延續(xù)性護(hù)理干預(yù)聯(lián)合健康飲食對(duì)老年乳腺癌患者的應(yīng)用效果及價(jià)值評(píng)價(jià)
江麗君 李娜
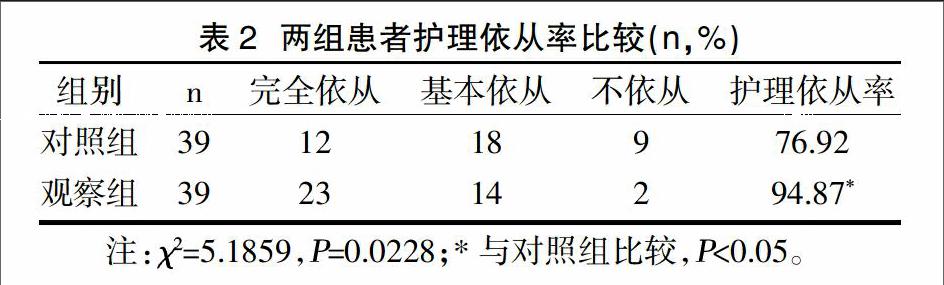
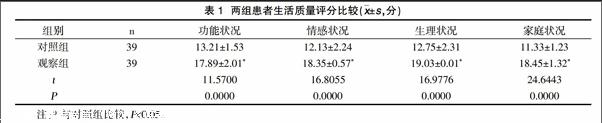
摘要:目的 觀察延續(xù)性護(hù)理干預(yù)聯(lián)合健康飲食對(duì)老年乳腺癌患者的臨床應(yīng)用效果及價(jià)值。方法 隨機(jī)選取我院2014年11月~2015年11月收治的78例老年乳腺癌患者,根據(jù)護(hù)理方法的不同分為對(duì)照組與觀察組。對(duì)照組39例,行常規(guī)護(hù)理。觀察組39例,基于常規(guī)護(hù)理行延續(xù)性護(hù)理干預(yù)聯(lián)合健康飲食。比較兩組患者生活質(zhì)量評(píng)分及護(hù)理依從率。結(jié)果 觀察組生活質(zhì)量評(píng)分明顯高于對(duì)照組,差異具有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。觀察組護(hù)理依從率(94.87%)高于對(duì)照組(76.92%),差異具有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 對(duì)老年乳腺癌患者實(shí)施延續(xù)性護(hù)理干預(yù)聯(lián)合健康飲食,可提高患者的生活質(zhì)量與護(hù)理依從率,從而有助于臨床療效的提高。
關(guān)鍵詞:延續(xù)性護(hù)理;健康飲食;老年;乳腺癌
中圖分類號(hào):R473.73 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)識(shí)碼:A 文章編號(hào):1006-1959(2017)26-0116-02
Abstract:Objective To observe the effect and value of continuous nursing intervention combined with healthy diet on the clinical effect of elderly patients with breast cancer.Methods A total of 78 elderly patients with breast cancer admitted to our hospital from November 2014 to November 2015 were randomly divided into control group and observation group according to different nursing methods.The control group of 39 cases,routine care.The observation group of 39 cases,based on the routine nursing continuous nursing intervention combined with healthy diet.Quality of life scores and nursing adherence rates were compared between the two groups.Results The quality of life of observation group was significantly higher than that of control group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).The rate of nursing compliance in the observation group(94.87%)was higher than that in the control group(76.92%),the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).Conclusion The implementation of continuous nursing intervention in elderly patients with breast cancer combined with healthy diet can improve the quality of life of patients and compliance rate of nursing, thus contributing to the improvement of clinical efficacy.
Key words:Continuity of care;Healthy diet;Elderly;Breast cancer
乳腺癌是常見(jiàn)的一種婦科疾病,發(fā)病率較高,居女性腫瘤疾病的第一位[1]。目前,乳腺癌患者經(jīng)過(guò)住院治療病情均會(huì)得到有效控制,但患者出院后復(fù)發(fā)率較高,降低了患者的生活質(zhì)量。因此,應(yīng)對(duì)患者實(shí)施延續(xù)性護(hù)理,以提高臨床療效。
1 資料與方法
1.1一般資料
隨機(jī)選取我院2014年11月~2015年11月收治的78例老年乳腺癌患者,根據(jù)護(hù)理方法的不同分為對(duì)照組與觀察組。對(duì)照組39例,行常規(guī)護(hù)理,年齡61~72歲,平均年齡(66.53±2.34)歲;TNM分期:Ⅰ期11例,Ⅱ期26例,Ⅲ期2例。觀察組39例,基于常規(guī)護(hù)理行延續(xù)性護(hù)理干預(yù)聯(lián)合健康飲食,年齡60~71歲,平均年齡(66.55±2.36)歲;TNM分期:Ⅰ期14例,Ⅱ期24例,Ⅲ期1例。兩組患者一般資料比較差異不具有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P>0.05),可進(jìn)行對(duì)比。
1.2入排標(biāo)準(zhǔn)
納入標(biāo)準(zhǔn):①本次研究對(duì)象均符合《中國(guó)抗癌協(xié)會(huì)乳腺癌診治指南與規(guī)范(2013版)》[2]中關(guān)于乳腺癌的診斷標(biāo)準(zhǔn),即可觸及乳腺腫塊,伴刺痛、隱痛,乳頭溢液,乳暈、乳頭明顯異常等;②本次研究已經(jīng)我院倫理學(xué)委員會(huì)批準(zhǔn),且患者知情同意。排……

