70~79歲老年人體質測評指標的篩選與實測
呂 俊,張藝宏
?
70~79歲老年人體質測評指標的篩選與實測
呂 俊,張藝宏
成都體育學院,四川 成都,610041。
目的:篩選適合70~79歲老年人體質測試的指標,并進行實際測試,為開展70~79歲老年人體質監測與體質檢測工作進行探索性的實驗研究。方法:通過文獻資料法、問卷調查法篩選適合70~79歲老年人的體質測試指標,并選取老年志愿者294名進行測試。結果:(1)經過文獻分析和專家問卷調查,篩選出身高、體重、肺活量、坐位體前屈、閉眼單腳站立、選擇反應時、腰圍、臀圍、握力、30s坐站測試和2min原地踏步測試作為70~79歲老年人體質評估的測試項目,BMI與腰臀比作為評估的派生指標;(2)測試表明,所有參加志愿測試的70-79歲老年人均能獨立完成各個項目的測試,測試項目的可靠性、有效性符合測量要求,測試項目實施的安全性、可行性和簡易性符合高齡老年人特點;(3)實測結果顯示:隨著年齡的增加,70~79歲老年人體質測試結果呈下降趨勢,而體重,腰圍,臀圍則呈現上升趨勢。結論:選定的70~79歲老年人體質測試指標在理論上和操作上具有可靠性、有效性、安全性、可行性,符合測量要求以及高齡老年人的特點。
身體測量;老年人;高齡老年人;體質;評估指標;國民體質監測
1 測試指標的篩選
1.1 初選指標
通過文獻查詢相關高齡老年人各個國家及地區測試指標,結合我國國民體質監測60~69歲老年人指標,初步篩選出23個適合70~79歲老年人體質測試指標(見表1)。
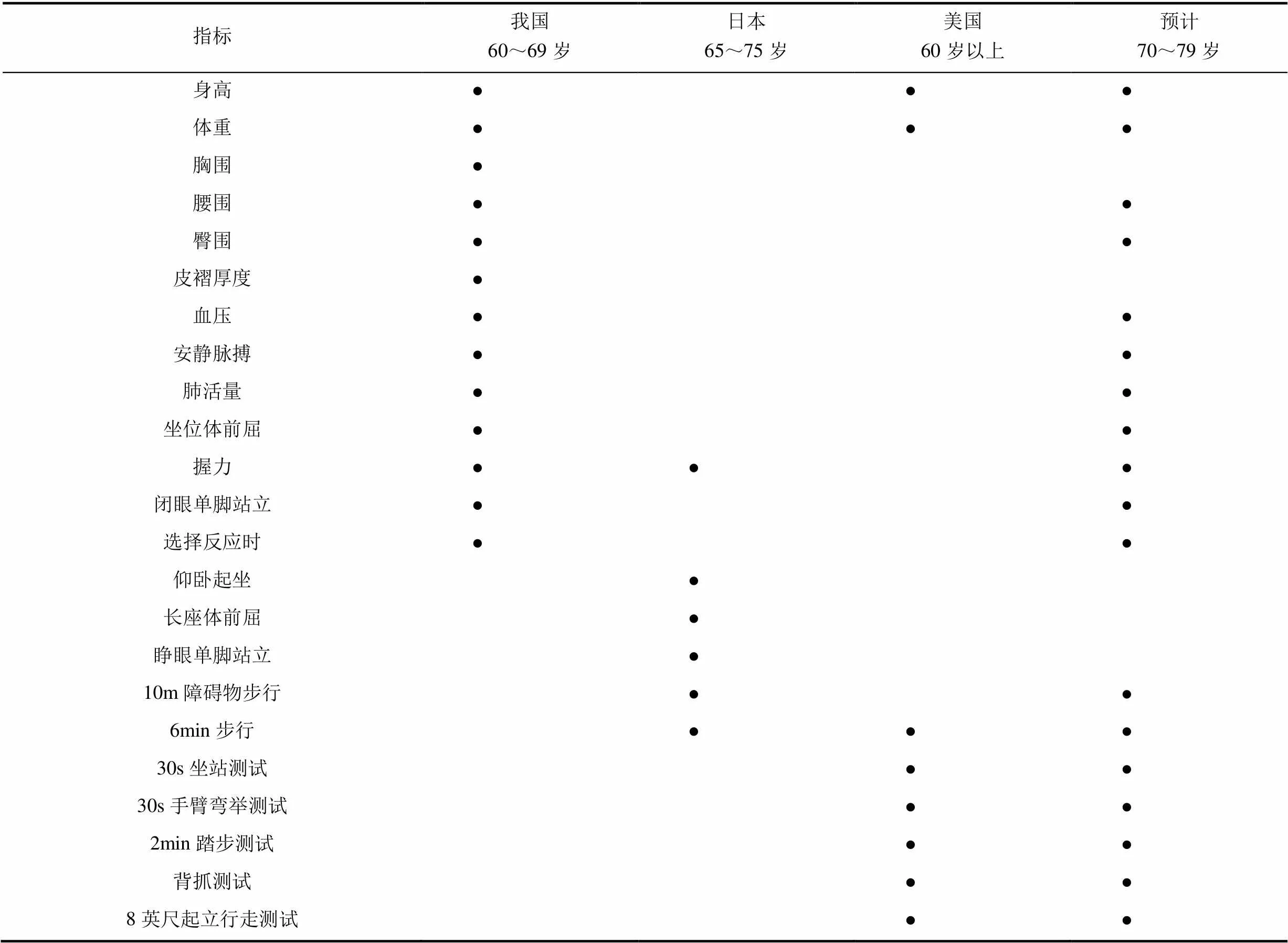
表1 70-79歲老年人體質測試初選指標
說明:●表示該年齡段有此項檢測指標
指標說明如下:
身高、體重、胸圍、腰圍、臀圍、皮褶厚度、血壓、安靜脈搏、肺活量、坐位體前屈、握力、閉眼單腳站立、選擇反應時為國民體質監測指標[1],測試方法見《2014年國民體質監測手冊》[2]。
仰臥起坐、長座體前屈、睜眼單腳站立、10m障礙物步行為日本65歲~79歲老年人體力活動測試的項目[3]。
6min步行、30s坐站測試、30s手臂彎舉測試、2min踏步測試、背抓測試和8英尺起立行走測試為美國Functional Fitness Test中的測試項目[4][5]。
1.2 終選指標
本研究共選取7位國內體質研究及運動醫學權威專家進行問卷咨詢,最終確定測試項目為:體重、身高、胸圍、腰圍、臀圍、坐位體前屈、握力、閉眼單腳站立、肺活量、30s坐站測試、2min原地踏步、腰臀比、BMI。
2 實測對象與方法
2.1 實測對象
在成都市2017年體質測試中,募集70歲以上的老年人進行測試,參加測試的老年人均自愿參加,測試地點有相應的醫務工作人員。納入標準:年齡70~79歲的老年人;近5年內未做過手術的;自述無重大疾病,身體健康;在每個項目介紹后,自認為能堅持下來的,填寫調查者知情同意書。老年人自述無重大疾病,身體健康。經過后期數據整理,剔除79歲以上樣本量以及完成測試項目低于5項樣本量,最終獲得有效樣本量294人。其中,男性平均年齡74.21歲,女性平均年齡72.73歲; 70~74歲男性54位,女性128位;75~79歲男性53位,女性59位(表2)。
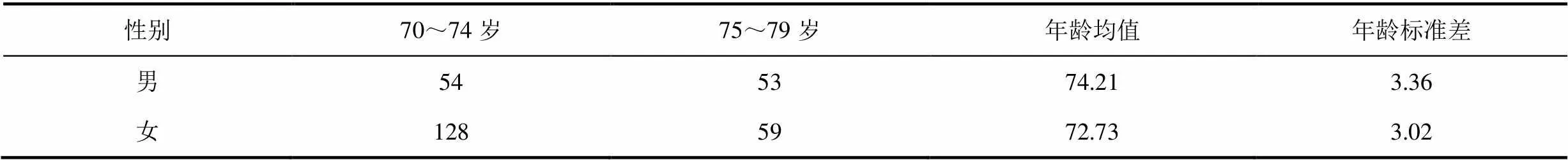
表2 各年齡段測試樣本量(n)
2.2 方法
2.2.1 測試方法 身高、體重、肺活量、坐位體前屈、閉眼單腳站、選擇反應時、腰圍、臀圍、握力9項指標,在各測試點采用國家體育總局2014年統一配發的體質測試器材,按照國家統一規定的方法進行測試。30s坐站、2min原地踏步指標按照相應規定和方法進行測試[9]。通過形態指標計算得到派生指標BMI、腰臀比。
2.2.2 統計方法用 EXCEL2010和SPSS19.0對指標數據進行統計學分析,計量資料平均數±標準差表示,平均數的差異性使用獨立樣本檢驗,統計假設檢驗水準為=0.05。
3 實測結果
3.1 70~79歲老年人體質總體情況
本次測試通過《70~79歲老年人體質評估測評項目》從身體形態、身體機能和身體素質三個方面13個體質指標,對老年人體質進行分析,以下是測試項目的結果統計(見表3、表4)。
3.2 不同年齡組男性體質指標的特征及變化趨勢
男性高齡老年人身體形態指標中,70~74歲組的身高、體重、BMI、腰臀比與75~79歲組差別很小,而75~79歲組的腰圍、臀圍顯著高于70~74歲組(P<0.05)。在身體機能和身體素質指標中,肺活量、握力、坐位體前屈、30s坐站測試、2min原地踏步測試兩組間有一些差異,但無顯著性。閉眼單腳站立和選擇反應時則70~74歲組顯著好于75~79歲組(P<0.05)(表3)。
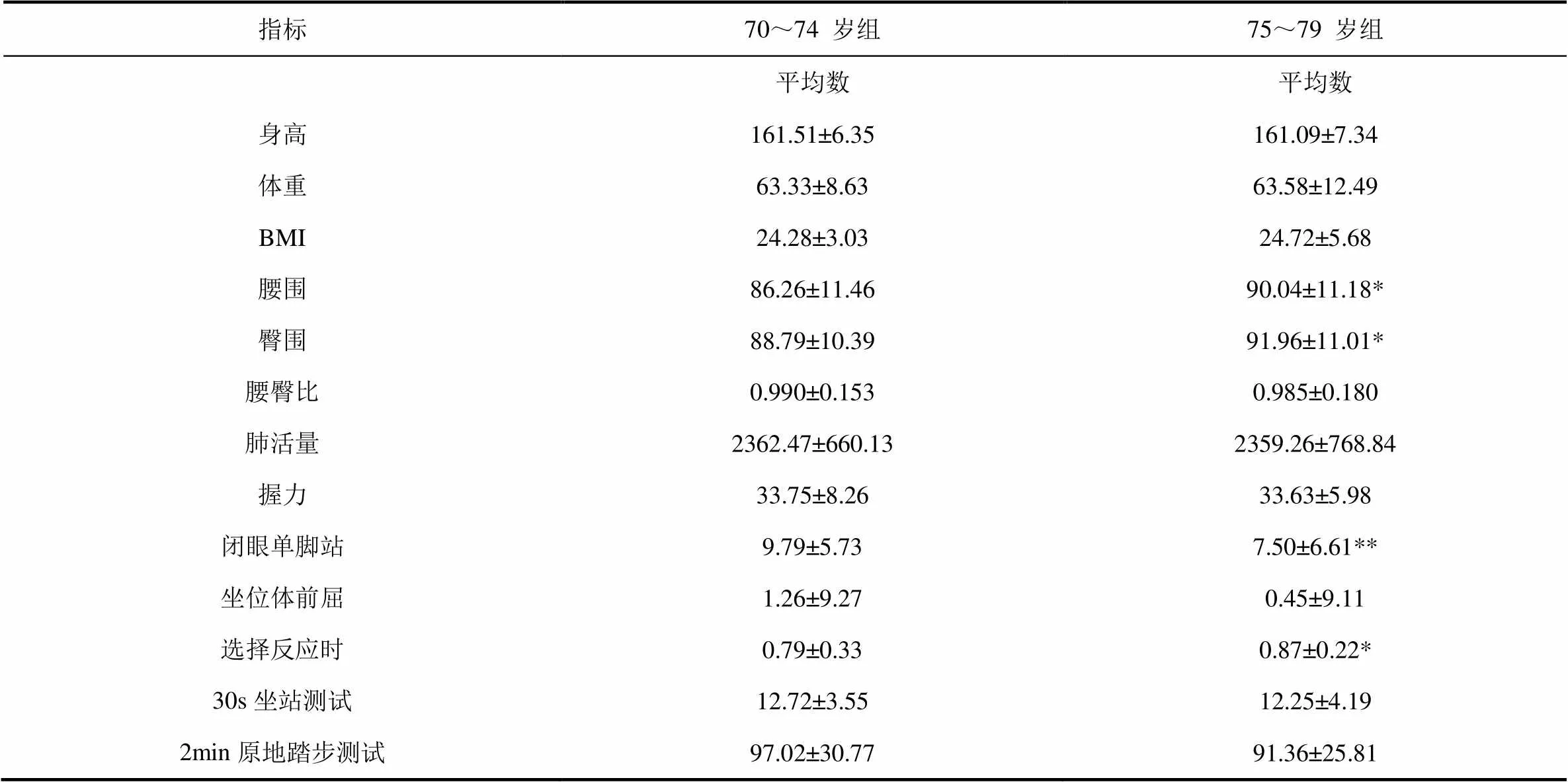
表3 男性高齡老人體質測試結果(平均數±標準差)
注:兩個年齡組比較,*為<0.05,**為<0.01。
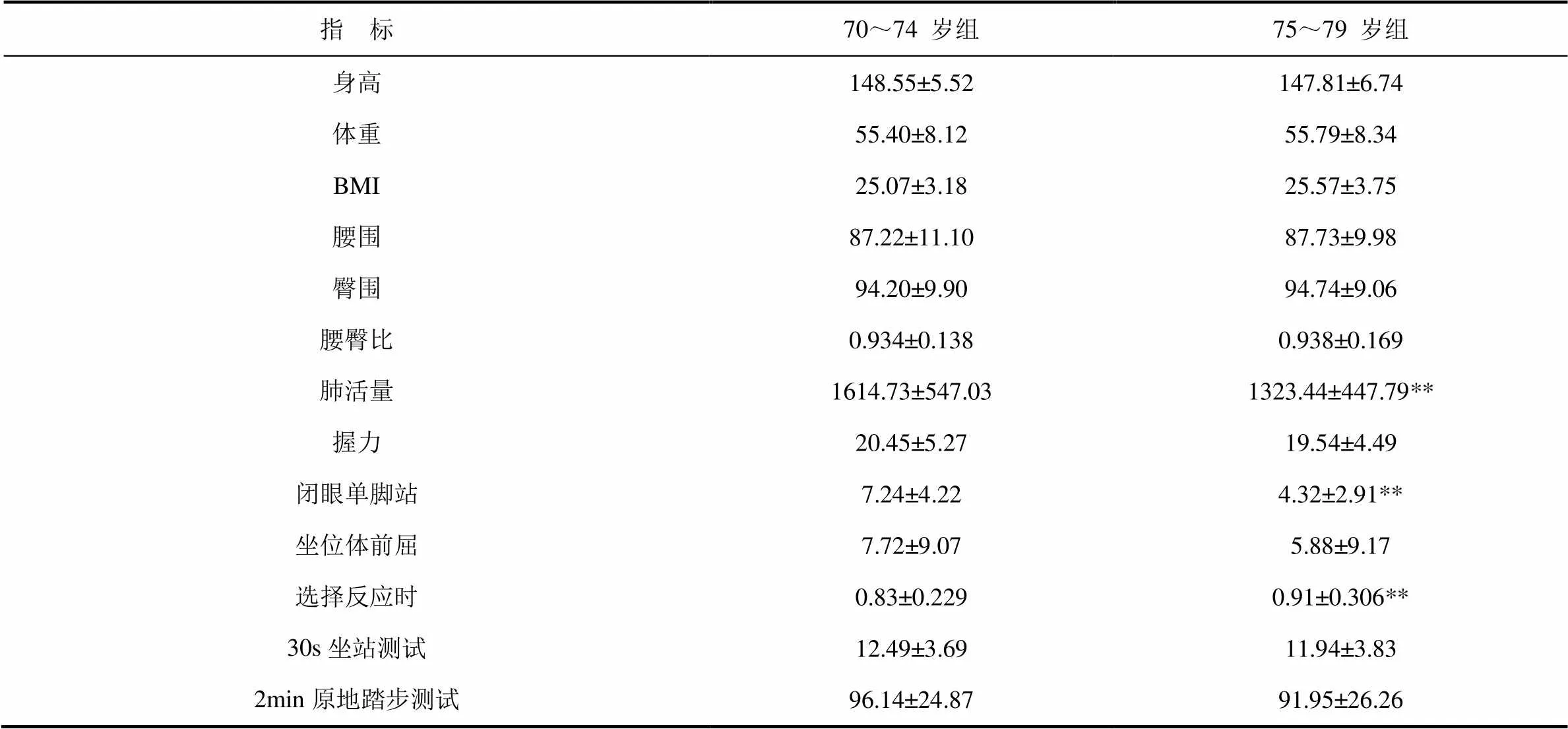
表4 女性高齡老人體質測試結果(平均數±標準差)
注:兩個年齡組比較,*為<0.05,**為<0.01。
3.3 不同年齡組女性體質指標的特征及變化趨勢
在身體形態的指標中,這些測試項目中,70~74歲組的身高、體重、BMI值、腰圍、臀圍和腰臀比與75~79歲組差別很小。在身體機能和身體素質指標中,握力、坐位體前屈30s坐站測試、2min原地踏步測試兩組間有一些差異,但無顯著性。肺活量、閉眼單腳站立和選擇反應時則70~74歲組顯著好于75~79歲組(P<0.01)(表4)。
4 結 論
(1)本研究通過專家問卷、實際測試和測試數據的分析驗證,選定70~79歲老年人體質測試的指標為:身高、體重、肺活量、坐位體前屈、睜眼單腳站立、選擇反應時、腰圍、臀圍、握力、30s坐站、2min原地踏步、BMI、腰臀比。
(2)選定的70~79歲老年人體質測試指標在理論上和操作上具有可靠性、有效性、安全性、可行性,符合測量要求以及高齡老年人的特點。
(3)實測結果顯示:隨著年齡的增加,70~79歲老年人體質測試成績呈下降趨勢,而體重,腰圍,臀圍則呈現上升趨勢。
[1] 江崇民,于道中,季成葉,蔡 睿. 《國民體質測定標準》的研制[J].體育科學,2004(03):33~36.
[2] 國家國民體質監測中心編.2014年國民體質監測工作手冊[Z].
[3] 日本文部省.新體力テスト実施要項(65歲~79歲).日本:日本文部省,2001,11.
[4] Rikli ,R.E, &Jones ,C.J.(1999b). Functional fitness normative scores for community-residing adults, ages 60-94 . Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, 6, 160~179.
[5] Rikli , R.E, &Jones ,C.J.(1999a). Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults . Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, 6, 127~159 .
Selection and Measurement of Physical Fitness Evaluation Indicators for 70~79 Year Old People
LU Jun, ZHANG Yihong
Chengdu Sport University, Sichuan Chengdu, 610041, China.
Objective To screen indexes suitable for physical fitness test for 70-79 year-olds and carry out practical tests. To carry out an exploratory experimental study for physical fitness monitoring and physical fitness testing for 70-79-year-olds.Methods Through the literature data method and questionnaire survey, physical fitness test indicators suitable for 70-79-year-olds were screened. 294 elderly volunteers were selected for testing. Results 1.After literature analysis and expert survey, the height, weight, vital capacity, sitting flexion, standing on one foot, reaction time, waist circumference, hip circumference, grip force, 30-second sitting test and 2 minutes were selected. As a test item for assessing the physical fitness of 70 to 79-year-olds, the BMI and waist-to-hip ratios are used as the derived indicators for evaluation. 2. Tests show that all 70-79-year-olds who participated in the voluntary test can independently complete the testing of various projects. The reliability and effectiveness of the test project meet the measurement requirements. The safety, feasibility and simplicity of the test project implementation are in line with the old age. The characteristics of the elderly. 3. The measured results show that with the increase of age, the physical fitness test results of 70-79-year-olds showed a downward trend, while weight, waist circumference, and hip circumference showed an upward trend. Conclusions The physical fitness test indexes of selected 70 to 79-year-olds are theoretically and operationally reliable, effective, safe, and feasible. They meet the measurement requirements and the characteristics of older people.
Physical measurement; Seniors; Older seniors; Physical fitness; Assessment index
G804.26
A
1007―6891(2018)06―0034―03
10.13932/j.cnki.sctykx.2018.06.09
2018-06-26
2018-07-31

