蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾幼蟲的捕食作用
唐藝婷 王孟卿 李玉艷 劉晨曦 毛建軍 陳紅印 張禮生


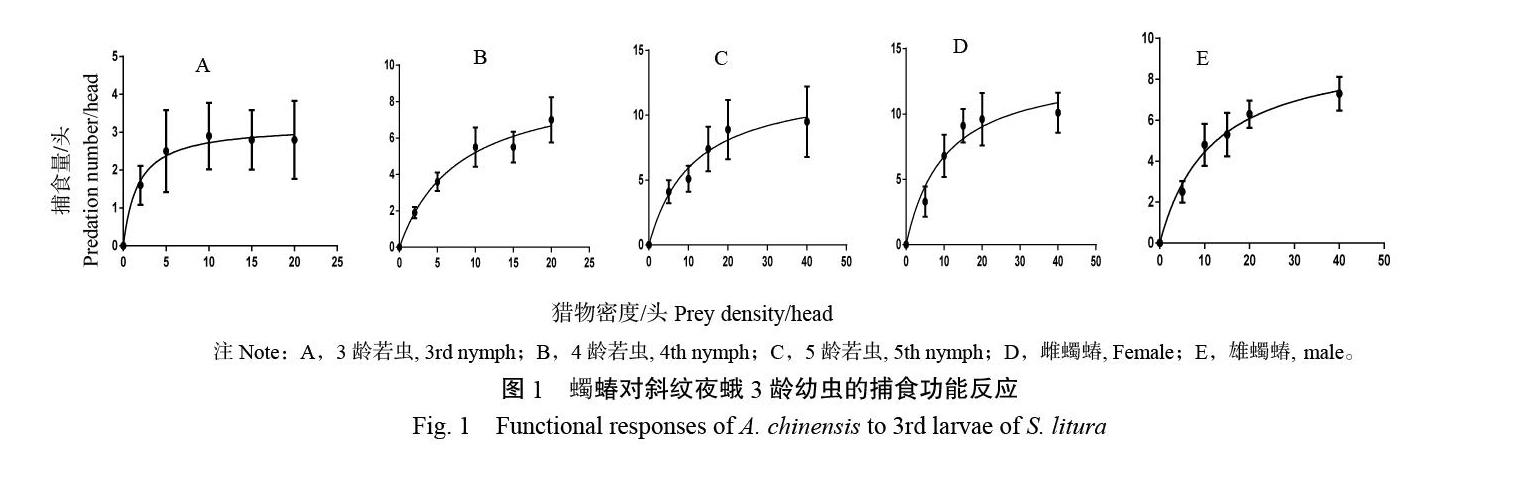
摘? 要:為明確蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾的捕食能力,在實驗室條件下進行蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲及成蟲對斜紋夜蛾3齡幼蟲的捕食能力測試,數據采用HollingⅡ功能反應模型進行擬合以明確其捕食潛能,利用Hassell模型擬合并測定了蠋蝽自身密度對斜紋夜蛾捕食作用的影響。結果表明,蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲及成蟲對斜紋夜蛾幼蟲的捕食模型均符合HollingⅡ模型;蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲和成蟲瞬時攻擊率順序是3齡(1.873)>雌成蟲(1.329)>4齡(1.187)> 5齡(1.125)>雄成蟲(0.828);蠋蝽雌成蟲的日最大捕食量最大,為13.699頭。隨著斜紋夜蛾3齡幼蟲密度增大,蠋蝽的搜尋效應逐漸降低,雌成蟲的搜尋效應明顯大于其他蟲態。隨著天敵蠋蝽密度增大,干擾增強,平均捕食量隨之降低。本研究顯示出蠋蝽雌成蟲對斜紋夜蛾具有較大的捕食潛能。
關鍵詞:蠋蝽;斜紋夜蛾;生物防治;功能反應
Predation ofArma chinensisonSpodoptera lituraLarvae
TANG Yiting, WANG Mengqing*, LI Yuyan, LIU Chenxi, MAO Jianjun, CHEN Hongyin, ZHANG Lisheng
(USDA-ARS Sino-American Biological Control Laboratory, Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193, China)
Abstract: In order to know the parasitoidism ofArma chinensis?onSpodoptera litura, the predation of 3-5 instar nymph and adult ofA.chinensisonS. liturawas studied in laboratory. Experimental data was fitted to the mathematical model HollingⅡ in which controlling effects were determined by parameters of preying potential capacity. The influences of the predators density functional response were determined by the mathematical model Hassell. The results showed that 3-5 instar nymph and adult predators exhibited Holling II functional responses, with the order of attacking efficiency being 3rd (1.873) >female (1.329) >4th(1.187) >5th(1.125)>male(0.828). The maximum daily predation number of female was 13.699. With the increase of preys density, predators searching effect decreases gradually, and the searching effect of female was obviously larger than that of other stages. As the density ofA. chinensissincreased, the interference was stronger and the average predation decreased. It indicated that femaleA. chinensishas a greater predation potential forS. litura.
Keywords:Arma chinensis;Spodoptera litura; biological control; functional response
斜紋夜蛾Spodoptera lituraFabricius屬鱗翅目,夜蛾科,是一種間歇性發生的世界性害蟲,在我國各地均有分布,為害嚴重。其幼蟲取食煙草、葡萄、棉花、辣椒等多種寄主植物,近年來,斜紋夜蛾對煙草的危害尤為嚴重,對煙葉品質和產量影響較大,其幼蟲啃食煙葉旺長期-采收期的中、下部,3齡后幼蟲進入暴食期,可轉移為害。嚴乃勝等[1]報道斜紋夜蛾在云南賓川煙草上大發生,發生嚴重的煙田被害植株率達90%以上,被害葉率在50%左右。利用生物防治的方法控制斜紋夜蛾符合國家綠色發展的要求,可提升煙葉品質。
目前已報道的防治斜紋夜蛾的捕食性天敵主要有紅彩真獵蝽Harpactor fuscipes(Fabrieius),叉角厲蝽CantheconideaFurcellat(Walff),煙盲蝽Crytopeltis tenuis (Reuter),蜘蛛等[2-6]。蠋蝽Arma chinensis?(Fallou)屬于半翅目Hemiptera,蝽科Pentatomidae,益蝽亞科Asopinae,是一種優良的天敵昆蟲,在我國多省均有分布,它的成蟲和若蟲均能夠捕食多種鱗翅目、鞘翅目、雙翅目等害蟲的成蟲和幼蟲[7]。張曉軍等[8]研究了蠋蝽對榆紫葉甲Ambrostoma quadriimopressum?Motschlsky的捕食作用,充分顯示了蠋蝽的捕食潛力。筆者也從田間和實驗室觀察到蠋蝽取食多種鱗翅目幼蟲和成蟲,如:二化螟Chilo suppressalis(Walker),甜菜夜蛾Spodoptera exiguaHübner,美國白蛾Hyphantria cunea(Drury),棉鈴蟲Helicoverpa armigera(Hübner),小菜蛾Plutella xylostella(L.)等。目前蠋蝽的人工飼料和大量飼養技術已經取得明顯的進展[9-13],但是關于蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾的捕食量數據目前還沒有報道。
本研究結果表明,蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲和成蟲均有較強的捕食能力,且捕食模型符合HollingⅡ圓盤方程,這與其他捕食蝽對獵物的捕食功能反應模型一致[2-6,17]。數據表明,蠋蝽雌成蟲處理斜紋夜蛾3齡幼蟲的時間最短只需0.073 d,其日最大捕食量13.699頭,控害效能為18.205,均較蠋蝽其他齡期以及雄成蟲高,與張曉軍等[8]研究結果蠋蝽捕食榆紫葉甲表現出蠋蝽5齡若蟲的捕食量最大有所不同,但是和紅彩真獵蝽[3],叉角厲蝽[4],蜘蛛[6]等研究結果一致,均是雌成蟲對斜紋夜蛾表現出最大捕食量。
蠋蝽的攻擊率順序表現為:3齡若蟲(1.873)>雌成蟲(1.329)>4齡若蟲(1.187)>5齡若蟲(1.125)>雄成蟲(0.828)。低齡若蟲(3齡)最積極,可能是3齡蠋蝽若蟲體積小,對于24 h的饑餓處理反應明顯,急于捕食。成蟲中雌蟲的攻擊率強于雄蟲因為雌性成蟲產卵需要更多的能量。
搜尋效應是捕食者在捕食過程中對寄主攻擊的一種行為效應,其模型為S=aTr/(1+aThN)[15]。通常情況下,隨著獵物密度增加,捕食者的搜尋效應會降低。本研究表明隨著斜紋夜蛾密度的增大,蠋蝽搜尋效應逐漸降低。在相同獵物密度下,蠋蝽雌成蟲對斜紋夜蛾的搜尋效應最大,搜尋能力較強。
蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲及成蟲捕食斜紋夜蛾平均捕食量,隨著天敵密度的增加而降低。利用Hassell模型(A=aP-b)能較好地反映出蠋蝽自身密度的干擾效應。其中蠋蝽雌成蟲對斜紋夜蛾3齡幼蟲的捕食量最大,與上述捕食功能反應表現一致。蠋蝽5齡若蟲和成蟲的自身密度干擾系數相對較小,說明體積大的蠋蝽更傾向于單獨捕食。
研究捕食者和獵物的相互作用有利于優化生防策略。本試驗通過建立的蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾的功能反應模型和自身密度干擾模型,明確了蠋蝽3~5齡若蟲和成蟲對斜紋夜蛾3齡幼蟲的的捕食量,以實現利用最小的釋放成本達到最佳的釋放目的。但本試驗是在室內,并且是在狹小的養蟲盒內下完成,而自然條件下存在諸多因素(氣候,溫濕度,降雨量)影響捕食者的捕食作用,因此還需要在本研究的基礎上,在田間進一步評價蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾自然種群的控制能力。
4 ?結? 論
根據本試驗結果,蠋蝽對斜紋夜蛾具有一定的捕食能力,在理論上通過釋放蠋蝽防治斜紋夜蛾是可行的。試驗研究表明,蠋蝽5齡若蟲和成蟲對斜紋夜蛾具有較強的捕食能力,在田間應用時可多釋放蠋蝽5齡若蟲和成蟲,盡快降低斜紋夜蛾種群數量,減少斜紋夜蛾對煙草的為害。
參考文獻
[1]???????? 嚴乃勝,羅佑珍,邱光鵬,等. 斜紋夜蛾的發育起溫度和有效積溫研究[J]. 云南農業大學學報,2000,15(1):21-23.
YAN N S, LUO Y Z, QIU G P, et al. Studies on development threshold temperature and effective temperature summation and themal constant of tobaccoSpodoptera litura[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University, 2000, 15(1): 21- 23.
- 謝建軍,胡美英,許再福. 斜紋夜蛾的天敵及其生物防治[J]. 昆蟲天敵,1999,21(2):82-92.
XIE J J, HU M Y, XU Z F. Nature enemies and biological control ofSpodoptera litura?Fabricius. Nature Enemy of Insects, 1999, 21(2): 82-92.
- 鄧海濱,王珍,陳永明,等. 紅彩真獵蝽對斜紋夜蛾和煙青蟲的捕食功能反應[J]. 廣東農業科學,2012,39(13):107-109.
DENG H B, WANG Z, CHEN Y M, et al. Predation of Harpactor fuscipes on Helicoverpa assulta andSpodoptera litura[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 39(13): 107-109.
- 陳然,梁廣文,張拯研,等. 叉角厲蝽對斜紋夜蛾的捕食功能反應[J]. 環境昆蟲學報,2015,37(2):401-406.
CHEN R, LIANG G W, ZHANG Z Y, et al. The functional response ofCahtheconidea furcellata(Hemiptera: Asopinae) toSpodoptera litura(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)[J]. Jouranal of Environment Entomology, 2015, 37(2): 401-406.
- 官寶斌,陳家驊,陳乾錦,等. 煙盲蝽對斜紋夜蛾幼蟲和煙蚜的捕食功能反應[J]. 中國煙草學報,1999,5(4):21-24.
GUAN B B, CHAN J H, CHEN Q J, et al. The predations capacity and functional response of?Crytopeltis tenuis?Renter to aphidius and larvae ofSpodoptera lituraFabricius[J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 1999, 5(4): 21-24.
- 秦厚國,葉正襄,丁建,等. 兩種蜘蛛對斜紋夜蛾捕食作用及模擬模型的研究[J]. 棉花學報,2002,14(2):126-129.
QIN H G, YE Z X, DING J, et al. Studies on predation and simulation models of two spider enemies onSpodoptera lituraFabricius[J]. Cotton Science, 2002, 14(2): 126-129.
- 鄒德玉,徐維紅,劉佰明,等. 天敵昆蟲蠋蝽的研究進展與展望[J]. 環境昆蟲學報,2016,38(4):857-865.
ZOU D Y, XU W H, LIU B M, et al.? Research progress and prospects ofArma chinensisFallou (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae)[J]. Jouranal of Environment Entomology, 2016, 38 (4): 857-865.
- 張曉軍,張健,孫守慧. 蠋蝽對榆紫葉甲的捕食作用[J]. 中國森林病蟲,2016,35(1):13-15.
ZHANG X J, ZHANG J, SUN S H. Predation ofArma?chinensis?on Ambrostoma quadriimopressum[J].?Forest Pest and Disease, 2016, 35(1): 13-15.
- 潘明真,張海平,張長華,等. 飼養密度和性比對蠋蝽存活和繁殖生物學特性的影響[J]. 中國生物防治學報,2018,34(1):52-58.
PAN M Z, ZHANG H P, ZHANG C H, et al. Effect of rearing density and ratio of adultArma chinensis?(Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) on their survl, fecundity and offsprings suitability[J].??Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2018, 34(1): 52-58.
- 李嬌嬌,張長華,易忠經,等. 三種獵物對蠋蝽生長發育和繁殖的影響[J]. 中國生物防治學報,2016,32(5):552-561.?
LI J J, ZHANG C H, YI Z J, et al. Effect of three prey species on development and fecundity of the predatory stinkbug Arma?chinensis?(Hemiptera: Pentatomidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2016, 32(5): 552 -561.
- ZOU D Y, COUDRON T A, LIU C, et al. Nutrigenomics in?Arma chinensis: transcriptome analysis of Arma chinensis?fed on artificial diet and Chinese oaksilk? moth?Antheraea pernyi?pupae[J]. PLoS ONE, 2013, 8(4): e60881.
- 廖平,苗少明,許若男,等. 新型蠋蝽若蟲液體人工飼料效果評價[J]. 中國生物防治學報,2019,35(1):9-14.
LIAO P, MIAO S M, XU R N, et al. Evaluation of a new liquid diet ofArma chinensis?(Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) [J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2019, 35(1): 9-14.
- 張健,周毓麟,孫守慧. 利用人工飼料連代飼養蠋蝽若蟲效果評價[J]. 中國森林病蟲,2017,36(4):37-40.
ZHANG J, ZHOU Y L, SUN S H. Rearing ofArma chinensis?(Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) on an artificial diet[J]. Forest Pest and Disease, 2017, 36(4): 37-40.
- HOLLING C S. Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism[J]. The Canadian Entomologist, 1959, 91(7): 385-398.
- 丁巖欽. 昆蟲數學生態學[M]. 北京:科學出版社,1994:257-258,303-304.
DING Q Y. Insect mathematical ecology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994: 257-258, 303-304.
- HASSEL M P. A population model for the interaction between?Cyzenisal bicans?(Fall) (Tachinidae) and?Opero phterabrumata(L.) (Geometridae) at Wytham, Berkshire[J]. Journal of Animal Ecology, 1969, 38(3): 567-576.
- 唐藝婷,郭義,何國瑋,等. 不同齡期的益蝽對粘蟲的捕食功能反應[J]. 中國生物防治學報,2018,34(6):825-830.
TANG Y T, GUO Y, HE G W, et al. Functional responses ofPicromerus lewisi?Scott (Hemiptera:? Pentatomidae) AttackingMythimna separata (Walker) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae)[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2018, 34(6): 825-830.

