癱中醫(yī)證候的胃動(dòng)力相關(guān)研究[J].國(guó)際醫(yī)藥衛(wèi)生導(dǎo)報(bào),2009,15(4):81-83.
[19] 尚瑩瑩,黃天生,肖定洪.糖尿病胃輕癱中醫(yī)理論及臨床研究進(jìn)展[J].中醫(yī)研究,2013,26(1):75-77.
[20] 張萍,劉占芬,王春梅,等.調(diào)理脾胃針?lè)ㄖ委熖悄虿∥篙p癱療效觀察[J].中國(guó)針灸,2007,27(4):258-260.
(收稿日期:2016-12-27)

