小兒支氣管哮喘血T、B淋巴細胞異常表達的臨床意義
文 勃,王成林,羅 麗,馮 楊
(雅安市人民醫院,四川 雅安 625000)
小兒支氣管哮喘血T、B淋巴細胞異常表達的臨床意義
文 勃,王成林,羅 麗,馮 楊
(雅安市人民醫院,四川 雅安 625000)
目的 探討小兒支氣管哮喘血T、B淋巴細胞異常表達的臨床意義。方法 選擇2016年1至10月在雅安市人民醫院就診的哮喘患兒198例為研究對象(哮喘組),按照1:1配對,隨機選取同期體檢兒童為對照組;在哮喘組患兒中急性發作期107例,緩解期91例,對照組198例。檢測哮喘急性發作、哮喘緩解和對照組兒童外周血的T淋巴細胞(CD3、CD3+CD4+、CD3+CD8+和CD4+/CD8+)、B淋巴細胞(CD19+CD23+),比較其相關指標的差異。結果 哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD3+CD4+、CD19+CD23+分別明顯高于哮喘緩解期(t值分別為2.479和2.341,均P<0.05)和對照組的患者(t值分別為2.421和2.524,均P<0.05);哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD4+/CD8+明顯高于哮喘緩解期的患兒和對照組,經比較均有顯著性差異(t值分別為2.516和2.325,均P<0.05)。結論 支氣管哮喘患兒外周血T、B淋巴細胞明顯異常高表達,可作為支氣管哮喘輕重程度及治療效果的評價指標。
支氣管哮喘;B淋巴細胞;T淋巴細胞;兒童;治療效果
支氣管哮喘(bronchial asthma,以下簡稱哮喘)是一種以慢性氣道炎癥和氣道高反應性為特征的異質性疾病,多于兒童期發病。雖然在西方發達國家哮喘的發病率趨于穩定,但在發展中國家,其發病率呈逐年升高趨勢,成為嚴重影響兒童生長發育的慢性疾病之一,給患兒家庭及社會帶來了沉重的經濟負擔。細胞免疫的主要執行者為T淋巴細胞,體液免疫的主要執行者為B淋巴細胞,淋巴細胞的失衡與小兒支氣管哮喘的發病密切相關[1-5]。T淋巴細胞和B淋巴細胞是否可作為小兒支氣管哮喘嚴重程度的評判標準及治療效果的隨訪指標有待研究。本資料對198例哮喘患兒和按1:1配對同期體檢兒童的外周血T淋巴細胞(CD3、CD3+CD4+、CD3+CD8+和CD4+/CD8+)、B淋巴細胞(CD19+CD23+)進行檢測分析,比較其相關指標的差異,為探討外周血淋巴細胞相關指標在小兒哮喘患兒中的臨床應用價值提供理論依據。
1對象與方法
1.1研究對象
收集2016年1至10月在雅安市人民醫院就診的哮喘患兒為研究對象(哮喘組),按照1:1配對,隨機選取同期在本院體檢的兒童為對照組。將符合支氣管哮喘納入標準的患兒,根據有無臨床癥狀的急性發作分為急性發作期和緩解期。納入標準:患兒年齡為1~14周歲,并符合兒童哮喘的臨床診斷標準[6];排除標準:①年齡<1歲或者>14歲;②首次喘息發作;③近2周有糖皮質激素或免疫調節劑的使用史;④合并有其他免疫性疾病、心肺腦基礎疾病等;⑤對照組兒童排除既往反復感染病史及喘息史,近2周有糖皮質激素或免疫調節劑的使用史,存在特應性體質及過敏性疾病家族史,存在心肺腦基礎疾病和/或免疫疾病等基礎疾病。
1.2標本采集
收集患兒的年齡、性別等基本信息,記錄淋巴細胞亞群主要參數,包括T淋巴細胞(CD3、CD3+CD4+、CD3+CD8+和CD4+/CD8+)和B淋巴細胞(CD19+CD23+)及免疫球蛋白E(IgE)。采用MACSQuant八色流式細胞儀(德國)及貝克曼庫爾特Gallios流式細胞儀(美國)對標本血進行淋巴細胞亞群檢測。
1.3統計學方法

2結果
2.1研究對象的一般資料
本次共納入符合標準的研究對象396例。哮喘組198例,其中急性發作期患兒107例,占54.04%,哮喘緩解期患兒91例,占45.96%;對照組198例,見表1。
2.2兩組T淋巴細胞亞群的檢測情況
哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD3+CD4+和CD4+/CD8+均明顯高于哮喘組緩解期患兒和對照組兒童,經比較有顯著性差異(均P<0.05);哮喘組緩解期患兒的CD3+CD4+和CD4+/CD8+均高于對照組兒童,經比較有顯著性差異(均P<0.05),見表2。
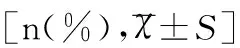
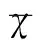
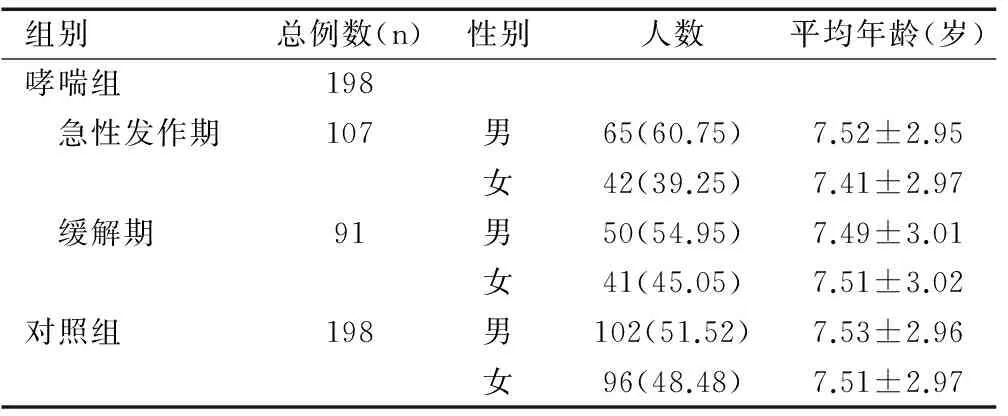
組別總例數(n)性別人數平均年齡(歲)哮喘組198 急性發作期107男65(60.75)7.52±2.95女42(39.25)7.41±2.97 緩解期91男50(54.95)7.49±3.01女41(45.05)7.51±3.02對照組198男102(51.52)7.53±2.96女96(48.48)7.51±2.97

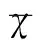
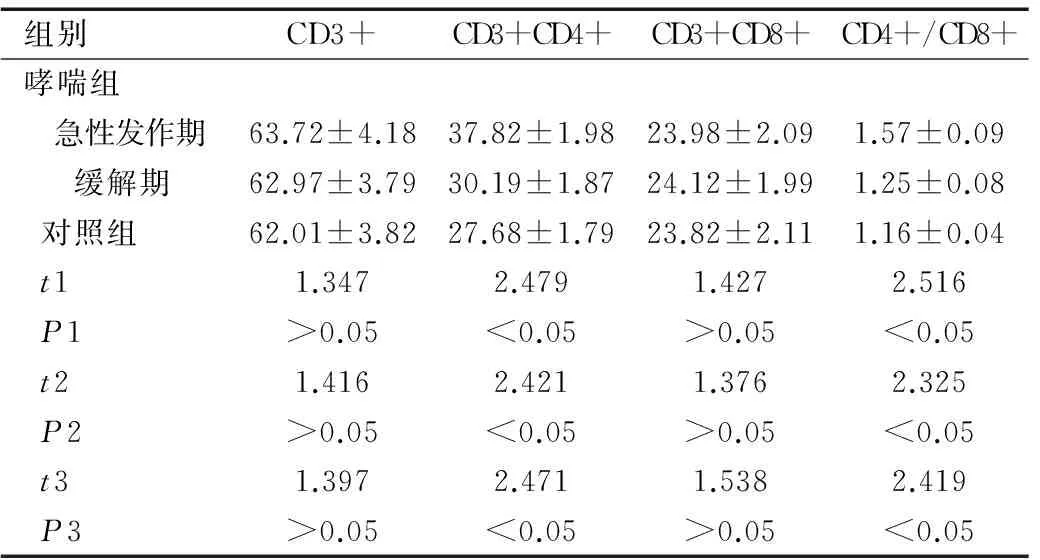
組別CD3+CD3+CD4+CD3+CD8+CD4+/CD8+哮喘組 急性發作期63.72±4.1837.82±1.9823.98±2.091.57±0.09 緩解期62.97±3.7930.19±1.8724.12±1.991.25±0.08對照組62.01±3.8227.68±1.7923.82±2.111.16±0.04t11.3472.4791.4272.516P1>0.05<0.05>0.05<0.05t21.4162.4211.3762.325P2>0.05<0.05>0.05<0.05t31.3972.4711.5382.419P3>0.05<0.05>0.05<0.05
注:t1和P1為哮喘組急性發作期與緩解期之間的比較;t2和P2為哮喘組急性發作期與對照組之間的比較;t3和P3為哮喘組緩解期與對照組之間的比較。
2.3兩組B淋巴細胞和IgE的檢測情況
哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD19+CD23+明顯高于哮喘組緩解期患兒和對照組兒童,經比較均有顯著性差異(均P<0.05);哮喘組急性發作期患兒IgE明顯高于哮喘組緩解期患兒和對照組兒童,經比較均有顯著性差異(均P<0.05),見表3。
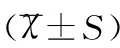
組別CD19+CD23+IgE(mIU/mL)哮喘組 急性發作期25.82±5.86256.79±79.82 緩解期13.78±2.99178.42±81.54對照組4.18±2.0965.41±21.32t12.3412.421P1<0.05<0.05t22.5242.379P2<0.05<0.05t32.3372.282P3<0.05<0.05
注:t1和P1為哮喘組急性發作期與緩解期之間的比較;t2和P2為哮喘組急性發作期與對照組之間的比較;t3和P3為哮喘組緩解期與對照組之間的比較。
3討論
支氣管哮喘被認為是遺傳、環境、免疫病理機制共同參與的多基因遺傳性疾病。支氣管哮喘的具體發病機制尚未明確,但免疫機制在哮喘發生發展中的作用成為近年來的研究熱點,以期為哮喘的診斷、治療、控制提供新的方向。有研究顯示體內細胞免疫失衡與哮喘發生、發展存在密切關系[7-11]。
3.1血清T淋巴細胞異常表達在小兒支氣管哮喘中的臨床意義
作為細胞免疫的主要功能執行者,T淋巴細胞受不同協同刺激信號影響,其中CD4/CD8比值平衡是維持機體免疫平衡的關鍵環節,機體在受到變應原刺激后,外周T細胞亞群含量會出現異常變化,速發性哮喘多見CD8+細胞水平下降,遲發性哮喘多見CD4+細胞水平增多[12-13]。本研究結果顯示,哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD3+CD4+和CD4+/CD8+均分別明顯高于哮喘組緩解期患兒和對照組兒童(均P<0.05),說明患兒血清T淋巴細胞水平與患者疾病狀態密切相關,可作為支氣管哮喘輕重程度及治療效果的評價指標。
3.2外周血B淋巴細胞異常表達在小兒支氣管哮喘中的臨床意義
體液免疫的主要執行者為B淋巴細胞。CD19和CD23分別是B淋巴細胞膜上的特征標志及IgE的低親和力受體,其中CD23可介導細胞間的粘附,促進嗜堿性粒細胞釋放組胺,調節IgE的合成和分泌,觸發IgE介導炎癥遞質的釋放和Ⅰ型變態反應的產生[14-16]。本研究中哮喘組急性發作期患兒的CD19+CD23+和IgE均明顯高于哮喘組緩解期患兒和對照組兒童(均P<0.05),說明患兒血清B淋巴細胞水平及與IgE水平患者疾病狀態密切相關,可作為支氣管哮喘輕重程度及治療效果的評價指標。
總之,支氣管哮喘患兒外周血T、B淋巴細胞明顯異常高表達,可作為支氣管哮喘病情程度及治療效果的評價指標。本研究的不足為樣本量較小,更重要的結果還有待多中心、大樣本的研究證實。
[1]Ishimori A, Harada N, Chiba A,etal.Circulating activated innate lymphoid cells and mucosal-associated invariant T cells are associated with airflow limitation in patients with asthma[J].Allergol Int,2017,66(2):302-309.
[2]Chu M, Chu I M, Yung E C,etal.Aberrant expression of novel cytokine IL-38 and regulatory T lymphocytes in childhood asthma[J].Molecules,2016,21(7):E933.
[3]Amin K.The role of the T lymphocytes and remodeling in asthma[J].Inflammation,2016,39(4):1475-1482.
[4]Raemdonck K, Baker K, Dale N,etal.CD4+ and CD8+ T cells play a central role in a HDM driven model of allergic asthma[J].Respir Res,2016,17:45.
[5]Zuska-Prot M, Ziókowski H, Jaroszewski J J,etal.Distribution of CD4+CD8+ double positive T cells in a mouse model of allergic asthma[J].Pol J Vet Sci,2016,19(1):217-219.
[6]中華醫學會呼吸病學分會哮喘學組.支氣管哮喘防治指南(2016年版)[J].中華結核和呼吸雜志,2016,39(9):675-697.
[7]Ling M F, Luster A D.Allergen-specific CD4(+) T cells in human asthma[J].Ann Am Thorac Soc,2016,Suppl 1:S25-S30.
[8]Troy N M, Hollams E M, Holt P G,etal.Differential gene network analysis for the identification of asthma-associated therapeutic targets in allergen-specific T-helper memory responses[J].BMC Med Genomics,2016,9:9.
[9]Yang S H, Yu C L, Yang Y H,etal.The immune-modulatory effects of a mixed herbal formula on dendritic cells and CD4+ T lymphocytes in the treatment of dust mite allergy asthma and perennial allergic rhinitis[J].J Asthma,2016,53(4):446-451.
[10]Schedel M, Jia Y, Michel S,etal. 1,25D3 prevents CD8(+)Tc2 skewing and asthma development through VDR binding changes to the Cyp11a1 promoter[J].Nat Commun,2016,7:10213.
[11]Wang W, Li P, Yang J.Decreased circulating interleukin-35 levels are related to interleukin-4-producing CD8+ T cells in patients with allergic asthma[J].Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol,2015,14(4):379-385.
[12]Li X M, Peng J, Gu W,etal.TCDD-iInduced activation of Aryl hdrocarbon receptor inhibits Th17 polarization and regulates non-eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthma[J].PLoS One,2016,11(3):e0150551.
[13]Tao B, Ruan G, Wang D,etal.Imbalance of peripheral Th17 and regulatory T cells in children with allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma[J].Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol,2015,14(3):273-279.
[14]Haenen S, Vanoirbeek J A, De Vooght V,etal.Proteomic alterations in B lymphocytes of sensitized mice in a model of chemical-induced asthma[J].PLoS One,2015,10(9):e0138791.
[15]Kamekura R, Shigehara K, Miyajima S,etal.Alteration of circulating type 2 follicular helper T cells and regulatory B cells underlies the comorbid association of allergic rhinitis with bronchial asthma[J].Clin Immunol,2015,158(2):204-211.
[16]Hong G U, Lim J Y, Kim N G,etal.IgE and IgA produced by OX40-OX40L or CD40-CD40L interaction in B cells-mast cells re-activate FcεRI or FcαRI on mast cells in mouse allergic asthma[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2015,754:199-210.
[專業責任編輯:侯 偉]
Clinical significance of abnormal expressions of T and B lymphocytes in children with bronchial asthma
WEN Bo, WANG Cheng-lin, LUO Li, FENG Yang
(Ya’an People’s Hospital, Sichuan Ya’an 625000, China)
Objective To investigate the clinical significance of abnormal expressions of T and B lymphocytes in children with bronchial asthma. Methods Altogether 198 children with bronchial asthma treated in Ya’an People’s Hospital from January to October in 2016 were selected as study objects (asthma group), and healthy children receiving physical examination at the same time were randomly selected as control group according to 1:1 matching. In asthma group there were 107 cases in acute stage and 91 cases in remission stage, and 198 children were in the control group. T lymphocyte (CD3, CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+ and CD4+/CD8+) and B lymphocyte (CD19+CD23+) in peripheral blood of children in acute stage and in remission stage and of children in the control group were tested, and relative indexes were compared. Results Levels of CD3+CD4+ and CD19+CD23+ of cases in acute stage were significantly higher than those in remission stage (tvalue was 2.479 and 2.341, respectively, bothP<0.05) and those in the control group (tvalue was 2.421 and 2.524, respectively, bothP<0.05). Level of CD4+/CD8+ of cases in acute stage was significantly higher than that of cases in remission stage and in the control group, and the differences had statistic significance (tvalue was 2.516 and 2.325, respectively, bothP<0.05). Conclusion Expressions of T and B lymphocytes in peripheral blood of children with bronchial asthma are obviously high-expressed, which can be used as an index to evaluate the severity and therapeutic effect of bronchial asthma.
bronchial asthma; B lymphocytes; T lymphocytes; children; therapeutic effect
2016-11-08
文 勃(1980-),男,主治醫師,主要從事兒科臨床工作。
王成林,主任醫師。
10.3969/j.issn.1673-5293.2017.06.014
R562.2
A
1673-5293(2017)06-0659-03

