VitalStim電刺激對腦梗死伴吞咽障礙患者康復訓練效果的影響
李曉純 周尤成 張明霞 李廣興

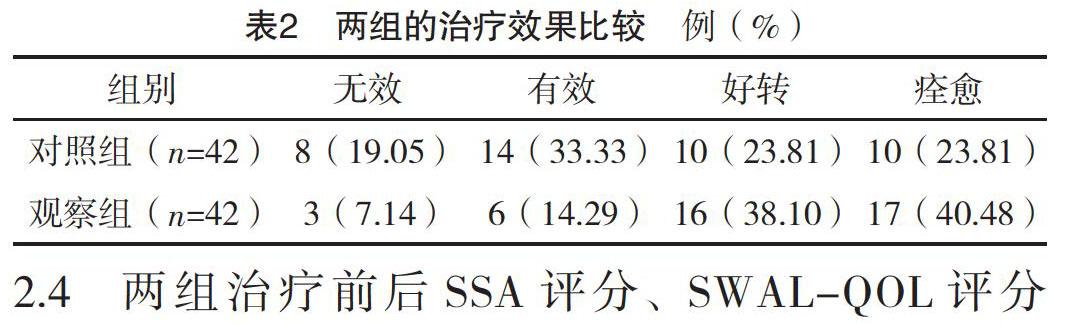

【摘要】 目的:觀察VitalStim電刺激對腦梗死伴吞咽障礙患者康復訓練效果的影響。方法:選取2017年5月-2018年5月于本院住院的腦梗死伴吞咽困難的中老年患者84例為研究對象,通過隨機抽簽將所有患者分為兩組,奇數號為對照組,偶數號為觀察組,每組42例。對照組給予常規治療與吞咽功能康復訓練,觀察組在對照組的基礎上實施VitalStim電刺激治療。治療4周后兩組通過洼田飲水試驗和標準吞咽功能評估量表(SSA)評估吞咽功能,采用吞咽障礙特異性生活質量量表(SWAL-QOL)評價生活質量。結果:治療4周后,兩組吞咽功能分級情況比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。治療4周后,觀察組治療效果優于對照組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。治療4周后,兩組的SSA評分均低于治療前,且觀察組低于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05);治療4周后,兩組的SWAL-QOL評分均高于治療前,且觀察組高于對照組,差異均有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論:電刺激療法可提高腦梗死伴吞咽障礙患者康復訓練的療效,改善生存質量。
【關鍵詞】 電刺激 腦梗死 吞咽障礙 康復訓練
[Abstract] Objective: To observe the effect of VitalStim electric stimulation on rehabilitation training of patients with cerebral infarction and swallowing disorder. Method: A total of 84 middle-aged and elderly patients with cerebral infarction and dysphagia hospitalized in our hospital from May 2017 to May 2018 were selected as the study objects. All the patients were randomly drawn, the odd number was the control group, the even sign was the observation group, 42 cases in each group. The control group was given routine treatment and rehabilitation training of swallowing function, the observation group was treated with VitalStim on the basis of the control group. After 4 weeks of treatment, SWAL-QOL was used to evaluate the quality of life (QOL), and SWAL-QOL was used to evaluate the swallowing function by drinking water test and standard swallowing function assessment scale (SSA). Result: After 4 weeks of treatment, comparison of swallowing function grades between the two groups, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After 4 weeks of treatment, the treatment effect of the observation group was better than that of the control group, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After 4 weeks of treatment, both groups had lower SSA scores than those before treatment, and the observation group was lower than that of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After 4 weeks of treatment, both groups had higher SWAL-QOL scores than those before treatment, and the observation group was higher than that of the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion: Electrical stimulation therapy can improve the effect of rehabilitation training for patients with cerebral infarction with dysphagia and improve the quality of life.[Key words] Electrical stimulation Cerebral infarction Swallowing disorder Rehabilitation trainingFirst-authors address: Foshan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Foshan 528000, China
腦梗死是一種發病率較高的心腦血管疾病,發病人群主要為中老年,腦梗死后常見并發癥包括吞咽障礙,有研究表明,30%~65%腦梗死患者可并發吞咽障礙,43%~54%有吞咽障礙患者會出現誤吸[1]。臨床上,腦梗死又稱缺血性腦卒中,約37%的患者在發生肺炎等一系列并發癥后需要鼻飼飲食。鼻飼飲食不但會給患者帶來巨大的痛苦,而且家屬認可率低。吞咽困難是食物誤吸入氣道引發肺炎的重要因素之一[2]。傳統的治療方法是在常規治療的基礎上,進行早期物理康復訓練包括基礎吞咽功能訓練、聲門開閉訓練和飲食過程訓練等,加強患者自我控制能力,通過反復訓練,在中樞神經系統建立新的吞咽反射。經臨床試驗顯示,這種方法在患者腦梗死后早期確實有效,但耗時長,需要患者完全配合,作用局限性大。……

