松江區全科醫師知識技能掌握及培訓需求調查分析
黃慧 褚天運 朱玉龍

摘 要 目的:了解松江區全科醫師相關知識技能的掌握情況及培訓需求,為衛生行政部門和社區衛生服務中心有針對性的進行全科醫學培訓提供建議。方法:采取分層抽樣方法選取九亭鎮、新橋鎮、洞涇鎮、小昆山鎮、石湖蕩鎮及泖港鎮等6家社區衛生服務中心的170名全科醫師為調查對象進行問卷調查。調查內容包括全科醫師的基本情況、培訓動機、培訓方式及時長、全科醫師對相關專業知識的熟悉程度及培訓需求。結果:①100.0%的全科醫師認為非常需要或需要掌握院前急救的基本知識及高危人群和慢性疾病病例管理的相關知識。②100.0%的全科醫師認為非常需要和需要掌握全科6大系統的相關知識;7.5%的全科醫師認為完全不需要掌握與婦女、兒童保健相關的知識和技術;1.1%的全科醫師認為完全不需要掌握常規藥物使用的相關知識。③全科醫師中醫藥服務相關知識的掌握及部分掌握比例之和僅為59.1%;2.2%的全科醫師認為不需要掌握處理倫理和社會問題技巧的相關知識。④全科醫師常用化驗檢查及結果解讀相關知識未掌握比例高達20.4%;全科醫師認為完全不需要掌握傳染病的預防和檢測及社區常用康復技術的相關知識,占比分別為3.2%、2.2%。結論:建議衛生行政部門完善全科醫師培訓考核體系,全力推進全科醫師培訓工作。同時及時發現培訓中存在的薄弱環節和亟待解決的問題,提出整改措施,提升全科醫師的培訓效果。
關鍵詞 全科醫師;知識技能;培訓需求
中圖分類號:R197.1 文獻標志碼:A 文章編號:1006-1533(2019)16-0013-05
Investigation and analysis of the mastery of knowledge and skills and training needs of general practitioners in Songjiang District
HUANG Hui, CHU Tianyun, ZHU Yulong
(General Practice Department of Xiaokunshan Community Health Service Center of Songjiang District, Shanghai 201616, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To understand the mastery of knowledge and skills and training needs of general practitioners in Songjiang District for providing advice for the health administrative department and community health service center to conduct targeted general medical training. Methods: A stratified sampling method was used to select 170 general practitioners from six community health service centers, including Jiuting Town, Xinqiao Town, Dongjing Town, Xiaokunshan Town, Shihudang Town and Maogang Town to conduct a questionnaire survey. The survey contents included the basic situation of the general practitioner, the motivation of the training, the training method and time, the familiarity with relevant professional knowledge and the training needs of the general practitioner. Results: (1)100.0% of general practitioners thought that it was very necessary or necessary to have a basic knowledge of pre-hospital first aid and knowledge about high-risk populations and chronic disease case management.(2)100.0% of general practitioners thought that it was very necessary and necessary to master the relevant knowledge of the six major systems of general medicine; 7.5% of general practitioners thought that there was no need to master the knowledge and skills related to womens and childrens health; 1.1% of general practitioners thought that they did not need to master the knowledge of routine drug use at all. (3) The sum of mastery and partial mastery proportions of TCM service knowledge of general practitioners was only 59.1%; 2.2% of general practitioners thought that there was no need to master the relevant knowledge to deal with ethical and social problem skills. (4) The proportion of general practitioners who had not mastered the knowledge of laboratory tests and interpretation of results was as high as 20.4%; the general practitioner thought that there was no need to master the prevention and detection of infectious diseases and the knowledge of common rehabilitation techniques in the community, accounting for 3.2% and 2.2%, respectively. Conclusion: It is suggested that the health administrative department should perfect the system of training and assessment of general practitioners and make full efforts to promote the training of general practitioners. At the same time, the existing weak links and urgent problems in the training should be found out in time, and corrective measures should be put forward to improve the training effect of general practitioners.

據楊慧敏等[6]的調查顯示,高學歷、高職稱的醫療工作者在社區衛生服務中心從事全科醫學工作的比例較低。因此,要提升社區衛生服務中心全科醫師的總體素養和業務水平,必須先綜合提升其社會地位和經濟收入,吸引更多的高素質醫務工作者從事全科醫學工作。同時從制度層面加強宣傳,讓社會、政府更多的了解全科醫師的工作內容,不斷穩定全科醫師隊伍,把全科醫學真正落到實處,惠及社區居民。
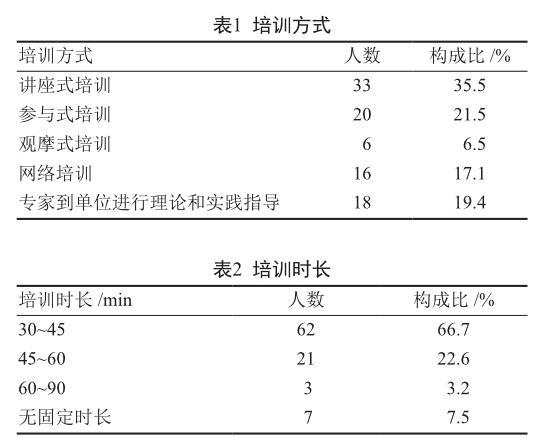
93名全科醫師的培訓動機均為工作需要或自我提升,其中52名(55.9%)的培訓動機為工作需要,其余41名(44.1%)為自我提升,說明全科醫師都具有強烈的培訓學習需求。多數全科醫師選擇的培訓形式為講座式培訓(35.5%),這可能與醫師習慣于講座式授課方式有關。培訓時長上多數(66.7%)全科醫師選擇了30~45 min,也提示培訓組織者應盡量控制授課時長。
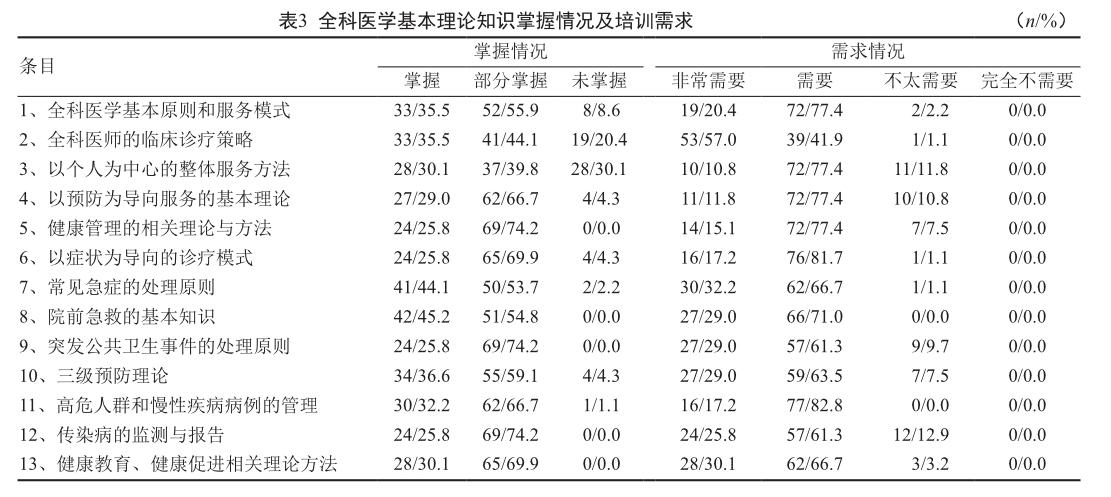
全科醫師對常見急癥的處理原則及院前急救的基本知識掌握情況均較好,完全掌握的人數均超過了40.0%;100.0%的全科醫師認為非常需要或需要掌握院前急救的基本知識及高危人群和慢性疾病病例管理的相關知識;未掌握的主要是以個人為中心的整體服務方法和全科醫師的臨床診療策略,說明全科醫師的整體觀念不強,可能仍然存在以專科觀念看待全科專業的情況。100.0%的全科醫師認為非常需要和需要掌握全科6大系統的相關知識;中醫藥服務的掌握及部分掌握比例之和僅為59.1%,說明全科醫師對中醫藥知識的掌握較為薄弱,這可能與社區衛生服務中心普遍設有中醫科、有專職中醫醫師有關。全科醫師未掌握比例較高的幾個條目為常用化驗檢查及結果解讀,X線、心電圖的圖像識別及社區常用康復技術,其中常用化驗檢查及結果解讀的未掌握比例高達20.4%。提示我們今后培訓中應多增加這些方面的內容,以彌補不足。
從全科醫師對相關專業知識的熟悉程度看,應強化公共衛生知識的相關培訓,著重考慮全科醫師的實際需求,達到“熟臨床、懂公衛、具人文、會管理”的培養目標,進一步完善和優化培訓項目。實施培訓的過程當中,還可以開展人際溝通等公共關系學的培訓,全面提升全科醫師的預防醫學知識和人文素養。
綜上所述,松江區全科醫師接受培訓的意愿比較強烈,建議衛生行政部門完善全科醫師培訓考核體系,推出有益的新舉措,加大經費投入,提升培訓的數量及質量,全力推進全科醫師的培訓工作[7]。同時應及時發現培訓中存在的薄弱環節和亟待解決的問題,提升全科醫師的培訓效果。本次研究樣本量有限,因此存在一定的選擇偏倚,自行設計的問卷也可能會導致重要信息的遺漏,以上情況有待進一步研究完善。
參考文獻
[1] 秦懷金. 關于我國社區衛生服務發展與改革的思考[J]. 中國衛生政策研究, 2012, 5(3): 1-3.
[2] 楊秉輝, 祝墡珠. 全科醫學概論[M]. 3版. 北京: 人民衛生出版社, 2008: 9-10.
[3] 劉堃, 張濱, 唐貴忠. 重慶市貧困地區鄉鎮全科醫師培訓狀況調查[J]. 現代預防醫學, 2009, 36(16): 3059-3061.
[4] 祝墡珠. 關于全科醫師制度建立的問題及建議[J]. 中華全科醫師雜志, 2011, 10(10): 703-704.
[5] 顧杰, 江孫芳, 祝墡珠, 等. 上海市全科醫師培訓需求調查和相關因素分析[J]. 中華全科醫師雜志, 2012, 11(8): 575-578.
[6] 楊慧敏, 尹德盧, 辛倩倩, 等. 我國基層全科醫生隊伍現狀和繼續醫學教育內容需求分析[J]. 中華全科醫學, 2018, 16(10): 1591-1594.
[7] 方呂, 張勘. 上海市全科醫師規范化培訓的進展與挑戰[J]. 上海醫藥, 2012, 33(20): 17-22.

