乳腺導管內癌的X線表現與分子分型的對照研究
黃社磊+馬捷+蔣華景
[摘要] 目的 探討乳腺導管內癌的X線表現與分子分型的關系。 方法 回顧性分析133例136側DCIS的X線表現及組織病理學、免疫組織化學結果。 結果 (1)136側乳腺導管內癌X線表現為單純鈣化(32.4%)、鈣化伴局灶性不對稱/腫塊(29.4%),鈣化出現率61.8%。鈣化形態以細小多形性(58.3%)、段樣分布多見(54.8%);形態分布組合以細小多形性鈣化成簇分布多見。腫塊的形態多為不規則形(62.5%)、邊緣模糊(43.8%)、高密度(75%)。(2)DCIS以Luminal A型多見,Her-2過表達型次之。(3)ER/PR(+)、Her-2(-)X線表現單純鈣化多見35.6%、34.6%,形態為細小多形性68.6%、71.7%、成簇分布52.9%、52.2%;ER/PR(-)、Her-2過表達多表現為鈣化伴局灶性不對稱/腫塊38.8%、36.2%,鈣化形態前者為細小多形性57.6%、段樣分布69.7%,后者為線樣分支狀52.6%、段樣分布65.8%。(4)Ki-67增殖指數≤10%時,83.3%ER(+)、80.6%Her-2(-),鈣化形態多為細小多形性(88.2%);當Ki-67增殖指數>31%時,56.4%ER(+)、48.7%Her-2(-),鈣化形態為線樣分支狀48.3%。 結論 DCIS分子分型以Luminal A型多見。X線以鈣化為主要表現,形態多為細小多形性、線樣分支狀;分布以段樣及成簇多見。鈣化的分布、形態及形態分布組合與ER、PR、Her-2及Ki-67增殖指數有關。
[關鍵詞] 數字化乳腺X線攝影;癌;導管;激素受體;人表皮生長因子受體;分子分型
[中圖分類號] R737.9 [文獻標識碼] A [文章編號] 2095-0616(2017)13-13-04
[Abstract] Objective To explore the relationship the X-ray appearance and molecule subtype of the Breast DCIS (Ductal Carcinoma In Situ,DCIS),in order to know more about them. Methods The main X-ray appearance,histopathology and immunhistochemistry of the 133 cases DCIS (all 136 latero-breast) were retrospectively analyzed. Results (1)The main X-ray appearance of the 136 laterals DCIS were calcification 32.4%,calcification with focal dissymmetry/mass 29.4%,the frequency of calcification of all cases was 61.8%.The main morphous and distribution of calcifications was fine pleomorphic calcifications 58.3% and segmental 54.8% respectively,the main combination of morphous and distribution of calcifications was clustering fine pleomorphic calcifications.The appearance of the mass were irregular 62.5%,ambigutiy boundary 43.8%,high density 75%.(2)The molecule subtype of the Luminal A was the most frequent found in the different grade DCIS.(3)The main X-ray appearance of the ER/PR(+) and Her-2(-) DCIS were purely calcifications (35.6% vs 34.6%),the appearance of calcifications of them were fine pleomorphic calcifications (68.6% vs 71.7%),cluster(52.9% vs 52.2%).However,the main X-ray appearance of the ER/PR(-) and Her-2(+) DCIS were calcification with focal dissymmetry/mass (38.8% vs 36.2%),the appearance of calcifications the ER/PR(-)DCIS were fine pleomorphic (57.6%),segment (69.7%).While the Her-2(+) DCIS were linear branching (52.6%),segment (65.8%).(4)The proliferation index of the Ki-67≤10%,the proportion of ER(+) and Her-2(-) DCIS were 83.3% vs 80.6%,and the morphous of calcification was fine pleomorphic calcifications (88.2%).While the proliferation index of the Ki-67>31%,the proportion of ER (+) and Her-2(-) DCIS were 56.4% vs 48.7%,and the morphous of calcification was linear branching (48.3%). Conclusion The Luminal A is the most frequent found in the molecule subtypes of the DCIS.The main X-ray appearance of the DCIS is calcifications,the main morphous of the calcifications are fine pleomorphic and linear branching,the main distrutions of them are segment and clustered.The morphous,distrutions,combination of the morphous and distrutions of the calcifications are relevanted with ER, PR, Her-2 and the proliferation index of the Ki-67.
[Key words] Digital mammographic screening;Carcinoma;Duct;Hormone receptors;Her-2;Molecular typing
乳腺導管內癌(ductal carcinoma in situ,DCIS)是局限于導管內基底膜內而不侵犯間質的一類乳腺導管上皮細胞惡性增生,約占全部乳腺癌的20%,影像學(X線等)的發展和廣泛應用顯著提高了DCIS的檢出率[1]可根據雌激素受體(ER)、孕激素受體(PR)、人類上皮生長因子(HER-2)的表達水平以及細胞增殖指數(Ki-67)將乳腺癌劃分為4類分子亞型:包括Luminal A型、Luminal B型、HER-2陽性和三陰性乳腺癌,分子分型與乳腺癌治療和預后具有密切關系[2]。本研究分析DCIS的X線各種表現,重點觀察在鈣化方面的X線形態及分布表現,探討其與分子分型之間的聯系。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料
回顧性分析133例我院于2010年1月~2016年12月期間收治的DCIS女性患者的臨床資料。納入標準:(1)經手術病理組織檢查確診為DCIS;(2)患者臨床資料及X線、術后病理資料完整。排除標準:(1)接受放化療治療;(2)合并浸潤性導管癌;(3)合并其他類型腫瘤。本研究經我院醫學倫理委員會審核通過,所有患者均知情同意。
1.2 儀器與方法
采用飛利浦數字化乳腺X線機(Digital Mammography,DM),由兩位具有10年以上X線圖像診斷經驗的醫師進行雙盲法閱片,X線表現根據美國放射學會的乳腺影像報告和數據系統2003年第四版(BI-RADS分類)[2]標準分為:(1)主要征象:①腫塊:形態、邊緣及密度;②鈣化:形態、分布;③鈣化伴腫塊;④結構扭曲;⑤特殊征象;⑵相關征象包括:局部血運增加、病變結構扭曲、乳頭及皮膚回縮、相鄰皮膚增厚、腋窩淋巴結腫大等。記錄患者主要征象和相關征象。
1.3 病理學診斷
根據病理組織切片中細胞核的異型性、核分裂、管腔內壞死程度將DCIS劃分為低、中、高病變級別。應用4種標記免疫組化雌激素受體(ER)、孕激素受體(PR)、人類上皮生長因子(HER-2)及細胞增殖指數(Ki-67)將乳腺癌劃分為4類分子亞型:包括Luminal A型、Luminal B型、HER-2陽性和三陰性乳腺癌。
1.4 統計學處理
采用SPSS19.0軟件進行統計學處理和分析,計數資料采用百分比表示,采用χ2檢驗,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 一般情況
133例患者,年齡24~79歲。體格檢查結果:腫塊67側,乳頭溢液10側,其中血性溢液7側,檢查前觸診陰性59側。前哨淋巴結有轉移4側、腋窩淋巴結轉移7側。
2.2 病理結果
三種組織級別分子分型結果差異有統計學意義(χ2=17.731,P=0.007),低級別病變組織Luminal A型比例顯著高于中高級別,三陰性型均為高級別病變。見表1。
2.3 X線表現
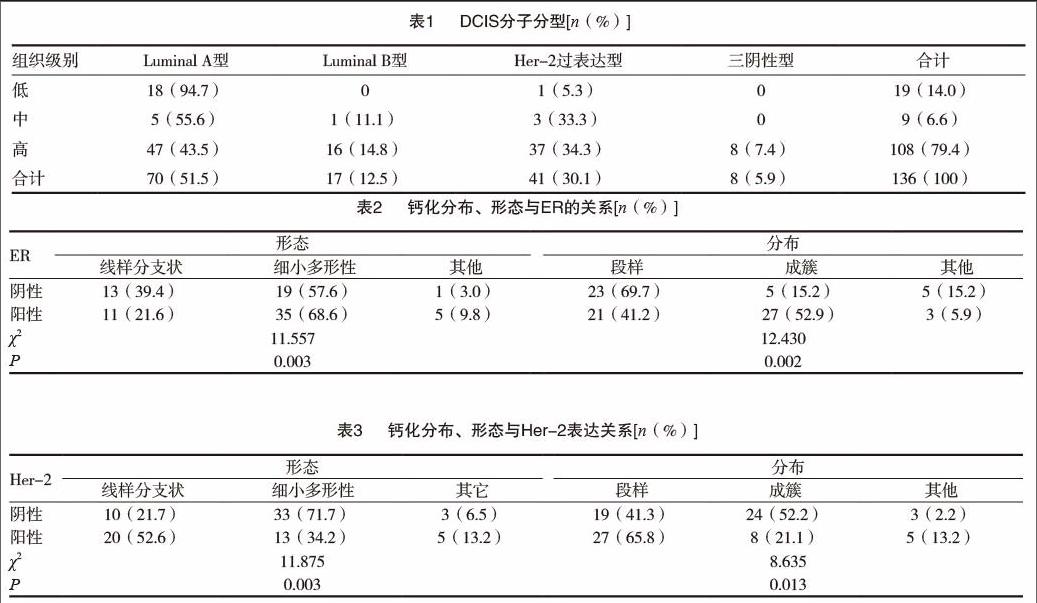
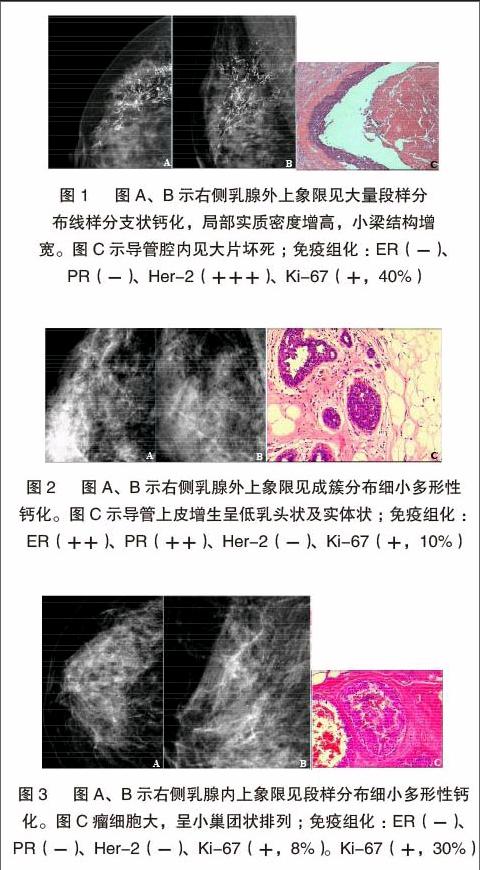
(1)鈣化伴局灶性不對稱/腫塊40例(29.4%)、單純鈣化44例(32.4%)。鈣化形態:細小多形性49例(58.3%)、線樣分支狀30例(35.7%);段樣分布46例(54.8%)、成簇分布30例(35.7%);形態分布組合多以細小多形性鈣化成簇分布,有23例(27.7%),以段樣分布的細小多形性鈣化22例(26.5%)。形態:不規則形20例(62.5%),橢圓形7例(21.9%),腫塊邊緣模糊14例(43.8%)、毛刺狀表現8例(25%);密度:高密度24例(75%)、等密度7例(21.9%)。(2)單純鈣化多見于三陰性、Luminal A型及Luminal B型乳腺癌,鈣化伴局灶性不對稱/腫塊為主要表現見于Her-2陽性乳腺癌,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。(3)單純鈣化多見于ER/PR陽性者(36%),此類患者鈣化形態以細小多形性鈣化成簇多見(占42.3%),其次為單純腫塊(25.3%);鈣化伴局灶性不對稱/腫塊多見于ER/PR陰性者(占38%),其次表現為單純鈣化(26%);鈣化形態分布多以線樣分支狀鈣化段樣分布為主(45.2%),此類差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。因此,得出結論:鈣化的分布及形態與Her-2及ER/PR的表達有關,見下表2 ~ 3及圖1 ~ 3。(4)當細胞增殖指數(Ki-67)≤10%時,83.8%ER表現為陽性、81.1%Her-2表現為陰性;當細胞增殖指數(Ki-67)>30%時,56.4%ER表現為陽性、48.7%Her-2表現為陰性,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。
3 討論
目前對DCIS的病程演變的認識還不是很透徹。相關文獻報道,低級別DCIS的女性中有14%~60%的患者可進展為浸潤性乳腺癌。由于DCIS患者在治療過程中多采取了相關干預措施,因此尚不清楚高級別DCIS女性進展為浸潤性乳腺癌的風險度[3]。研究表明,鈣化是DCIS患者最主要的X線表現,細小多形性鈣化、線樣或線樣分支狀鈣化是其主要征象[4]。極少數(約5%)的患者是在因其他原因進行乳腺手術切除標本中偶然發現。DCIS的組織學分型能夠用來預測經保守治療乳腺癌患者復發風險,并用來評估保乳手術的臨床療效,Wang[5]等研究認為X線、分子分型與腫瘤標記物等聯合應用能提高對DCIS患者預后的評估,并給予個體化治療方案。本研究表明,DCIS患者鈣化灶的形成與腫瘤細胞的分泌、變性及壞死后的鈣鹽沉積具有一定相關性,鈣化形態與病理分型及其預后亦存在有相關性。研究數據提示線樣鈣化通常預示發生高級別的浸潤性癌的風險較高,患者預后也較差[6-8]。Muttarak[9] 等認為,段樣分布的線樣或線樣分支狀鈣化常見于高級別 DCIS中;單發或多發成簇分布的細小多形性鈣化常見于中級別DCIS中;成簇分布的細點狀鈣化常見于低級別DCIS中。本研究也表明,鈣化的形態、分布及形態分布組合與ER/PR、Her-2表達有關,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。ER/PR(+)鈣化形態為細小多形性(69.2%)、成簇分布(51.9%);ER/PR(-)為細小多形性(59.4%)、段樣分布(75%)。Her-2(-)患者中,鈣化為細小多形性(67.3%),成簇分布(80%),Her-2(+)為線樣分支狀66.7%、段樣分布多見(58.7%)。ER/PR(弱+)及Her-2(強+)與段樣分布線樣分支狀鈣化的出現有關;若ER/PR(-),Her-2(強+)與線樣分支狀鈣化有關。
Tanei[10]等研究認為ER/PR與Ki-67的表達負相關,表明腫瘤內分泌的治療效果不理想,細胞增殖指數Ki-67較大時與較差的臨床治療結果相關。本研究中,Ki-67增殖指數與ER/PR、Her-2表達差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),但與鈣化形態、分布有關,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。當Ki-67增殖率≤10%時,83.3%ER(+)、80.6%Her-2(-),細小多形性鈣化形態(占88.2%);當Ki-67增殖率為>30%時,56.4%ER(+)、48.7%Her-2(-),線樣分支狀鈣化形態(占48.3%)。提示細小多形性鈣化、ER(+)與低細胞增殖指數Ki-67相關。
大多數學者將ER(-)/Her-2(強+)與ER(-)/Her-2(-)DCIS對比研究發現,前者更易出現微小鈣化,同時在ER(-)DCIS中,腫塊的邊緣、出現的鈣化及腫瘤分期和Her-2表達的情況密切相關[11-16]。本研究顯示ER(-)/Her-2強+)與ER(-)/Her-2(-)DCIS的出現鈣化率分別為63.4%(26/41)、75%(6/8),與相關文獻報道不一致,究其原因,筆者認為可能與ER(-)/Her-2(-)病例過少有一定關系。
總之,DCIS大多以細小多形性鈣化為主,不同病理分子分型的DCIS患者,其X線表現也不一樣。本研究表明,DCIS鈣化的分布及形態可以反映PR、ER、、Her-2及Ki-67的表達情況;X線表現以單純細小多形性鈣化為主并呈成簇分布時,預示著ER/PR(+)、Her-2(-)及細胞增殖指數Ki-67較低可能。而鈣化為線樣分支狀并段樣分布的出現,提示ER/PR(-)、Her-2(強+)及細胞增殖指數Ki-67較高可能。通過對DCIS鈣化分布及形態的全面、仔細地分析,對推斷其病理分型、為臨床提供治療方案信息及評估患者預后具有較高應用價值。
[參考文獻]
[1] Virnig BA,Tuttle TM,Shamliyan T,et al.Ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast:a systematic review of incidence,treatment,and outcomes[J].J Natl Cancer Inst,2010,102(3):170-178.
[2] Radiology ACO.Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS)[M].American College of Radiology,2003.
[3] Vaidya Y,Vaidya P,Vaidya T.Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast[J].Indian Journal of Surgery,2015,77(2):1-6.
[4] Evans A,Clements K,Maxwell A,et al.Lesion size is a major determinant of the mammographic features of ductal carcinoma in situ: findings from the Sloane project[J].Breast Cancer Research,2008,65(3):181-184.
[5] Wang X,Chao L,Chen L,et al.Correlation of mammographic calcifications with Her-2/neu overexpression in primary breast carcinomas[J].Journal of Digital Imaging,2008,21(2):170-176.
[6] Stomper PC,Geradts J,Edge SB,et al.Mammographic predictors of the presence and size of invasive carcinomas associated with malignant microcalcification lesions without a mass[J].Ajr American Journal of Roentgenology,2003,181(6):1679-1684.
[7] Tabár L,Chen HH,Duffy SW,et al.A novel method for prediction of long-term outcome of women with T1a,T1b,and 10-14 mm invasive breast cancers:a prospective study[J].Lancet,2000,355(9202):429-433.
[8] Berg WA,Arnoldus CL,Teferra E,et al.Biopsy of amorphous breast calcifications:pathologic outcome and yield at stereotactic biopsy[J].Radiology,2001,221(2):495-503.
[9] Muttarak M,Kongmebhol P,Sukhamwang N.Breast calcifications:which are malignant?[J].Singapore Medical Journal,2009,50(9):907.
[10] Tanei T,Shimomura A,Shimazu K,et al.Prognostic significance of Ki67 index after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer[J].European Journal of Surgical Oncology the Journal of the European Society of Surgical Oncology & the British Association of Surgical Oncology,2011,37(2):155.
[11] Shin HJ,Kim HH,Huh MO,et al.Correlation between mammographic and sonographic findings and prognostic factors in patients with node-negative invasive breast cancer[J].British Journal of Radiology,2011,84(997):19.
[12] Ayadi L,Khabir A,Amouri H,et al.Correlation of HER-2 over-expression with clinico-pathological parameters in Tunisian breast carcinoma[J].World Journal of Surgical Oncology,2008,6(1):1-8.
[13] Ko ES,Lee BH,Kim HA,et al.Triple-negative breast cancer:correlation between imaging and pathological findings[J].European Radiology,2010,20(5):1111-1117.
[14] Almasri NM,Hamad MA.Immunohistochemical evaluation of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 and estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast carcinoma in Jordan[J].Breast Cancer Research,2005,7(5):R598.
[15] Huang HJ,Neven P,Drijkoningen M,et al.Hormone receptors do not predict the HER2/neu status in all age groups of women with an operable breast cancer[J].Annals of Oncology,2005,16(11):1755-1761.
[16] Seo BK,Pisano ED,Kuzimak CM,et al.Correlation of HER-2/neu overexpression with mammography and age distribution in primary breast carcinomas[J].Academic Radiology,2006,13(10):1211-1218.
(收稿日期:2017-05-02)

