血糖波動對2型糖尿病大鼠認知功能及N-甲基-D-天門冬氨酸受體表達的影響
何焰鵬 劉國榮
[摘要]目的 探討血糖波動對2型糖尿病大鼠認知功能及N-甲基-D-天(門)冬氨酸(NMDA)受體表達的影響。方法 33只清潔級雄性SD大鼠,適應性喂養1周后,隨機取11只作為正常對照組,其余大鼠用于建立2型糖尿病模型。采用小劑量鏈脲佐菌素45 mg/kg腹腔注射建立2型糖尿病模型,非同日兩次測得的隨機血糖>16.7 mmol/L為造模成功。將模型大鼠隨機分為持續高血糖組(n=11)和血糖波動組(n=11),2型糖尿病模型成功后,血糖波動組大鼠皮下注射普通胰島素2次/d,誘導血糖波動大鼠模型。比較三組大鼠的潛伏期、潛伏期距離、穿越平臺次數及12周后大鼠海馬組織中NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達。結果 血糖波動組大鼠的潛伏期長于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠的潛伏期長于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);血糖波動組大鼠的潛伏期距離長于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠的潛伏期距離長于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);血糖波動組大鼠穿越平臺次數少于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠穿越平臺次數少于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);血糖波動組大鼠海馬組織中的NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平低于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠海馬組織中的NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平低于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 血糖波動比持續高血糖更能加重大鼠認知功能的損害。糖尿病大鼠海馬組織NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達量降低,且血糖波動同持續高血糖相比,NR2B亞基mRNA表達量降低更加明顯。
[關鍵詞]2型糖尿病大鼠模型;血糖波動;學習和記憶;潛伏期;潛伏期距離;N-甲基-D-天(門)冬氨酸受體
[中圖分類號] R332? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1674-4721(2019)10(c)-0020-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the effect of blood glucose fluctuation on cognitive function and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor expression in type 2 diabetic rats. Methods Thirty-three male clean Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly selected 11 ones for normal control group after one week of adaptive feeding. The rest were used to establish the type 2 diabetic rats model. A model of type 2 diabetes mellitus was established by intraperitoneal injection of a low-dose streptozotocin (45 mg/kg). The standard of successful modeling was the value of glucose >16.7 mmol/L measured randomly twice a day. After that, rats were randomly divided into persistent hyperglycemia group (n=11) and glucose fluctuation group (n=11). After successful type 2 diabetes model, rats in the blood glucose fluctuation group were subcutaneously injected with insulin twice a day to induce the blood glucose fluctuation rat model. The latency, latency distance, number of plateau crossings and the expression of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in hippocampus of rats after 12 weeks were compared among the three groups. Results The latent period of the rats in the glucose fluctuation group was longer than that in the normal control group and the persistent hyperglycemia group, the latency of the rats in the persistent hyperglycemia group was longer than that in the normal control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The latency of the blood glucose fluctuation group was longer than that of the normal control group and the persistent hyperglycemia group, the latency of the rats in the persistent hyperglycemic group was longer than that in the normal control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The number of crossing platform in the blood glucose fluctuation group was fewer than that in the normal control group and the persistent hyperglycemia group, the number of crossing platform in the persistent hyperglycemic group was fewer than that in the normal control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The expression level of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit mRNA in hippocampal tissues of the glucose fluctuation group was lower than that of the normal control group and the persistent hyperglycemia group, the expression level of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit mRNA in the hippocampus of the persistent hyperglycemic group was lower than that of the normal control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Glucose fluctuation can aggravate cognitive impairment in rats more than persistent hyperglycemia. The expression of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit in hippocampus of diabetic rats is decreased, and the expression of NR2B subunit is decreased more significantly than that of persistent hyperglycemia.
[Key words] Type 2 diabetic rat model; Glucose fluctuation; Learning and memory; Latency; Distance of latent period; N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
糖尿病是一種以血葡萄糖升高為特征的慢性代謝性疾病,主要表現為持續碳水化合物、脂肪、蛋白質代謝功能紊亂,糖尿病及其引發的慢性并發癥給社會和家庭帶來沉重的心理及經濟負擔。大量研究顯示[1-4],糖尿病會損害中樞神經系統,臨床上不僅表現為認知功能障礙,而且易促進大腦形態結構和生理結構發生改變。海馬組織是人及高等動物學習和記憶不可或缺的神經結構之一,一方面其參與記憶的編碼,另一方面其參與記憶再現的加工過程[2-8]。
1材料與方法
1.1實驗用動物
33只清潔級雄性SD大鼠購自北京科奧協力動物有限公司,衛生許可證號是SCXK(京)2009-0012。實驗過程嚴格遵守《實驗動物福利與動物實驗科學》[9]。
1.2主要試劑和儀器
Trizol試劑(寶生物工程(大連)有限公司,批號:15596-026),鏈脲佐菌素(美國Sigma公司,批號:V900890-1G),反轉錄試劑盒(寶生物工程(大連)有限公司,批號:RP1105)等。Morris水迷宮系統(由XR-XM101型圖像采集分析軟件、攝像頭等組成,購自北京碩林苑科技有限公司),T100型Thermal CyclerPCR儀(日本Bioer公司)。
1.3方法
33只清潔級雄性SD大鼠,適應性喂養1周后,隨機取11只作為正常對照組,其余大鼠用于建立2型糖尿病模型。采用小劑量鏈脲佐菌素45 mg/kg腹腔注射建立2型糖尿病模型,非同日兩次測得的隨機血糖>16.7 mmol/L為造模成功。將模型大鼠隨機分為持續高血糖組(n=11)和血糖波動組(n=11),2型糖尿病模型成功后,血糖波動組大鼠皮下注射普通胰島素2次/d,誘導血糖波動大鼠模型。正常對照組及持續高血糖組腹腔注射0.9%生理鹽水,持續高血糖組和血糖波動組大鼠繼續給予高糖高脂飼料,正常對照組給予普通飼料,飼養12周,持續高血糖組存活10只,死亡1只(死于感染),血糖波動組存活9只,死亡2只(死于低血糖)。
1.4觀察指標及評價標準
比較三組大鼠的潛伏期、潛伏期距離、穿越平臺次數及大鼠海馬組織中N-甲基-D-天(門)冬氨酸(NMDA)受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達。①12周后采用Morris水迷宮對大鼠學習和記憶能力進行評估,包括潛伏期、潛伏期距離及穿越平臺次數等。②斷頭法處死SD大鼠,解剖分離出海馬組織,采用反轉錄-聚合酶鏈式反應(RT-PCR)檢測大鼠海馬組織中NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA的表達。
1.5統計學方法
采用統計學軟件SPSS 19.0分析數據,計量資料以均數±標準差(x±s)表示,多組間比較采用單因素分析,兩兩比較采用t檢驗,以P<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
2結果
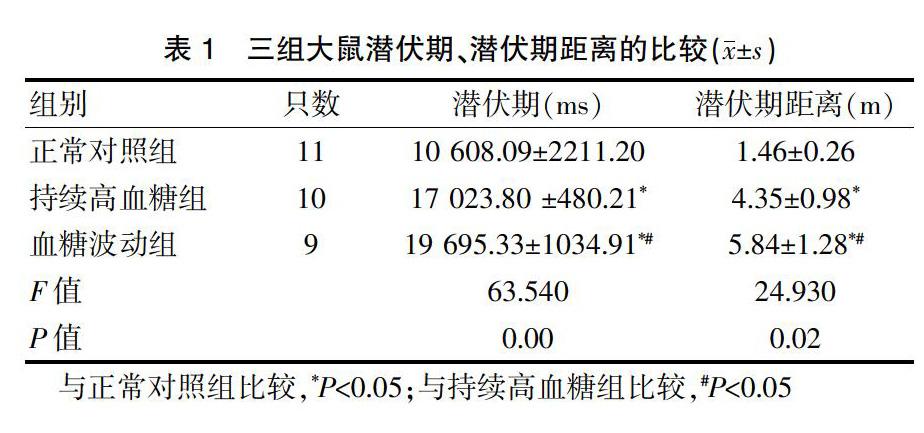
2.1三組大鼠潛伏期、潛伏期距離的比較
血糖波動組大鼠的潛伏期長于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠的潛伏期長于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);血糖波動組大鼠的潛伏期距離長于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠的潛伏期距離長于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)(表1)。
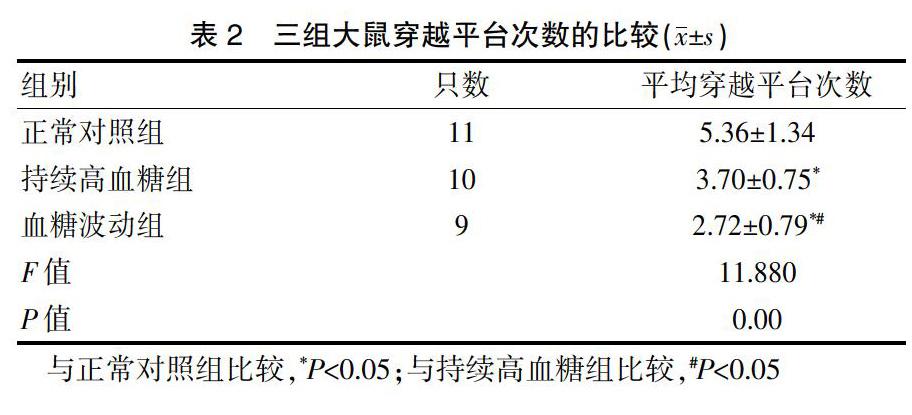
2.2三組大鼠穿越平臺次數的比較
血糖波動組大鼠的穿越平臺次數少于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠的穿越平臺次數少于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)(表2)。
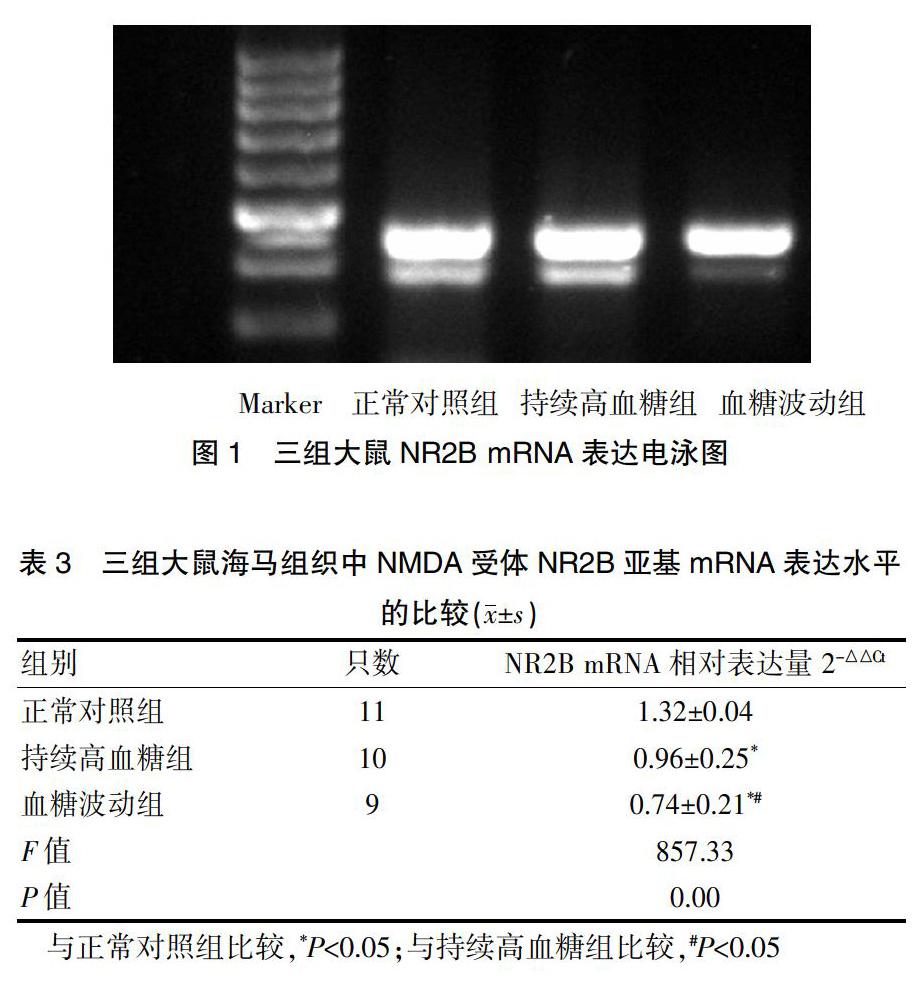
2.3三組大鼠海馬組織中NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平的比較
血糖波動組大鼠海馬組織中的NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平低于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,持續高血糖組大鼠海馬組織中的NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平低于正常對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)(圖1、表3)。
3討論
海馬是中樞神經系統的重要結構,NMDA受體數量和結構的改變會影響學習和記憶能力,可能由于應激引起神經活動的改變,神經末梢釋放不同的神經遞質,導致NMDA受體表達下降。NMDA受體由NR1、NR2(A、B、C、D)、NR3(A、B)3類同源性亞基組成[10-13]。NR2亞基為調節亞基,包含多個基因家族;其分布呈區域性,NR2A、NR2B主要分布在端腦,突觸外NMDA受體主要含有NR2B,NR2B亞基與學習記憶能力關系亦十分密切[14]。
本研究結果顯示,血糖波動組大鼠海馬組織中的NMDA受體NR2B亞基mRNA表達水平低于正常對照組和持續高血糖組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。提示血糖波動能降低NR2B亞基的表達。當NR2B mRNA表達下降會影響NMDA受體的數量,導致可塑性突觸形成異常,可塑性突觸是信息儲存的場所,信息儲存異常會導致學習和記憶能力下降,因此NR2B亞基表達下降會誘發認知功能障礙。此外,NMDA受體數量減少,使Ca2+內流減少,從而阻礙了長時程增強,進一步阻礙了學習和記憶能力的形成。因此,NR2B亞基表達下降與大鼠學習和記憶能力平行。血糖波動組大鼠認知功能損害嚴重,表現以NR2B亞基下調為主要特點,從而加速了糖尿病認知功能障礙的發生發展[15-17]。
綜上所述,血糖波動對2型糖尿病大鼠的認知功能損害較為嚴重,NMDA受體是學習記憶能力的主要受體,NMDA受體亞基的功能主要集中于NR2B亞基,NR2B亞基表達量的大幅度下降,進一步顯示血糖波動通過影響NR2B亞基的表達來加重認知功能障礙[18]。因此很好地控制2型糖尿病患者血糖波動有利于延緩認知功能障礙的發生,對于糖尿病患者醫護人員要正規的指導其口服藥物及胰島素使用方法,盡量避免出現大幅度的血糖波動,同時對糖尿病患者是否應早期給予抗癡呆藥物及認知康復治療,盡可能延緩癡呆發生的年齡,需進行更深入地研究。
[參考文獻]
[1]Trudeana F,Gagnaonb S,Massicotte G.Hippocampal aynaptic plasticity and glutamate receptor regulation:influences of diabetes mellitus[J].Eur J Pharmacol,2004,490(1-3):177-186.
[2]Phillips GD,Jones GN,Callaghan M,et al.Hemiataxia:a novel presentation of Anti-NMDA receptor antibody mediated enc ephalitisin an adolescent[J].Case Rep Psychiatry,2017,69(12):25-28.
[3]Li C,Liu C,Lin F,et al.Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitisassociated with mediastinal teratoma:a rare case report and literature review[J].J Thorac Dis,2017,9(12):E1118-E1121.
[4]Kobayashi M,Nishioka K,Takanashi M,et al.Anti-NMDA receptor encephalitisdue to large -cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the uterus[J].J Neurol Sci,2017,383:72-74.
[5]李強.NMDA受體與學習記憶關系的研究進展[J].上海交通大學學報(醫學版),2010,30(10):1285-1287.
[6]陳誼,蔡文瑋,盛凈.糖尿病模型大鼠認知功能障礙及海馬N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受體表達變化[J].實用醫學雜志,2010,26(17):3098-3101.
[7]Wang H,Peng RY.Basic roles of key molecules connected with NMDAR signaling pathway on regulating learning and memory and synaptic plasticity[J].Mil Med Res,2016,3(1):26.
[8]Viaccoz A,Desestret V,Ducray F,et al.Clinical specificities of adult male patients with NMDA receptor antibodies encephalitis[J].Neurology,2014,82(7):556-563.
[9]賀爭鳴,李根平,李冠民,等.實驗動物福利與動物實驗科學[M].北京:科學出版社,2011.
[10]彭朝勝,曹悅鞍.糖尿病患者血糖波動的臨床意義與研究進展[J].海軍總醫院報,2011,24(3):173-176.
[11]Kumari K,Sahni N,Kumari V,et al.Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspart ate-receptor encephalitisin youngfemales[J].Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim,2017,45(6):377-379.
[12]李新玲,朱向陽,黃懷宇,等.老年2型糖尿病患者認知功能障礙與平均血糖波動幅度的關系[J].中華老年醫學雜志,2012,31(12):1066-1069.
[13]Kaznowska-Bystryk I,Gorynska A,Solski J.Evaluation of metabolic control in patients with type 2 diabetes[J].Wiad Lek,2011,64(3):170-175.
[14]Pilli NR,Inamadugu JK,Mullangi R,et al.Simultaneous determination of atorvastatin,amlodipine,rarnipril and benazepril in human plasma by LC-MS/MS and its application to a human pharmacokinetic study[J].Biomed Chromatogr,2011,25(4):439-449.
[15]Ghosh C,Jain I,Gaur S,et al.Simultaneous estimation of atorvastatin and its two metabolites from human plasma by ESI-LC-MS/MS[J].Drug Test Anal,2011,3(6):352-362.
[16]Galani VJ,Vyas M.In vivo and In vitro drug interactions study of glimepride with atorvastatin and rosuvastatin[J].J Young Pharm,2010,2(2):196-200.
[17]廖潔,雷閩湘,胡維.大鼠糖尿病血糖波動模型的建立[J].中國醫師雜志.2010,12(2):157-161.
[18]林永忠,孫長凱,吳旻,等.胰島素對糖尿病大鼠認知功能及腦星形膠質細胞GFAP表達的影響[J].大連醫科大學學報,2012,34(4):324-328.
(收稿日期:2018-10-08? 本文編輯:劉克明)

