胃潰瘍患者再次感染幽門螺桿菌的影響因素
肖丹 徐惠敏 余中貴
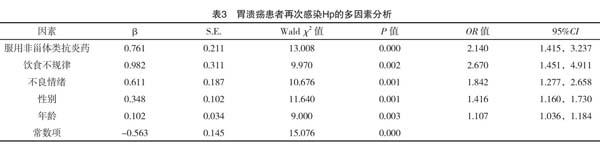
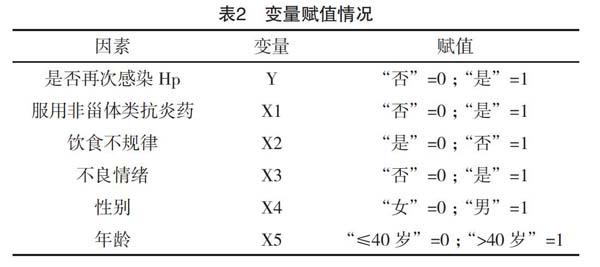

【摘要】 目的:探究胃潰瘍患者再次感染幽門螺桿菌的影響因素。方法:選擇2014年1月-2018年1月筆者所在醫(yī)院收治的289例胃潰瘍患者作為研究對象,失訪11例,根據(jù)治療后1年隨訪結果,將患者分成再次感染組(n=53)和正常組(n=225)。單因素分析胃潰瘍患者一般資料,對差異有統(tǒng)計學意義的單因素進行非條件Logistic多因素回歸分析,探究再次感染幽門螺桿菌的影響因素并建立預測模型。結果:278例患者Hp再次感染率為15.09%(53/278)。再次感染組中男性、年齡>40歲、體質指數(shù)>24.0 kg/m2、有家族胃病史、服用非甾體類抗炎藥、有吸煙史及飲酒史、糖尿病、飲食規(guī)律、喜食碳酸飲料及存在不良情緒比例均高于正常組(P<0.05);Logistic回歸分析表明,服用非甾體類抗炎藥[OR=2.140,95%CI(1.415,3.237)]、飲食不規(guī)律[OR=2.670,95%CI(1.451,4.911)]、不良情緒[OR=1.842,95%CI(1.277,2.658)]、性別[OR=1.416,95%CI(1.160,1.730)]和年齡[OR=1.107,95%CI(1.036,1.184)]均是胃潰瘍患者再次感染幽門螺桿菌的獨立影響因素(P<0.05)。結論:針對胃潰瘍患者,臨床宜根據(jù)性別、年齡、飲食、服藥及心理狀態(tài)等方面進行綜合干預,以降低再次感染率,改善生活質量。
【關鍵詞】 胃潰瘍 再次感染 幽門螺桿菌 影響因素
doi:10.14033/j.cnki.cfmr.2020.16.007 文獻標識碼 B 文章編號 1674-6805(2020)16-00-04
Influence Factors of Re-infection of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients with Gastric Ulcer/XIAO Dan, XU Huimin, YU Zhonggui. //Chinese and Foreign Medical Research, 2020, 18(16): -22
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the influence factors of re-infection of helicobacter pylori in patients with gastric ulcer. Method: A total of 289 cases with gastric ulcer admitted to our hospital from January 2014 to January 2018 were selected as subjects, 11 cases were lost to follow-up. According to the results of one year follow-up after treatment, patients were divided into the re-infection group (n=53) and the normal group (n=225). The basic information of two groups was analyzed by univariate analysis, and unconditional Logistic multivariate regression analysis was performed on the univariate factors with statistically significant differences, so as to explore the influence factors of re-infection of helicobacter pylori and establish a prediction model. Result: The re-infection rate in 278 patients was 15.09% (53/278). In the re-infection group, the proportion of male, age>40 years old, body mass index>24.0 kg/m2, family history of gastropathy, use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, history of smoking and drinking, diabetes, dietary rules, appetite for carbonated drinks and presence of adverse emotions were all higher than those of the normal group (P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [OR=2.140, 95%CI (1.415, 3.237)], eating disorders [OR=2.670, 95%CI (1.451, 4.911)], negative emotion [OR=1.842, 95%CI (1.277, 2.658)], gender [OR=1.416, 95%CI (1.160, 1.730)] and age [OR=1.107, 95%CI (1.036, 1.184)] were independent influence factors of re-infection of helicobacter pylori in patients with gastric ulcer (P<0.05). Conclusion: For patients with stomach ulcer, comprehensive interventions should be carried out according to sex, age, diet, medication and psychological state, so as to reduce the re-infection rate and improve the quality of life.
[Key words] Gastric ulcer Re-infection Helicobacter pylori Influence factors
First-authors address: Huizhou First Hospital, Huizhou 516001, China
胃潰瘍是指發(fā)生于胃角、胃竇及賁門等部位的潰瘍病變,是消化系統(tǒng)常見疾病,臨床表現(xiàn)為上腹持續(xù)疼痛、胃出血及穿孔等,若不及時有效控制疾病進程,不僅會干擾患者正常生活和工作,還會在特定情況下誘發(fā)胃癌,危及生命安全[1-2]。胃潰瘍病因較復雜,主要與幽門螺桿菌(Helicobacter pylori,Hp)感染有關,當Hp侵襲胃黏膜時,機體自身應激反應會誘發(fā)炎癥反應、水解尿素反應及降低免疫功能,最終引發(fā)胃潰瘍[3-4]。臨床針對Hp誘發(fā)的胃潰瘍通常應用四聯(lián)療法,可在6~8周內控制并治愈胃潰瘍,消除Hp感染。但臨床上仍有再次感染Hp的患者,不僅影響其治療依從性,還會增加胃潰瘍復發(fā)風險[5]。目前,關于胃潰瘍治療后再次感染Hp的影響因素的研究相對較少。為降低胃……

