亞龍灣砂質(zhì)海岸侵蝕監(jiān)測(cè)和評(píng)價(jià)
石海瑩 陳周 呂宇波


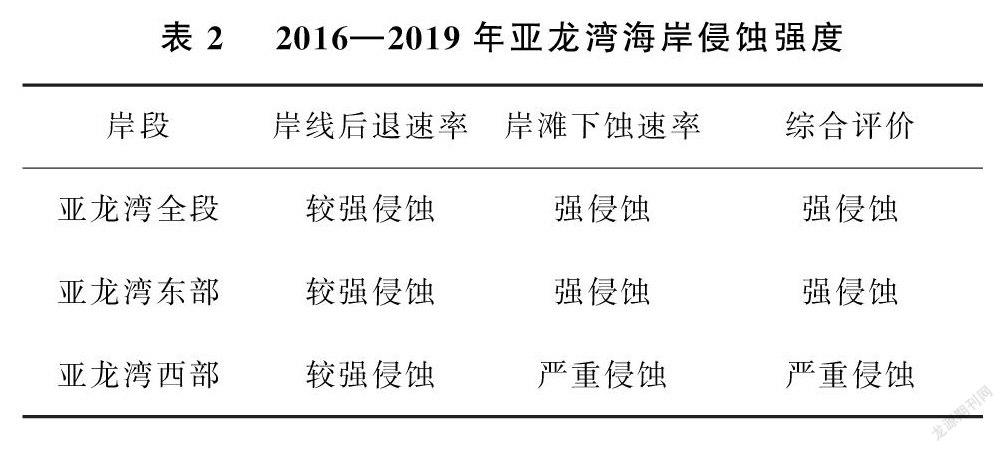
摘要:為保護(hù)亞龍灣砂質(zhì)海岸及其生態(tài)系統(tǒng) , 文章采用2016年和2019年的監(jiān)測(cè)數(shù)據(jù)以及2008年的歷史數(shù)據(jù) ,依據(jù)相關(guān)技術(shù)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)和方法 ,從岸線后退速率和岸灘下蝕速率2個(gè)方面綜合評(píng)價(jià)亞龍灣砂質(zhì)海岸的侵蝕狀況和侵蝕強(qiáng)度 , 并分析其原因。研究結(jié)果表明:亞龍灣砂質(zhì)海岸存在持續(xù)性較強(qiáng)且較嚴(yán)重的海岸侵蝕;2008-2016年岸線后退速率和年均土地?fù)p失面積分別約為-1.00m/a和2080m2 ,2016-2019年岸線后退速率和年均土地?fù)p失面積分別約為-1.80 m/a 和9836 m2 , 亞龍灣海岸侵蝕有明顯加劇的趨勢(shì);2016-2019年亞龍灣東部和西部海岸的岸灘下蝕速率分別約為-13.3 cm/a和-36.2 cm/a, 西部岸灘下蝕速率遠(yuǎn)高于東部岸灘;亞龍灣全段為強(qiáng)侵蝕等級(jí) , 其中東部岸段為強(qiáng)侵蝕等級(jí) , 西部岸段為嚴(yán)重侵蝕等級(jí);造成亞龍灣海岸侵蝕的原因主要包括海岸工程建設(shè)、植被破壞和海平面上升。
關(guān)鍵詞:砂質(zhì)海岸;海岸侵蝕;侵蝕強(qiáng)度;岸線后退;岸灘下蝕
中圖分類號(hào):P737.17????? 文獻(xiàn)標(biāo)志碼:A?????? 文章編號(hào):1005-9857(2021)12-0080-05
Monitoring and Evaluation of Coastal Erosion ofSandy Beach in Yalong Bay
SHI Haiying,CHEN Zhou,LYU Yubo
(Ocean Monitoring and Forecasting Center of Hainan Province,Haikou 570206,China)
Abstract:According to related technical standards and methods, in order to protect sandy beach ofYalong Bay and its ecosystem, monitoring data in 2016 and 2019 as well as historical data in 2008were adopted to comprehensively evaluate sandy coastal erosion and erosion intensity by coastlineretreat rate and coast erosion rate,and its causes were analyzed. The results showed that thesandy beach of Yalong Bay had suffered a long-term serious coastal erosion. During 2008 to 2016,coastline retreat rate was –1.00 m/a and average annual loss of land area was 2 080 m2. During2016 to 2019, coastline retreat rate and average annual loss of land area were –1.80 m/a and9 836 m2 respectively. Research data showed that there was an increasing tendency of coastal erosion in Yalong Bay. Besides, the rate of intertidal topology down-cutting of eastern coast was-13.3 cm/a, and that of western coast was -36.2 cm/a. The results showed that the west coastof Yalong Bay suffered more severer erosion. With respect to the coastal erosion intensity, thewhole section of Yalong Bay experienced serious erosion, more specifically, the east coast experiences serious, while the west coast mild. Coastal engineering construction, vegetation deterioration and sea level rise were the main causes for coastal erosion in Yalong Bay.
Keywords:Sandy beach,Coastal erosion,Erosion intensity,Coastline recession,Intertidal topologydown-cutting
0 引言
自20世紀(jì)50年代末期以來 ,我國(guó)約70%的砂質(zhì)海岸和大部分粉砂淤泥質(zhì)海岸遭受侵蝕[1] ,侵蝕岸線長(zhǎng)度超過全國(guó)海岸線總長(zhǎng)度的33%。持續(xù)的全球氣候變暖使得極地冰蓋融化、海平面緩慢上升、海岸線后退、近岸海洋動(dòng)力增強(qiáng)和風(fēng)暴潮發(fā)生次數(shù)增加 ,導(dǎo)致海岸侵蝕進(jìn)一步加劇[2]。海南島的海岸侵蝕現(xiàn)象非常普遍 ,早在20世紀(jì)90年代海南省就有約79%的海岸線受到侵蝕[3]。相對(duì)于其他海岸類型 ,砂質(zhì)海岸最不穩(wěn)定 , 極易遭受侵蝕而后退 , 而海南島砂質(zhì)岸線約占海岸線總長(zhǎng)度的43%[4]。……

