3個早發糖尿病家系HNF1α基因篩查研究
康曉麗++丁文宇++張勇++趙珂++王志斌++王堯++郭振奎
DOI:10.16658/j.cnki.1672-4062.2017.05.005
[摘要] 目的 通過對3個疑為MODY3的早發糖尿病家系成員HNF1α基因分子篩查,探討該基因分子缺陷是否為其主要發病因素。方法 抽取家系成員外周血,應用聚合酶鏈式反應技術對HNF1ɑ基因全部外顯子及外顯子內含子拼接區進行擴增,PCR產物直接測序,測序結果與NCBI數據庫中標準序列比對分析。結果 發現3個編碼區錯義突變:R272S、I27L、S487N,2個同義突變:I17L、L459L,6個非編碼區堿基改變:IVS1+91A>G、IVS5+9C>G、IVS7+7G>A、IVS8-24T>C、IVS9+197G>T、IVS9+438G>A。R272S在F1家系中的分布與糖尿病的發生共分離;除R272S外的其他堿基改變均為多態性改變,且和糖尿病的發生無明顯相關性。結論 該研究發現10個多態性位點; R272S突變在F1家系中與糖尿病的發生共分離,初步判斷該家系是由突變R272S導致的MODY3家系。
[關鍵詞] 青少年的成人起病型糖尿病(MODY);HNF1α;R272S;突變;多態性
[中圖分類號] R587 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 1672-4062(2017)03(a)-0005-03
Research on Screening of 3 Familial Early-onset Diabetes Pedigrees HNF1α Genes
KANG Xiao-li1,2, DING Wen-yu2, ZHANG Yong2, ZHAO Ke2, WANG Zhi-bin2, WANG Yao2, GUO Zhen-kui2
1.College of Medicine and Life Science of Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences of Jinan University,Jinan,Shandong Province, 250000 China;2.Institute of Endocrinology and Metabolism of Shandong Province,Jinan,Shandong Province, 250000 China
[Abstract] Objective To screen 3 familial early-onset diabetes pedigrees HNF1α genes and study whether the gene molecule defect is the major pathogenic factor. Methods The peripheral blood of families was extracted and the all exons and exon and intron split joint center were expanded by the polymerase chain reaction, and the PCR products sequence results and standardized sequence in NCBI database were compared and analyzed. Results 3 code area missense mutations were found: R272S,I27L,S487N, 2 samesense mutations: I17L and L459L, 6 noncoding region basic group changes: IVS1+91A>G, IVS5+9C>G, IVS7+7G>A, IVS8-24T>C, IVS9+197G>T, IVS9+438G>A, and there was a coseparation distribution of R272S in the F1 family and occurrence of diabetes, and other basic group changes were polymorphisms changes in addition to R272S, and there was no obvious correlation with the occurrence of diabetes. Conclusion The research shows that there ae 10 polymorphic sites, and R272S mutation has a coseparation with the occurrence of diabetes, and we can initially determine that the family is the MODY3 family caused by R272S mutation.
[Key words] MODY; HNF1α; R272S; Mutation; Polymorphism
青少年起病的成人型糖尿病3型(MODY3)由HNF1α基因突變所致,該基因定位在12q24.2,在肝臟、腎臟、腸、β細胞中均有表達,是調控胰島素分泌的關鍵轉錄因子,至今已發現了近200種HNF 1α基因突變[1]。該研究對3個家系共26例樣本的HNF1α外顯子及拼接區進行直接測序,探索其堿基改變與糖尿病發生的關系,以期能發現新的MODY3基因致病位點。
1 對象與方法
1.1 對象
選取3個疑為MODY3的早發糖尿病家系,分別用F1、F2、F3來表示,先證者均為就診于山東內分泌與代謝病醫院的糖尿病患者,均為山東地區漢族居民,共有特點:①發病年齡小于45歲;②家族中至少兩代為糖尿病患者;③病初服用磺脲類藥物治療效果較好;④胰島細胞抗體和谷氨酸脫梭酶抗體陰性;⑤BMI多正常。
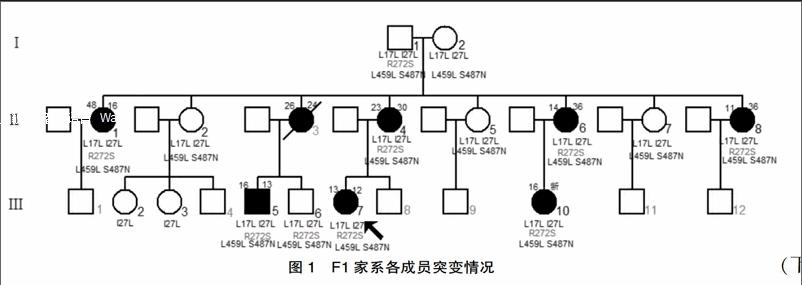
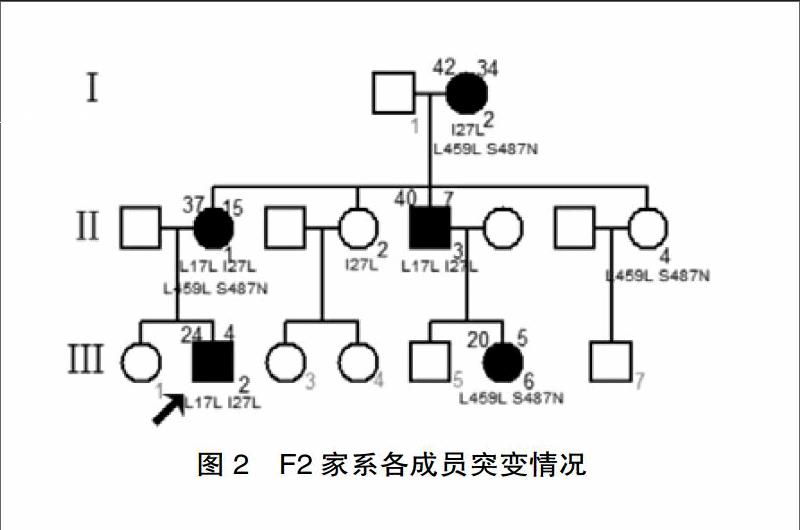
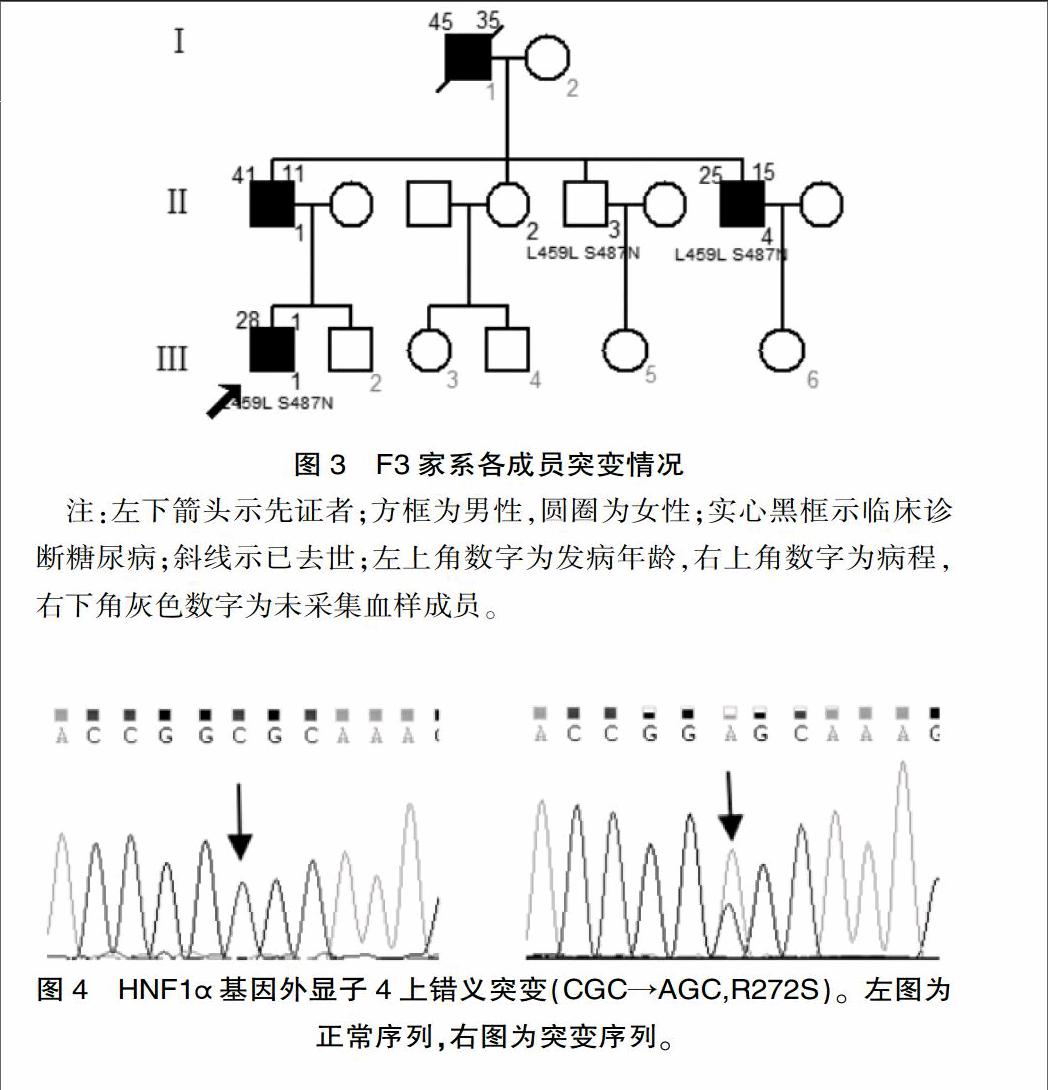
現收集F1家系15例、F2家系7例、F3家系4例的外周血進行該基因研究。其中包括F1家系中糖耐量異常者2例(Ⅰ1、Ⅲ6)。(各家系成員血樣采集情況及發病情況見圖1、2、3)選擇無親緣關系的健康人16名作為對照,男性8名,女性8名,無糖尿病家族史,平均年齡(40.12±19.37)歲,體重指數(23.60±3.97)kg/m2。
1.2 方法
經倫理委員會及患者知情同意后,提取3個家系中26例成員的外周血DNA,PCR擴增HNF1α基因全部外顯子及外顯子與內含子拼接區。將檢測出目的片段的未純化PCR產物送到華大基因直接測序。
2 結果
該研究中發現3個編碼區錯義突變:R272S、I27L、S487N,2個同義突變:I17L、L459L,6個非編碼區堿基改變:IVS1+91A>G、IVS5+9C>G、IVS7+7G>A、IVS8-24T>C、IVS9+197G>T、IVS9+438G>A。上述堿基改變均于F1家系中發現,并且R272S、IVS5+9C>G、IVS8-24T>C、IVS9+197G>T、IVS9+438G>A只出現于該家系中;其他4種編碼區堿基改變及2種非編碼區堿基改變均于3個家系及健康對照組檢出。F1家系中糖代謝異常的9名成員均攜帶HNF1α基因4號外顯子雜合突變c.814C>A,該突變位點導致第272位氨基酸由精氨酸突變為絲氨酸(R272S,突變測序圖見圖4),其中除R272S外的其他堿基改變均可在NCBI中查到相關SNP信息,且和糖尿病的發生無明顯相關性,而錯義突變R272S在F1家系中與糖尿病的發生共分離(測序成員攜帶的編碼區突變見圖1、2、3)。
3 討論
該研究結果顯示R272S突變在F1家系中與糖尿病的發生共分離。該突變位于HNF1α基因的DNA結合區,該區的基因突變可導致轉錄因子與靶基因結合異常,影響靶基因轉錄。而它的靶基因包括胰島素分泌相關的基因和糖代謝相關的基因等。R272S在國外的文獻中出現過[2],但未對其做出功能分析,國內尚未見該位點的報道。Prabi預測網站分析顯示該突變致使其二級結構由α螺旋變為不規則卷曲及延伸鏈,這種改變極有可能形成新的活性位點,導致蛋白功能改變。另外,應用蛋白功能預測網站都顯示R272S突變有較強的致病性。
該研究尚發現4種編碼區突變,即I27L、S487N、I17L、L459L,這4種多態性位點已在印度[3]、泰國[4]、墨西哥[5]、歐洲[6]也有所報道。Holmkvist等[7]研究發現I27L、S487N與口服葡萄糖后胰島素分泌的減少有關,而Urhammer等[8]的研究發現I27L、S487N兩種多態性胰島素分泌無相關性。在該研究中,未發現這4種編碼區突變與糖尿病相關的證據,并且在健康對照組中亦有較高的檢出率,分別為0.69、0.69、0.875、0.875。
綜上,該研究發現10種多態性位點;R272S在F1家系中與糖尿病的發生共分離,初步判斷HNF1α為該家系糖尿病發生的致病基因。
[參考文獻]
[1] S. Ellard,K. Colclough, Mutations in the genes encoding the transcription factors hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (HNF1A) and 4 alpha (HNF4A) in maturity onset diabetes of the young[J].Hum Mutat, 2006,27(9):854-869.
[2] Bellanne-Chantelot C, Carette C, Riveline J P, et al. The type and the position of HNF1A mutation modulate age at diagnosis of diabetes in patients with maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3)[J]. Diabetes,2008,57(2):503-508.
[3] Radha V, EK J, Anuradha S, et al. Identification of novel variants in the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1α gene in South India patients with maturity onset diabetes of young[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,2009,94(6):1959-1965.
[4] Plengvidhya N, Boonyasrisawat W, Chongjaroen N, et al. Mutations of maturity-onset diabetes mellitus[J].Clin Endocrinol,2009,70(6):847-835.
[5] Doningue-Lopez A, Miliar-Gareia A, Segura-Kato Y X, et al. Mutations in MODY genes are not common cause of early-onset type2 diabetes in Mexican families[J].JOP,2005,6(3):238-245.
[6] Yamagota K, Oda N, Kaisaki P J, et al. Mutations in the hepatic nuclear factor-1alpha gene in maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY3)[J]. Nature,1996,384(6608):455-458.
[7] Holmkvist J,Cervin C,Lyssenko V,et al.Common variants in HNF1alpha and risk of type2 diabetes[J].Diabetologia,2006,49(12):2882-2891.
[8] Urhammer S A, Moller A M, Nyholm B, et al. The effect of two frequent amino acid variants of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-1 alpha gene on estimates of the pancreatic beta-cell function in Caucasian glucose-tolerant first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic patients[J].J Clin Endocrinol Metab,1998, 83(11):3992-3995.
(收稿日期:2016-12-02)

