頸項(xiàng)透明層結(jié)合孕中期血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)在雙胎唐氏篩查中的價(jià)值評(píng)估
林廣城 夏成靜 譚燕清 池瑞招 李貴芹

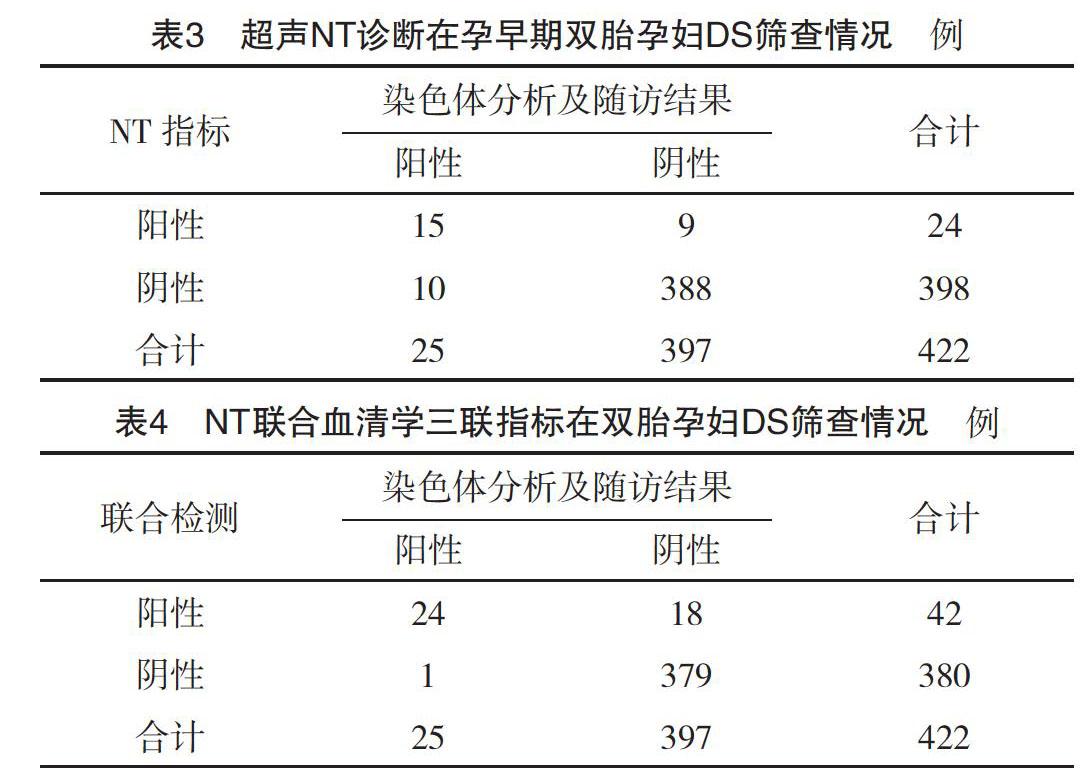
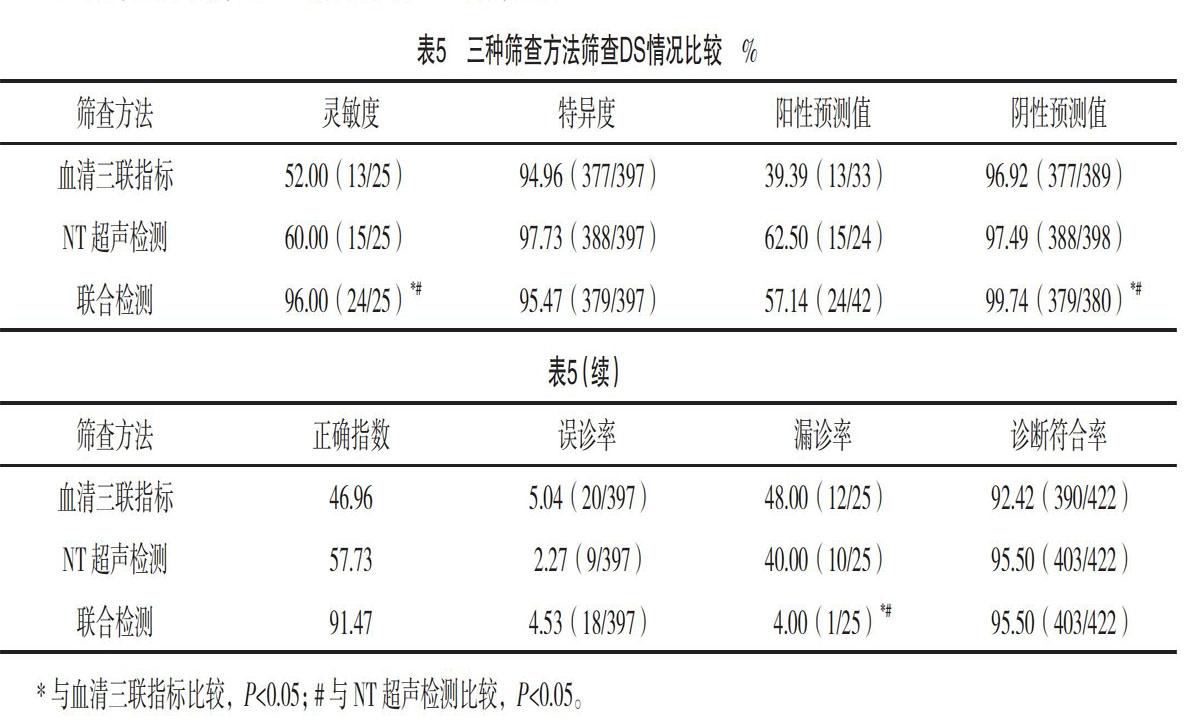
【摘要】 目的:探討孕早期頸項(xiàng)透明層(NT)結(jié)合孕中期血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)對(duì)雙胎妊娠唐氏綜合征(DS)篩查的應(yīng)用效果。方法:選取2017年7月-2019年6月于深圳市龍崗區(qū)第七人民醫(yī)院、深圳市光明新區(qū)人民醫(yī)院及中山大學(xué)第八附屬醫(yī)院產(chǎn)前診斷科進(jìn)行圍產(chǎn)保健的雙胎妊娠孕婦422例,均于妊娠11~13+6周行胎兒NT超聲檢測(cè),并于妊娠14~19周測(cè)定血清甲胎蛋白(alpha fetoprotein,AFP)、β-人絨毛膜促性腺激素(β-human chorionic gonadotro,β-hCG)和游離雌三醇(uncojugated estriol,uE3)濃度。以染色體分析及隨訪結(jié)果作為金標(biāo)準(zhǔn),分析NT、血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)(AFP+β-hCG+uE3)及兩者聯(lián)合檢測(cè)的DS篩查價(jià)值。結(jié)果:有25例確診為DS。血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)DS篩查陽(yáng)性率為7.82%(33/422);NT超聲DS篩查陽(yáng)性率為5.69%(24/422);聯(lián)合檢測(cè)DS篩查陽(yáng)性率為9.95%(42/422)。均聯(lián)合檢測(cè)的靈敏度(96.00%)均高于血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)(52.00%)與NT超聲(60.00%),而漏診率(4.00%)低于血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)(48.00%)與NT超聲(40.00%),差異均有統(tǒng)計(jì)學(xué)意義(P<0.05)。結(jié)論:孕早期NT聯(lián)合孕中期血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo)檢測(cè)可保證特異度,顯著提高靈敏度、降低漏診率,對(duì)DS篩查具有臨床意義。
【關(guān)鍵詞】 頸項(xiàng)透明層 血清三聯(lián)指標(biāo) 雙胎妊娠 唐氏綜合征
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the application effect of early pregnancy nuchal translucency (NT) combined with serum triple index in the second trimester on twin pregnancy Downs syndrome (DS) screening. Method: From July 2017 to June 2019, 422 twin pregnancy women received perinatal care in the prenatal diagnosis department of the Shenzhen Longgang District Seventh Peoples Hospital, Shenzhen Guangming New District Peoples Hospital and Sun Yat-sen University Eighth Affiliated Hospital were selected. All of them received NT ultrasound detection at 11-13+6 weeks of gestation. And serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP), β-human chorionic gonadotro (β-hCG) and uncojugated estriol (uE3) were measured at 14 to 19 weeks of gestation. The results of chromosome analysis and follow-up were used as the gold standard to analyze the DS screening value of NT, serum triple index (AFP + β-hCG + uE3) and the combination of both. Result: There were 25 confirmed cases of DS. The DS screening positive rate of serum triple index was 7.82% (33/422). The DS screening positive rate of NT ultrasound was 5.69% (24/422). The DS screening positive rate of combined detection was 9.95% (42/422). The sensitivity of combined detection (96.00%) were higher than those of serum triple index (52.00%) and NT ultrasound (60.00%), while the rate of missed diagnosis (4.00%) were lower than those of serum triple index (48.00%) and NT ultrasound (40.00%), the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: NT in early pregnancy combined with serum triple index in the second trimester detection can ensure specificity, significantly improve sensitivity, and reduce the rate of missed diagnosis, which has clinical significance for DS screening.[Key words] Nuchal translucency Serum triple index Twin pregnancy Downs syndromeFirst-authors address: Seventh Peoples Hospital of Longgang District in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518114, China
唐氏綜合征(Downs syndrome,DS)即21-三體綜合征是人類最常見(jiàn)的染色體異常引起的疾病,臨床表現(xiàn)以中到重度智力及體格發(fā)育障礙為主,由于缺乏有效的治療手段,患兒的出生將給家庭及社會(huì)帶來(lái)沉重的精神和經(jīng)濟(jì)負(fù)擔(dān),因此產(chǎn)前診斷DS并及時(shí)終止妊娠,降低此類患兒的出生,對(duì)于減輕家庭社會(huì)負(fù)擔(dān),提高人口素質(zhì)有重要意義[1-2]。據(jù)統(tǒng)計(jì),雙胎妊娠孕婦懷有DS胎兒的概率遠(yuǎn)高于單胎妊娠孕婦,而隨著我國(guó)生育政策的放寬和輔助生殖技術(shù)的發(fā)展,雙胎妊娠率逐年升高[3]。然而,對(duì)于雙胎妊娠孕婦胎兒DS的篩查仍是目前國(guó)內(nèi)外DS產(chǎn)前篩查的一個(gè)盲區(qū)[4]。……

