小兒呼吸道傳染病特點分析
李文
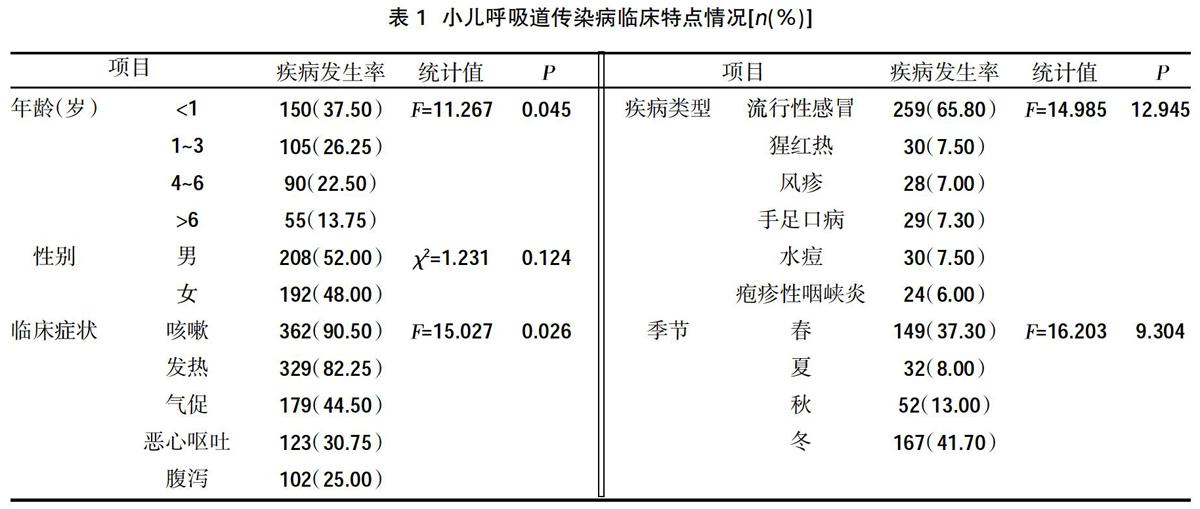
摘要:目的 ?分析小兒呼吸道傳染病的臨床特點。方法 ?選取2018年2月~2019年7月我院收治的400例小兒呼吸道傳染病患兒為研究對象,收集患兒基本資料(年齡、性別、臨床癥狀、疾病類型、發病季節)并進行分析。結果 ?不同年齡段小兒呼吸道傳染病發生率、臨床癥狀(咳嗽、發熱、氣促、惡心嘔吐、腹瀉)發生率比較,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),其中<1歲的疾病發生率均高于1~3歲、4~6歲及>6歲患兒,咳嗽、發熱癥狀發生率均高于氣促、惡心嘔吐、腹瀉,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);不同性別疾病發生率比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);流行性感冒發生率(65.80%)高于猩紅熱(7.50%)、風疹(7.00%)、手足口病(7.30%)、水痘(7.50%)、皰疹性咽峽炎(6.00%),差異有統計學意義(P<0.05);春、冬季疾病發生率均高于夏、秋季,且冬季高于春季,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。結論 ?小兒呼吸道傳染病多發于<1歲小兒,臨床以咳嗽、發熱為主要癥狀,并以流行性感染冒為主要疾病類型,且多發于冬季,臨床針對以上疾病特點,積極制定針對性預防措施,以預防小兒呼吸道傳染病的發生和傳染。
關鍵詞:小兒呼吸道傳染病;臨床特點;預防措施
中圖分類號:R725.6 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.043
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)18-0133-02
Analysis of Characteristics of Respiratory Infections in Children
LI Wen
(Department of Pediatrics,Tianjin Dagang Hospital,Tianjin 300270,China)
Abstract:Objective ?To analyze the clinical characteristics of respiratory infectious diseases in children.Methods ?A total of 400 children with respiratory tract infectious diseases admitted to our hospital from February 2018 to July 2019 were selected as the research objects. The basic data of the children (age, gender, clinical symptoms, disease type, and season of onset) were collected and analyzed.Results ?The incidence of respiratory tract infectious diseases and the incidence of clinical symptoms (cough, fever, shortness of breath, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea) in children of different ages were compared,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Among them, the incidence of diseases less than 1 year old was all children older than 1 to 3 years old, 4 to 6 years old, and> 6 years old, the incidence of cough and fever symptoms were higher than that of shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); diseases of different genders occurred compared with the rates, the difference was not statistically significant (v>0.05); the incidence of influenza (65.80%) was higher than scarlet fever (7.50%), rubella (7.00%), hand, foot and mouth disease (7.30%), and chickenpox (7.50%),herpetic angina (6.00%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05); the incidence of disease in spring and winter was higher than that in summer and autumn, and winter was higher than that in spring, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion ?Pediatric respiratory tract infectious diseases mostly occurred in children less than 1 year old, with cough and fever as the main clinical symptoms, and epidemic infections as the main disease types, and most of them occurred in winter. According to the characteristics of the above diseases, the clinic actively developed targeted preventive measures. To prevent the occurrence and infection of respiratory infectious diseases in children.
Key words:Respiratory tract infectious diseases in children;Clinical features;Preventive measures
小兒呼吸系統感染(pediatric respiratory system infection)是兒科常見疾病,多由病毒、細菌、支原體和衣原體感染所致,臨床主要以流行性感冒、風疹、水痘、麻疹等疾病為表現,具有一定的傳染性[1]。由于小兒免疫功能尚未完全發育成熟,抵抗力低,容易發生呼吸道傳染病。一旦發生呼吸系統感染,會影響患者的身體健康和正常生長發育[2]。了解小兒呼吸道傳染病特點,并積極制定針對性的預防措施,有助于降低疾病發生率和預防疾病傳染率,為臨床小兒的健康成長提供一定指導。本研究選取2018年2月~2019年7月400例醫院收治小兒呼吸道傳染病患兒的臨床資料并分析疾病臨床特點,現報道如下。
1資料與方法
1.1一般資料 ?選取2018年2月~2019年7月天津市大港醫院收治的400例小兒呼吸道傳染病患兒為研究對象。本研究納入患者均自愿參加本研究,并簽署知情同意書。……

