老年糖尿病患者合并感染后胰島素泵強化治療的有效性分析
陳豐收 鄭妹容
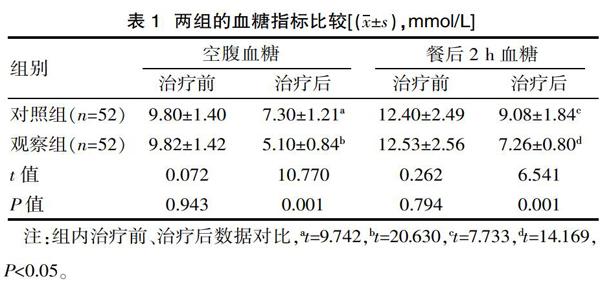
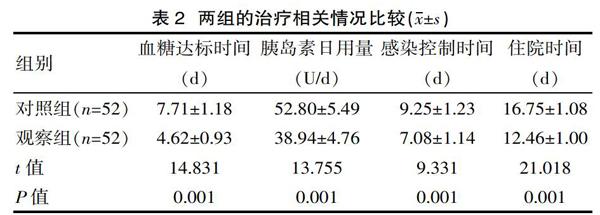
[摘要] 目的 研究老年糖尿病患者合并感染后胰島素泵強化治療的有效性。方法 該次納入2018年5月—2019年4月收治的104例老年糖尿病合并感染患者展開研究,按照隨機數(shù)字表法分為兩組,對照組52例予以胰島素皮下注射治療,觀察組52例實施胰島素泵強化治療。將兩組的血糖指標(biāo)、治療相關(guān)情況進行比對。結(jié)果 觀察組老年糖尿病合并感染患者治療后的空腹血糖、餐后2 h血糖均低于對照組,血糖達標(biāo)時間、感染控制時間、住院時間短于對照組,胰島素日用量少于對照組(P<0.05)。結(jié)論 胰島素泵強化治療老年糖尿病合并感染患者的血糖控制及感染控制效果顯著。
[關(guān)鍵詞] 糖尿病;感染;胰島素泵;血糖
[中圖分類號] R587.2? ? ? ? ? [文獻標(biāo)識碼] A? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1672-4062(2020)03(a)-0052-03
Effectiveness of Intensive Insulin Pump Therapy in Elderly Patients with Diabetes Complicated by Infection
CHEN Feng-shou1, ZHENG Mei-rong2
1.Department of Emergency, Quanzhou First Hospital, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, 362000 China; 2.Physical Examination Center, Quanzhou First Hospital, Quanzhou, Fujian Province, 362000 China
[Abstract] Objective To study the effectiveness of intensive insulin pump therapy in elderly patients with diabetes complicated by infection. Methods A total of 104 elderly patients with diabetes complicated with infection who were treated from May 2018 to April 2019 were included in this study. They were divided into two groups according to the random number table method. 52 patients in the control group were treated with subcutaneous insulin injection and 52 patients in the observation group Intensive insulin pump treatment. The blood glucose indexes and treatment-related conditions of the two groups were compared. Results The fasting blood glucose and 2h postprandial blood glucose of elderly patients with diabetes and infection in the observation group were lower than those in the control group. The blood glucose reaching time, infection control time, and hospitalization time were shorter than those in the control group. It has statistical significance(P<0.05). Conclusion Insulin pump intensive treatment of elderly patients with diabetes and infection has significant blood glucose control and infection control effect.
[Key words] Diabetes; Infection; Insulin pump; Blood glucose
慢性病發(fā)生率隨著人口老齡化進程的加快、人們生活方式的改變而不斷升高,糖尿病是臨床常見且多發(fā)的慢性疾病,近年來糖尿病的發(fā)病率呈現(xiàn)逐年增長的趨勢,老年人為高發(fā)群體。若是糖尿病患者的血糖水平長期未得到有效控制,會對患者的多個系統(tǒng)、組織造成損害,另外老年糖尿病患者存在機體功能減退、免疫功能下降等情況,容易出現(xiàn)感染癥狀,加重病情且增加了臨床治療難度[1-2]。胰島素在糖尿病合并感染的治療中較為常用,以往常規(guī)胰島素皮下注射雖可在一定程度上控制血糖水平,但出現(xiàn)低血糖等不良事件的可能性較大,且需反復(fù)多次注射,會導(dǎo)致患者的依從性降低,進而影響臨床療效。因此該文納入2018年5月—2019年4月收治的104例老年糖尿病合并感染患者進行研究,對胰島素泵強化治療該病的效果進行分析,以常規(guī)胰島素皮下注射治療為對照,旨在為臨床治療老年糖尿病合并感染患者選擇更加有效、安全的方法,現(xiàn)報道如下。……

