數據挖掘技術在探索治療艾滋病中藥性能特征中的應用
賴科云 賴昌生
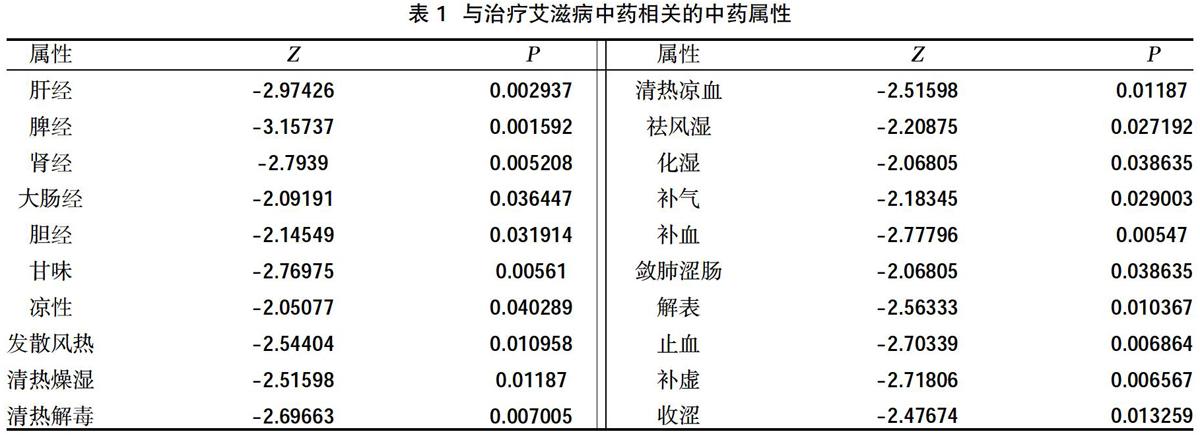
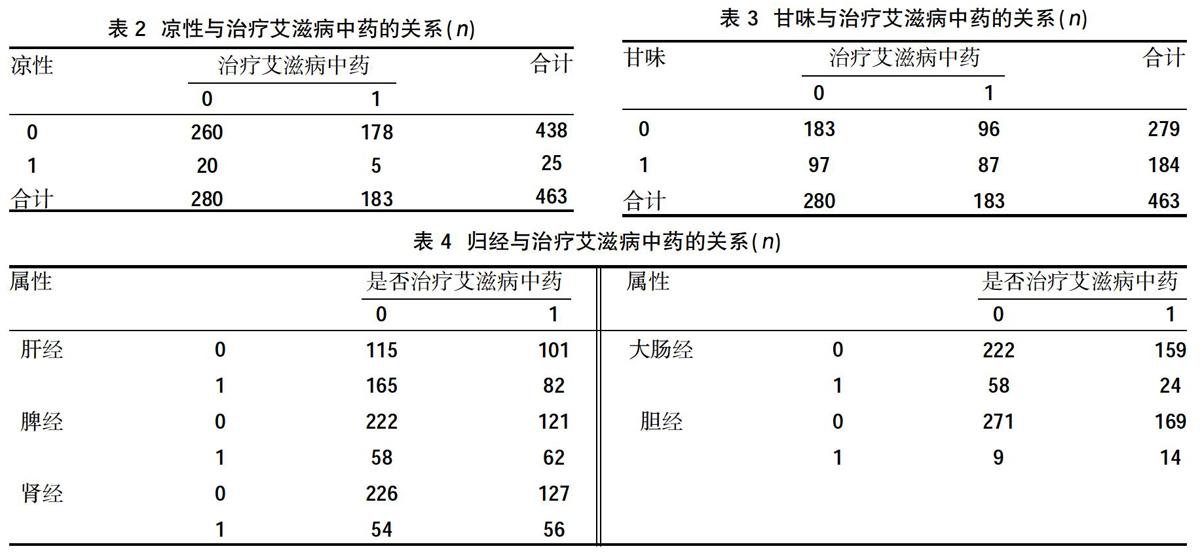
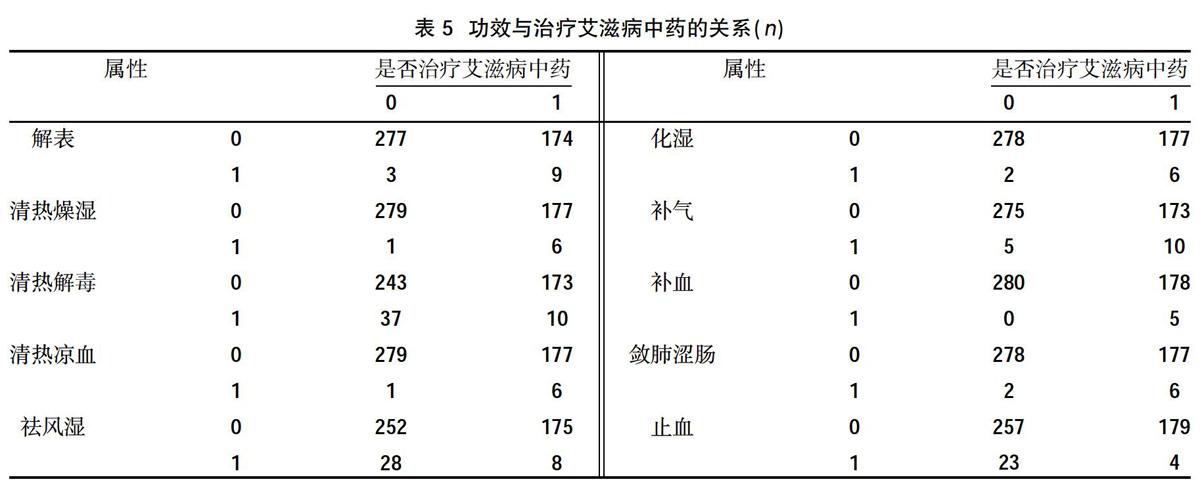
摘要:目的 ?應用數據挖掘技術研究治療艾滋病中藥的性能特征。方法 ?以 “艾滋病”“HIV”“AIDS”“中醫藥”為關鍵詞,計算機檢索1992年1月~2018年12月中國知網(CNKI)收錄中醫或中西醫結合治療艾滋病文獻中的方劑和藥物,整理入選方劑的藥物,確定治療艾滋病的中藥,以“是否為治療艾滋病中藥”為目標字段,以中藥性能為輸入字段,運用非參數統計、交叉表和卡方檢驗等方法比較治療與非治療艾滋病中藥在四氣、五味、歸經和功效方面的差異。結果 ?在四氣方面,治療艾滋病中藥中涼性藥物比例低于非治療艾滋病中藥,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩者在寒、熱、溫、平等藥性方面比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);在五味方面,治療艾滋病中藥的甘味比例高于非治療滋病中藥,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩者在辛、苦、咸、酸、澀、淡方面比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05);在歸經方面,治療艾滋病中藥歸脾經、腎經、膽經的比例高于非治療艾滋病中藥,在歸經肝經、大腸經方面低于非治療艾滋病中藥,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩者在歸心、肺、膀胱、小腸、胃經方面比較,差異無統計學意義P>0.05);在功效方面,治療艾滋病中藥的發散風熱、清熱燥濕、清熱涼血、芳香化濕、補氣、補血、斂肺澀腸、解表、補虛、收澀高于非治療艾滋病中藥,在清熱解毒、祛風濕功效方面低于非治療艾滋病中藥,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05),兩者在清虛熱、瀉下、芳香化濕、峻下逐水、利水消腫、利尿通淋、利濕退黃、溫里、理氣、消食、驅蟲、止血、溫化寒痰、清化熱痰、止咳平喘、活血化瘀、重鎮安神、養心安神、平抑肝陽、息風止痙、開竅、補氣、補陽、補血、補陰、止汗、固精縮尿止帶方面比較,差異無統計學意義(P>0.05)。結論 ?與非治療艾滋病中藥比較,治療艾滋病中藥四氣中涼性較少,五味以甘味為主,歸經以脾經、腎經等為主要病位,具有補氣、補血、化濕、清熱燥溫等功效。
關鍵詞:數據挖掘;艾滋病;中藥性能;四氣;五味
中圖分類號:R512.91;R243 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文獻標識碼:A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.18.052
文章編號:1006-1959(2020)18-0154-05
Application of Data Mining Technology in Exploring the Performance Characteristics
of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Treating AIDS
LAI Ke-yun1,LAI Chang-sheng2
(1.Heilongjiang University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang,China;
2.Department of Science and Education,Yulin Red Cross Hospital,Yulin 537000,Guangxi,China)
Abstract:Objective ?To apply data mining technology to study the performance characteristics of Chinese medicine for treating AIDS.Methods ?Using "AIDS", "HIV", "AIDS", and "Chinese medicine" as keywords, a computer search from January 1992 to December 2018 included prescriptions and drugs in the literature on Chinese medicine or integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine for the treatment of AIDS in China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI),sort out the selected prescription drugs, determine the Chinese medicine for AIDS, take "whether it was a Chinese medicine for AIDS" as the target field, use the performance of the Chinese medicine as the input field, and use non-parametric statistics, cross-tabulation and chi-square test to compare treatment and non-treatment differences in the four qi, five flavors, meridian and efficacy of AIDS Chinese medicine.Results ?In terms of the four qi, the proportion of cold medicines in AIDS treatment was lower than that in non-AIDS treatments,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).There was no statistically significant difference between the two in terms of cold, heat, temperature, and equivalence (P>0.05); in terms of five flavors, the proportion of sweetness of Chinese medicine for treating AIDS was higher than that of non-treatment Chinese medicine for AIDS,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). There was no statistically significant difference between the two in terms of pungency, bitterness, saltiness, sourness, astringency, and lightness (P>0.05); in terms of return of menstruation, the traditional Chinese medicine for treating AIDS was related to the spleen meridian, kidney meridian, and gall bladder meridian proportion was higher than that of non-treatment AIDS traditional Chinese medicine, and lower than non-treatment AIDS traditional medicine in the liver meridian and large intestine meridian,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The two are compared in the Guixin, lung, bladder, small intestine, and stomach meridian,the difference was not statistically significant (P>0.05); in terms of efficacy, the traditional Chinese medicine for treating AIDS could disperse wind-heat, clear heat and dry dampness, clear heat and cool blood, aromatize dampness, nourish qi, nourish blood, astringe the lungs, astringe the intestines, relieve the skin Deficiency and astringency are higher than non-AIDS traditional Chinese medicines, and lower than non-AIDS traditional Chinese medicines in terms of heat-clearing, detoxifying, and rheumatism,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The two were in clearing deficiency heat, purging diarrhea, aromatizing dampness, relieve water to eliminate swelling, diuresis and relieve dampness, relieve dampness, warm up, regulate qi, eliminate food, deworming, stop bleeding, warm up cold phlegm, clear hot phlegm, relieve cough and relieve asthma, promote blood circulation and remove blood stasis, rejuvenate the mind,there were no statistically significant differences in nourishing the mind and calming the nerves, suppressing liver-yang, stopping wind and relieving spasm, resuscitating, tonifying qi, tonifying yang, tonifying blood, tonifying yin, stopping perspiration, and consolidating and constricting urinary stop bands (P>0.05).Conclusion ?Compared with non-AIDS Chinese medicines, Chinese medicines for the treatment of AIDS had less cooling properties in the four qi, the five flavors are mainly sweet, and the main pathologies of the meridians were the spleen meridian and the kidney meridian. It had the functions of nourishing qi, nourishing blood, removing dampness, and clearing heat and dryness gentle effect.
Key words:Data mining;AIDS;Performance of traditional Chinese medicine;Four qi;Five flavors
艾滋病(acquired immunodeficiency syndrome,AIDS)是一種由人類免疫缺陷病毒(human immunodeficiency virus,HIV)引起的,以全身免疫系統嚴重損害為特征的傳染性疾病。……

