PAI-1對氣道平滑肌增殖和ERK表達的影響
王亮,朱述陽,于晨希,劉文靜,朱潔晨
(徐州醫科大學附屬醫院 呼吸內科,江蘇 徐州 221006)
PAI-1對氣道平滑肌增殖和ERK表達的影響
王亮,朱述陽,于晨希,劉文靜,朱潔晨
(徐州醫科大學附屬醫院 呼吸內科,江蘇 徐州 221006)
目的 探討纖溶酶原激活物抑制物-1(PAI-1)對氣道平滑肌增殖的調控作用,以及對細胞外調節蛋白激酶(ERK)表達的影響。方法 體外培養小鼠氣道平滑肌細胞(ASMCs)并分為7組:空白對照組、PAI-1 5 μg/L 組、PAI-1 10 μg/L 組、PAI-1 20 μg/L 組、PAI-1 40 μg/L 組、PAI-1 80 μg/L 組、PAI-1 100 μg/L組。放入37℃培養箱分別培養12、24和48 h,采用CCK-8檢測ASMCs的A值,計算增殖率。以增殖率最高的實驗組的濃度和作用時間作為PAI-1作用最適濃度和最適作用時間,進一步分6組:A組(空白對照);B組(PAI-1 20 μg/L);C 組(PAI-1 40 μg/L);D 組(PAI-1 80 μg/L);E 組(PAI-1 100 μg/L);F 組(PAI-1 最適濃度+ERK通道抑制劑PD98059 10 μmol/L),用CCK-8檢測ASMCs的增殖,Western blot檢測ERK蛋白的表達,實時熒光定量聚合酶鏈反應檢測ERK mRNA的表達。結果 5~100 μg/L PAI-1作用ASMCs 12、24和48 h后細胞增殖率結果顯示,在相同濃度下,不同時間各組比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),以48 h時ASMCs增殖率最高;在相同時間下,不同濃度各組比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),80 μg/L PAI-1的ASMCs增殖率最高;故選取48 h為最適作用時間,80 μg/L為最適濃度進行后續實驗。再次分組的實驗結果表明,B、C、D、E組的ERK磷酸化水平和ERK mRNA的相對表達量與A組比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),B、C、D、E組增高;B、C、D、E組兩兩比較結果顯示,除B組與E組比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)外,其余各組兩兩比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),當PAI-1濃度波動于20~80 μg/L時,ERK磷酸化水平和ERK mRNA相對表達量隨濃度升高而增高,>80 μg/L后則不再增高;加入PD98059的F組與D組比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),ERK磷酸化水平和ERK mRNA表達降低。結論 外源性PAI-1可以通過促進ERK通路的表達,進而促進ASMCs的增殖。
纖溶酶原激活物抑制物-1;細胞外調節蛋白激酶;氣道平滑肌細胞;哮喘
哮喘是一種以慢性氣道炎癥為特征的異質性疾病[1]。哮喘的反復發作可引起氣道重塑,導致不可逆氣流受限及持續性非特異性支氣管高反應性,因此氣道重塑被認為是除氣道慢性炎癥之外,哮喘的另一個主要特征。哮喘的氣道重塑主要表現為氣道平滑肌細胞(airway smooth muscle cell,ASMCs)量的增加、上皮細胞增生、杯狀細胞化生、網狀基底膜增厚、血管生成等[2]。其中,ASMCs量的增加是氣道重塑最重要的影響因素,而參與該環節的機制中包含ASMCs增殖、肥大及遷移[3]。纖溶酶原激活物抑制物-1(plasminogen activator inhibitor-1,PAI-1)是絲氨酸蛋白酶抑制劑家族成員之一,是尿激酶型纖溶酶原激活物和組織型纖溶酶原激活物主要的生理抑制劑。在細胞周期中,PAl-1轉錄水平的變化及其在細胞內的積聚對細胞形態的維持、細胞與其間質的黏附、細胞增殖、信號轉導及基因表達等都有重要意義[4]。已有臨床研究和體外實驗發現,PAI-1在哮喘發病及氣道重塑中發揮重要作用[5-8]。本研究旨在觀察PAI-1小鼠ASMCs中細胞外調節蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)通路的干預作用,從細胞分子水平研究PAI-1對體外培養的小鼠ASMCs增殖的影響。
1 材料與方法
1.1 實驗材料
清潔級雌性BALB/c小鼠11只、體重20~24 g(徐州醫學院實驗動物中心提供),PAI-1(大連美侖生物技術有限公司),α-平滑肌肌動蛋白(α-smooth muscle actin,α-SMA)(武漢博士德生物工程有限公司),活細胞計數法(cell counting kit-8,CCK-8)試劑盒(上海碧云天生物技術研究所),兔抗甘油醛-3-磷酸脫氫酶(glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase,GAPDH)(杭州賢至生物有限公司),兔抗ERK(武漢三鷹生物技術有限公司),兔抗p-ERK(美國CST公司),ERK激酶抑制劑PD98059(美國Sigma-Aldrich公司),辣根過氧化物酶標記的山羊抗兔二抗(武漢博士德生物工程有限公司),Trizol裂解液(北京艾德萊生物科技有限公司),dNTP Mixture(北京天根生化科技有限公司),2×All-in-oneTMqPCR Mix(美國Vazvme公司),Ex Taq、DL2000 DNA Marke(日本 TaKaRa公司)。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 ASMCs的培養及鑒定 無菌分離小鼠氣道平滑肌組織,采用貼壁法培養原代ASMCs[9];用胰酶消化法進行傳代,并自然純化[9],實驗用第4和5代。培養的ASMCs采用免疫組織化學法檢測α-SMA的表達,并進行鑒別。
1.2.2 CCK-8法 取上述對數生長期細胞,用含15%胎牛血清改良伊格爾培養基(dulbecco's modified eagle medium,DMEM),將細胞密度調整到1×105個 /ml,接種于 96 孔板,100 μl/孔,在周邊加入100 μl無菌磷酸鹽緩沖溶液。培養24 h后,換不含血清的DMEM培養24 h,使細胞生長同步于G0期。根據不同處理方法將細胞分為7組:空白對照組、PAI-1 5μg/L組、PAI-1 10μg/L組、PAI-1 20μg/L組、PAI-1 40 μg/L 組、PAI-1 80 μg/L 組、PAI-1 100 μg/L組,每組重復7次,放入37℃培養箱分別培養12、24和48 h。按照每孔培養基總體積的10%加入CCK-8溶液,繼續孵育4 h,用酶標儀測定450 nm處的吸光度值,依據公式計算增殖率,增殖率=(A處理組/A陰性對照組-1)×100%。再根據以上7個實驗組的增殖率結果,以增殖率最高的實驗組的濃度和作用時間作為PAI-1作用最適濃度和最適作用時間,進一步分6組進行后續檢測,具體分組如下:A組(空白對照組);B組(PAI-1 20 μg/L);C 組(PAI-1 40 μg/L);D 組(PAI-1 80 μg/L);E 組(PAI-1 100 μg/L);F組(PAI-1 最適濃度+ERK通道抑制劑PD98059 10μmol/L)。
1.2.3 Western blot檢測 ASMCs按上述A、B、C 3組干預后,倒掉培養液,洗滌細胞3次,加入無線電免疫沉淀裂解液和苯甲基磺酰氟混合物,置于冰上裂解30 min,刮下細胞移至1.5 ml離心管中,4℃、12 000 r/min離心5 min,取上清液,聚氰基丙烯酸正丁酯法測定蛋白濃度。取40 μg樣品蛋白進行聚丙烯酰胺凝膠電泳,然后將蛋白轉移至聚偏氟乙烯膜上,用含5%脫脂奶粉的三羥甲基氨基甲烷緩沖鹽溶液(tris buffered saline and tween 20,TBST)(封閉液)浸泡聚偏氟乙烯膜,室溫搖床封閉2 h,加入GAPDH 一抗(1∶1 000)、ERK 一抗(1∶5 000)、p-ERK 一抗(1∶2 000),4℃孵育過夜,TBST 洗膜 5或6次,5 min/次,加入辣根過氧化物酶標記的羊抗兔二抗(1∶5 000),37℃搖床孵育 2 h,再次洗膜,滴加增強化學發光試劑顯影,曝光成像,用Band Scan分析膠片灰度值。
1.2.4 實時熒光定量聚合酶鏈反應(quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction,qRT-PCR) 收集各組細胞,采用Trizol法提取細胞總RNA,逆轉錄為cDNA,于-20℃冰箱冷藏保存。以β-actin作為內參基因,qRT-PCR檢測ERK mRNA的相對表達量。β-actin正向引物:5'-CCCATCTATGAGGGTTA CGC-3',反向引物:5'-TTTAATGTCACGCACGATTT C-3';ERK 正向引物:5'-GGCTTTCTGACCGAGTATG TG-3',反向引物:5'-TTTAGGTCCTCTTGGGATGG-3'。總反應體系20 μl,主要反應條件:95℃預變性10 min,95℃變性 30 s,60℃退火 30 s,共 40 個循環后進行溶解曲線檢測。每個反應管內的熒光信號達到設定的閾值時所經歷的循環數定義為Ct值;每對引物在每個模板中做3個重復管,得到的Ct值取平均值,每個目的基因的Ct平均值減去對應模板的內參基因的Ct平均值,得到△Ct。根據公式ΔCt=(Ct目的基因-Ct內參基因)和ΔΔCt=(ΔCt研究組-ΔCt對照組),最終數據以2-△△Ct進行分析。
1.3 統計學方法
數據分析采用SPSS 20.0和Graph Pad 5.1統計軟件,計量資料以均數±標準差(±s)表示,多組比較用單因素方差分析或重復測量設計的方差分析,進一步兩兩比較用LSD-t法,P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2 結果
2.1 ASMCs的鑒定
倒置光學顯微鏡下觀察,培養的小鼠ASMCs呈梭形,束狀排列,細胞間相互交錯呈峰谷狀(見圖1A)。免疫細胞化學檢測發現,α-SMA呈陽性,其胞質內可見紅色熒光,證實培養的細胞為ASMCs(見圖 1B)。

圖1 小鼠ASMCs
2.2 CCK-8法檢測結果
2.2.1 不同濃度PAI-1對ASMCs增殖的影響CCK-8法分別檢測12、24和48 h時各組ASMCs的A值,計算細胞增殖率。結果表明,80 μg/L PAI-1作用 48 h時,ASMCs增殖率為(46.64±0.830)%,為最高值。不同濃度PAI-1體外刺激ASMCs 12、24和48h后的增殖率比較,采用重復測量設計的方差分析,球形檢驗結果表明差異無統計學意義(P=0.210),認為多次測量結果間無相關性,故采用單變量方差分析。結果顯示:①不同時間ASMCs的增殖率比較,差異有統計學意義(F=3 826.486,P=0.000),作用 48 h時,ASMCs的增殖率最大;②不同濃度PAI-1刺激下ASMCs的增殖率比較,差異有統計學意義(F=1 825.566,P=0.000),PAI-1 80 μg/L 刺激下 ASMCs的增殖率最大;③不同濃度PAI-1刺激下ASMCs的增殖率變化趨勢比較,差異有統計學意義(F=289.290,P=0.000)。見附表和圖 2。
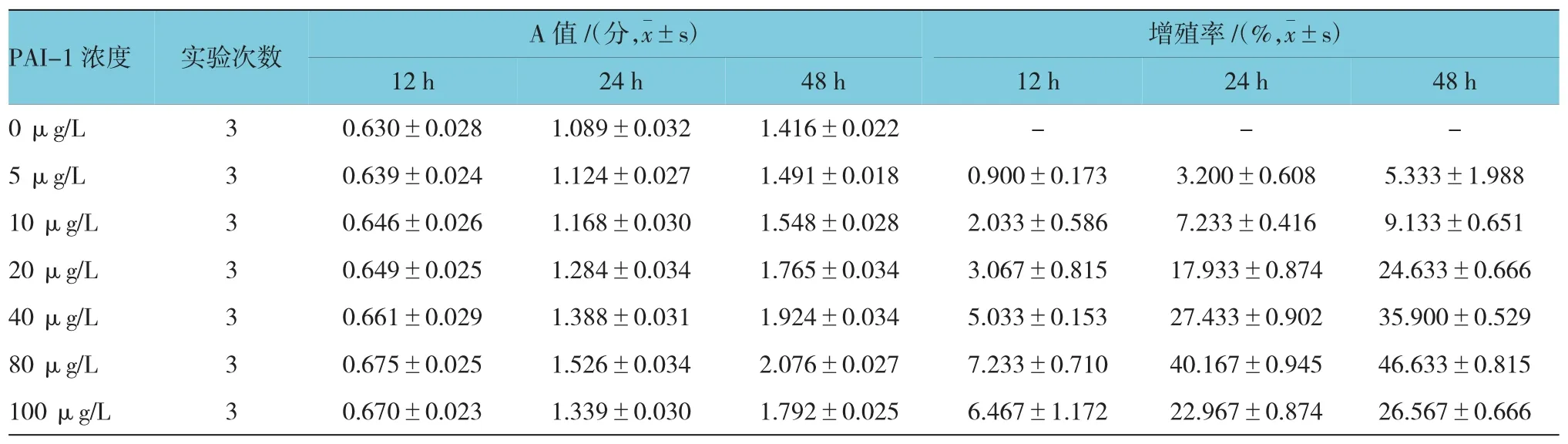
附表 不同濃度PAI-1體外刺激ASMCs各時間的A值和增殖率比較
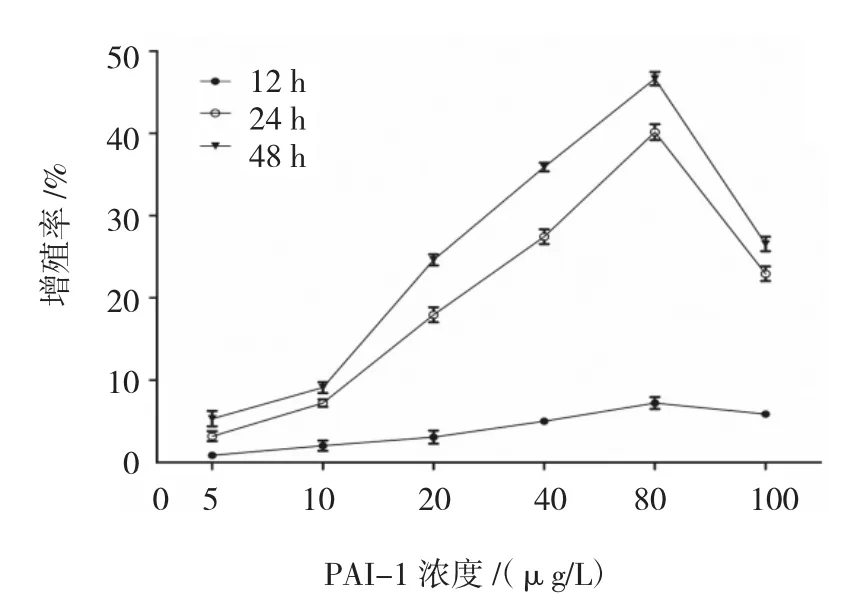
圖2 不同濃度PAI-1體外刺激ASMCs各時間的增殖率變化趨勢
2.2.2 同時加入PD98059和PAI-1對ASMCs生長的影響 各組A值比較,經單因素方差分析,差異有統計學意義(F=142.980,P=0.000)。進一步組間兩兩比較,經LSD-t檢驗,B、C、D、E 組與A組比較,差異有統計學意義(t=8.218、17.177、22.817 和 8.930,均 P=0.000),B、C、D、E 組高于 A 組,提示各濃度PAI-1均可引起ASMCs增殖;F組(PAI-1 80 μg/L+PD98059 80 μg/L)與A組比較,差異有統計學意義(t=3.874,P=0.002),F組高于 A 組,表明 ERK 抑制劑PD98059部分抑制PAI-1引起的ASMCs增殖;F組與D組比較,差異有統計學意義(t=18.943,P=0.000),F組低于D組,提示PAI-1所引起的ASMCs增殖,可能與ERK通道有關(見圖3)。
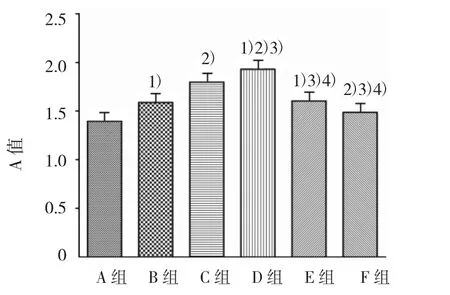
圖3 ASMCs作用48 h各組的A值比較
2.3 PAI-1對小鼠ASMCs的ERK蛋白表達影響
各組ERK蛋白、p-ERK蛋白表達及ERK磷酸化水平比較,經單因素方差分析,差異有統計學意義(F=72.294、87.809 和 27.946,均 P=0.000)。①各組ERK蛋白表達水平比較,經LSD-t檢驗,B、C、D、E組高于A組,D組高于B、C、E組,C組高于B、E組,D組高于F組(P<0.05);B組與E組比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);②各組p-ERK蛋白表達水平比較,經 LSD-t檢驗,B、C、D、E 組高于 A 組,D 組高于B、C、E組,C組高于B、E組,D 組高于 F組(P<0.05);B組與E組比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);③各組 ERK 磷酸化水平比較,經 LSD-t檢驗,B、C、D、E 組高于A組,提示各濃度PAI-1均可促進ERK1/2磷酸化;D 組高于B、C、E 組,C組高于 B、E 組(P<0.05),B組與E組比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05),表明當PAI-1濃度波動于20~80 μg/L時,ERK1/2磷酸化水平隨濃度升高而增高,>80 μg/L,ERK1/2磷酸化水平則不再增高;D組高于F組(t=8.612,P=0.000),顯示PAI-1引起ERK1/2磷酸化增高的現象可被PD98059抑制。見圖4。
2.4 PAI-1對小鼠ASMCs細胞ERK mRNA表達的影響
各組ERK mRNA水平比較,經單因素方差分析,差異有統計學意義(F=229.035,P=0.000)。進一步各組間兩兩比較,經LSD-t檢驗,B、C、D、E組高于A組,D組高于B、C、E組,C組高于 B、E組,D組高于F組(P<0.05);B組與E組比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。見圖 5。
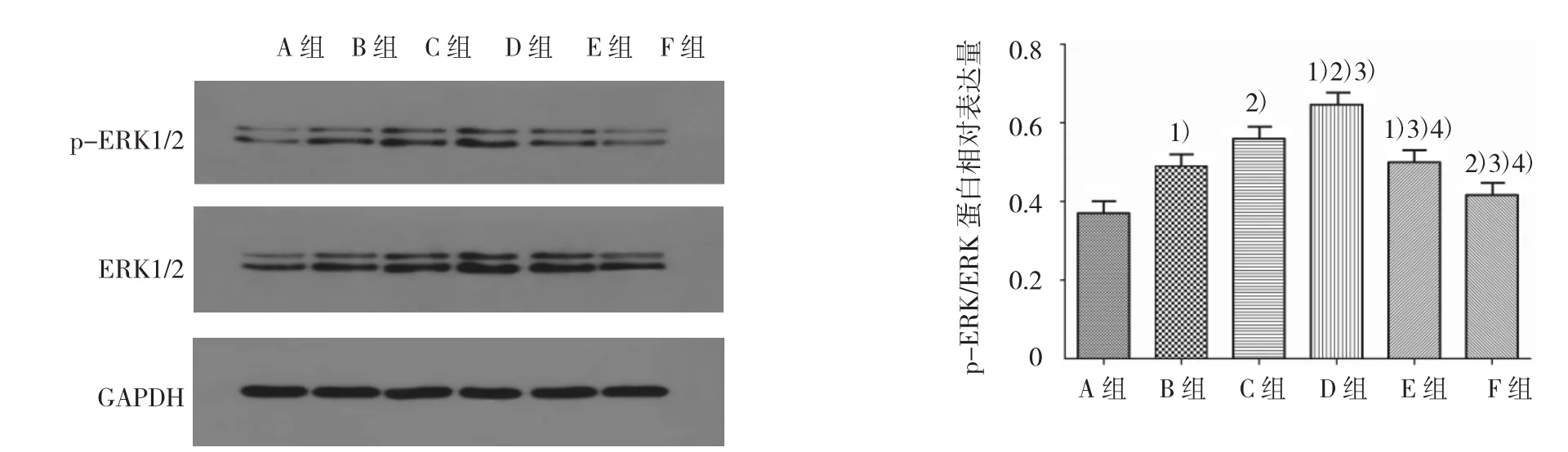
圖4 各組ASMCs的ERK蛋白表達水平
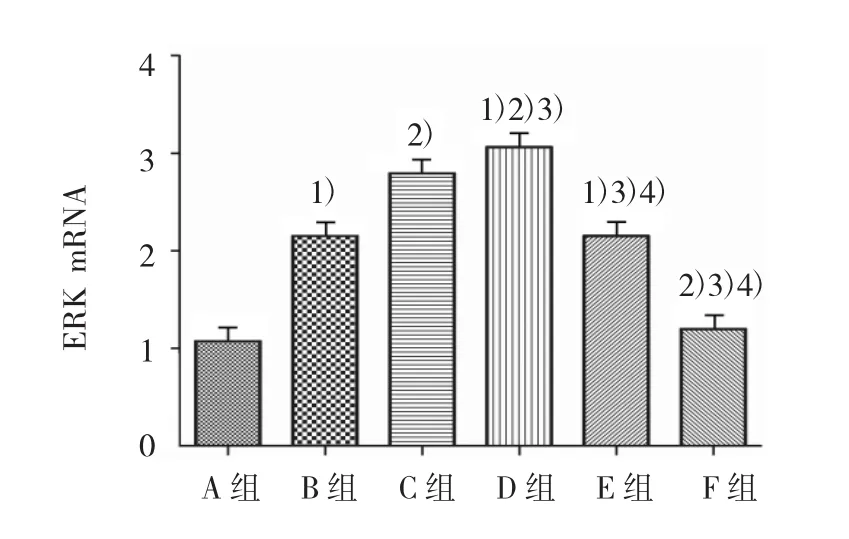
圖5 各組ASMCs的ERK mRNA表達水平比較
3 討論
氣道重塑是慢性哮喘反復發作和頑固性哮喘的重要病理基礎,其中ASMCs的增殖是其重要環節之一[10]。WOODRUFF等[11]指出,難治性哮喘患者與正常人相比,ASMCs的數量增加(50~80)%,這一現象主要由平滑肌的增殖而不是肥大引起。JAMES等[12]研究表明,在致死性哮喘(主要是重度哮喘)患者中,氣道平滑肌層厚度增加是由于大、中、小氣道的ASMCs增生;無論是致死性或是非致死性哮喘,ASMCs肥大均發生在大氣道。過度增殖的ASMCs引起氣道管腔狹窄,氣流通過受限,且ASMCs增殖會導致氣道高反應[13],使氣道對變應刺激源更加敏感,收縮更為強烈,導致更為嚴重的急性發作。同時增殖后的ASMCs由收縮型向增殖/合成型轉化[14],分泌大量細胞因子參與哮喘的炎癥反應,炎癥可進一步促進氣道重塑,導致惡性循環。由此可見ASMCs增殖處于哮喘氣道重塑的關鍵環節,抑制ASMCs增殖可能成為治療難治性哮喘的一個重要靶點。
PAI-1是纖溶系統中重要的調控物質之一,其主要作用是抑制u-PA和t-PA。在正常情況下,PAI-1在血漿中的含量是極低的(0~60 ng/ml),大部分以潛在活性形式存在于血小板中(200~300 ng/ml)[15-16]。在一些病理條件下,如感染、中風、心肌梗死、糖尿病、肥胖癥、敗血癥和癌癥等,PAI-1水平升高[17-18]。異常的PAI-1表達也在哮喘中存在。已有研究證實,PAI-1在致死性哮喘患者增多的肥大細胞內高度表達[5],且PAI-1的4G等位基因頻率增多與血漿中PAI-1的高表達相關,患有哮喘的父母易于將該等位基因遺傳給孩子[6-7]。哮喘患者升高的PAI-1血漿水平也與減少的用力肺活量相關[19]。體外實驗表明,PAI-1可通過促進氣道炎癥、氣道重塑及氣道高反應,在哮喘發病機制中扮演重要角色[3,8,20-23]。目前,關于 PAI-l對哮喘氣道重塑的研究主要集中兩方面,即PAI-1通過抑制纖溶和MMP-9的活化,促進纖維蛋白和細胞外基質沉積[8,23]、PAI-1通過影響VEGF的活化調節血管生成[8,22],但是PAI-1對ASMCs增殖的影響國內外還少有研究。本研究結果顯示,PAI-1能促進體外培養ASMCs增殖,并有一定的時間和濃度依賴性。PAI-1在各時間均能刺激ASMCs的增殖,隨時間延長,刺激增強;在各劑量中,從5μg/L增至80μg/L,增殖率逐漸升高,>80μg/L后,增殖率不再增加。
ERK是EAPKs家族中的一員,主要包括2種異構體ERK1和ERK2,ERK1/2可由生長因子通過Ras-Raf-MEK通路的磷酸化而被激活,與細胞增殖、轉化及分化相關的MAPK[24-25]。有研究表明,TGF-β1可通過激活ERK信號途徑促進ASMCs的增殖,羅紅霉素能夠抑制上述途徑[26-29]。XIE等[27]實驗表明,ERK1/2信號通路在哮喘大鼠ASMCs由收縮型向增殖/合成型轉化中發揮關鍵作用。YAO等[28]研究表明,白楊素能夠通過抑制ERK1/2信號途徑的激活,從而抑制人ASMCs的增殖。CHEN等[30]研究發現,PAI-1可能促進ERK的表達增加,從而導致血管平滑肌細胞的增殖。本研究結果顯示,PAI-1可以促進大鼠ASMCs的增殖,與ERK信號通路有關,該效應存在一定的濃度依賴性;PD98059可以抑制該效應,但不能恢復至對照水平,說明ERK通路可能不是PAI-1引起大鼠ASMCs增殖的唯一效應通路。
綜上所述,在體外實驗中,外源性PAI-1可以通過促進ERK通路的磷酸化,而促進ASMCs的增殖。而減少PAI-1的作用和抑制ERK通路的磷酸化可減少ASMCs的增殖,從而可能減緩哮喘氣道重塑的發生。
[1]BOUSQUET J,HUMBERT M.GINA 2015:the latest iteration of a magnificent journey[J].European Respiratory Journal,2015,46(3):579-582.
[2]AL-MUHSEN S,JOHNSON J R,HAMID Q.Remodeling in asthma[J].Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2011,128(3):451-462.
[3]JOHNSON P R A,BURGESS J K.Airway smooth muscle and fibroblasts in the pathogenesis of asthma[J].Current Allergy and Asthma Reports,2004,4(2):102-108.
[4]M?YNARSKA A,WASZYROWSKI T,KASPRZAK J D.Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(PAI-1):pathogenetic role in coronary disease[J].Kardiologia Polska,2007,65(9):1109.
[5]CHO S H,TAM S W,DEMISSIE-SANDERS S,et al.Production of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by human mast cells and its possible role in asthma[J].The Journal of Immunology,2000,165(6):3154-3161.
[6]CHO S H,HALL I P,WHEATLEY A,et al.Possible role of the 4G/5G polymorphism of the plasminogen activatorinhibitor1 gene in the development of asthma[J].Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2001,108(2):212-214.
[7]PAMPUCH A,KOWAL K,BODZENTA-LUKASZYK A,et al.The 675 4G/5G plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter polymorphism in house dust mite-sensitive allergic asthma patients[J].Allergy,2006,61(2):234-238.
[8]OH C K,ARIUE B,ALBAN R F,et al.PAI-1 promotes extracellular matrix deposition in the airways of a murine asthma model[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2002,294(5):1155-1160.
[9]卓致遠,黃茂,崔學范,等.組織貼塊法培養小鼠氣道平滑肌細胞[J].中國組織化學與細胞化學雜志,2007,16(2):247-250.
[10]HASSAN M,JO T,RISSE P A,et al.Airway smooth muscle remodeling is a dynamic process in severe long-standing asthma[J].Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology,2010,125(5):1037-1045.
[11]WOODRUFF P G,DOLGANOV G M,FERRANDO R E,et al.Hyperplasia of smooth muscle in mild to moderate asthma without changes in cell size or gene expression[J].American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,2004,169(9):1001-1006.
[12]JAMES A.Airway remodeling in asthma[J].Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine,2005,11(1):1-6.
[13]BROOK B S,PEEL S E,HALL I P,et al.A biomechanical model of agonist-initiated contraction in the asthmatic airway[J].Respiratory Physiology Neurobiology,2010,170(1):44-58.
[14]DAMERA G,DRUEY K M,COOPER P R,et al.An RGS4-mediated phenotypic switch of bronchial smooth muscle cells promotes fixed airway obstruction in asthma[J].PLoS One,2012,7(1),DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0028504.
[15]BROGREN H,KARLSSON L,ANDERSSON M,et al.Platelets synthesize large amounts of active plasminogen activator inhibitor 1[J].Blood,2004,104(13):3943-3948.
[16]CRAEN B V D,DECLERCK P J,GILS A.The biochemistry,physiology and pathological roles of PAI-1 and the requirements for PAI-1 inhibition in vivo[J].Thrombosis Research,2012,130(4):576-585.
[17]GRAMLING M W,CHURCH F C.Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is an aggregate response factor with pleiotropic effects on cell signaling in vascular disease and the tumor microenvironment[J].Thrombosis Research,2010,125(5):377-381.
[18]DECLERCK P J,GILS A.Three decades of research on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1:a multifaceted serpin[C].Seminars in Thrombosis and Hemostasis,2013,39(4):356-364.
[19]CHO S,KANG J,LYTTLE C,et al.Association of elevated plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 levels with diminished lung function in patients with asthma[J].Annals of Allergy Asthma Immunology,2011,106(5):371-377.
[20]SWAISGOOD C M,ARONICA M A,SWAIDANI S,et al.Plasminogen is an important regulator in the pathogenesis of a murine model of asthma[J].American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine,2007,176(4):333-342.
[21]TEZUKA T,OGAWA H,AZUMA M,et al.IMD-4690,a novel specific inhibitor for plasminogen activator inhibitor-1,reduces allergic airway remodeling in a mouse model of chronic asthma via regulating angiogenesis and remodeling-related mediators[J].PLoS One,2015,10(3):DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.e0121615.
[22]MIYAMOTO S,HATTORI N,SENOO T,et al.Intra-airway administration of small interfering RNA targeting plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 attenuates allergic asthma in mice[J].American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology,2011,301(6):L908-L916.
[23]LEE S H,EREN M,VAUGHAN D E,et al.A plasminogen activatorinhibitor-1 inhibitorreducesairwayremodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma[J].American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology,2012,46(6):842-846.
[24]ANDREEFF M.Targeted therapy of acute myeloid leukemia[M].New York:Springer,2015:275-305.
[25]黃文林,朱孝峰.信號轉導與疾病[M].第2版.北京:人民衛生出版社,2012:275-305.
[26]CHEN G,KHALIL N.TGF-β1increases proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells by phosphorylation of map kinases[J].Respiratory Research,2006,7(1):2.
[27]XIE M,LIU X S,XU Y J,et al.ERK1/2 signaling pathway modulates the airway smooth muscle cell phenotype in the rat model of chronic asthma[J].Respiration,2007,74(6):680-690.
[28]YAO J,ZHANG Y S,FENG G Z,et al.Chrysin inhibits human airway smooth muscle cells proliferation through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway[J].Molecular Medicine Reports,2015,12(5):7693-7698.
[29]DAI Y,LI F,WU L,et al.Roxithromycin treatment inhibits TGF-beta1-induced activation of ERK and AKT and downregulation of caveolin-1 in rat airway smooth muscle cells[J].Respir Res,2014,15:96.
[30]CHEN Y,BUDD R C,KELM R J,et al.Augmentation of proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1[J].Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology,2006,26(8):1777-1783.
Effect of PAI-1 on proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells and expression of extracellular regulated protein kinase
Liang Wang,Shu-yang Zhu,Chen-xi Yu,Wen-jing Liu,Jie-chen Zhu
(Department of Respiratory Medicine,the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University,Xuzhou,Jiangsu 221006,China)
Objective To investigate the regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1(PAI-1)on the proliferation of airway smooth muscle cells (ASMCs)and its effect on extracellular regulated protein kinase(ERK).Methods The ASMCs of mice culturedin vitrowere divided into 7 groups:control group,PAI-1 5 μg/L group,PAI-1 10 μg/L group,PAI-1 20 μg/L group,PAI-1 40 μg/L group,PAI-1 80 μg/L group and PAI-1 100 μg/L group.All groups were cultured respectively for 12,24 and 48 h in a 37℃ incubator.The absorbance values were tested by CCK-8,and the proliferation rates were calculated.The concentration and intervention time of the experimental group with the highest proliferation rate were taken as the optimal concentration and time of PAI-1 action.Then the subjects were further divided into 6 groups:group A(blank control),group B(PAI-1 20 μg/L),group C(PAI-1 40 μg/L),group D(PAI-1 80 μg/L),group E(PAI-1 100 μg/L)and group F (the optimal concentration of PAI-1+the inhibitor of ERK PD98059 10 μmol/L).The proliferation of ASMCs was detected by CCK-8.The expression of ERK protein was detected by Western blot.And the expression of ERK mRNA was detected by qRT-PCR.Results After 5-100 μg/L PAI-1 acted upon ASMCs for 12,24 and 48 h,the proliferation rates of each test group at different time points were statistically different (P<0.05),and the proliferation rates reached the maximal levels at the 48th h;at the same time point the proliferation rates of the test groups with different concentrations were statistically different(P<0.05),and the proliferation rates of ASMCs reached the peak at the concentration of 80 μg/L.Therefore,80 μg/L of PAI-1 was chosen to be the optimum concentration,and 48 hours was set to be the optimal intervention period for the subsequent experiments.In the subsequent experiments,the results showed that compared to the group A,ERK phosphorylation levels and the expressions of ERK mRNA in the groups B,C,D and E were significantly increased (P<0.05);in the pairwise comparison of the groups B,C,D and E,the ERK phosphorylation levels and the expressions of ERK mRNA in the ASMCs were statistically different only between the groups B and E (P < 0.05).When PAI-1 concentration varied from 20 to 80 μg/L,ERK phosphorylation leveland the expression ofERK mRNA increased with the concentration;when the concentration went up over 80 μg/L,the phosphorylation level of ERK no longer increased.Compared with the group D,the ERK phosphorylation level and the expression of ERK mRNA were decreased in the group F(added with PD98059)(P<0.05).Conclusions Exogenous PAI-1 may promote the proliferation of ASMCs through ERK pathway.
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1;extracellular regulated protein kinase;airway smooth muscle cells;asthma
R562.25
A
10.3969/j.issn.1005-8982.2017.26.004
1005-8982(2017)26-0018-07
2016-03-14
朱述陽,E-mail:jiechenz356@sohu.com
(童穎丹 編輯)

