生物膜化生物肥對馬尾松幼苗氣體交換和生物量累積的影響
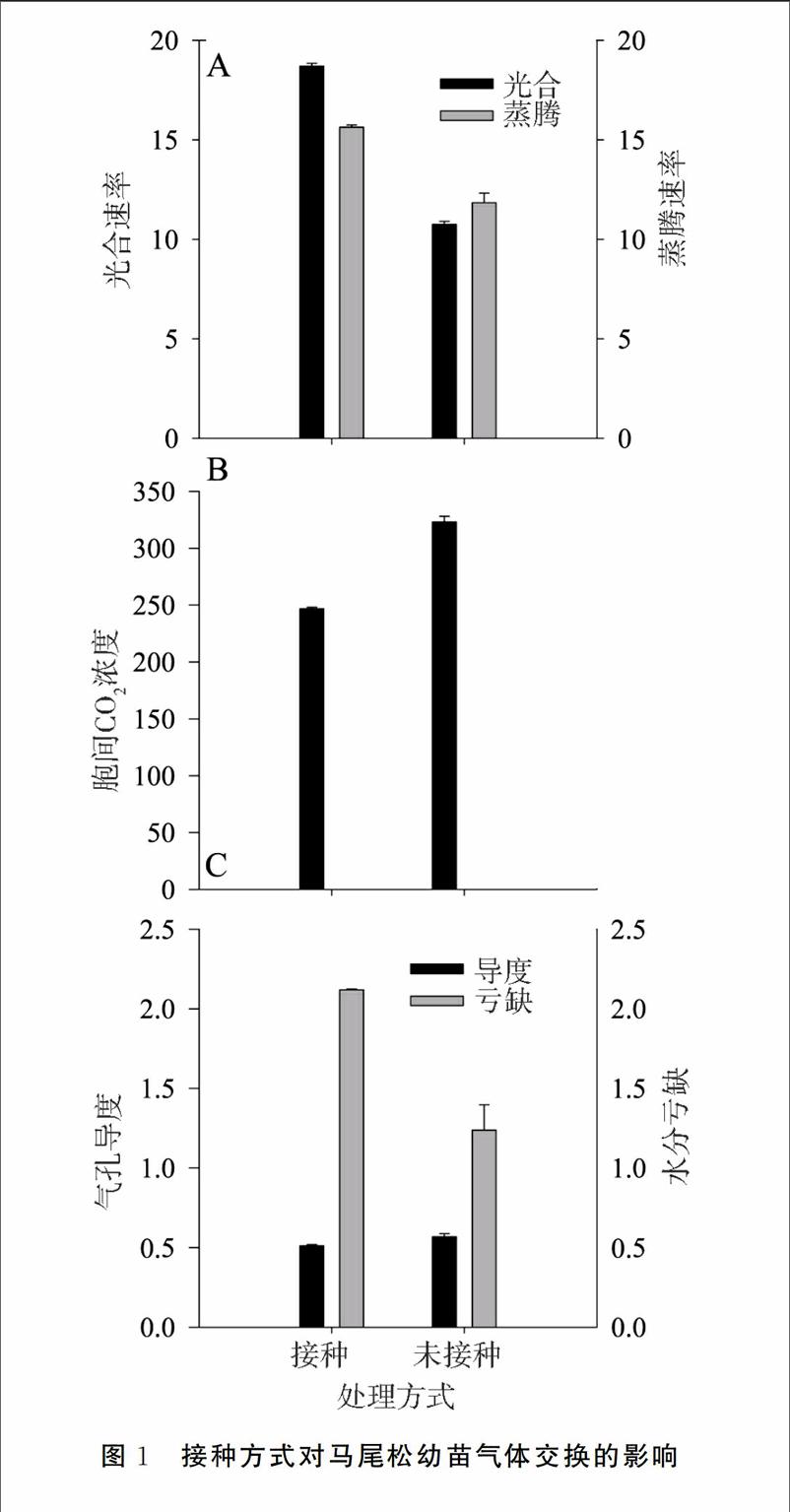


摘要:生物膜化生物肥是目前國際上流行的一種生物肥,因不同的植物所需的微生物種類不同,在其應用到實際生產之前需進行相應的實驗,為了更好地培育馬尾松幼苗,本研究利用一種自制的生物膜化生物肥,將其應用到馬尾松幼苗的培育上,以期檢驗其效果。實驗結果表明,生物膜化生物肥的使用可以顯著地增加馬尾松幼苗的凈光合速率,而顯著地降低其胞間二氧化碳濃度,但顯著降低光能和水分利用效率。生物膜化生物肥可以顯著地增大Y(II)、ETR和Fv/Fm,而對qP和qN沒有顯著的影響。光合速率的增大導致馬尾松幼苗的根、地上部分以及總生物量地顯著增加。這些結果表明,本生物膜化生物肥能夠應用到馬尾松幼苗的培育。
關鍵詞:生物膜化生物肥;馬尾松;氣體交換;生物量累積
中圖分類號:S723.1+3文獻標識碼:A文章編號:1004-3020(2017)05-006-04The Effects of Biofilmed Biofertilizer Infection on Gas Exchange
and Biomass Accumulation of Pinus massoniana SeedlingsXiang Qingsong
(Forestry Bureau of JianshiEnshi445300)
Abstract: Biofilmed biofertilizers (BFBF) are different from regular biofertilizers. Different plants symbiose with different microorganisms, therefore BFBF should be tested before they are used in agriculture and forestry. In the present study, a new BFBF was used in culture of Pinus massonicana seedlings. These results showed that the BFBF significantly increased net photosynthesis rate and decreased intercellular CO2 concentration, and at the same time significantly reduced the use efficiency of water and light. The BFBF significantly increased Y(II), ETR, and Fv/Fm, but showed no effect on qP and qN. Increase in net photosynthesis rate induced by the BFBF resulted in significant increase in root biomass, shoot biomass, and total biomass.
Key words:biofilmed biofertilizer;Pinus massoniana;gas exchange;biomass accumulation
在中國目前的經濟發展狀況下,農村大部分青壯年勞力紛紛進入城市工作,留守在農村的為老弱婦女。這些人無力在保證農作物生長良好、產量高的條件下,繼續保持農田肥力的持續維持。在農作過程中,他們大量使用化學肥料,而極少使用有機肥,從而使農田肥力持續下降,同時對農田周圍的河流湖泊造成面源污染。
面對嚴重的環境問題,環境友好型的農業耕作栽培技術得到了廣泛的推廣[1]。這些技術的推廣旨在維持農田土壤的持續性以及農業害蟲的管理。在這種大背景下,生物膜化生物肥的使用為人們大力提倡。……

