糖尿病合并高血壓患者腦微出血和腦梗塞的關系
徐萌 潘琳娜 季瑩
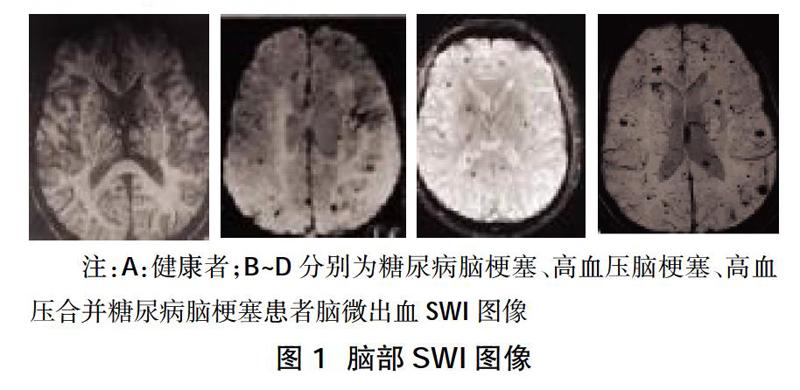
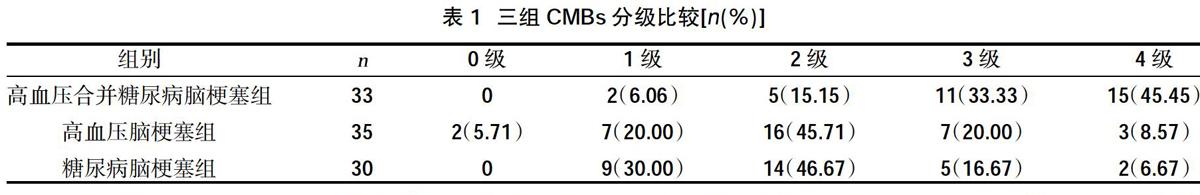

摘要:目的 ?探討糖尿病合并高血壓患者與腦微出血(CMBs)和腦梗塞的關系。方法 ?選取2015年2月~2017年5月于江西省中西醫結合醫院接受治療的急性期腦梗塞患者98例,根據有無糖尿病、高血壓分為高血壓合并糖尿病腦梗塞組(33例)、高血壓腦梗塞組(35例)、糖尿病腦梗塞組(30例),同時選取于我院進行體檢的健康志愿者(30例)組成健康組。所有入選者均接受全身磁共振掃描儀檢查,觀察糖尿病合并高血壓腦梗塞患者腦微出血SWI表現,比較三組CMBs分級,分析CMBs分級與糖尿病合并高血壓相關性分析。結果 ?經影像學檢查顯示,糖尿病合并高血壓患者發生腦梗塞后,腦微出血情況與單純糖尿病腦梗塞患者、高血壓腦梗塞患者、健康者比較橢圓形低信號區明顯增強;高血壓合并糖尿病腦梗塞組CMBs3級、4級發生率高于高血壓腦梗塞組、糖尿病腦梗塞組(P<0.05);經Spearman相關性分析發現,CMBs分級與糖尿病合并高血壓呈正相關(r=0.364,P=0.183)。結論 ?急性期腦梗塞患者合并糖尿病和高血壓疾病可增加CMBs分級,通過對患者糖尿病、高血壓疾病的控制,可對患者發生CMBs預防及治療提供指導。
關鍵詞:腦微出血;腦梗塞;糖尿病合并高血壓;CMBs分級
中圖分類號:R743.3 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.025
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)18-0083-02
The Relationship Between Cerebral Microbleeds and Cerebral Infarction
in Diabetic Patients with Hypertension
XU Meng1,PAN Lin-na1,JI Ying2
(1.Department of Neurosurgery,Jiangxi Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine,
Nanchang 330008,Jiangxi,China;
2.Department of Pharmacy,Jiangxi Cancer Hospital,Nanchang 330029,Jiangxi,China)
Abstract:Objective ?To investigate the relationship between patients with diabetes and hypertension and cerebral microbleeds (CMBs) and cerebral infarction.Methods ?A total of 98 patients with acute cerebral infarction who were treated in Jiangxi Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine from February 2015 to May 2017 were selected. According to the presence or absence of diabetes and hypertension, they were divided into hypertension and diabetic cerebral infarction group (33 cases), The hypertensive cerebral infarction group (35 cases), the diabetic cerebral infarction group (30 cases), and healthy volunteers (30 cases) who underwent physical examination in our hospital were selected to form the healthy group. All selected subjects were examined by whole-body magnetic resonance scanner to observe the SWI performance of cerebral microbleeds in patients with diabetes and hypertensive cerebral infarction, compare the three groups of CMBs classification, and analyze the correlation between CMBs classification and diabetes with hypertension.Results ?The imaging examination showed that after cerebral infarction in diabetic patients with hypertension, the situation of cerebral microbleeds was significantly enhanced compared with patients with simple diabetic cerebral infarction, hypertensive cerebral infarction patients, and healthy people; the oval low signal area was significantly enhanced; hypertension complicated with diabetic cerebral infarction the incidence of CMBs grade 3 and 4 in the group was higher than that of the hypertensive cerebral infarction group and the diabetic cerebral infarction group(P<0.05);Spearman correlation analysis showed that the CMBs grade was positively correlated with diabetes and hypertension (r=0.364,P=0.183).Conclusion ?Patients with acute cerebral infarction combined with diabetes and hypertension could increase the classification of CMBs. Through the control of diabetes and hypertension, it could provide guidance for the prevention and treatment of CMBs in patients.
Key words:Cerebral microbleeds;Cerebral infarction;Diabetes with hypertension;CMBs classification
腦微出血(cerebral microbleeds,CMBs)是由于腦部微小血管病變所致的含鐵黃素沉積,可出現于帕金森病、缺血性腦血管病及健康的老年人中。有研究指出[1],高血壓是CMBs發生的獨立危險因素,高血壓人群CMBs發生率明顯高于健康人群。隨著糖尿病腦病概念的提出,發現糖尿病可對神經系統產生影響,是認知功能障礙的獨立危險因素,而CMBs與認知功能障礙的發生存在緊密聯系,因此糖尿病可能對CMBs的發生具有一定影響。本研究選擇我院2015年2月~2017年5月收治的急性期腦梗塞患者作為研究對象,分析糖尿病合并高血壓患者腦微出血和腦梗塞的關系,以期為此類患者腦梗塞的預防和治療提供參考,現報道如下。……

