油氣懸架囊式蓄能器真實氣體多變指數模型建立及驗證
王云超,魏 彬,楊岳霖
油氣懸架囊式蓄能器真實氣體多變指數模型建立及驗證
王云超,魏 彬,楊岳霖
(集美大學機械與能源工程學院,廈門 361021)
蓄能器內氮氣多變過程模型的精度是影響油氣懸架系統特性分析的關鍵因素之一。為了更加精準地描述蓄能器內氮氣的真實多變過程,該文利用蓄能器試驗臺開展了蓄能器不同振幅和頻率的正弦激勵試驗,通過試驗數據綜合分析發現氮氣體積壓縮率和體積壓縮速率與氣體壓力呈一定線性關系。在此基礎提出了一種基于體積壓縮率和體積壓縮速率的真實氣體多變指數模型。為了驗證模型的正確性和準確性,通過蓄能器試驗數據對提出的多變指數模型中的2個變量系數進行辨識和模型仿真結果的對比驗證,并利用6個懸掛缸的整車油氣懸架系統試驗平臺對模型進行試驗驗證,結果表明:仿真預測結果與試驗數據的平均誤差為5.12%,最大誤差小于10.9%,滿足工程設計的要求。該囊式蓄能器的氣體多變指數模型為更加準確研究油氣懸架系統真實特性奠定了基礎。
車輛;試驗;模型;懸架;蓄能器;遲滯環
0 引 言
油氣懸架系統以其高度的非線性特性及高能量密度等優點[1],被廣泛應用于越野車領域。油氣懸架系統的研究也經歷了從單個懸架系統的特性研究[1-6]到不同連通方式的整車油氣懸架系統特性仿真分析和研究[7-15]。已有研究大部分都是基于理想氣體的多變過程建立的油氣懸架系統模型[2-15],而實際油氣懸架系統內的氮氣的多變過程并非理想的多變過程[1]。Kat等[16]曾強調只有經過正確參數驗證的模型獲得的結果才有意義。為此,很多學者針對實際氣體的多變過程進行了深入的研究[17-30],主要集中在2個方面:1)從熱傳遞和能量守恒角度研究氣體多變過程模型[17-26];2)從理論和試驗角度研究確定氣體多變指數的問題[27-30]。
根據能量守恒定律,在BWR(Benedict-Webb-Rubin)真實氣體模型的基礎上[17],Otis等[18]建立了一個熱對流模型來描述氣體熱動力學過程,并建立了一個熱時間常數模型。Els等[19]在此基礎上,分析了油氣懸架系統對時間和溫度的依賴性。Pourmovahed等[20]提出了一種基于試驗數據的熱時間常數關聯模型,并準確預測蓄能器的熱力學損失和壓縮或膨脹過程中的氣體壓力和溫度歷史。Els等[21]進一步建立了一個氣體與油液、環境的熱傳遞模型,并發現油氣懸架系統內存在顯著的固有阻尼,這主要根源于熱傳遞不是單純的溫度變化或能量積累。吳宏濤等[22]通過熱平衡試驗研究了激勵振幅、激勵頻率和溫度變化等對油氣懸架動態特性的影響規律。Westhuizen等[1]對比分析了3種理想氣體模型和2種實際氣體模型的實用性,認為應該根據實際需要選擇合適的模型。陳軼杰等[23]建立了油氣懸架的自然對流熱力學模型。黃夏旭等[24]利用熱學理論、氣體狀態方程,建立包含缸筒、活塞桿熱容的非公路自卸車油氣懸架系統的集中參數熱力學模型。但是研究發現針對具體的蓄能器及其工作范圍,熱時間常數必須通過試驗測量獲得。最近,Victor等[25]的研究發現:當壓縮比變化時,對于采用恒定熱時間常數的模型,預測精度會降低。范基等[26]經過試驗研究闡釋了熱時間常數并不是一個常數,即使同一個蓄能器,也會隨工況和蓄能器容量的變化而不同。總之,熱時間常數確定問題是以上研究的主要困難,另外,模型驗證方面還缺乏高頻振動的試驗驗證,而且以上研究主要針對活塞式蓄能器(piston-type hydraulic accumulator)。
其他部分學者試圖通過理論推導和試驗方法確定氣體多變過程指數的實際取值,從而描述真實氣體的多變過程。封士彩等[27-28]通過試驗研究認為實際狀態的氣體多變指數值要比理論值大,其取值與激勵頻率有關。王德偉[29]認為氣體壓縮速率對氣體多變指數影響較大,并構造一個氣體壓縮率的氣體多變指數模型,試圖找出蓄能器在充壓過程中氣體多變指數具體數值的確定方法,但是,其模型的正確性缺乏試驗驗證。吳曉元等[30]從理論角度對氣囊式蓄能器氣體多變指數的數值域問題進行了推導和分析,認為氣囊式蓄能器氣體多變指數的值域范圍為1~1.4。但是,這些都是基于理想氣體多變過程獲得的結果,與實際還存在一定的誤差。總之,以上研究依然無法描述蓄能器內真實氣體的壓力和體積關系圖中遲滯環的現象。
綜上所述,為了描述氣體多變過程指數描述蓄能器的遲滯現象和簡化蓄能器內氣體的建模,本文通過對蓄能器多個工況的試驗數據綜合分析,發現影響蓄能器特性的2個關鍵因素,并提出一種真實氣體多變指數模型,并進行了仿真和試驗分析和驗證。
1 蓄能器的氮氣正弦激勵試驗和分析
1.1 試驗儀器及原理
試驗原理:利用伺服激勵油缸控制一個被動液壓缸按照正弦規律運動,其無桿腔的油口與蓄能器進油口連接,蓄能器的充氣口接有一個壓力傳感器,用來測量蓄能器內氣體的壓力變化,如圖1a。測試系統主要參數如表1所示。
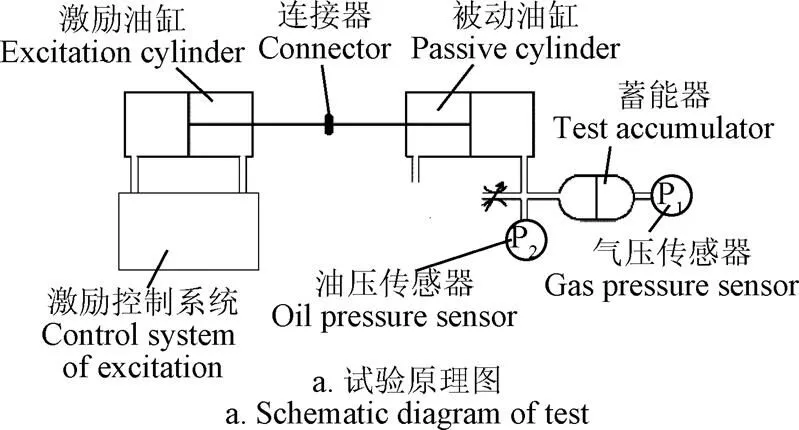
表1 試驗臺主要參數
主要儀器設備:1)MEACON的MIK-P300系列壓力傳感器;2)Novotechnik的TP1系列位移傳感器;3)上海元隆工業自動化電器有限公司(YOLON)HOB系列油缸;4)北京機床所精密機電有限公司QDY-Ⅱ系列電液伺服閥,型號:QDY6;5)SVA系列伺服放大器,型號:SVA-Ⅱ(TY)型;6)被動油缸為自制油缸。
根據試驗臺的工作范圍,確定如下試驗內容:1)振幅20 mm,頻率為0.1~0.4 Hz的4種正弦激勵試驗;2)頻率為0.4 Hz,振幅為5~20 mm的4種正弦激勵試驗。
試驗方法:通過控制正弦激勵的振幅和頻率,分析激振幅值和頻率對氣體壓力的影響,從而分析氣體壓力的主要影響因素。
1.2 試驗結果及分析
經過蓄能器氮氣試驗數據綜合分析發現2個影響氣體壓力的主要因素,為了便于對試驗結果進行分析,首先對其進行定義:
體積壓縮率:
=?Δ/0(1)
體積壓縮速率:
=Δ/0(2)
式中0蓄能器的體積,L;Δ為蓄能器內的氮氣體積變化量(L),Δ,,分別為被動油缸的無桿腔面積(100 cm2)和位移量(10 cm),等于激勵油缸的位移(被動油缸被壓縮為正,即氣囊被壓縮時,位移為正);Δ為Δ的變化率,Δ;為被壓縮油缸的運動速度(10 cm/s)。試驗結果如圖2所示。

圖2 正弦激勵下氣體壓力與體積壓縮率的關系
由圖2a可知,對應于體積壓縮率最小和最大值的各頻率下的氣體壓力曲線分別交于(?0.06,3.07)和(0.06,4.99),說明激振頻率對氣體壓力變化斜率(剛度)沒有明顯影響。但是隨著振動頻率的提高,蓄能器內氣體的遲滯環越來越大,說明蓄能器內的氣體內阻尼不斷增大。主要是由于真實氣體內部分子間的相互作用加劇導致阻尼力增大以及散熱時間減少所致,另外,油液從被動油缸無桿腔到蓄能器的管路和接口也會有部分阻尼的影響,但管路阻尼專項試驗結果表明該阻尼影響小于0.015 MPa。由于試驗條件限制,尚缺乏較高頻率振動試驗數據,而相同振幅下較高頻振動時的體積壓縮率極值對應的氣體壓力點是否仍然匯交于一點仍需進一步的試驗驗證。
由圖2b可知,隨著正弦激勵的振幅從5 mm增大到20 mm,各振幅壓力曲線的最小和最大體積壓縮率對應的氣體壓力基本位于(?0.065,3.074)和(0.065,4.105)兩點的連線上,即氣體壓力與體積壓縮率成線性關系。同樣由于試驗條件限制,未進一步探討更大振幅、更高頻率激勵作用的試驗研究,因此,體積壓縮率的極值點對應的氣體壓力點是否依然存在線性關系仍需進一步驗證。
2 真實氣體多變指數模型
2.1 體積壓縮率和體積壓縮速率對多變指數的影響
蓄能器內的氮氣多變過程是不可逆的,因此,氣體多變指數在該過程中按照一定方式進行變化[1]。
理想氣體多變過程方程
00=PV (3)
式中0為蓄能器充氣壓力,Pa;為蓄能器氣體瞬時體積,mm3;為蓄能器氣體瞬時壓力,為氣體多變指數,其值由氣體比熱容、比定壓熱容及比定容熱容決定。
由式(3)可得氣體多變指數為
=lg(0/)/lg(/0) (4)
將圖2中的試驗數據代入式(4),得到真實氣體多變指數,利用Matlab繪制氣體多變指數隨體積壓縮率的變化規律,如圖3所示。
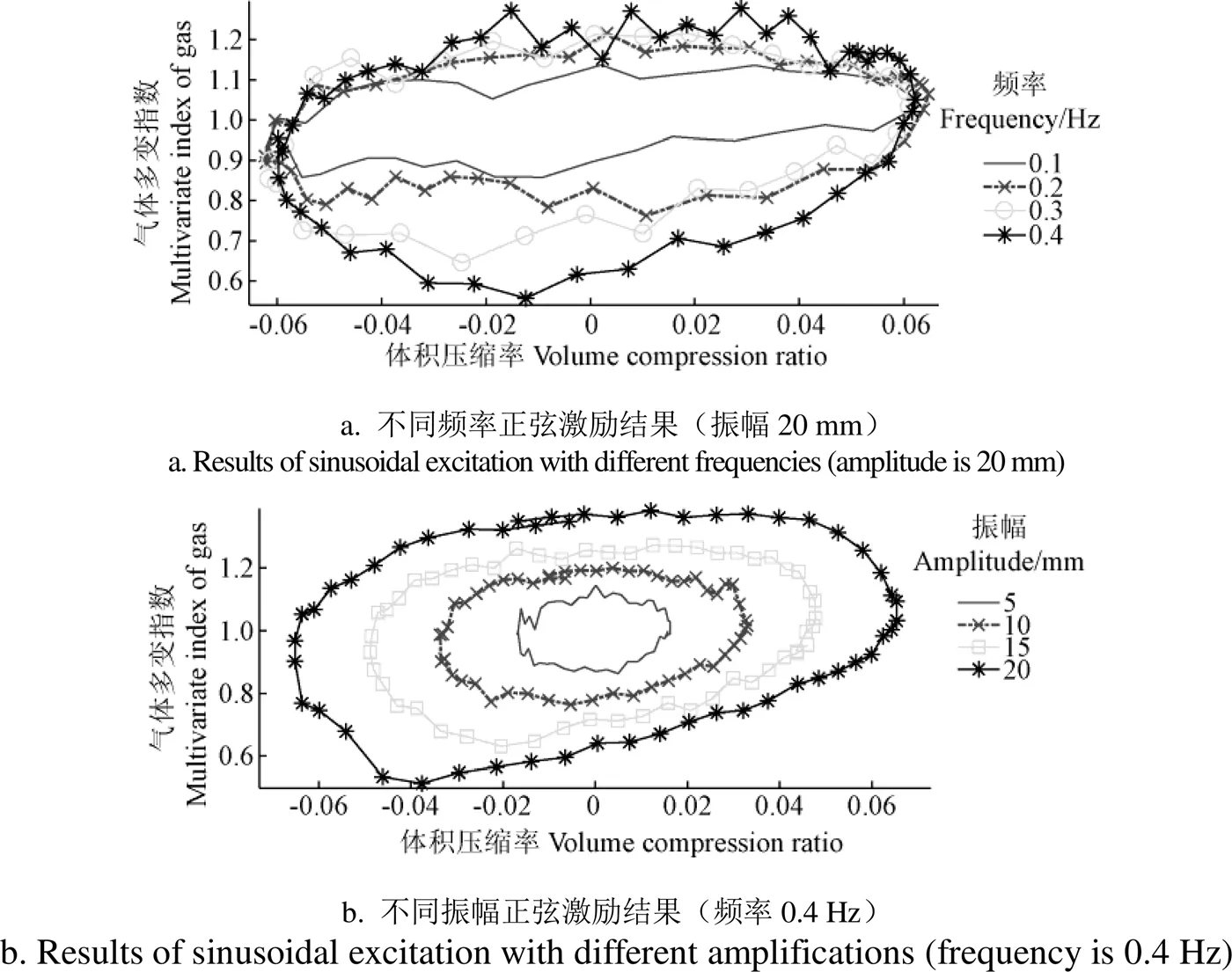
圖3 正弦激勵下氣體多變指數與體積壓縮率的關系
從圖3a不同頻率的氣體多變指數變化可以看出,不同頻率的振動,其極限體積的氣體多變指數也基本交于一點。另外,頻率對壓縮過程的影響不大,而對膨脹過程的影響比較明顯,其主要是由激振速度信號引起的,試驗的激勵位移信號近似正弦,但激振油缸信號在膨脹過程的實際速度明顯大于壓縮行程。這也反映了壓縮速度對氣體壓力和多變指數的影響,具體詳見圖4a,從圖中可以看出氣體多變指數與壓縮速率表現為一定的線性比例。
從圖3b可以看出,隨著振幅增大,氣體多變指數也不斷增大,并且氣體多變指數的變化范圍也不斷增大。另外,還發現不同振幅的氣體多變指數的極值點近似一條直線上,說明在一定頻率下,氣體壓縮率與氣體多變指數呈一定線性關系。這也反映了激振速度對氣體多變指數的影響,具體詳見圖4b,從圖中也可以看出氣體多變指數與壓縮速率成一定線性比例。
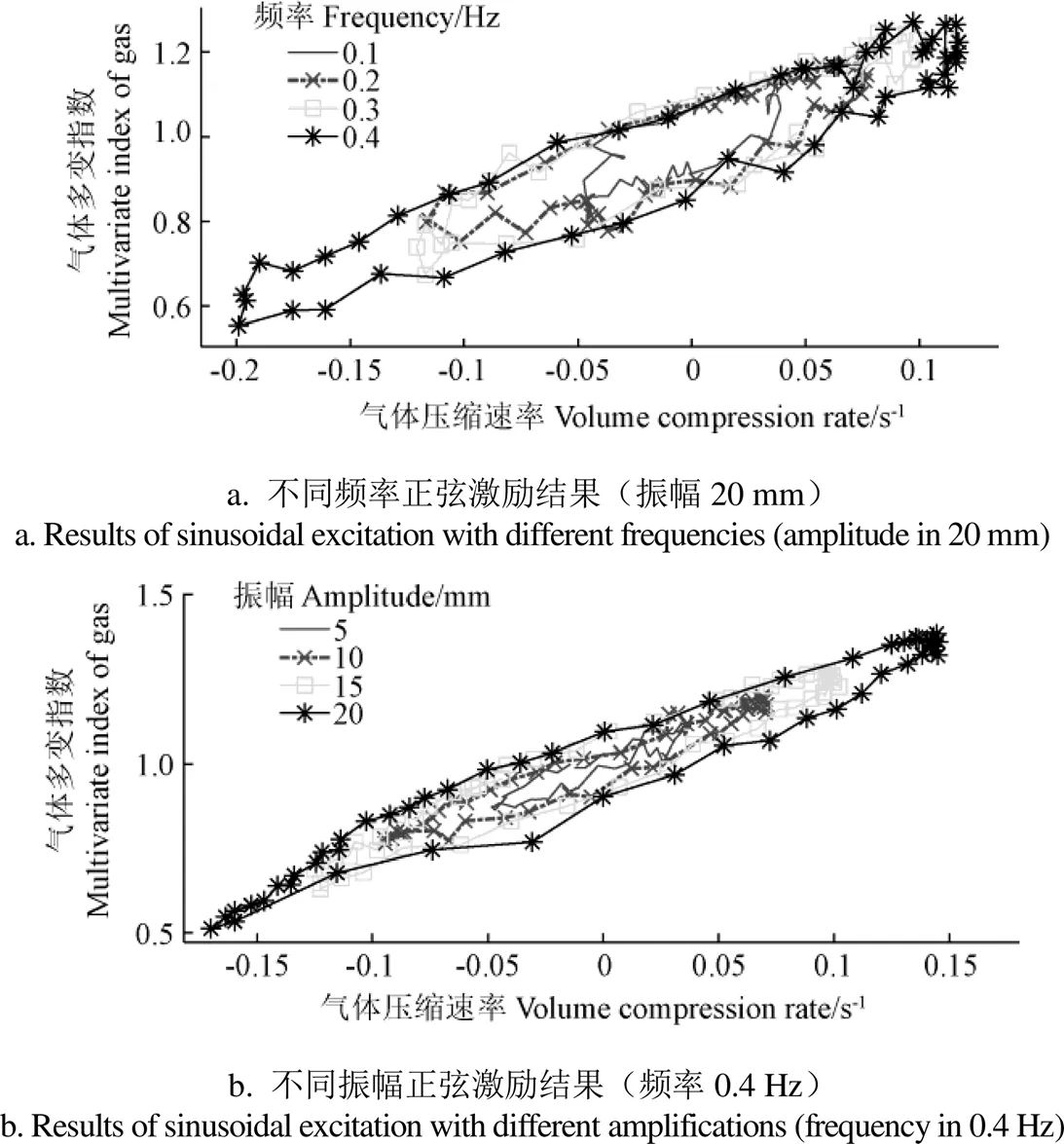
圖4 正弦激勵下氣體多變指數與體積縮速率的關系
2.2 真實氣體多變指數模型
假設不考慮氣體壓縮率和氣體壓縮速率的影響時,蓄能器內氣體的變化為等溫過程,即氣體多變指數為1。因此,真實氣體的多變過程指數可以表示為
=1+1+2(5)
式中1為氣體多變指數體積壓縮率系數,其值由圖3b中體積壓縮率的最小和最大值對應的氣體多變指數連線的斜率決定,即可通過試驗數據辨識獲得。1理論上可以根據真實氣體的BWR模型,由2個極限位置的氣體溫度和質量體積數值以及公式(5)和理想氣體的多變過程狀態方程計算獲得。但是其涉及到氣體溫度的預測中熱時間常數的確定問題。因此,導致其回歸為傳統方法,失去本方法的意義。如果環境溫度不隨氣體溫度變化,1為0。如果將蓄能器內的氮氣視為一個振動系統,1可等效為系統的剛度系數;為彈性變形量;2為氣體多變指數體積壓縮速率系數,其數值由圖4a中體積壓縮速率的最小和最大值對應的氣體多變指數連線的斜率決定,反映了壓縮速率引起的氣體內能(熱交換和做功綜合作用結果)、氣體內阻尼等的綜合影響,2可等效為振動系統的阻尼系數;為速度,mm/s。
2.3 真實氣體多變指數模型的驗證
為了驗證真實氣體多變指數模型的正確性和精度,利用蓄能器的試驗數據對式(5)中的2個系數1和2進行辨識,可得1=2.4,2=1.5,將這2個系數代入式(5)可獲得多變指數,再將代入多變過程狀態方程,可得
=0(0/)1+2.4η+1.5ε(6)
將蓄能器各個工況測得的、和代入公式(6),利用Matlab軟件,對各種工況的仿真結果與試驗數據進行對比,結果如圖5所示。
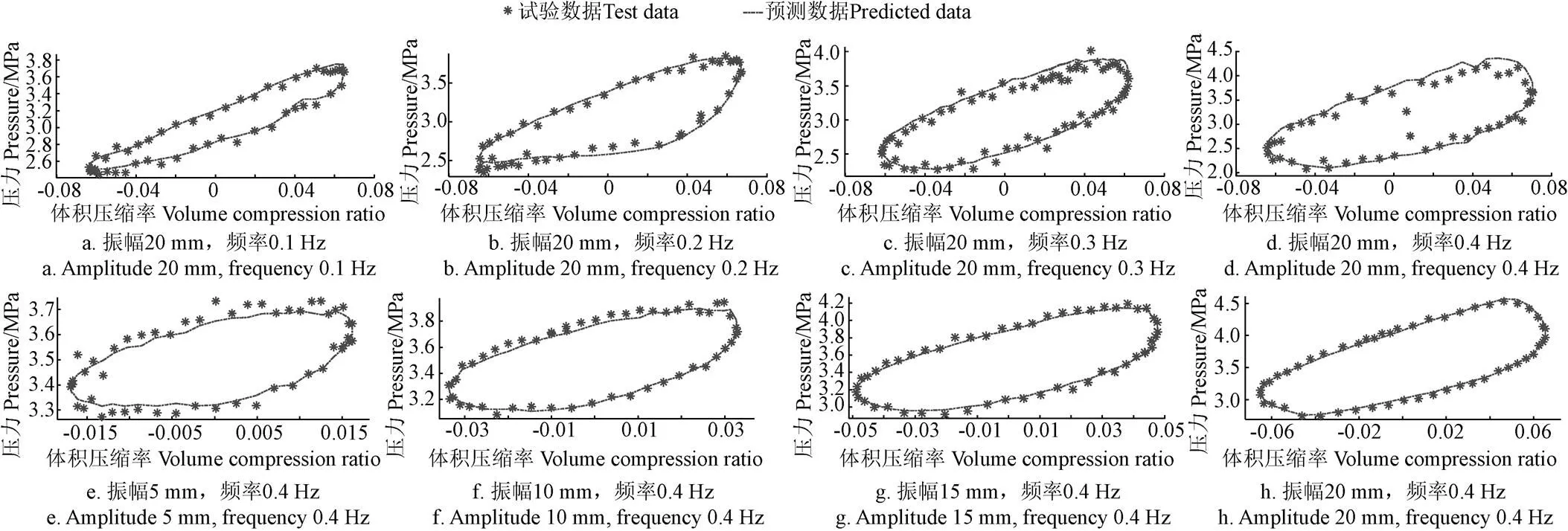
圖5 正弦激勵下氣體模型預測壓力與試驗數據對比(蓄能器充氣壓力2 MPa,充油壓力3.5 MPa)
由圖5可知,正弦激勵下氣體模型預測壓力與試驗結果的整體平均誤差為4.05%。圖5 d圖的誤差最大,為10%,該誤差是測量值出現了明顯波動造成的,相同工況的測試結果(圖5h)的最大誤差只有2.25%。
為了進一步驗證模型,多變指數模型中的1和2保持不變,將蓄能器的充氣壓力降為1.5 MPa,充油后平衡位置的壓力為3.5 MPa,振幅0.02 m,不同頻率的仿真和測試結果對比如圖6所示,由圖可知,正弦激勵下氣體模型預測壓力與試驗結果的最大誤差為9.06%,整體平均偏差為2.01%。
從不同頻率、振幅的仿真模型預測和測試數據的對比結果看,真實氣體多變指數模型能夠很好的跟蹤真實氣體的多變過程。即便是改變了蓄能器的充氣壓力,其仍然能夠很好地預測試驗結果。
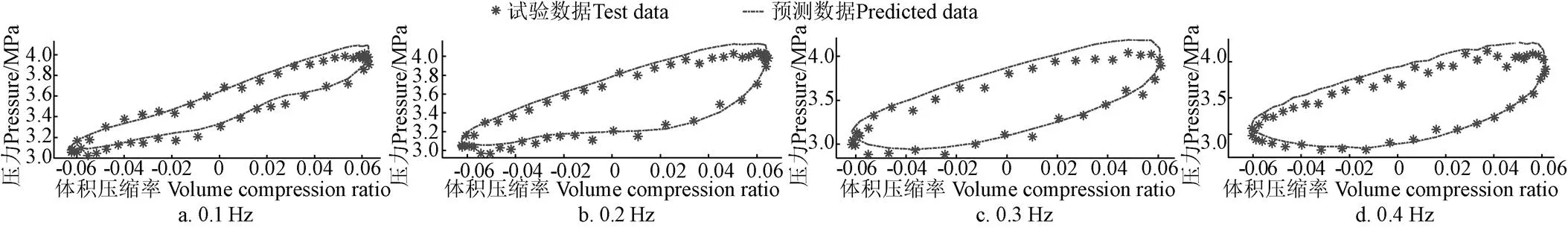
圖6 正弦激勵下氣體模型預測壓力與試驗數據對比(振幅20 mm,蓄能器充氣壓力1.5 MPa,充油壓力3.5 MPa)
3 整車油氣懸架系統性能驗證試驗
3.1 試驗儀器設備
為了進一步分析驗證真實氣體多變指數模型的適用性,多變指數模型中的1和2仍然保持不變,利用自主開發的整車懸架系統綜合性能測試平臺(圖7)進行了側傾工況試驗,試驗參數及設置如表2所示。
根據試驗臺的工作范圍,確定以下試驗內容:1)振幅20 mm,頻率為0.1~0.4 Hz的4種正弦激勵試驗;2)頻率為0.4 Hz,振幅為5~20 mm的4種正弦激勵試驗。
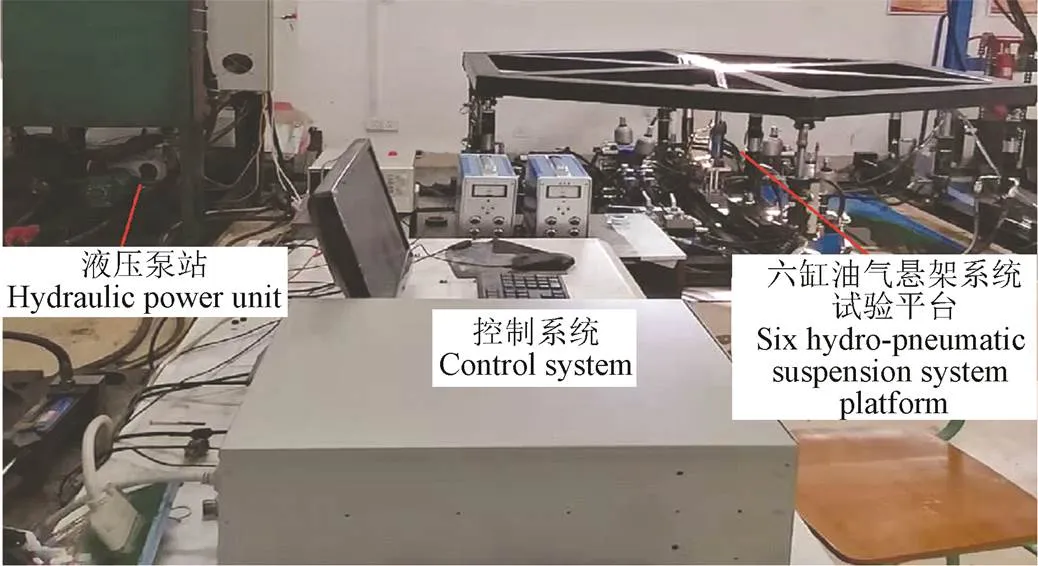
圖7 整車油氣懸架系統測試平臺
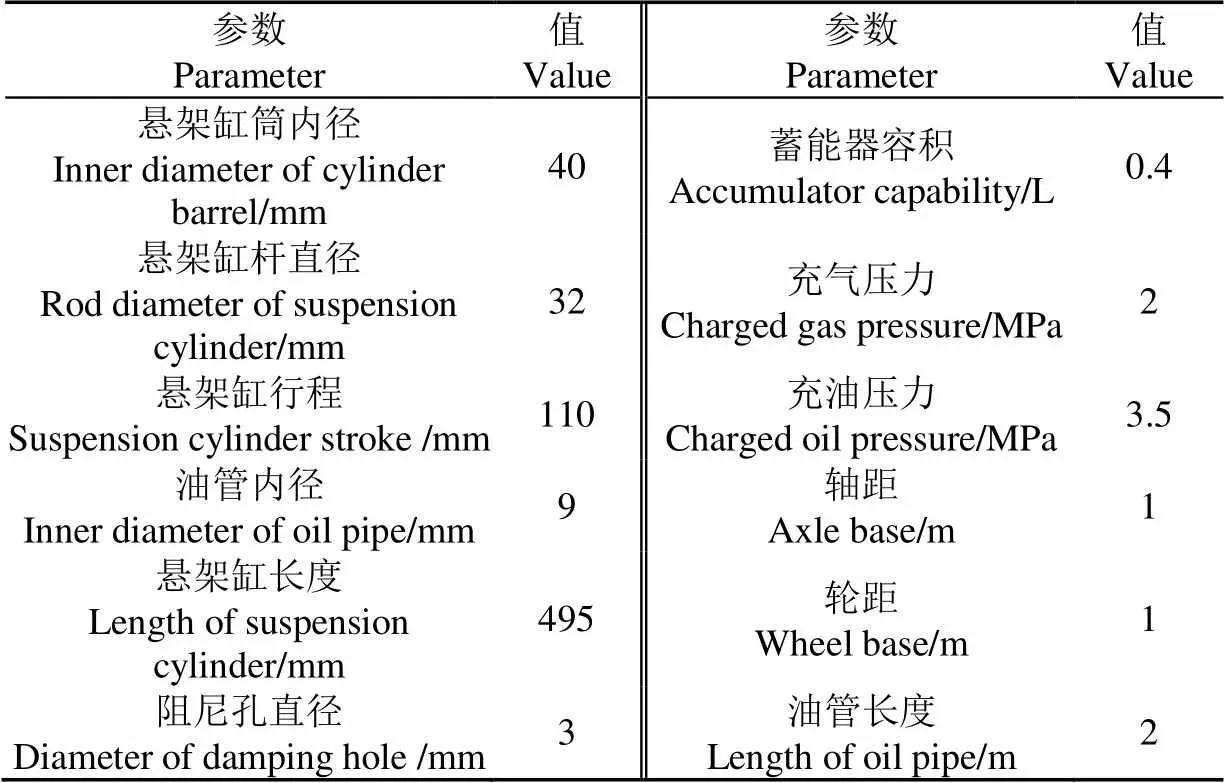
表2 測試平臺主要參數
試驗方法:通過控制正弦激勵的振幅和頻率,獲得不同激振幅值和頻率下的懸架系統的側傾力矩,驗證基于氣體多變指數模型的6缸油氣懸架系統聯合仿真模型的預測精度。
3.2 測試和仿真對比驗證
整車油氣懸架系統的側傾力矩測試和仿真對比結果如圖8和圖9所示。由圖可以看出,油氣懸架系統剛度(各曲線的極值點(2個頂點)連線的斜率)的預測值和測試結果具有很好的一致性。而油氣懸架系統的阻尼力(曲線的遲滯環的大小)預測結果和測試結果存在一定的偏差,最大誤差為10.9%,總體平均誤差為5.12%。因此,本文提出的真實氣體多變指數模型在一定范圍內具有較高的預測精度。
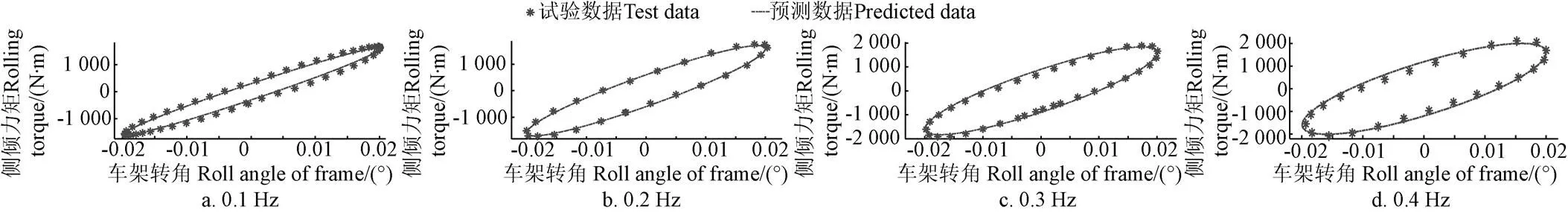
圖8 振幅20 mm下不同頻率正弦激勵的側傾力矩預測與試驗數據對比
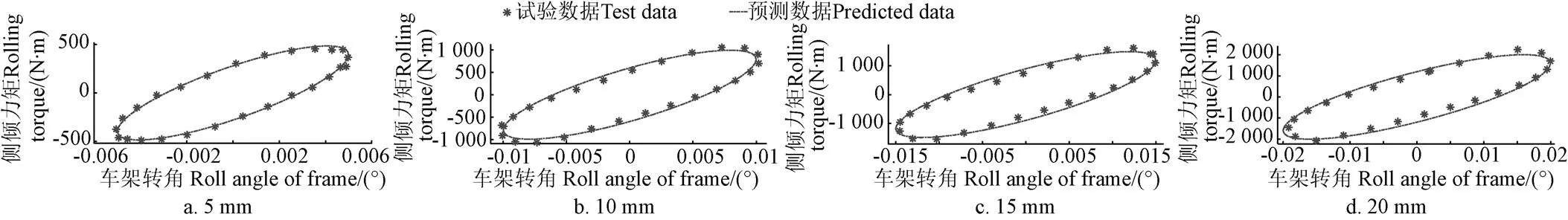
圖9 不同振幅正弦激勵的側傾力矩預測值與試驗數據對比(頻率0.4 Hz)
4 結 論
本文分析了油氣懸架系統蓄能器氮氣建模現狀及存在的問題,針對存在的問題開展研究,并取得以下成果:
1)通過蓄能器的試驗研究發現:真實的氮氣多變過程的2個主要影響因素為體積壓縮率和體積壓縮速率。
2)針對2個主要影響因素提出了一種新的氣體多變指數模型,該模型具有參數少、模型簡單、便于試驗辨識等優點。在研究范圍內,該模型的整體平均誤差小于4.05%,最大誤差為9.06%。
3)不同振幅和頻率的蓄能器和整車油氣懸架系統的試驗驗證表明:基于提出的真實氣體多變指數模型的油氣懸架系統仿真模型的預測結果和試驗數據的整體平均誤差為5.12%,最大誤差為10.9%,具有較高精度。
[1] S Francois van der Westhuizen, P Schalk Els. Comparison of different gas models to calculate the spring force of a hydropneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2015, 57: 41-59.
[2] 李仲興,郭子權,王傳建,等. 越野車用兩級壓力式油氣彈簧的建模與仿真[J]. 振動. 測試與診斷,2017,37(3):512-517,629.
Li Zhongxing, Guo Zhiquan, Wang Chuanjian, et al. Modeling and simulating of a two-stage pressure hydro-pnenumatic spring for off-road vehicle[J]. Journal of Vibration, Measurement & Diagnosis, 2017, 37(3): 512-517, 629. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 樂文超,時巖,彭安琪,等. 基于主動油氣懸架的某重型車平順性研究[J]. 振動與沖擊,2016,35(24):183-188.
Yue Wenchao, Shi Yan, Peng Anqi, et al. Study on ride comfort of a heavy vehicle based on active hydro-pneumatic suspension[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(24): 183-188. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 陳雨,陳隨英,杜岳峰,等. 基于摩擦阻尼的高地隙農機底盤懸架減振特性[J]. 農業工程學報,2016,32(7):51-57.
Chen Yu, Chen Suiying, Du Yuefeng, et al. Damping characteristics of chassis suspension system of high clearance agricultural machinery based on friction damper[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(7): 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Nieto A J, Morales A L, Gonza lez A, et al. An analytical model of pneumatic suspensions based on an experimental characterization[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2008, 313: 290-307.
[6] Yin Y, Rakheja S, Yang J, et al. Characterization of a hydro-pneumatic suspension strut with gas-oil emulsion[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 106: 319-333.
[7] 田文朋,易小剛,郭磊,等. 七橋混合耦連油氣懸架車輛仿真與試驗[J]. 中國機械工程,2018,29(9):1084-1089.
Tian Wenpeng, Yi Xiaogang, Guo Lei, et al. Simulation and experiments for seven spindled hybrid coupled hydro pneumatic suspension vehicles[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(9): 1084-1089. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 田文朋,楊宜坤,王偉. 油氣懸架耦連形式對車輛穩定性的影響[J]. 汽車工程,2017,39(12):1362-1367,1389.
Tian Wenpeng, Yang Yikun, Wang Wei. The influence of the interconnection forms of hydro-pneumatic suspension on vehicle stability[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(12): 1362-1367, 1389. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 孫會來,金純,張文明,等. 考慮驅動電機激振的電動車油氣懸架系統振動分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2014,30(12):51-57.
Sun Huilai, Jin Chun, Zhang Wenming, et al. Vibration analysis of hydro-pneumatic suspension system based on drive motor excitation force[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(12): 51-57. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] Yin Yuming, Rakheja Subhash, Boileau Paul-Emile. Multi- performance analyses and design optimisation of hydro-pneumatic suspension system for an articulated frame-steered vehicle[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2019, 57(1): 108-133.
[11] Cao D, Rakheja S, Su C Y. Roll-and pitch-plane coupled hydro-pneumatic suspension: Part 1: feasibility analysis and suspension properties[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(3): 361-386.
[12] Zhu Hengjia, Yang James, Yunqing Zhang. Modeling and optimization for pneumatically pitch-interconnected suspensions of a vehicle[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2018, 432: 290-309.
[13] Smith W A, Zhang N, Jeyakumaran J. Hydraulically interconnected vehicle suspension: theoretical and experimental ride analysis[J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2010, 48(1): 41-64.
[14] Kyuhyun Sim, Hwayoung Lee, Ji Won Yoon, et al. Effectiveness evaluation of hydro-pneumatic and semi-active cab suspension for the improvement of ride comfort of agricultural tractors[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 2017, 69: 23-32.
[15] Zheng Enlai, Zhong Xinyu, Zhu Rui, et al. Investigation into the vibration characteristics of agricultural wheeled tractor- implement system with hydro-pneumatic suspension on the front axle[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2019, 186: 14-33.
[16] Kat C J, Els P S. Validation metric based on relative error[J]. Mathematical and computer modelling of dynamical systems: methods, tools and application in engineering and related sciences, 2012, 18(5): 487-520.
[17] Cooper H W, Goldfranck J C. B-W-R constants and new correlations[J]. Hydrocarbon Processing, 1967, 46(12): 141-146.
[18] Otis D R, Pourmovahed A. An algorithm for computing nonflow gas processes in gas springs and hydro- pneumatic accumulators[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 1985, 107: 93-96.
[19] Els P S, Grobbelaar B. Investigation of the time- and temperature dependency of hydro-pneumatic suspension systems[J]. SAE Technical Paper Series, 1993, 3: 55-62.
[20] Pourmovahed A, Otis DR. An experimental thermal time constant correlation for hydraulic accumulators[J]. Transactions of the ASME, Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, 1990, 112: 116-121.
[21] Els P S, Grobbelaar B. Heat transfer effects on hydropneumatic suspension systems[J]. Journal of Terramechanics, 1999, 36: 197-205.
[22] 吳宏濤,張明. 油氣彈簧熱平衡仿真及試驗研究[J]. 車輛與動力技術,2007,107(3):37-40.
Wu Hongtao, Zhang Ming. Hydro-pneumatic spring thermal equilibrium simulation and test research[J]. Vehicle and Power Technology, 2007, 107(3): 37-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 陳軼杰,趙博,張旭,等. 基于隨機激勵的油氣懸掛溫升現象研究[J]. 機械強度,2010,32(6):869-872.
Chen Yijie, Zhao Bo, Zhang Xu, et al. Research on the temperature rise of hydro-pneumatic suspension under the random power[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 2010, 32(6): 869-872. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 黃夏旭,申焱華,楊玨,等. 基于集中參數熱模型法的自卸車油氣懸架系統熱分析[J]. 農業工程學報,2013,29(10):64-70.
Huang Xiaxu, Shen Yanhua, Yang Jue, et al. Thermal analysis of hydro-pneumatic suspension system for dumper based on a lumped-parameter thermal model[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(10): 64-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Victor Irizar, Casper Schousboe Andreasen. Hydraulic pitch control system for wind turbines: Advanced modeling and verification of an hydraulic accumulator[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2017, 79: 1-22.
[26] 范基,吳勁. 蓄能器的蓄能性能研究[J]. 液壓工業,1990(2):2-6.
[27] 封士彩. 氣囊式蓄能器氣體多變指數理論值和實際值的確定[J]. 液壓與氣動,2002(5):3-5.
Feng Shicai. Determining the air polytropic exponent value both theoretical and practical for bladder accumulator[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2002(5): 3-5. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 封士彩,徐勇,鹿洪禹. 工程車輛油氣懸架蓄能器性能的試驗研究[J]. 工程機械,2001(9):8-11,1.
Feng Shicai, Xu Yong, Lu Hongyu. Test and study for the performance of oil-gas suspension accumulators on engineering vehicles[J]. Construction Machinery and Equipment, 2001(9): 8-11,1. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 王德偉. 蓄能器充壓過程中氣體多變指數的確定[J]. 液壓與氣動,2007(9):78-79.
Wang Dewei. Determination of the gas polytropic exponent in the charge process of the energy accumulator[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2007(9): 78-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 吳曉元,陳忠基,王世東,等. 氣囊式蓄能器氣體多變指數值域的研究[J]. 鞍山科技大學學報,2003(3):204-220.
Wu Xiaoyuan, Chen Zhongji, Wang Shidong, et al. Study of range of air polytropic exponent value for bladder accumulator[J]. Journal of University of Science and Technology Liaoning, 2003(3): 204-220. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Establishment and verification of real gas multivariate index model for hydro-pneumatic suspension system
Wang Yunchao, Wei Bin, Yang Yuelin
(,,361021,)
One of the problems in the analysis of the dynamics performance of off-road vehicles is the effect of the accuracy of the hydro-pneumatic suspension model. However, the accuracy of the model for the polytropic process of nitrogen in the gas-charged hydraulic accumulator is one of the key factors, which affects the accuracy of the model for the hydro-pneumatic suspension systems. The traditional approach based on the energy equation and the Benedict-Webb-Rubin equations deduces the well-known thermal time constant model. However, researchers indicate that the thermal time constant varies with the change in the accumulator size and operating cases. Other researchers attempt to modify the multivariate index to model the real gas behavior, but the hysteresis loop representing the energy losses in a cycle can’t be described because the multivariate index is treated as a constant value. In this paper, an attempt was made to describe the hysteresis loop by adopting a variable multivariate index. On the accumulator rig, some tests excited by the sinusoidal displacement with four different amplitudes and frequencies respectively were carried out. The plots of the gas pressures versus the gas volume ratio and the gas volume rate respectively were made according to the experimental data from the accumulator test by using the Matlab software. A comprehensive analysis of experimental data showed that the relationship between the gas pressure and both the volume compression ratio and the volume compression rate were very close. To analyze the relationship between the multivariate index and the two parameters respectively, the formula of the multivariate index was deduced based on the ideal gas approach and multivariate index. By substituting the experimental data from the accumulator test into the formula, the plots of the multivariate index versus the two parameters respectively were also made. The plots illustrated that the multivariate index was closely proportional to the two parameters, respectively. Based on the analysis, a novel method was proposed to build a multivariate index model with the two parameters to describe the real gas behavior. In order to verify the correctness and the accuracy of the proposed multivariate index model, the two coefficients in the model were identified by using the experimental data from the previous accumulators test, and the coefficient of the volume compression ratio in the model was 2.4 for the test accumulator, and the coefficient of the volume compression rate was 1.5. Moreover, substituting the values of the two parameters, which were determined by the different operating cases, into the proposed multivariate index model with the two identified coefficients gave a comparison with these experimental data. Furthermore, a co-simulation model, which was based on the multivariate index model, for six hydro-pneumatic suspension systems was built to check the application of the multivariate index model in the hydro-pneumatic suspension systems of the overall vehicle. And a platform for the hydro-pneumatic suspension systems of the overall vehicle invented and designed by our laboratory, which was the first platform with the capability to test the comprehensive characteristics of multiple suspension systems, was used to test the rolling characteristics of the six hydro-pneumatic suspension systems. Several tests were carried out under the sinusoidal displacements with four different amplitudes and frequencies, respectively. The comparison of the co-simulation results and experimental data showed that the average discrepancy was equal to 5.12% and the maximum discrepancy was less than 10.9%. Therefore, a good correlation was achieved. It further demonstrated that the proposed multivariate index model can describe the behavior of the real nitrogen in the accumulator. But the proposed model should be further verified by using more experimental data from much higher frequency tests, and the influence of dissipated energy on the two coefficients in the proposed model should be explored.
vehicle; experiments; models; suspensions; hydraulic accumulator; hysteresis loops
王云超,魏 彬,楊岳霖. 油氣懸架囊式蓄能器真實氣體多變指數模型建立及驗證[J]. 農業工程學報,2019,35(20):10-16.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Wang Yunchao, Wei Bin, Yang Yuelin. Establishment and verification of real gas multivariate index model for hydro-pneumatic suspension system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(20): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.002 http://www.tcsae.org
2019-05-12
2019-09-29
國家自然科學基金資助項目(51575233)
王云超,教授,從事多軸車輛的轉向系統和懸架系統研究。Email:ychaowang@jmu.edu,cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.20.002
TH137.8+1
A
1002-6819(2019)-20-0010-07

