氣態(tài)活性氮排放的環(huán)境影響研究進展
趙晨旭 徐 鵬 廖雅君 欒勝基,2#
(1.北京大學深圳研究生院環(huán)境與能源學院,城市人居環(huán)境科學與技術深圳市重點實驗室,廣東 深圳 518055; 2.深港產學研基地環(huán)境模擬與污染控制重點實驗室,廣東 深圳 518057)
氣態(tài)活性氮排放的環(huán)境影響研究進展
趙晨旭1徐 鵬1廖雅君1欒勝基1,2#
(1.北京大學深圳研究生院環(huán)境與能源學院,城市人居環(huán)境科學與技術深圳市重點實驗室,廣東 深圳 518055; 2.深港產學研基地環(huán)境模擬與污染控制重點實驗室,廣東 深圳 518057)
大氣中過量的氣態(tài)活性氮積累導致大氣環(huán)境污染,對氣候變化、人體和生態(tài)系統(tǒng)健康都產生了不利影響。綜述了氣態(tài)活性氮排放清單估算方法的研究現狀。從氣候變化和大氣環(huán)境質量兩個方面討論了N2O、NH3和NOx等氣態(tài)活性氮的環(huán)境效應,并對未來氣態(tài)活性氮的研究方向進行了展望。
氣態(tài)活性氮 排放清單 氣候變化 大氣環(huán)境質量 減控
氮循環(huán)是自然界中重要的物質循環(huán)之一,而氮循環(huán)中的氮元素主要以不活潑的N2存在。在自然界中,不活潑的N2轉化成可被生物利用的活性氮(Nr),主要通過閃電固氮和生物固氮完成;20世紀初,人類成功實現了人工合成氨(NH3)。自此以后,人類為了滿足不斷增長的糧食需求和能源需求,開始極大地改變自然氮循環(huán)過程,向大氣環(huán)境排放的Nr越來越多。據估算,1860年全球人類活動排放的Nr僅為15 Tg,1990年增長到了156 Tg[1]。
大氣環(huán)境中的Nr主要以氣態(tài)形式存在,雖然能提高農田生態(tài)系統(tǒng)的生產力,但同時也會帶來一系列不良的環(huán)境影響。大氣中的氣態(tài)Nr參與各種大氣化學反應,促進氣溶膠、PM2.5等的形成。氣態(tài)Nr主要包括N2O、NH3和NOx。N2O在大氣中滯留時間長且具有溫室氣體,NO2和NH3又是PM2.5的重要前驅物,對霧霾的形成有重要影響[2]。NOx在霧霾及光化學煙霧的形成中起重要作用。因此,本研究綜述了氣態(tài)Nr的排放清單估算方法研究現狀,從氣候變化和大氣環(huán)境質量兩個方面分析了氣態(tài)Nr的環(huán)境影響。
1 氣態(tài)Nr排放清單估算方法研究現狀
氣態(tài)Nr排放與經濟發(fā)展、產業(yè)結構、環(huán)境和氣候特征等都密切相關,國內外學者在綜合考慮相關影響因素的基礎上,構建了一系列不同尺度的氣態(tài)Nr排放清單估算方法,主要有直接測量法和模型計算法兩種。常用的農業(yè)源氣態(tài)Nr排放直接測量法有靜態(tài)箱法[3]、風洞法[4]、反向擴散反演法[5]等;工業(yè)源氣態(tài)Nr排放清直接測量法有臺架實驗法[6]、道路車載測試法[7]、道路遙感測試法[8]、隧道實驗法[9]等,主要針對移動排放源。這些直接測量法在時間和空間上受到限制,影響其應用,國內外學者提出諸多計算模型。計算模型有兩類,一類是經驗模型又稱“黑箱模型”,不涉及復雜的污染物遷移轉化和函數方程,如NARSES模型[10]、RAINS模型[11]、MOBILE系列模型[12]等;一類是過程機制模型,能夠對氣態(tài)Nr產生的機制、遷移轉化以及較為復雜的時空傳輸過程進行具體的模擬和本土化修正,適用范圍更廣,如DYNAMO動態(tài)NH3模型[13]、DNDC反硝化分解模型[14]、生物地球化學循環(huán)CENTURY/DAYCENT模型[15]等。近年來,一些學者將衛(wèi)星遙感反演法和高精度空氣質量模型法也應用于氣態(tài)Nr排放清單的估算。
21世紀以來,學者們也越來越重視中國氣態(tài)Nr排放清單的研究,應用相關估算方法對中國的各類人為源氣態(tài)Nr排放清單進行了研究(見表1)。目前,氣態(tài)Nr排放清單估算方法研究中,源解析不清晰、排放源低估和忽視等是中國氣態(tài)Nr定量估算的主要不確定性來源。通過氣態(tài)Nr排放清單的估算發(fā)現,氣態(tài)Nr污染正在成為比CO2排放更為嚴重的大氣環(huán)境問題。王躍思等[36]對京津冀地區(qū)大氣污染成分進行了研究,發(fā)現北京NH3濃度居高不下。
2 氣態(tài)Nr對氣候變化的影響
氣候變化受地面、大氣、海洋中的一系列物理、化學和生物過程影響,人類對于全球氣候變化的影響主要是溫室氣體(GHGs)的排放。氣態(tài)Nr對氣候變化的直接和間接影響如圖1所示。NOx和NH3能促進氣溶膠的生成,間接導致降溫作用。NOx還能通過與CH4、O3反應對氣候變化產生間接降溫作用。但是N2O在大氣中的停留時間長達114年,而且單分子N2O增溫潛勢是CO2的298倍,所以盡管其在大氣中含量很低,但增溫作用不可忽視。1998年以來,全球大氣中的N2O正在以每年0.26%(質量分數)的速度增長;截至2005年,N2O增加導致的全球輻射強度的增加量就有(0.16±0.02) W/m2[37]。大氣氮沉降和氮肥施用會增加土壤Nr的富集,土壤Nr可以使土壤固碳能力增強,從而抑制土壤CO2的釋放,但CH4釋放量會增加[38]。此外,NOx還會促進近地面O3生成,導致植物的碳吸收能力減弱,相當于間接增加了大氣中的CO2。
目前,N2O對氣候變化的影響研究較多,相對也研究的比較透徹,主要是通過不同排放源N2O排放清單的建立實現對其溫室效應的定量評估。TIAN等[39]對中國陸地生態(tài)系統(tǒng)N2O排放通量及其全球增溫效應進行評估發(fā)現,中國東南地區(qū)對N2O排放貢獻最大。TIAN等[26]對中國農田氮肥施用導致的N2O排放與氣候變化關系的研究表明,氮肥施用導致的N2O排放增加可以使土壤固碳能力增強,減少釋放CO2,兩者對氣候變化影響的效應可以相互抵消。但近幾年,氮肥施用量增加導致土壤N2O排放迅速增加,不能與土壤固碳能力增強導致的降溫作用相抵消。工業(yè)生產過程和化石燃料燃燒對N2O的排放貢獻分別約為9.8%、9.1%,其增溫效應不容忽視[40]。中國工業(yè)生產過程排放的N2O未來10年的減排潛力約為1.54 Tg,可見中國工業(yè)生產過程的N2O減排潛力巨大[41]。
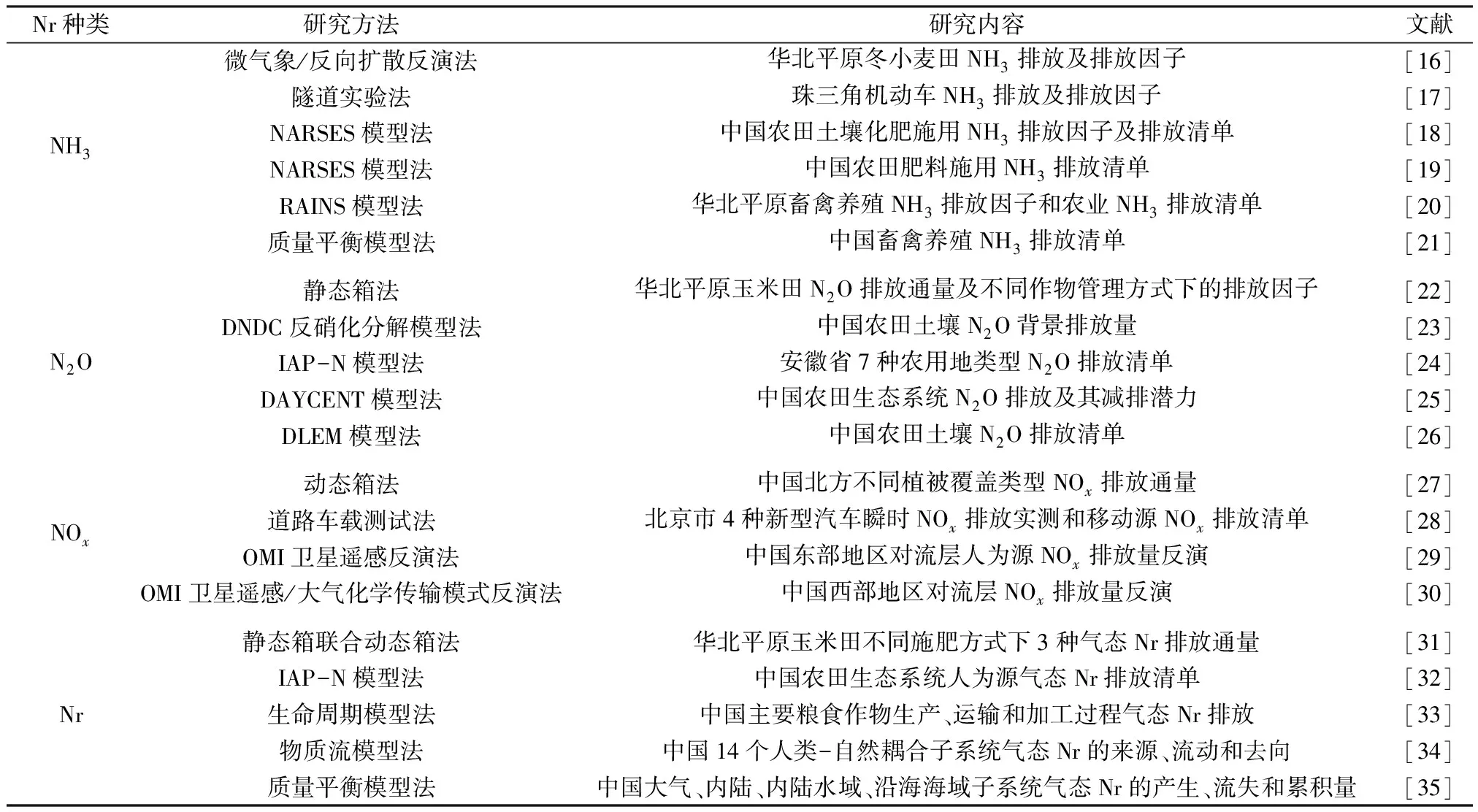
表1 21世紀以來中國各類氣態(tài)Nr排放清單主要研究工作
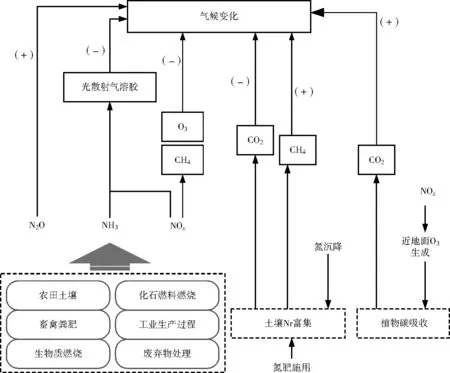
注:(+)、(-)分別表示升溫作用和降溫作用。圖1 氣態(tài)Nr對氣候變化的直接和間接影響Fig.1 The direct and indirect effects of gaseous Nr on climate change
3 氣態(tài)Nr對大氣環(huán)境質量的影響
NH3是大氣中重要的堿性氣體,對大氣酸沉降起了至關重要的影響作用[42]。NOx是大氣PM2.5的重要前驅物[43]。PM2.5是城市大氣二次污染物的標志性污染物[44],對霧霾的形成有重要影響[45]。此外,NOx參與大氣化學過程可形成硝酸和硝酸鹽顆粒物,形成酸雨[46]。NOx還會與平流層O3反應,引起平流層O3枯竭。NOx與揮發(fā)性有機物(VOCs)反應可引起光化學煙霧[47]。
近年來,中國學者對不同區(qū)域的NH3和NOx排放造成的大氣污染進行了不少研究。WANG等[48]建議,將城市移動源的NH3排放納入大氣PM2.5污染的減控對象。WEI等[49]發(fā)現,NH3對PM2.5的形成有很大的促進作用。WANG等[50]研究表明,區(qū)域大氣污染控制要對氣態(tài)Nr和相關前驅物同時進行減控。
4 展 望
(1) 加強氣態(tài)Nr污染源的識別和污染特征分析。一方面,需要加強對氮污染嚴重地區(qū)的氣態(tài)Nr監(jiān)測,識別主要排放源;另一方面,要分析這些排放源的排放特征及其造成的環(huán)境污染特征。
(2) 結合區(qū)域大氣污染問題對氣態(tài)Nr的大氣環(huán)境效應進行深入研究。開展對復雜氮循環(huán)的生物地球化學過程機制研究,重點要結合中國的實際情況有針對性地從氣態(tài)Nr排放的角度來緩解中國區(qū)域大氣環(huán)境污染。
(3) 推進氣態(tài)Nr減控措施的研究和實施。在農村,可從技術層面對農業(yè)氣態(tài)Nr進行減控,如合理施肥、動物飼料合理配比等;也可從政策層面對農業(yè)氣態(tài)Nr進行減控,如實施種養(yǎng)結合制度、畜牧業(yè)結構優(yōu)化等。在城市,可從工業(yè)源、交通源等源頭排放進行減控。
[1] GALLOWAY J N,TOWNSEND A R,ERISMAN J W,et al.Transformation of the nitrogen cycle:recent trends,questions,and potential solutions[J].Science,2008,320(5878):889-892.
[2] ANDERSON N,STRADER R,DAVIDSON C.Airborne reduced nitrogen:ammonia emissions from agriculture and other sources[J].Environment International,2003,29(2/3):277-286.
[3] OERTEL C,HERKLOTZ K,MATSCHULLAT J,et al.Nitric oxide emissions from soils:a case study with temperate soils from Saxony,Germany[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2012,66(8):2343-2351.
[4] MEISINGER J J,LEFCOURT A M,THOMPSON R B.Construction and validation of small mobile wind tunnels for studying ammonia volatilization[J].Applied Engineering in Agriculture,2001,17(3):375-381.
[5] SMITH E,GORDON R,BOURQUE C,et al.Comparison of three simple field methods for ammonia volatilization from manure[J].Canadian Journal of Soil Science,2007,87(4):469-477.
[6] GILL L J,BLAKEMAN P G,TWIGG M V,et al.The use of NOxadsorber catalysts on diesel engines[J].Topics in Catalysis,2004,28(1):157-164.
[7] DURBIN T D,JOHNSON K,COCKER D R I,et al.Evaluation and comparison of portable emissions measurement systems and federal reference methods for emissions from a back-up generator and a diesel truck operated on a chassis dynamometer[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2007,41(17):6199-6204.
[8] BEEVERS S D,WESTMORELAND E,DE JONG M C,et al.Trends in NOxand NO2emissions from road traffic in Great Britain[J].Atmospheric Environment,2012,54(5):107-116.
[9] CHENG Yan,LEE S C,HO K F,et al.On-road particulate matter (PM2.5) and gaseous emissions in the Shing Mun Tunnel,Hong Kong[J].Atmospheric Environment,2006,40(23):4235-4245.
[10] WEBB J,RYAN M,ANTHONY S G,et al.Cost-effective means of reducing ammonia emissions from UK agriculture using the NARSES model[J].Atmospheric Environment,2006,40(37):7222-7233.
[11] KLIMONT Z,BRINK C.Modelling of emissions of air pollutants and greenhouse gases from agricultural sources in Europe[R].Laxenburg:International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis,2004.
[12] CLAGGETT M,HOUK J.Comparing MOBILE6.2 and Emfac2007 emission factors[J].Journal of the Transportation Research Board,2008,20(8):51-57.
[13] REIDY B,MENZI H.Assessment of the ammonia abatement potential of different geographical regions and altitudinal zones based on a large-scale farm and manure management survey[J].Biosystems Engineering,2007,97(4):520-531.
[14] LUDWIG B,JAEGER N,PRIESACK E,et al.Application of the DNDC model to predict N2O emissions from sandy arable soils with differing fertilization in a long-term experiment[J].Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science,2011,174(3):350-358.
[15] DEL GROSSO S J,MOSIER A R,PARTON W J,et al.DAYCENT model analysis of past and contemporary soil N2O and net greenhouse gas flux for major crops in the USA[J].Soil & Tillage Research,2005,83(1):9-24.
[16] HUO Qing,CAI Xuhui,KANG Ling,et al.Estimating ammonia emissions from a winter wheat cropland in North China Plain with field experiments and inverse dispersion modeling[J].Atmospheric Environment,2015,104:1-10.
[17] LIU Tengyu,WANG Xinming,WANG Boguang,et al.Emission factor of ammonia (NH3) from on-road vehicles in China:tunnel tests in urban Guangzhou[J].Environmental Research Letters,2014,9(6):1-8.
[18] ZHANG Yisheng,LUAN Shengji,CHEN Liaoliao,et al.Estimating the volatilization of ammonia from synthetic nitrogenous fertilizers used in China[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2011,92(3):480-493.
[19] XU Peng,ZHANG Yisheng,GONG Weiwei,et al.An inventory of the emission of ammonia from agricultural fertilizer application in China for 2010 and its high-resolution spatial distribution[J].Atmospheric Environment,2015,115:141-148.
[20] ZHANG Y,DORE A J,MA L,et al.Agricultural ammonia emissions inventory and spatial distribution in the North China Plain[J].Environmental Pollution,2010,158(7):490-501.
[21] GAO Zhiling,MA Wenqi,ZHU Gaodi,et al.Estimating farm-gate ammonia emissions from major animal production systems in China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2013,79(7):20-28.
[22] ZHANG Yuanyuan,LIU Junfeng,MU Yujing,et al.Nitrous oxide emissions from a maize field during two consecutive growing seasons in the North China Plain[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2012,24(1):160-168.
[23] GU Jiangxin,ZHENG Xunhua,ZHANG Wen.Background nitrous oxide emissions from croplands in China in the year 2000[J].Plant and Soil,2009,320(1):307-320.
[24] 韓云芳,韓圣慧,嚴平.基于區(qū)域氮循環(huán)模型IAP-N的安徽省農用地N2O排放量估算[J].環(huán)境科學,2015,36(7):2395-2404.
[25] CHENG Kun,OGLE S M,PARTON W J,et al.Simulating greenhouse gas mitigation potentials for Chinese Croplands using the DAYCENT ecosystem model[J].Global Change Biology,2014,20(3):948-962.
[26] TIAN Hanqin,LU Chaoqun,MELILLO J,et al.Food benefit and climate warming potential of nitrogen fertilizer uses in China[J].Environmental Research Letters,2012,7(4):235-247.
[27] WANG Bing,LEE X Q,THENG B K G,et al.Diurnal and spatial variations of soil NOxfluxes in the northern steppe of China[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2015,32(6):54-61.
[28] ZHANG Shaojun,WU Ye,HU Jingnan,et al.Can Euro Ⅴ heavy-duty diesel engines,diesel hybrid and alternative fuel technologies mitigate NOxemissions?New evidence from on-road tests of buses in China[J].Applied Energy,2014,132(1):118-126.
[29] LIN Jintai.Satellite constraint for emissions of nitrogen oxides from anthropogenic,lightning and soil sources over East China on a high-resolution grid[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2011,11(6):2881-2898.
[30] CUI Y Z,LIN J T,SONG C,et al.Rapid growth in nitrogen dioxide pollution over Western China,2005-2013[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2015,15(23):6207-6221.
[31] ZHANG Yuanyuan,LIU Junfeng,MU Yujing,et al.Emissions of nitrous oxide,nitrogen oxides and ammonia from a maize field in the North China Plain[J].Atmospheric Environment,2011,45(17):2956-2961.
[32] ZHENG Xunhua,LIU Chunyan,HAN Shenghui.Description and application of a model for simulating regional nitrogen cycling and calculating nitrogen flux[J].Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2008,25(2):181-201.
[33] XIA Longlong,TI Chaopu,LI Bolun,et al.Greenhouse gas emissions and reactive nitrogen releases during the life-cycles of staple food production in China and their mitigation potential[J].Science of the Total Environment,2016,556:116-125.
[34] GU Baojing,JU Xiaotang,CHANG Jie,et al.Integrated reactive nitrogen budgets and future trends in China[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2015,112(28):8792-8797.
[35] CUI Shenghui,SHI Yalan,GROFFMAN P M,et al.Centennial-scale analysis of the creation and fate of reactive nitrogen in China (1910-2010)[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2013,110(6):2052-2057.
[36] 王躍思,姚利,劉子銳,等.京津冀大氣霾污染及控制策略思考[J].中國科學院院刊,2013,28(3):353-363.
[37] DAVIN E L,DE NOBLET DUCOUDRE N,FRIEDLINGSTEIN P.Impact of land cover change on surface climate:relevance of the radiative forcing concept[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2007,34(13):L13702.
[38] PINDER R W,DAVIDSON E A,GOODALE C L,et al.Climate change impacts of US reactive nitrogen[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2012,109(20):7671-7675.
[39] TIAN Hanqin,XU Xiaofeng,LU Chaoqun,et al.Net exchanges of CO2,CH4,and N2O between China’s terrestrial ecosystems and the atmosphere and their contributions to global climate warming[J].Journal of Geophysical Research (Biogeosciences),2011,116(2):G02011.
[40] CHEN Guoqian,ZHANG Bo.Greenhouse gas emissions in China 2007:inventory and input-output analysis[J].Energy Policy,2010,38(10):6180-6193.
[41] LI Li,XU Jianhua,HU Jianxin,et al.Reducing nitrous oxide emissions to mitigate climate change and protect the ozone layer[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48(9):5290-5297.
[42] LI Qianfeng,WANG Lilingjuan,SHAH S B,et al.Ammonia concentrations and modeling of inorganic particulate matter in the vicinity of an egg production facility in Southeastern USA[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2014,21(6):4675-4685.
[43] MEGARITIS A G,FOUNTOUKIS C,CHARALAMPIDIS P E,et al.Response of fine particulate matter concentrations to changes of emissions and temperature in Europe[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2013,13(6):3423-3443.
[44] 唐孝炎.大氣環(huán)境化學[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2006.
[45] YE Xingnan,MA Zhen,ZHANG Jiachen,et al.Important role of ammonia on haze formation in Shanghai[J].Environmental Research Letters,2011,6(2):38-46.
[46] CAO Junji,TIE Xuexi,DABBERDT W F,et al.On the potential high acid deposition in northeastern China[J].Journal of Geophysical Research (Atmospheres),2013,118(10):4834-4846.
[47] LEI H,WANG J X L.Sensitivities of NOxtransformation and the effects on surface ozone and nitrate[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2014,14(3):1385-1396.
[48] WANG Wenxin,WANG Shanshan,XU Jianhua,et al.Gas-phase ammonia and PM2.5ammonium in a busy traffic area of Nanjing,China[J].Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(2):1691-1702.
[49] WEI Lianfang,DUAN Jingchun,TAN Jihua,et al.Gas-to-particle conversion of atmospheric ammonia and sampling artifacts of ammonium in spring of Beijing[J].Science China Earth Sciences,2015,58(3):345-355.
[50] WANG Y,ZHANG Q Q,HE K,et al.Sulfate-nitrate-ammonium aerosols over China:response to 2000-2015 emission changes of sulfur dioxide,nitrogen oxides,and ammonia[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2013,13(5):2635-2652.
Researchprogressonenvironmentimpactofgaseousreactivenitrogenemission
ZHAOChenxu1,XUPeng1,LIAOYajun1,LUANShengji1,2.
(1.KeyLaboratoryforUrbanHabitatEnvironmentalScienceandTechnology,SchoolofEnvironmentandEnergy,PekingUniversityShenzhenGraduateSchool,ShenzhenGuangdong518055;2.KeyLaboratoryofEnvironmentalSimulationandPollutionControl,PKU-HKUSTShenzhen-HongKongInstitution,ShenzhenGuangdong518057)
Gaseous reactive nitrogen (Nr) accumulation is leading environmental pollution,resulting in bad effects on climate change,human health and ecosystem health. In this study,the research progress of gaseous Nr emission inventory estimation methods was summarized. The environmental effects of 3 kinds of Nr (N2O,NH3and NOx) were discussed from the aspcts of climate change and atmospheric environmental quality. Finally,future research directions were proposed.
gaseous reactive nitrogen; emission inventory; climate change; atmospheric environmental quality; reduce and control
2016-07-30)
趙晨旭,女,1993年生,碩士研究生,研究方向為環(huán)境規(guī)劃與管理、大氣污染與防治。#
。
10.15985/j.cnki.1001-3865.2017.05.021

