高分辨磁共振瘤壁成像在顱內未破裂動脈瘤中的應用
賴湘 張文波 葉敏 范偉雄 劉曉平
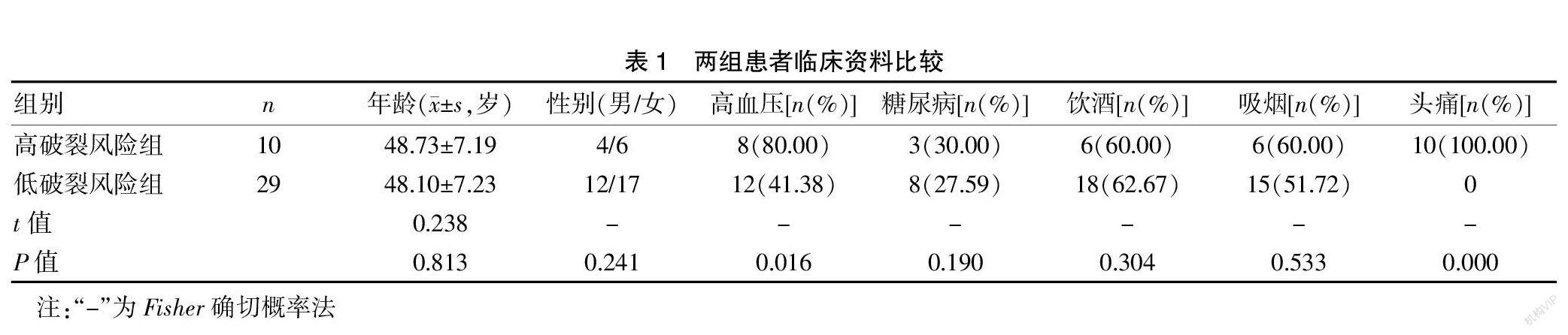
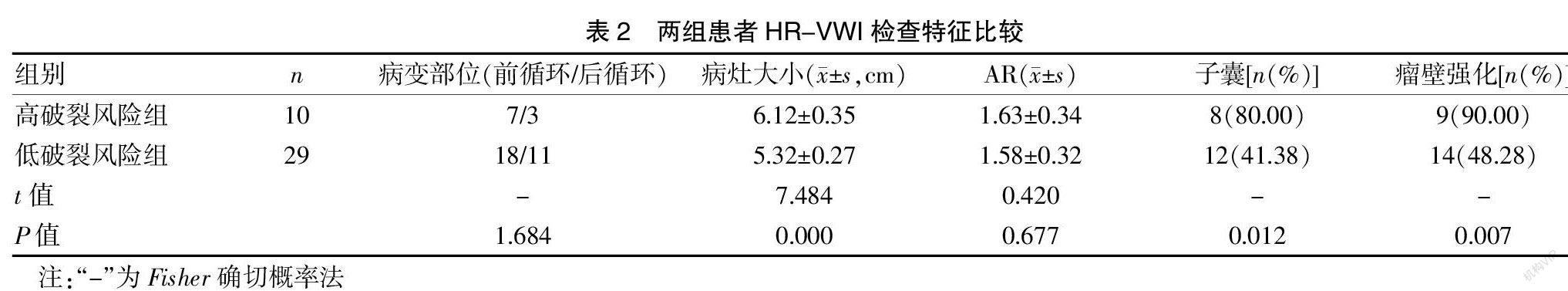
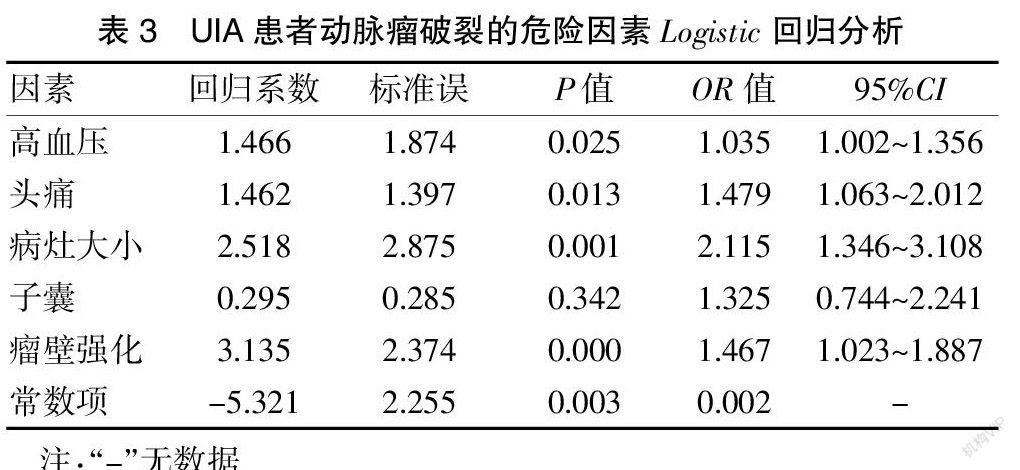
[摘要] 目的 研究高分辨磁共振瘤壁成像(HR-VWI)在顱內未破裂動脈瘤(UIA)中的應用。 方法 將梅州市人民醫院神經外科從2018年1月至2020年10月收治的擬行開顱手術夾閉或介入栓塞的UIA患者39例納入研究。對所有受試者均開展HR-VWI檢查,分析病變部位、病灶大小、瘤高與頸寬比(AR)、子囊、瘤壁強化情況。對所有受試者臨床癥狀進行破裂風險評估,并根據癥狀分為高破裂風險組10例和低破裂風險組29例。采集所有受試者的各項基線資料并進行對比。采用多因素Logistic回歸分析明確UIA患者動脈瘤破裂的危險因素。 結果 高破裂風險組高血壓及頭痛例數占比均明顯高于低破裂風險組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。高破裂風險組病灶大小及子囊、瘤壁強化例數占比均高于低破裂風險組,差異有統計學意義(P<0.05)。經多因素Logistic回歸分析可知,高血壓、頭痛、病灶大小、瘤壁強化均是UIA患者動脈瘤破裂的危險因素(OR>1,P<0.05)。 結論 HR-VWI應用于UIA的診斷中具有較高的價值,且可為動脈瘤破裂提供一定的輔助預測作用,值得臨床重點關注。
[關鍵詞] 顱內未破裂動脈瘤;高分辨磁共振;瘤壁成像;危險因素
[中圖分類號] R651? ? ? ? ? [文獻標識碼] B? ? ? ? ? [文章編號] 1673-9701(2021)24-0103-04
Application of high-resolution magnetic resonance vascular wall imaging in unruptured intracranial aneurysms
LAI Xiang1? ?ZHANG Wenbo1? ?YE Min1? ?FAN Weixiong2? ?LIU Xiaoping1
1.Department of Neurosurgery, Meizhou People's Hospital in Guangdong Province, Meizhou? ?514031, China; 2.Department of Magnetic Resonance, Meizhou People's Hospital in Guangdong Province, Meizhou? ?514031,China
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application of high-resolution magnetic resonance vascular wall imaging(HR-VWI)in unruptured intracranial aneurysms(UIA). Methods Thirty-nine UIA patients admitted to the Department of Neurosurgery of Meizhou People's Hospital from January 2018 to October 2020 who were scheduled to undergo craniotomy or interventional embolization were included. HR-VWI examinations were performed on all patients to analyze the lesion location, lesion size, aspect ratio(AR), ascus, and aneurysmal wall enhancement. The clinical symptoms of all patients were assessed for the risk of rupture. They were divided into the high rupture risk group with 10 patients and the low rupture risk group with 29 patients according to the symptoms. Baseline data of all patients were collected and compared. Multivariate Logistic regression analysis was conducted to clarify the risk factors of aneurysm rupture in UIA patients. Results The proportions of hypertension and headache in the high rupture risk group were significantly higher than those in the low rupture risk group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). The lesion size and proportions of patients with ascus and aneurysmal wall enhancement in the high rupture risk group were higher than those in the low rupture risk group,the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Multivariate Logistic regression analysis showed that hypertension, headache, lesion size, and aneurysmal wall enhancement were risk factors for aneurysm rupture in UIA patients(OR>1, P<0.05). Conclusion HR-VWI has high value in the diagnosis of UIA and certain auxiliary predictive effect for aneurysm rupture. Attention should be paid to it in clinical practice.

