火山渣吸附低溫水體中的效果
陳志宇, 張玉玲, 司超群, 初文磊, 陳在星, 馮凱婕
(吉林大學 環境與資源學院, 水資源與環境研究所, 長春 130021)
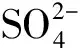
1 實 驗
1.1 儀器、 材料和試劑 722型紫外可見光分光光度計(上海洪紀儀器設備有限公司); SPX-250-D型全溫振蕩培養箱(上海博迅實業有限公司). 火山渣采自東北地區某廠火山巖礦區, 經自然風干、 去雜質后, 過0.5~2 mm篩備用. 所用Na2SO4,CaCl2,MgCl2,NaCl,NaNO3,HCl,NaOH等無機試劑均為國產分析純試劑.
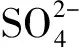
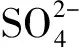
1.4 影響因素實驗
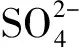
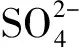
2 結果與討論
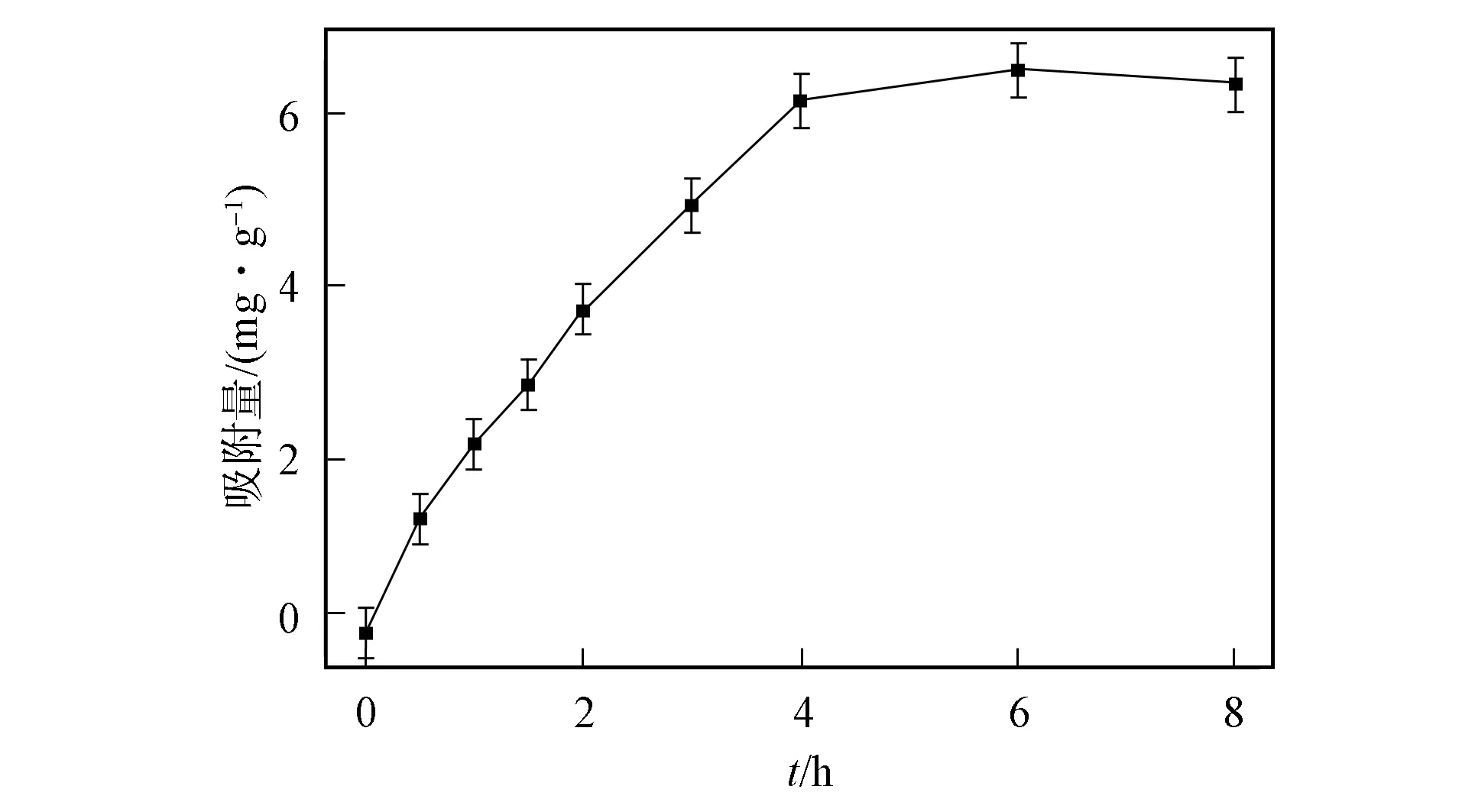
圖1 吸附量與時間的關系Fig.1 Relationship between adsorption amount and time

對吸附過程進行上述兩種吸附動力學方程擬合, 結果如圖2所示. 由圖2可見, 準二級擬合方程R2=0.987 5, 擬合效果更好, 吸附過程符合準二級動力學模型. 表明吸附過程受化學吸附機理控制, 涉及吸附劑與吸附質之間的電子共用或電子轉移.

圖2 吸附動力學的擬合結果Fig.2 Fitting results of adsorption kinetics

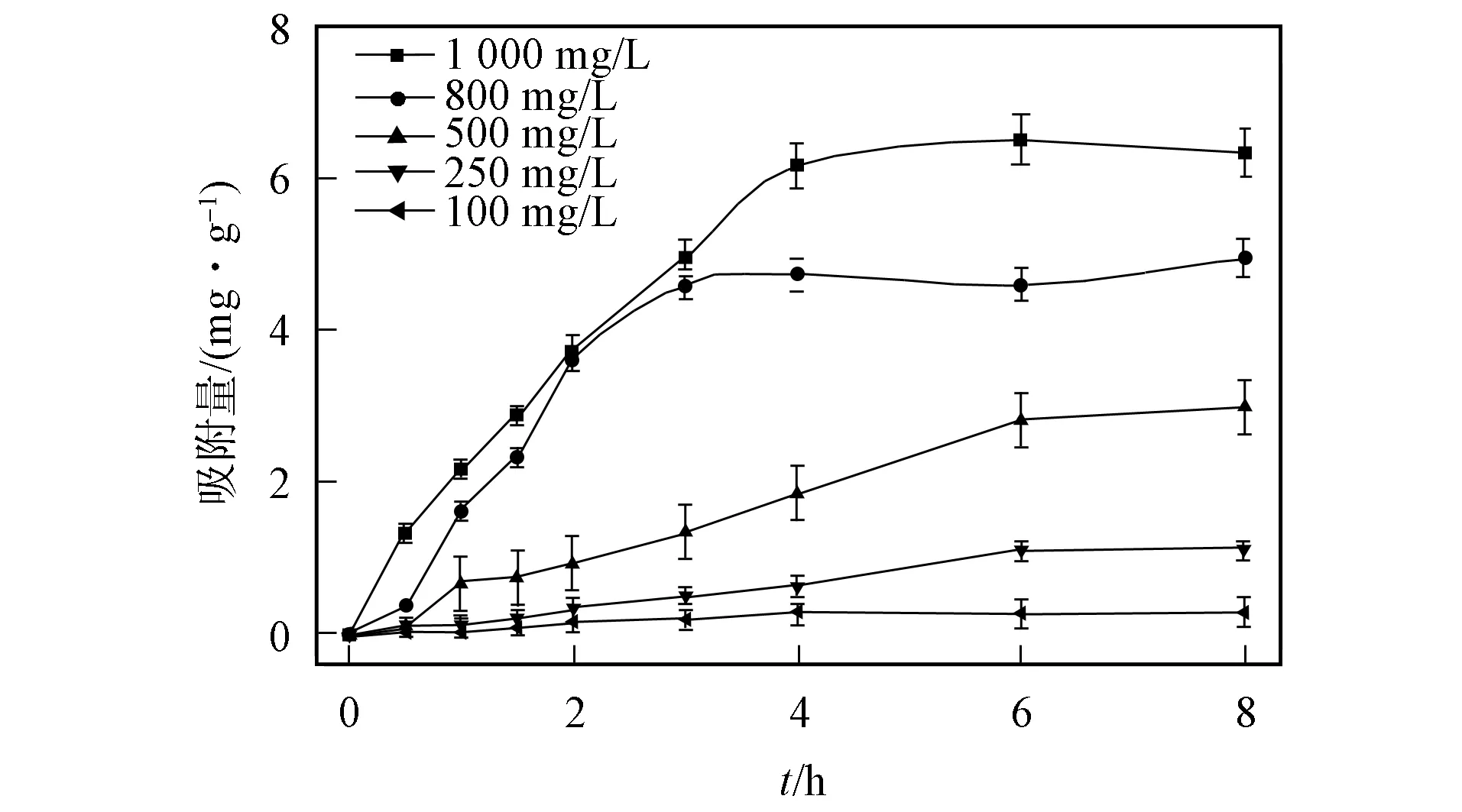
圖3 不同初始質量濃度吸附量與時間的關系Fig.3 Relationship between adsorption amount and time of different initial mass concentrations
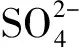
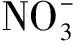

圖4 pH值與吸附量的關系Fig.4 Relationship between pH and adsorption amount

圖5 不同水化學離子對火山渣吸附的影響Fig.5 Effects of different hydrochemical ions on adsorption of S by scoria
綜上, 本文可得如下結論:
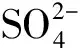
3) 火山渣可有效去除低溫水體中的硫酸鹽, 是經濟、 有效、 生態安全型的天然硅酸鹽礦物材料.
[1] 世界衛生組織. 飲用水水質準則 [M]. 4版. 上海: 上海交通大學出版社, 2011: 171. (World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality [M]. 4th ed. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University Press, 2011: 171.)
[2] 中華人民共和國國家質量監督檢驗檢疫總局. 地下水質量標準GB/T14848-93 [S]. 北京: 中國標準出版社, 1993. (General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Quality Standard for Ground Water GB/T14848-93 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1993.)
[3] 中華人民共和國衛生部. 生活飲用水衛生標準GB5749-2006 [S]. 北京: 中國標準出版社, 2006. (National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Standards for Drinking Water Quality GB5749-2006 [S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006.)
[4] 胡明成. 硫酸鹽的環境危害及含硫酸鹽廢水處理技術 [J]. 成都大學學報(自然科學版), 2012, 31(2): 181-184. (HU Mingcheng. Environmental Hazards by Sulfate and Treatment Method of Waste Water Containing Sulfate [J]. Journal of Chengdu University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 31(2): 181-184.)
[5] 曹曉磊, 盛宇星. 生物法處理含硫酸鹽重金屬廢水的研究進展 [J]. 環境科學與技術, 2015, 38(12Q): 181-185. (CAO Xiaolei, SHENG Yuxing. Recent Advances in Research of Treating Sulfate, Heavy Metals-Containing Wastewater by Anaerobic Bio-treatment Method [J]. Environment Science & Technology, 2015, 38(12Q): 181-185.)


[8] 姜艷. 高硫酸鹽礦井水處理研究 [J]. 環境工程, 2011, 29: 111-113. (JIANG Yan. Study on the Disposal of Higher Sulfate Mineral Water [J]. Environmental Engineering, 2011, 29: 111-113.)
[9] 王愛杰, 王麗燕, 任南琪, 等. 硫酸鹽廢水生物處理工藝研究進展 [J]. 哈爾濱工業大學學報, 2004, 36(11): 1446-1449. (WANG Aijie, WANG Liyan, REN Nanqi, et al. Bio-treatment of Sulfate-Laden Wastewater [J]. Journal of Harbin Institute Technology, 2004, 36(11): 1446-1449.)
[10] 高娃, 董欣, 鄭永章. 內蒙古錫盟地區火山渣及火山渣混凝土材料的性能初報 [J]. 河北科技師范學院學報, 2007, 21(4): 46-49. (GAO Wa, DONG Xin, ZHENG Yongzhang. An Experimental Study on the Properties of Trass and Trass Concrete in Ximeng Area of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Hebei Normal University of Science & Technology, 2007, 21(4): 46-49.)
[11] 楊福珍, 黃清友, 張建棟. 火山渣在路基工程中的應用 [J]. 內蒙古公路與運輸, 2006(4): 24-27. (YANG Fuzhen, HUANG Qingyou, ZHANG Jiandong. Application of Volcanic Scoria to the Subgrade Engineering [J]. Highways & Transportation in Inner Mongolia, 2006(4): 24-27.)
[12] ZHANG Shengyu, ZHANG Yuling, SU Xiaosi, et al.InsituRemediation of Petroleum Contaminated Groundwater by Permeable Reactive Barrier with Hydrothermal Palygorskite as Medium [J]. Chemical Research in Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(1): 37-41.
[13] ZHANG Yuling, DONG Tianzi, SU Xiaosi, et al. Effect of High Fluoride Groundwater Purification by Lightweight Aggregate Scoria [J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(1): 10.
[14] ZHANG Shengyu, LU Ying, LIN Xueyu, et al. Removal of Fluoride from Groundwater by Adsorption onto La(Ⅲ)- Al(Ⅲ) Loaded Scoria Adsorbent [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2014, 303: 1-5.

