探討護理干預對腦出血術后患者運動功能的效果和影響
鄭雪梅
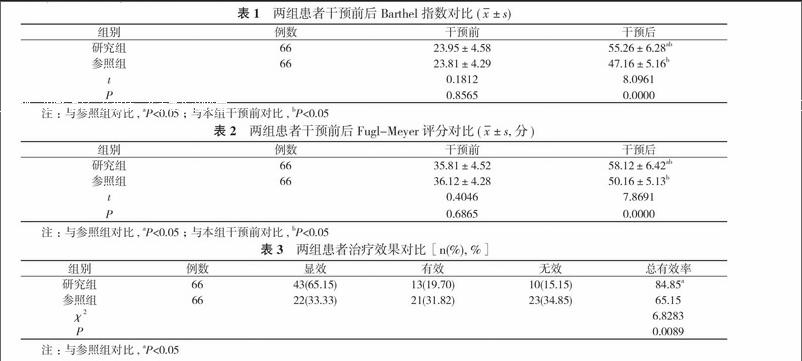
【摘要】 目的 探討護理干預對腦出血術后患者運動功能的效果和影響。方法 132例腦出血, 按照雙盲法分為研究組和參照組, 每組66例。參照組實施常規護理, 研究組實施運動康復護理干預。觀察比較兩組患者干預前后的Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分以及臨床治療效果。結果 干預前, 兩組患者Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分比較差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。干預后, 兩組患者Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分均高于干預前, 且研究組患者Barthel指數、Fugl-Meyer評分均顯著高于參照組, 差異具有統計學意義(P<0.05)。研究組患者的治療總有效率為84.85%, 參照組患者的治療總有效率為65.15%, 兩組患者的總有效率對比差異具有統計學意義(χ2=6.8283, P=0.0089<0.05)。結論 運動康復護理干預能夠有效改善腦出血術后患者的運動功能, 提高治療效果, 具有較高的臨床應用價值。
【關鍵詞】 護理干預;腦出血;運動功能;效果;影響
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2018.02.082
Discussion on effect and influence of nursing intervention on motor function of patients after intracerebral hemorrhage ZHENG Xue-mei. Department of Surgery, Enping Peoples Hospital, Enping 529400, China
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the effect and influence of nursing intervention on motor function of patients after intracerebral hemorrhage. Methods A total of 132 patients after intracerebral hemorrhage were divided by double-blind method into research group and control group, with 66 cases in each group. The control group received conventional nursing, and the research group received exercise rehabilitation nursing intervention. Observation and comparison were made on Barthel index, Fugl-Meyer score before and after intervention and clinical treatment effect between two groups. Results Before intervention, both groups had no statistically significant difference in Barthel index and Fugl-Meyer score (P>0.05). After intervention, both groups had higher Barthel index and Fugl-Meyer score than before treatment, and the research group had obviously higher Barthel index and Fugl-Meyer score than the control group. Their difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The research group had total treatment effective rate as 84.85%, while the control group had total treatment effective rate as 65.15%. Both groups had statistically significant difference in total effective rate (χ2=6.8283, P=0.0089<0.05). Conclusion Exercise rehabilitation nursing intervention can effectively improve the motor function of the patients after cerebral hemorrhage, and improve the treatment effect. It contains high clinical application value.
【Key words】 Nursing intervention; Intracerebral hemorrhage; Motor function; Effect; Influence
腦出血作為臨床中一種常見且多發性疾病, 多發生在老年人群中, 由于其發病率和病死率均較高[1], 不僅影響患者的生命健康, 也在一定程度上降低了患者的生活質量, 在這種情況下, 對腦出血術后患者運動功能的改善和治療就顯得尤為重要。本研究針對護理干預對腦出血術后患者運動功能的效果和影響進行分析和探討, 現報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1. 1 一般資料 隨機選取本院2015年1月~2017年6月收治的腦出血患者132例, 按照雙盲法分為研究組和參照組, 每組66例。研究組中男36例、女30例;年齡40~75歲, 平均年齡65.28歲;高血壓腦出血39例、腦血管瘤破裂出血1例、endprint
重型顱腦損傷腦出血26例。參照組中男35例、女31例, 年齡41~73歲, 平均年齡64.82歲;高血壓腦出血37例、腦血管瘤破裂出血2例、重型顱腦損傷腦出血27例。兩組患者一般資料比較, 差異無統計學意義(P>0.05), 可進行進一步實驗分析。
1. 2 方法 參照組實施常規護理, 即對患者實施抗感染治療、止血、營養神經治療, 保證患者日常作息、按時服藥和定期檢查。研究組……

