云計算中基于多目標優化的虛擬機整合算法
胡志剛 肖慧 李克勤

摘? ?要:云數據中心中存在著高能耗和高服務水平協議違約率的問題,為了解決此問題,提出了一種基于多目標優化的虛擬機整合算法. 綜合考慮能耗、服務質量和遷移開銷等多種因素,將虛擬機整合問題構建為一個具有資源約束的多目標優化問題. 使用蟻群系統算法對該多目標優化問題進行求解,進行虛擬機整合,獲得近似最優的虛擬機主機映射關系. 為了減少算法復雜度,利用CPU利用率雙閾值來判斷主機負載狀態,根據主機負載狀態分階段進行整合并使用不同的整合策略. 基于CloudSim平臺對多目標優化的虛擬機整合算法和其他6種虛擬機整合算法進行仿真實驗,將本文算法與現有虛擬機整合算法實驗結果進行比較,結果表明本文提出的算法在能耗和服務水平協議違約方面優化顯著,具有較好的綜合性能.
關鍵詞:云計算;虛擬機整合;蟻群系統算法;節能;服務質量
中圖分類號:TP338.8? ? ? ??? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標志碼:A
Abstract:There exist problems of high energy consumption and high Service Level Agreement (SLA) violation rates in cloud data centers,which urgently need to be resolved. In order to solve the above problems,a Multi-objective Virtual Machine Consolidation Algorithm (MOVMC) was proposed to reduce energy consumption and SLA violation. Taking into account multiple factors including energy consumption,service quality and migration overhead,the virtual machine consolidation problem was constructed as a resource-constrained multi-objective optimization problem. Ant colony system algorithm was employed to perform virtual machine consolidation and obtain the near-optimal mapping relation between virtual machines and hosts as the solution to the multi-objective optimization problem. In order to reduce the algorithm complexity,the double thresholds of CPU utilization were leveraged to judge the host load status and a multi-stage consolidation was performed according to the host load status,in which different consolidation strategies were used. Simulation experiments were conducted on CloudSim platform for MOVMC algorithm and six other virtual machine consolidation algorithms. The experimental results show that,compared with the existing virtual machine consolidation algorithm,the proposed algorithm has significant optimization in terms of energy consumption and SLA violation,and an excellent comprehensive performance.
Key words:cloud computing;virtual machine consolidation;ant colony system;energy saving;quality of service
近年來,隨著云計算商業模式和技術架構的越來越成熟,云用戶大幅度增加,為了滿足他們的需求而新建的數據中心、新置的服務器和制冷設備也隨之大幅度增加,解決數據中心的高能耗問題已經成為一個大的挑戰[1]. 同時,云用戶對云服務的性能需求也愈加具體嚴格化,用戶在交易前會與云服務商制定服務水平協議(Service Level Agreement,SLA)來規范化質量等級(Quality of Service,QoS)需求,以確保本次服務交易的完美達成[2]. 如果云服務商無法提供事先商定的QoS,違背用戶的期望,會給用戶造成不可預估的損失. 因此,在減少數據中心能耗的同時,提供用戶所期望的QoS是云計算發展迫切需要解決的問題.
虛擬機整合[3]可以根據變化的資源需求周期性地調整當前的虛擬機主機間映射關系,在主機間遷移虛擬機以充分并均衡地利用計算資源. 虛擬機整合技術主要包括啟發式貪心算法[4-7]、線性/約束規劃技術[8-11]和元啟發式算法[12-15]. 貪心算法因其時間復雜度低、實現簡單等優點被廣泛應用來進行虛擬機動態整合. 貪心算法雖然計算開銷低,但卻容易陷入局部最優而錯過最優解. 線性/約束規劃技術可以獲得最優解,但受問題規模和復雜性的限制,無法很好地擴展到大型數據中心. 近年來研究人員提出了許多基于生物啟發計算的元啟發整合算法,例如蟻群算法、基因算法、人工蜂群算法,可以有效幫助解決大規模問題并避免局部最優解. 蟻群系統算法(Ant Colony System,ACS)[16-17],作為蟻群算法的一種,通過在解空間中進行基于概率式的搜索,可以在多項式時間復雜度里找到近似最優解.
現有的虛擬機整合研究大多只關注了云數據中心的能耗問題. 然而,為了實現云系統交付的QoS,還應該同時考慮SLA違約問題. 虛擬機整合可以通過將虛擬機整合到盡可能少的主機上來降低能耗,然而過分整合可能會降低系統性能并導致SLA違
約[18]. 因此,最優虛擬機整合方法應在能耗和QoS之間取得平衡.
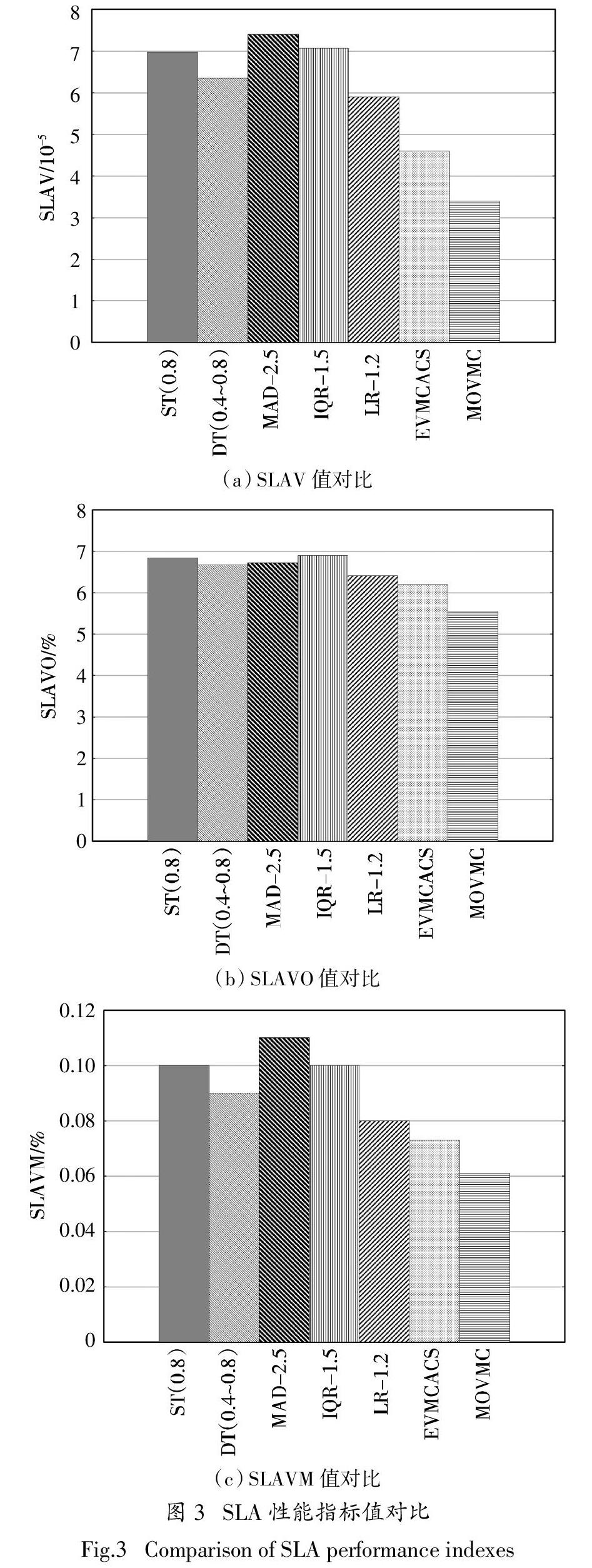
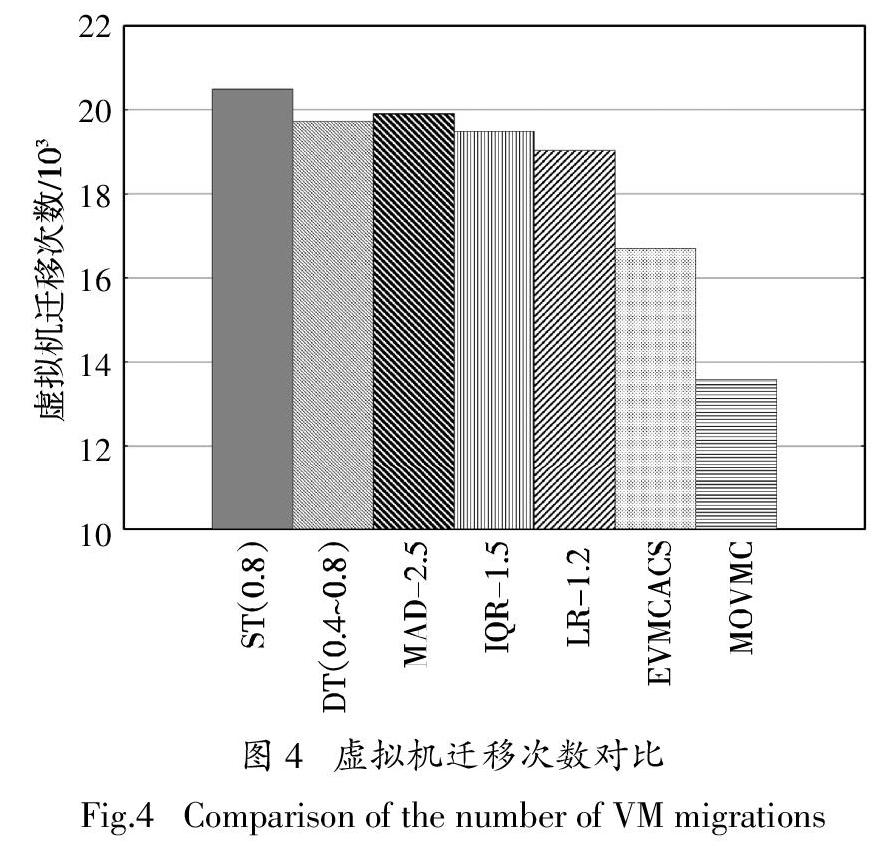
本文將虛擬機整合問題構建為一個多目標組合優化問題,優化目標包括降低能耗、保證QoS要求和減少遷移次數,提出了一種基于多目標優化的虛擬機整合算法(Multi-objective Virtual Machine Consolidation,MOVMC). 首先使用CPU利用率雙閾值[4]來判斷主機負載狀態,確定整合時機;然后基于ACS假設虛擬機和主機之間的映射關系是食物源,使用人工蟻群同時選擇待遷移虛擬機和目標主機,尋找虛擬機和主機之間的最佳映射關系. 通過在CloudSim平臺上使用真實工作負載來評估所提出的方法. 實驗結果表明,該方法在減少能耗、SLA違約和虛擬機遷移方面具有明顯的優勢.
4? ?結? ?論
本文提出了一種基于多目標組合優化的虛擬機整合算法,通過將虛擬機整合到合適的主機中來解決數據中心中高能耗和QoS降級的問題. 虛擬機整合問題被構建為一個多目標優化問題,基于雙閾值決定觸發虛擬機整合的條件. 將虛擬機與主機之間的映射關系比作食物源,基于ACS通過多階段整合來優化映射關系. 通過人工螞蟻的分布式搜索和協作,獲得虛擬機與主機之間的全局最優映射關系. 使用實際工作負載對所提出方法的性能進行評估,仿真結果表明,與其他方法相比,該方法能有效降低數據中心的能耗,并保證高水平QoS.
在未來的工作中,進一步研究在整合時間決策過程中,針對不斷變化的工作負載采用自適應閾值,做出更合理的遷移決策. 進行更多的仿真實驗來評估所提出的方法在實際工作負載中的性能.
參考文獻
[1]? ? 蔡立軍,何庭欽,孟濤,等. 基于層次拓撲樹的虛擬機節能分配算法[J].湖南大學學報(自然科學版),2017,44(2):137—148.
CAI L J,HE T Q,MENG T,et al. A network-aware two-phase virtual machine allocation algorithm[J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences),2017,44(2):137—148.(In Chinese)
[2]? ? ARDAGNA D,CASALE G,CIAVOTTA M,et al. Quality-of-service in cloud computing:modeling techniques and their applications[J]. Journal of Internet Services & Applications,2014,5(1):11—17.
[3]? ?FILHO M C S,MONTEIRO C C,IN?CIO P R M,et al. Approaches for optimizing virtual machine placement and migration in cloud environments:A survey[J]. Journal of Parallel & Distributed Computing,2017,111:222—250.
[4]? ?BELOGLAZOV A,ABAWAJY J,BUYYA R. Energy-aware resource allocation heuristics for efficient management of data centers for cloud computing[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems,2012,28(5):755—768.
[5] BELOGLAZOV A,BUYYA R. Optimal online deterministic algorithms and adaptive heuristics for energy and performance efficient dynamic consolidation of virtual machines in cloud data centers[J]. Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience,2012,24(13):1397—1420.
[6]? ? ZHOU Z,ABAWAJY J,CHOWDHURY M,et al. Minimizing SLA violation and power consumption in cloud data centers using adaptive energy-aware algorithms[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems,2018,86:836—850.
[7]? ?LI M F,BI J P,LI Z C. Improving consolidation of virtual machine based on virtual switching overhead estimation[J]. Journal of Network and Computer Applications,2016,59:158—167.
[8]? ?CHEN X,TANG J R,ZHANG Y. Towards a virtual machine migration algorithm based on multi-objective optimization[J]. International Journal of Mobile Computing & Multimedia Communications,2017,8(3):79—89.
[9]? ?CHEN L H,SHEN H Y,PLATT S. Cache contention aware virtual machine placement and migration in cloud datacenters[C]// 2016 IEEE 24th International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP). Singapore: IEEE,2016:1—10.
[10]? JOO K N,KIM S,KANG D K,et al. A VM vector management scheme for QoS constraint task scheduling in cloud environment[C]// International Conference on Cloud Computing. Korea:Springer International Publishing,2015:39—49.
[11]? HUANG Z,TSANG D H K. M-convex VM Consolidation:Towards a better VM workload consolidation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing,2016,4(4):415—428.
[12]? LI Z,YAN C,YU L,et al. Energy-aware and multi-resource overload probability constraint-based virtual machine dynamic consolidation method[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems,2018,80:139—156.
[13]? MOSA A,PATON N W. Optimizing virtual machine placement for energy and SLA in clouds using utility functions[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing,2016,5(1):1—17.
[14]? LI H J,ZHU G F,CUI C Y,et al. Energy-efficient migration and consolidation algorithm of virtual machines in data centers for cloud computing[J]. Computing,2016,98(3):303—317.
[15]? ARYANIA A,AGHDASI H S,KHANLI L M. Energy-aware virtual machine consolidation algorithm based on ant colony system[J]. Journal of Grid Computing,2018,16(3):477—491.
[16]? DORIGO M,CARO G D,GAMBARDELLA L M. Ant algorithms for discrete optimization[J]. Artificial Life,1999,5(2):137—172.
[17] DORIGO M,GAMBARDELLA L M. Ant colony system:A cooperative learning approach to the traveling salesman problem[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation,1997,1(1):53—56.
[18]? ZHAO H,WANG J,LIU F,et al. Power-aware and performance-guaranteed virtual machine placement in the cloud[J]. IEEE Transactions on Parallel & Distributed Systems,2018,29(6):1385—1400.
[19]? 吳小東,韓建軍. 云數據中心基于閾值的虛擬機遷移節能調度算法[J]. 華中科技大學學報(自然科學版),2018,46(9):30—34.
WU X D,HAN J J. Threshold-based energy-efficient VM scheduling in cloud datacenters[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology(Natural Sciences),2018,46(9):30—34. (In Chinese)
[20]? ZHENG Q H,LI R,LI X Q,et al. A multi-objective biogeography-based optimization for virtual machine placement[C]//2015 15th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster,Cloud and Grid Computing. Shenzhen:IEEE,2015:687—696.
[21]? CHEN Q,CHEN J X,ZHENG B Y,et al. Utilization-based VM consolidation scheme for power efficiency in cloud data centers[C]// IEEE International Conference on Communication Workshop. London:IEEE,2015:1928—1933.
[22]? LI Z H,YAN C Y,YU X R,et al. Bayesian network-based Virtual Machines consolidation method[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems,2018,16(3):477—491.
[23]? ZHANG F,LIU G,FU X,et al. A survey on virtual machine migration:challenges,techniques and open issues[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials,2018,20(2):1206—1243.
[24]? CALHEIROS R N,RANJAN R,BELOGLAZOV A,et al. CloudSim:a toolkit for modeling and simulation of cloud computing environments and evaluation of resource provisioning algorithms[J]. Software:Practice and Experience,2011,41(1):23—50.
[25]? DURAO F,CARVALHO J F S,FONSEKA A,et al. A systematic review on cloud computing[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing,2014,68(3):1321—1346.
[26]? PARK K S,PAI V S. COMON:A mostly-scalable monitoring system for planetlab[J]. ACM Sigops Operating Systems Review,2006,40(1):65—74.

