THE COMMUTATOR TYPE AND THE LEVI FORM TYPE IN C3
YIN Wan-ke,YUAN Ping-san,CHEN Ying-xiang
(School of Mathematics and Statistics,Wuhan University,Wuhan 430072,China)
Abstract:For any fixed(1,0)vector field of a pseudoconvex hypersurface in C3,we prove that its commutator type and Levi form type are equal to each other.This answers affirmatively a problem of D’Angelo in complex dimension three.
Keywords:finite type;pseudoconvex hypersurface;Bloom conjecture;sub-elliptic estimates
1 Introduction
The finite type conditions gave their rise from the investigation of the subellipticity of the-Neumann operator.For any boundary point of a smooth pseudoconvex domain in C2,Kohn[1]introduced three kinds of integer invariants,which are respectively the regular contact type,the commutator type and the Levi form type.Kohn proved that these invariants are equal to each other.When they are finite at a boundary point,the domain possesses local sub-elliptic estimates near this point.The domain is said to be of finite type if these invariants are finite at each boundary point of the domain.
Ever since then,much attention paid to generalize these finite type conditions to the higher dimensional case.Kohn[2]defined the subelliptic multiplier ideals near each boundary point of a pseudoconvex domain,and if 1 is in any of these ideals,the boundary point is said to be of finite ideal type.In[3],D’Angelo introduced the D’Angelo finite type condition in terms of the order of contact with respect to singular complex analytic varieties.Both of these finite type conditions imply the existence of the sub-elliptic estimates.Bloom[4]generalized Kohn’s type conditions in C2directly to higher dimensional spaces.More precisely,for a smooth real hypersurfaceM?Cnandp∈M,Bloom defined the regular contact typea(s)(M,p),the commutator typet(s)(M,p)and the Levi-form typec(s)(M,p)ofMatp.Bloom conjectured in[4]that these three invariants are the same when the hypersurface is pseudoconvex,which is known as the Bloom conjecture.Bloom-Graham[5]and Bloom[6]proved the conjecture fors=n?1.In[4],Bloom showed thata(1)(M,p)=c(1)(M,p)whenM?C3.Recently,Huang-Yin[7]proved that the Bloom conjecture holds fors=n?2.This,in particular,gave a complete solution of the conjecture in complex dimension 3.
For a fixed(1,0)type vector fieldLat a pointpof a smooth real hypersurface,D’Angelo introduced the commutator typet(L,p)and the Levi form typec(L,p).
In fact,letM?Cnbe a smooth real hypersurface withp∈M,and letρbe a defining function ofMnearp.Denote byM1(L)theC∞(M)-module spanned byLandFor anyk≥1,we inductively defineMk(L)to be theC∞(M)-module spanned byMk?1(L)and the elements of the of form[X,Y]withX∈Mk?1(L)andY∈M1(L).We say the commutator typefor anyF∈Mm?1(L)butfor a certainG∈Mm(L).We define the Levi form typec(L,p)=mif for anym?3 vector if eldsF1,···,Fm?3ofM1(L),we have
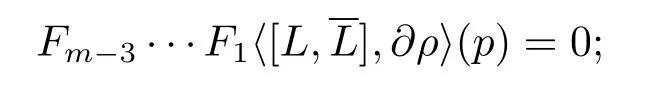
and for a certain choice ofm?2 vector fieldsG1,···,Gm?2ofM1(L),we have
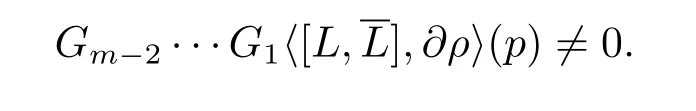
D’Angelo[8]conjectured that these two types equal to each other when the real hypersurface is pseudoconvex.He confirmed the conjecture when one of the type is exactly 4.The present paper is devoted to proving this conjecture when the real hypersurface is in C3.
Theorem 1.1LetMbe a smooth pseudoconvex hypersurface in C3andp∈M.For any fixed(1,0)vector fieldLnearp,we havet(L,p)=c(L,p).
2 Proof of Main Theorems
This section is devoted to the proof of Theorem 1.1.
Let(z1,,z2,w)be the coordinates in C3.Suppose thatp=0,and the defining function ofMtakes the form
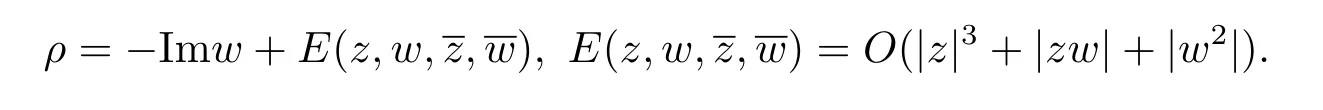
For anyj=1,2,write
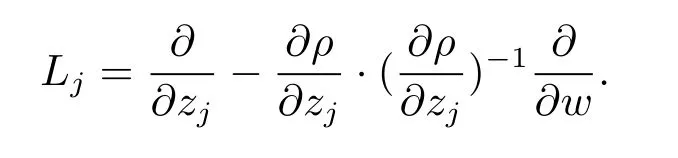
ThenL1andL2form a basis of the complex tangent vector fields of type(1,0)alongMnear 0.Suppose thatAfter a linear change of coordinates,we can assumeA1(0)60 andA2(0)=0.Notice that for any smooth functionfonMwithf(0)0,we havet(fL,0)=t(L,0)andc(fL,0)=c(L,0).Thus we can replaceLby,thenLtakes the form.
Denote byl0?2 the vanishing order ofand denote bym0?2 the vanishing order ofThe proof of main theorem is carried out for three cases,according to the values ofl0andm0.
Case IIn this case,we assumel0=m0=∞.
For any fixed integerk,after a holomorphic change of coordinates,we make
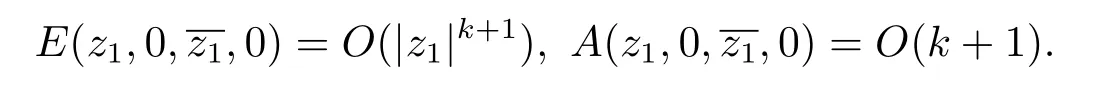
A direct computation shows thatt(L,0)≥kandc(L,0)≥k.By the arbitrariness ofk,we obtaint(L,0)=c(L,0)=+∞.
Case IIIn this case,we assumem0<∞andl0>m0.
After a holomorphic change of coordinates(see[4]or[7]),we makecontains no holomorphic or anti-holomorphic terms,and the terms of degreem0inis non-zero.Also,we make the vanishing order ofis at leastm0.Now,we introduce the following weighting system
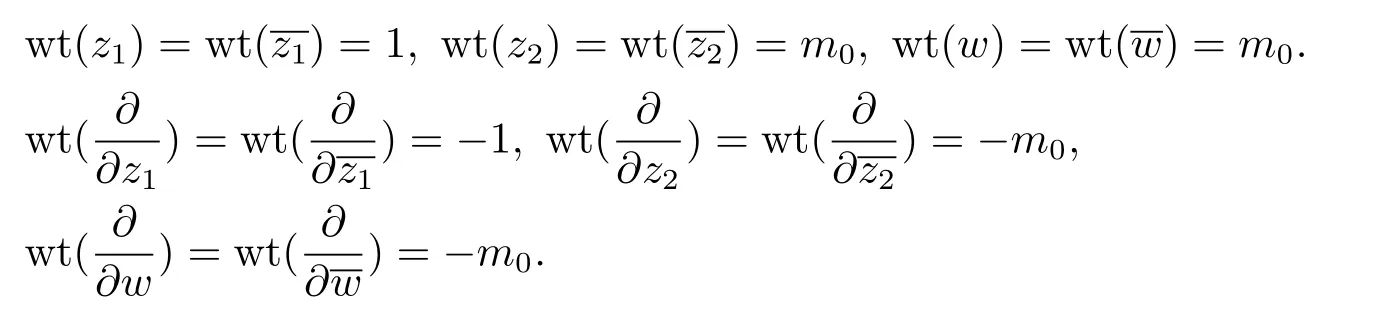
Define
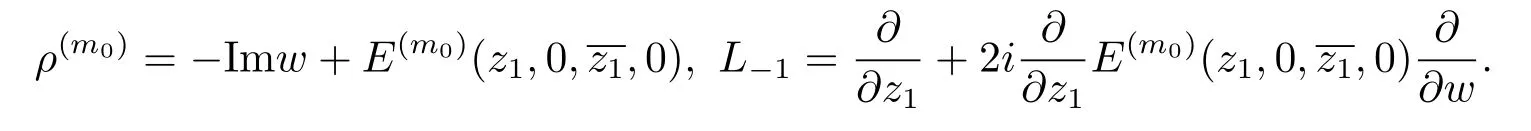
Denote byOwt(k)a smooth function or vector field with weighted degree at leastk.Then we have
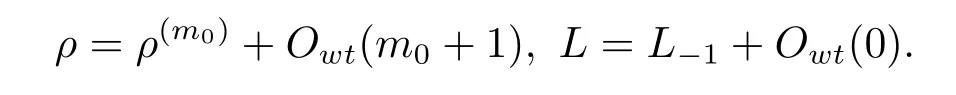
Thus for any 1≤j≤m0?2 andX1,···,Xj∈M1(L),the weighted degree of terms in
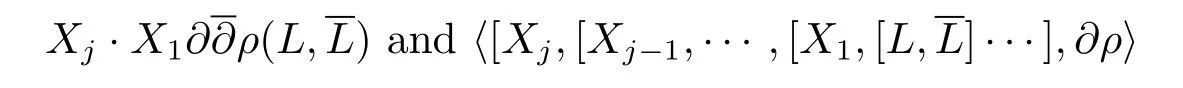
are at leastm0?j+2.Hence both of them are 0 when restricted to the origin for any 1≤j≤m0?3.Whenj=m0?2,by considering the weighted degree,we know
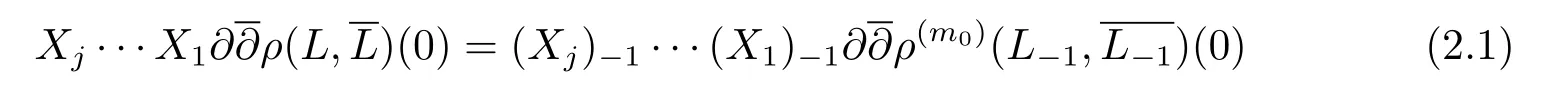
and
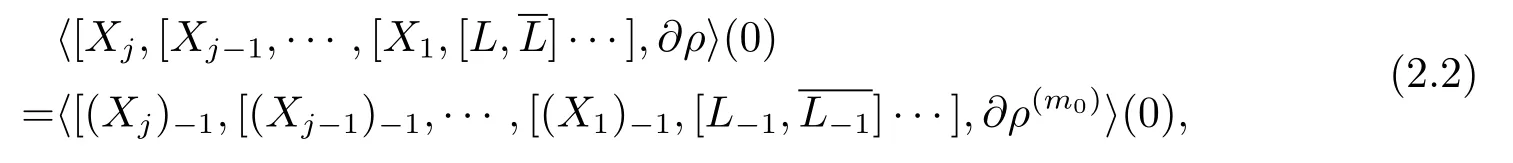
here(Xh)?1is the sum of the vector field terms inXhof weighted degree?1.
Notice thatL?1is an(1,0)tangent field of the real hypersurface defined byρ(m0)=0,which must be pseudoconvex.By the finite type theory is dimension 2(see[9]),we havet(L?1,0)=c(L?1,0)=m0.Thus in(2.1)and(2.2),we can chooseXhfor 1≤h≤m0?2 such that the two expressions are non-zero.This meanst(L,0)=c(L,0)=m0.
Case IIIIn this case,we assumem0<∞andl0≤m0?1.
After a holomorphic change of coordinates,we eliminate the holomorphic and antiholomorphic terms inEup to orderm0,and get rid of the holomorphic terms inAup to orderl0.As in Case II,we define
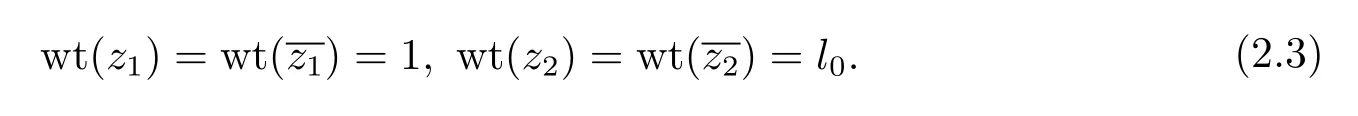
Denote bym1the lowest weighted vanishing order ofρ(z,00)with the weights given in(2.3).Thenm1≤m0.Define
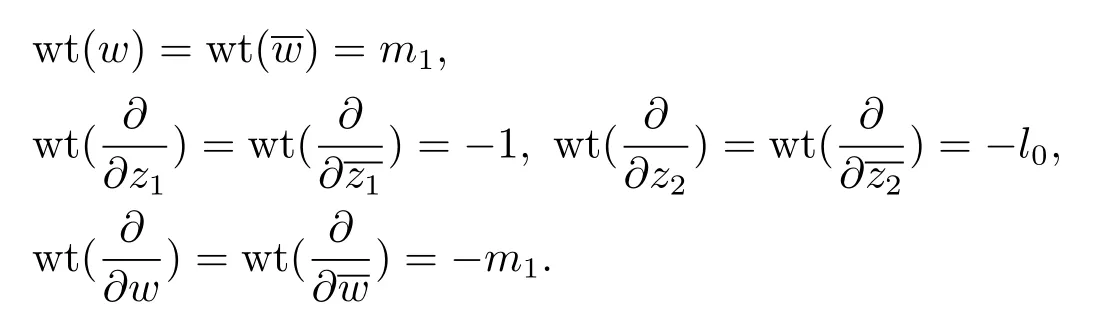
Write
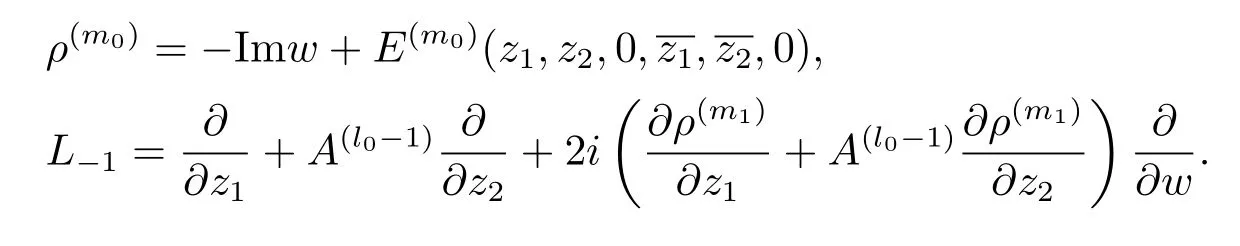
By our construction and definition,we have
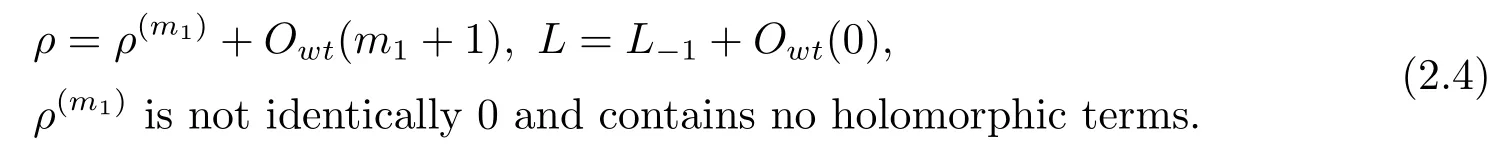
By a similar weighted degree estimate as in Case II,for any 1≤j≤m0?3 andX1,···,Xj∈M1(L),we know
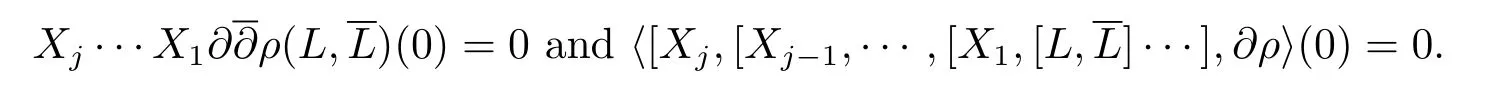
Also,for anyX1,·,Xm1?2∈M1(L),we have
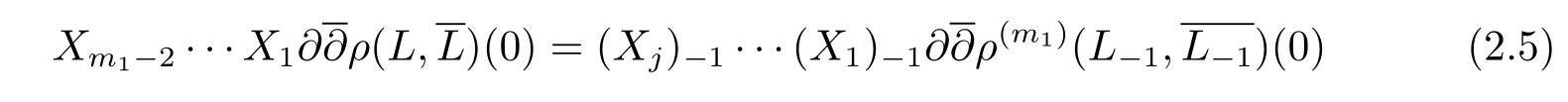
and
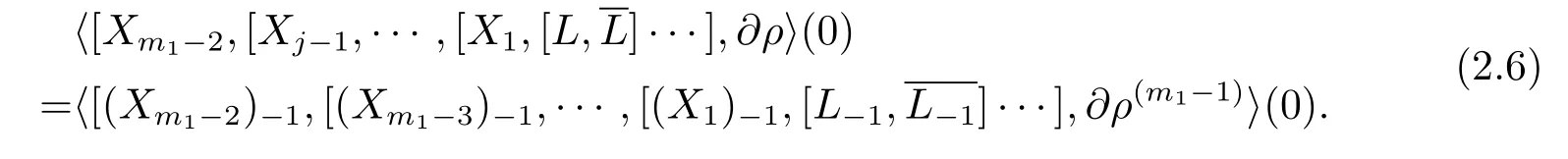
ConsiderL?1as a complex(1,0)tangent vector field ofM0:={ρ(m1)=0}.We claim thatt(L?1,0)=c(L?1,0)=m1.
SinceL?1is real analytic,by the Nagano Theorem,Re(L?1),Im(L?1)and their Lie brackets will generate a homogeneous real manifoldN0.
Suppose thatt(L?1,0)>m1,then for anyX1,·,Xm1?2∈M1(L?1),
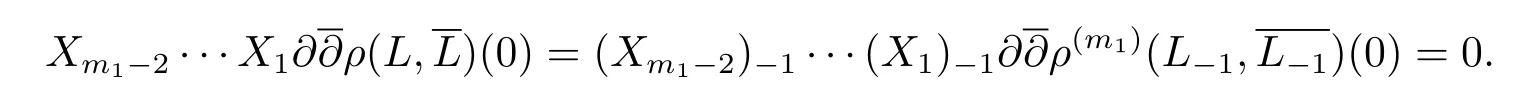
On the other hand,for anyj≥0,is a weighted homogeneous polynomial of degreem1?j?2.Hence it must be 0 when(z,w)=0 and1?2.Thusj≥0,we have
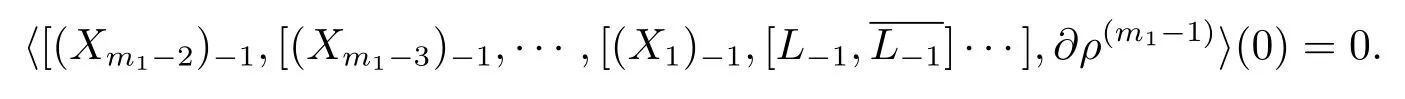

Next,suppose thatc(L?1,0)>m1,then for anyj≤m1?3,X1,···,Xj∈M1(L),we have A similar weighted degree argument shows that for anyj≥0,X1,···,Xj∈M1(L?1),we have
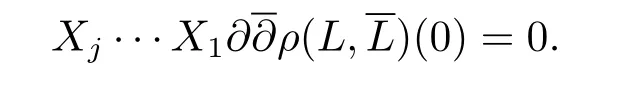
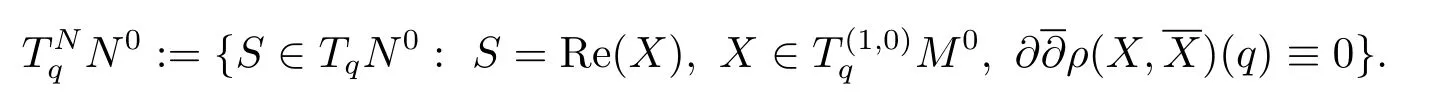
The proof of Theorem 1.1 is completed.
- 數(shù)學雜志的其它文章
- 完整Coriolis力與弱地形作用下的非齊次mKdV-Burgers方程
- 有窮平坦維數(shù)的同調轉換刻畫
- 正合范疇的整體Gorenstein維數(shù)
- S3中等參曲面的兩個特征
- FEKETE-SZEG PROBLEMS FOR SEVERAL QUASI-SUBORDINATION SUBCLASSES OF ANALYTIC AND BI-UNIVALENT FUNCTIONS ASSOCIATED WITH THE DZIOK-SRIVASTAVA OPERATOR
- NONCONFORMING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD FOR THE NONLINEAR KLEIN-GORDON EQUATION WITH MOVING GRIDS

