內毒素攻擊大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞時HO-1對高爾基體應激的影響*
李玉婷, 李香云, 史佳, 李翠, 余劍波
內毒素攻擊大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞時HO-1對高爾基體應激的影響*
李玉婷, 李香云, 史佳, 李翠, 余劍波△
(天津醫科大學南開臨床學院,天津市中西醫結合醫院·南開醫院麻醉與重癥醫學科,天津 300100)
探討內毒素誘導大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞損傷時血紅素加氧酶1(HO-1)對高爾基體應激的影響。體外培養大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞,采用脂多糖(LPS)誘導大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞建立細胞損傷模型。使用CCK-8法檢測細胞活力;使用DCFH-DA探針檢測細胞內活性氧簇(ROS)的生成;使用生物化學方法檢測超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性和丙二醛(MDA)水平;使用TUNEL染色和凋亡相關蛋白caspase-3/7活性檢測試劑盒檢測細胞凋亡;使用RT-qPCR和Western blot法檢測HO-1和高爾基體磷蛋白3(GOLPH3)的表達;使用Western blot法檢測高爾基體結構相關蛋白GM130、golgin-97和mannosidase II的表達。使用小干擾RNA(siRNA)沉默后,重復以上檢測。LPS刺激肺泡巨噬細胞下調細胞活力、SOD活性及GM130、golgin-97和mannosidase II表達水平,上調ROS和MDA含量及HO-1和GOLPH3表達水平,并導致TUNEL標記陽性細胞數增多,caspase-3/7活性增強(<0.05);基因沉默后,細胞活力、SOD活性及GM130、golgin-97和mannosidase II表達顯著下降,ROS和MDA含量及GOLPH3表達顯著上升,TUNEL標記陽性細胞數增多,caspase-3/-7活性顯著增強(<0.05)。內毒素誘導大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞損傷時,HO-1可減輕氧化應激和高爾基體應激反應,減少細胞凋亡。
高爾基體應激;血紅素加氧酶1;脂多糖;肺泡巨噬細胞;氧化應激
急性肺損傷(acute lung injury, ALI)是臨床常見的危重癥,具有高發病率和高死亡率。肺泡巨噬細胞可釋放細胞因子和趨化因子以招募炎癥細胞,引發炎癥風暴,在ALI后期可釋放抗炎因子,抑制炎癥細胞浸潤以介導肺部炎癥消退,并通過誘導增殖信號傳導以促進組織修復。因此,巨噬細胞可能是治療ALI的合適靶點之一[1-3]。
高爾基體是細胞死亡途徑中應激的傳感器和下游效應器之一[4]。應激狀態下,高爾基體結構和功能被破壞,離子穩態失衡,導致細胞氧化還原平衡改變,細胞死亡增加[4-5]。高爾基體磷蛋白3(Golgi phosphoprotein 3, GOLPH3)作為高爾基體應激的傳感器,在氧化應激過程中迅速上調,并向下游傳遞應激信號,誘導細胞內活性氧簇(reactive oxygen species, ROS)產生,促進高爾基體解體和細胞凋亡[4, 6-7]。高爾基體結構相關蛋白高爾基體基質蛋白130(Golgi matrix protein 130, GM130)、高爾基體蛋白97(golgin-97)和II類甘露糖苷酶(mannosidase II)對維持高爾基體結構極為重要,在氧化應激期間表達下降,可致高爾基體結構碎裂及功能受損,最終引起細胞凋亡[4, 6, 8-10]。因此,是否可通過調控高爾基體應激反應減輕LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞急性損傷值得進一步探究。
本研究組前期研究表明,血紅素加氧酶1(heme oxygenase-1, HO-1)是一種潛在的應激誘導蛋白,其在急性肺損傷中可通過改善線粒體動力學平衡及抑制內質網應激,以發揮內源性肺保護作用[11-13]。但HO-1在肺泡巨噬細胞內對高爾基體應激的調控,目前尚不清楚。本項工作擬通過構建脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide, LPS)誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞急性損傷模型,探究HO-1對高爾基體應激的調控作用,為研究其在急性肺損傷中的作用提供參考資料。
材料和方法
1 細胞和主要試劑
大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞系NR8383購自中國科學院。F12培養液和青鏈雙抗購自HyClone;胎牛血清購自四季青公司;LPS購自Sigma;-小干擾RNA(small interfering RNA, siRNA)購自GE Dharmacon;轉染試劑Lipofectamine 3000購自Invitrogen;qPCR引物由湖北百奧生物科技有限公司合成;逆轉錄試劑盒和實時熒光定量PCR試劑購自北京艾德萊生物科技有限公司;caspase-3/7試劑盒購自大連美侖生物技術有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase, SOD)試劑盒和丙二醛(malondialdehyde, MDA)試劑盒購自南京建成生物研究所;細胞計數試劑盒8(Cell Counting Kit-8, CCK8)購自上海生工生物工程公司;TUNEL細胞檢測試劑盒和DCFH-DA探針購自碧云天生物技術研究所;BCA蛋白定量試劑盒購自北京艾德萊生物科技有限公司;HO-1抗體、GOLPH3抗體和GM130抗體購自PTG;golgin-97抗體購自CST;mannosidase II抗體購自Santa;β-actin抗體、HRP標記的山羊抗兔抗體和HRP標記的山羊抗鼠抗體購自三箭生物技術有限公司。
2 主要方法
2.1細胞培養及分組將NR8383細胞培養于含10%胎牛血清和1%青鏈雙抗的F12培養液,置于37 ℃、5% CO2飽和濕度的培養箱中。每2 d更換1次培養液。待細胞密度為80%左右時離心收集并傳代。將細胞接種于12孔板,密度為5×107/L的細胞,采用隨機數字表法分為4組(=3):對照(control)組、LPS組、LPS+Scr-siRNA組和LPS+-siRNA組。對照組細胞正常培養,其余3組參考文獻[14]給予10 mg/L LPS制備肺泡巨噬細胞內毒素攻擊模型。
2.2細胞轉染及造模依據試劑說明,使用Lipofectamine 3000進行Scr-siRNA和siRNA轉染。LPS+Scr-siRNA組細胞中加入Scr-siRNA和Lipofectamine 3000轉染試劑,LPS+-siRNA組加入-siRNA和Lipofectamine 3000轉染試劑,培養24 h后,加入LPS 10 mg/L繼續培養24 h。
2.3細胞活力檢測96孔板接種NR8383細胞,細胞接種量每孔5 000個。細胞貼壁后按照試驗分組進行處理,再按照CCK-8試劑盒說明書操作,選擇酶標儀于450 nm波長檢測吸光度()值并計算相對細胞活力。
2.4ROS的檢測DCFH-DA用無血清培養液稀釋至10 μmol/L。細胞收集后懸浮于稀釋的DCFH-DA中30 min,每2~3 min混合一次,最后在無血清培養液中洗滌細胞3次。以485 nm和535 nm的激發波長和發射波長計算DCF熒光。
2.5SOD活性和MDA含量的測定收集處理后的細胞,嚴格按照SOD和MDA試劑盒說明書操作,采用721分光光度儀檢測值。
2.6caspase-3/7活性的檢測收集處理后的細胞,根據說明,使用caspase-3/7活性檢測試劑盒對樣本進行caspase-3/7活性的測定。
2.7TUNEL染色收集處理后的細胞,采用4%多聚甲醛固定細胞,根據TUNEL凋亡試劑盒說明書進行TUNEL染色,再采用DAPI染色液復染細胞核。置于熒光顯微鏡下觀察凋亡細胞,并通過計算TUNEL陽性細胞核數量占DAPI染色核數量的比例,計算凋亡細胞的百分率。
2.8RT-qPCR采用Trizol法[15]提取出NR8383細胞中的總RNA。逆轉錄合成cDNA,置于-20 ℃保存備用。RT-qPCR擴增目的基因mRNA。反應條件:95 ℃ 5 min;95 ℃ 10 s,60 ℃ 30 s,40個循環。采用熒光定量PCR儀測定Ct值,采用2-ΔΔCt法對目的基因的相對表達量進行分析。相應引物序列見表1。
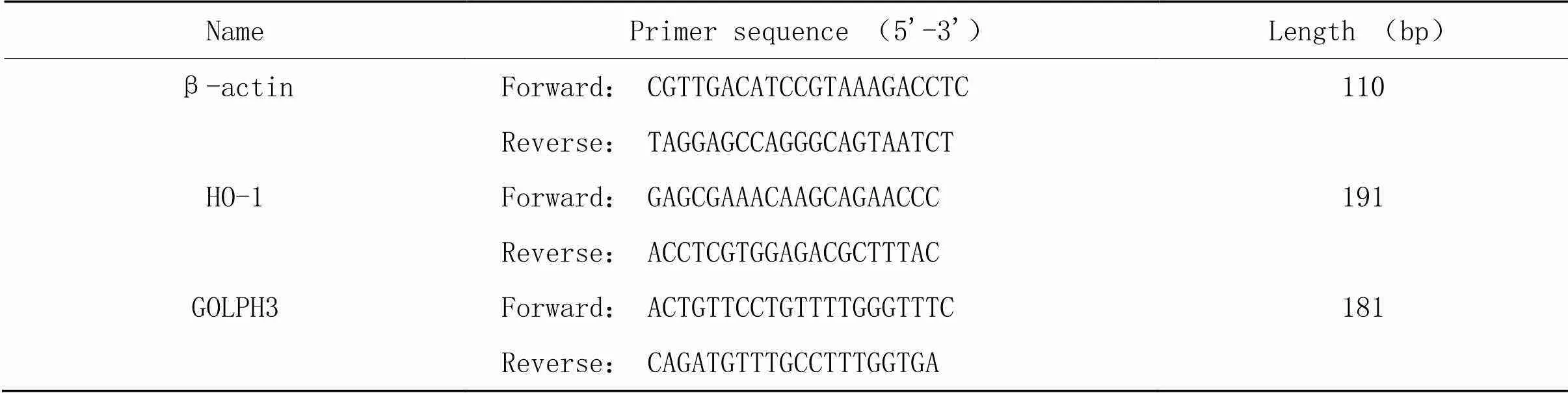
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
2.9Western blot實驗收集細胞后,采用全蛋白試劑提取試劑盒提取總蛋白并以BCA法測定蛋白濃度。取40 μg樣品于12% SDS-PAGE分離、轉至PVDF膜、5%的脫脂奶粉37 ℃封閉1 h、TBST洗膜后,分別加入抗HO-1(1∶1 000)、GOLPH3(1∶1 000)、GM130(1∶200)、golgin-97(1∶1 000)、mannosidase II(1∶200)和β-actin(1∶8 000)抗體,4 ℃孵育過夜。TBST洗膜4次,加入山羊抗兔或抗鼠Ⅱ抗(1∶10 000),室溫下孵育1 h。TBST洗脫4次后,置于ECL系統中顯影,采用ImageJ軟件分析蛋白條帶灰度值,以目的蛋白條帶灰度值與β-actin條帶灰度值的比值反映目的蛋白相對表達水平。
3 統計學處理
采用SPSS 24.0軟件進行分析。正態分布的計量資料以均數±標準差(mean±SD)表示。多組均數間比較采用單因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),組間兩兩比較采用Tukey′s事后檢驗進行比較。以<0.05為差異有統計學意義。
結果
1 肺泡巨噬細胞活力和氧化應激水平的變化
與對照組相比,LPS誘導肺泡巨噬細胞活力下降,ROS和MDA含量增加,SOD活性下降(<0.05);沉默-后,與LPS組相比,肺泡巨噬細胞活力顯著下降,ROS和MDA含量顯著增加,SOD活性顯著下降(<0.05),見圖1。
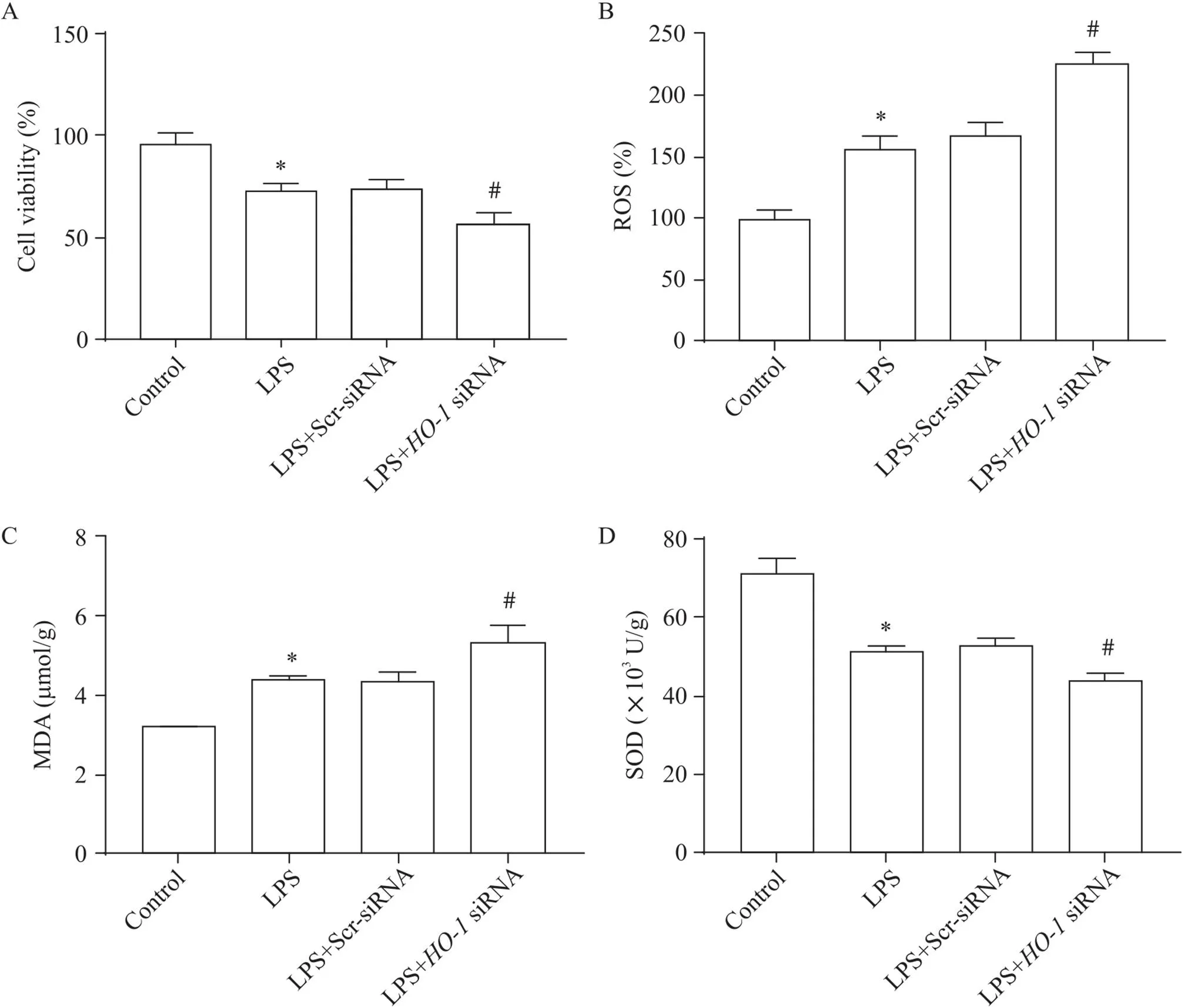
Figure 1.Cell viability, ROS content, MDA content and SOD activity in alveolar macrophages. A: the viability of alveolar macrophages was detected by CCK-8 assay; B: the level of ROS was analyzed by DCFH-DA probing; C: the change of MDA content was detected by MDA kit; D: the change of SOD activity was analyzed by SOD kit. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs LPS group.
2 HO-1和高爾基體應激蛋白GOLPH3表達的變化
RT-qPCR和Western blot結果顯示,與對照組相比,LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞HO-1表達增加(<0.05),高爾基體應激蛋白GOLPH3 mRNA和蛋白表達增加(<0.05);沉默后,其在肺泡巨噬細胞中的表達顯著下調(<0.05),見圖2、3,GOLPH3表達高于LPS組(<0.05),見圖4。
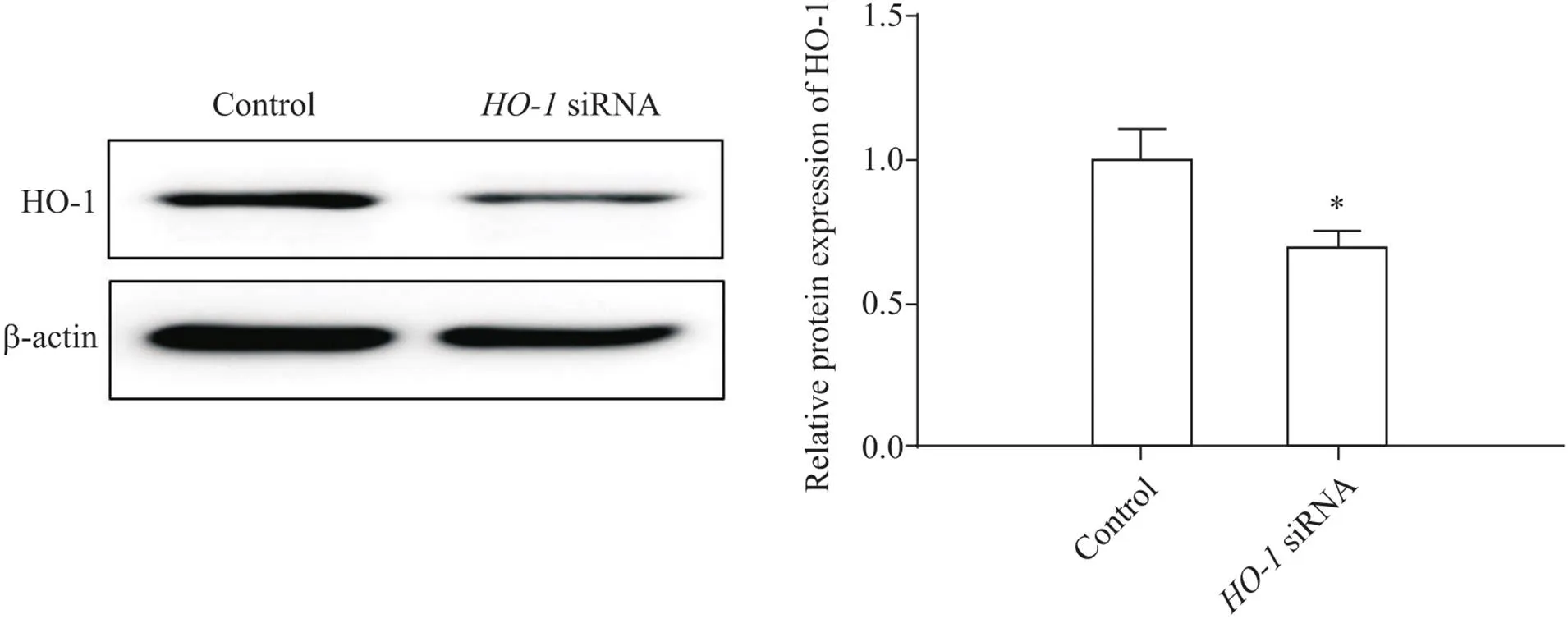
Figure2.The transfection efficiency of HO-1 siRNA in alveolar macrophages. The HO-1 protein level was detected by Western blot. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group.
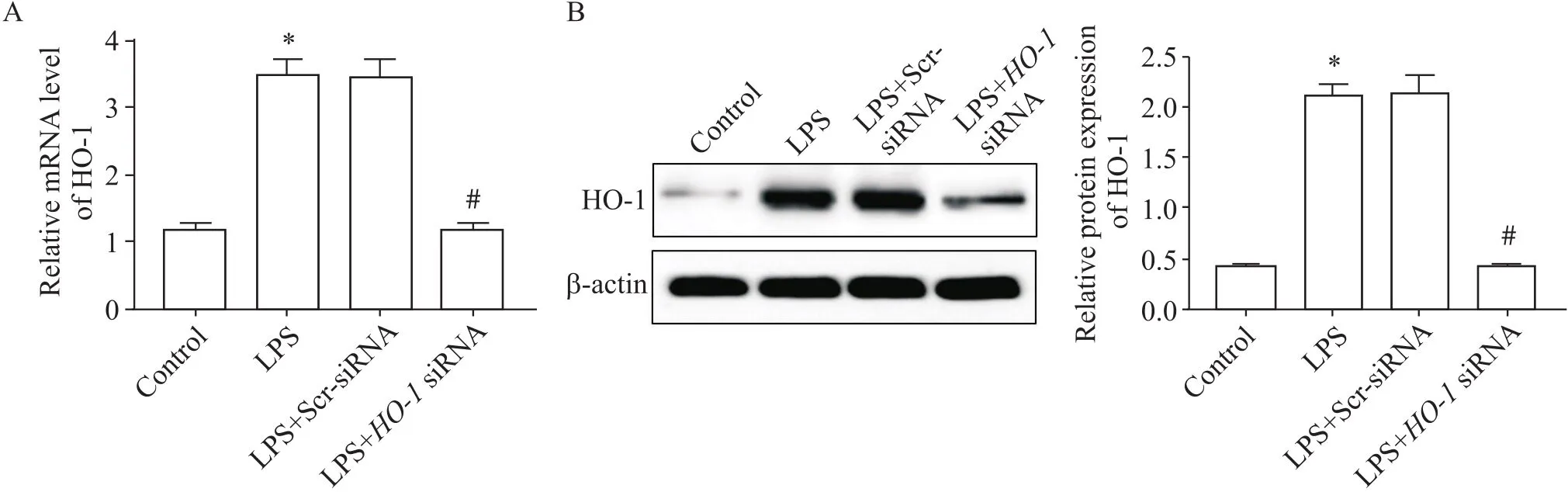
Figure 3.HO-1 expression levels in alveolar macrophages. A: HO-1 mRNA level in each group was measured by RT-qPCR; B: HO-1 protein expression in each group was measured by Western blot. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs LPS group.
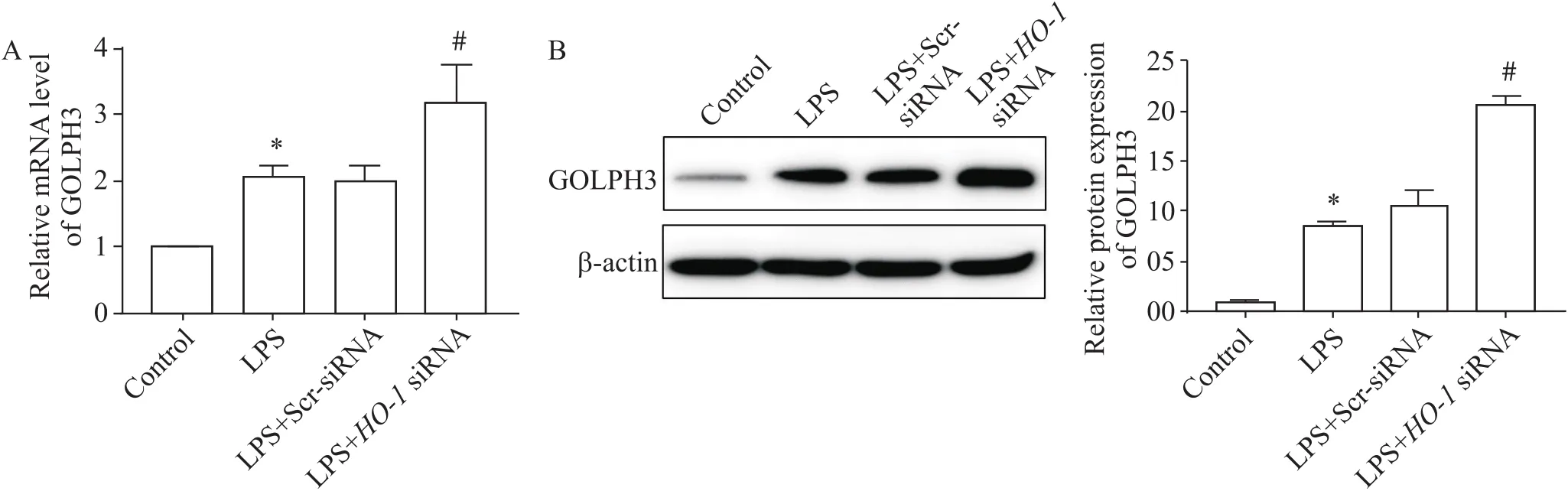
Figure 4.GOLPH3 expression levels in alveolar macrophages. A: GOLPH3 mRNA expression of each group was measured by RT-qPCR; B: GOLPH3 protein expression of each group was measured by western blot. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs LPS group.
3 高爾基體結構相關蛋白表達的變化
LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞中,高爾基體結構相關蛋白GM130、golgin-97及mannosidase II表達水平下降(<0.05);沉默-后,與LPS組相比,GM130、golgin-97及mannosidase II表達水平顯著下降(<0.05),見圖5。
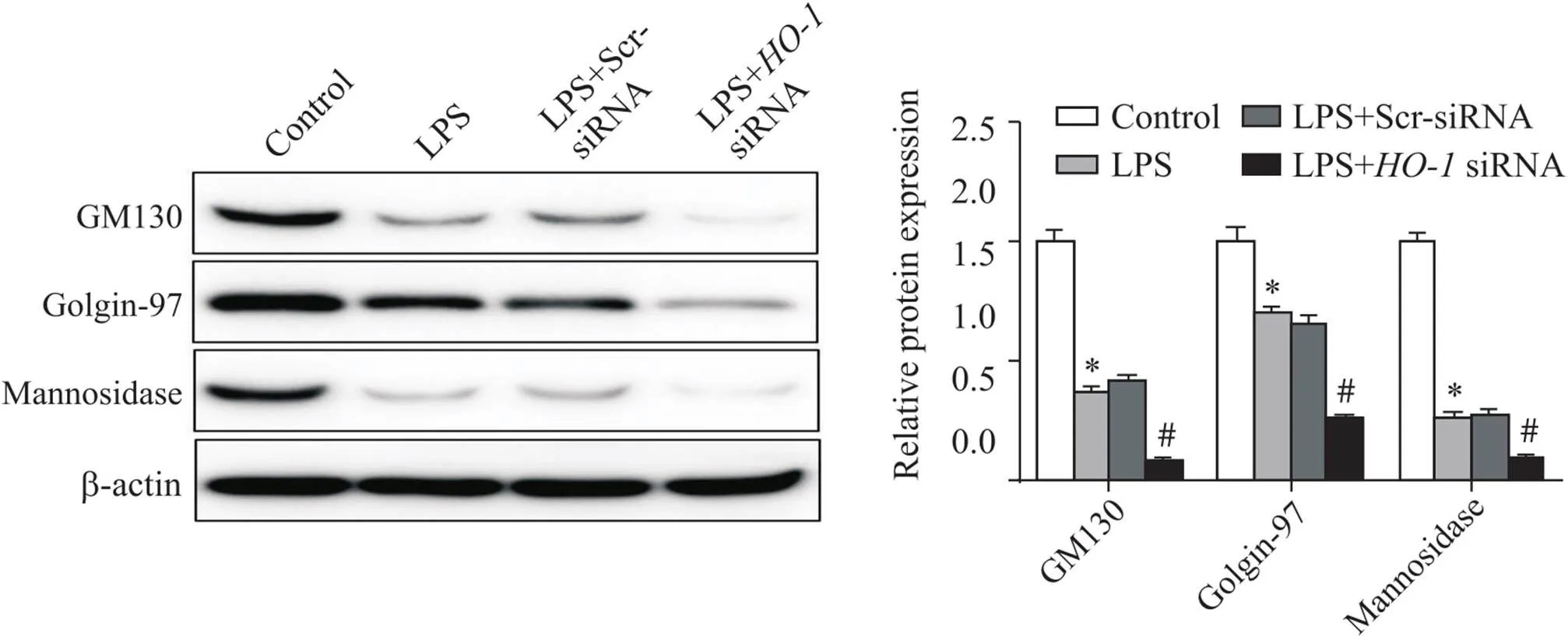
Figure 5.The expression of Golgi structure-related proteins (GM130, golgin-97 and mannosidase II) in alveolar macrophages measured by Western blot. Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs LPS group.
4 肺泡巨噬細胞凋亡的變化
與對照組相比,LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞中TUNEL標記陽性細胞數增多,caspase-3/7活性增強(<0.05);沉默-后,與LPS組相比,TUNEL標記陽性細胞顯著增多,caspase-3/7活性顯著增強(<0.05),見圖6。
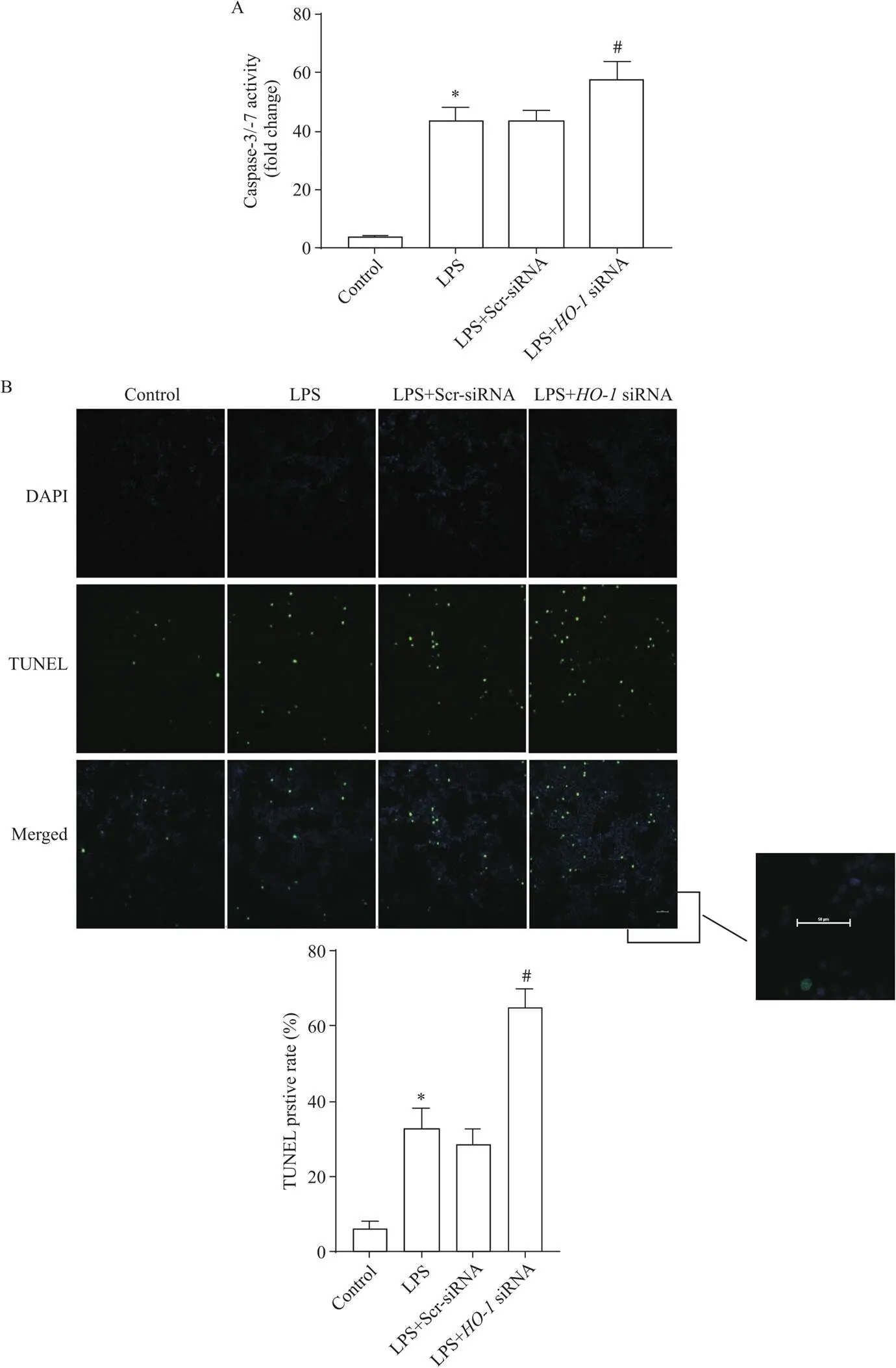
Figure 6.The apoptosis of alveolar macrophages in each group. A: the apoptosis of alveolar macrophages was detected by caspase-3/7 activity determination; B: the apoptosis of alveolar macrophages was detected by TUNEL assay (green: TUNEL-positive nuclei; blue: DAPI-stained nuclei; scale bar=50 μm). Mean±SD. n=3. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs LPS group.
討論
ALI是以彌漫性肺泡損傷、肺水腫、免疫細胞浸潤和肺順應性下降為特征的臨床綜合征,嚴重時可致患者死亡[16]。內毒素是ALI的常見原因,可激活巨噬細胞引發炎癥[17]。正常情況下,肺泡巨噬細胞具有維持肺免疫穩態和抑制固有免疫的雙重作用[2]。在ALI病程中,肺泡巨噬細胞主要通過早期啟動炎癥和晚期抑制炎癥免疫反應以發揮關鍵作用[16, 18]。研究表明,肺泡巨噬細胞功能障礙和凋亡增加會抑制肺部中性粒細胞清除,導致炎癥消退延遲和組織損傷[1, 18]。因此,肺泡巨噬細胞在ALI中的重要作用表明肺泡巨噬細胞可能是治療ALI的潛在靶點。
高爾基體是細胞內重要的信號中樞,具有重要生物合成和加工、運輸、分選等功能[19]。在氧化應激、DNA損傷和營養缺乏等應激條件下,高爾基體通過表達GOLPH3感知并啟動應激反應,高爾基體結構相關蛋白GM130、golgin-97等被切割降解,導致高爾基體結構碎裂和功能受損,引起細胞凋亡[4, 6, 10]。高爾基體應激也可向下游傳遞應激信號,促進細胞凋亡[4]。此外,許多位于高爾基體的促凋亡因子半胱天冬酶-2等可反向誘導高爾基體結構相關蛋白GM130、golgin-97和golgin-160等裂解[4,20-21]。研究表明,一些神經退行性疾病和神經發育疾病與高爾基體應激蛋白GOLPH3表達增加和高爾基體結構相關蛋白裂解密切相關[22-23]。本研究組前期研究表明,高爾基體應激在急性肺損傷中發揮重要作用[24],但在LPS刺激的肺泡巨噬細胞模型中的作用尚不清楚。因此,本實驗選擇LPS誘導NR838細胞以制備肺泡巨噬細胞急性損傷模型進行實驗,以探究高爾基體應激在LPS誘導急性肺損傷的作用機制提供研究依據。結果顯示,LPS攻擊肺泡巨噬細胞時,細胞氧化應激和高爾基體應激增加,高爾基體結構相關蛋白表達下降,細胞凋亡增加。
HO-1是一種重要的抗氧化酶,在LPS誘導的肺損傷、心肌損傷和腎損傷等多組織損傷中發揮保護性作用[25-27]。本課題組前期研究表明,HO-1可通過促進線粒體融合蛋白1、線粒體融合蛋白2和視神經萎縮蛋白1的表達,抑制線粒體分裂蛋白1和線粒體動力相關蛋白1的表達,以調節線粒體融合分裂平衡,減輕急性肺損傷[12, 28]。此外,HO-1還可通過調節線粒體質量控制,抑制內質網應激以發揮抗炎、抗氧化、抗凋亡作用[13, 29]。本實驗結果顯示,下調HO-1表達后,LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞氧化應激和高爾基體應激加重,高爾基體結構相關蛋白表達進一步下降,細胞凋亡顯著增加,表明HO-1可能通過調控高爾基體應激和氧化應激以減輕LPS誘導的肺泡巨噬細胞損傷,減少細胞凋亡。但HO-1調控高爾基體應激的具體機制,以及在體內實驗中HO-1是否可通過調控高爾基體應激,減輕細胞凋亡,以改善急性肺損傷仍需進一步研究。
綜上所述,內毒素攻擊大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞時,HO-1可以調控高爾基體應激和氧化應激,減少細胞凋亡。
[1] Liu HZ, Zhou KF, Liao LK, et al. Lipoxin A4 receptor agonist BML-111 induces autophagy in alveolar macrophages and protects from acute lung injury by activating MAPK signaling[J]. Respir Res, 2018, 19(1):243.
[2] Kumar V. Pulmonary innate immune response determines the outcome of inflammation during pneumonia and sepsis-associated acute lung injury[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11:1722.
[3]楊冰, 朱路明, 江麗麗, 等. 黃芩苷通過抑制HMGB-1減少U937巨噬細胞的M1型極化和減輕小鼠的急性肺損傷[J]. 中國病理生理雜志, 2021, 37(7):1233-1239.
Yang B, Zhu LM, Jiang LL, et al. Baicalin inhibits HMGB-1 to reduce M1 polarization of U937 macrophages and attenuate acute lung injury in mice[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2021, 37(7):1233-1239.
[4] Li T, You H, Mo XY, et al. GOLPH3 mediated Golgi stress response in modulating N2A cell death upon oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation injury[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2016, 53(2):1377-1385.
[5] Zhang YJ, Wang YH, Read E, et al. Golgi stress response, hydrogen sulfide metabolism, and intracellular calcium homeostasis[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2020, 32(9):583-601.
[6] Li J, Ahat E, Wang YZ. Golgi structure and function in health, stress, and diseases[J]. Results Probl Cell Differ, 2019, 67:441-485.
[7] Li T, You H, Zhang J, et al. Study of GOLPH3: a potential stress-inducible protein from Golgi apparatus[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2014, 49(3):1449-1459.
[8] Velasco A, Hendricks L, Moremen KW, et al. Cell type-dependent variations in the subcellular distribution of alpha-mannosidase I and II[J]. J Cell Biol, 1993, 122(1):39-51.
[9] Hicks SW, Machamer CE. Golgi structure in stress sensing and apoptosis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2005, 1744(3):406-414.
[10] Ireland SC, Huang HR, Zhang JC, et al. Hydrogen peroxide induces Arl1 degradation and impairs Golgi-mediated trafficking[J]. Mol Biol Cell, 2020, 31(17):1931-1942.
[11] Yu JB, Wang Y, Li Z, et al. Effect of heme oxygenase-1 on mitofusin-1 protein in LPS-induced ALI/ARDS in rats[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:36530.
[12] Yu JB, Shi J, Wang D, et al. Heme oxygenase-1/carbon monoxide-regulated mitochondrial dynamic equilibrium contributes to the attenuation of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rats and in lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages[J]. Anesthesiology, 2016, 125(6):1190-1201.
[13] 胡欣欣, 宮麗榮, 史佳, 等. HO-1在LPS致大鼠肺泡巨噬細胞凋亡中的內源性保護作用: 與內質網應激的關系[J]. 中華麻醉學雜志, 2020, 40(6):752-755.
Hu XX, Gong LR, Shi J, et al. Role of HO-1-induced endogenous protection in LPS-caused apoptosis in rat alveolar macrophages: relationship with endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Chin J Anesthesiol, 2020, 40(6):752-755.
[14] Shi J, Yu JB, Liu W, et al. Carbon monoxide alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress injury through suppressing the expression of Fis1 in NR8383 cells[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 349(1):162-167.
[15] Sim?es AE, Pereira DM, Amaral JD, et al. Efficient recovery of proteins from multiple source samples after TRIzol?or TRIzol?LS RNA extraction and long-term storage[J]. BMC Genomics, 2013, 14:181.
[16] Li Y, Chen X, Zhang H, et al. 4-Octyl itaconate alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2020, 14:5547-5558.
[17] Huang JH, Nong XP, Chen YL, et al. 3---caffeoyloleanolic acid improves acute lung injury via anti-inflammation and antioxidative stress-involved PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Chem Biol Drug Des, 2021, 98(1):114-126.
[18] Nepal S, Tiruppathi C, Tsukasaki Y, et al. STAT6 induces expression of Gas6 in macrophages to clear apoptotic neutrophils and resolve inflammation[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2019, 116(33):16513-16518.
[19] He Q, Liu H, Huang CX, et al. Herpes simplex virus 1-induced blood-brain barrier damage involves apoptosis associated with GM130-mediated Golgi stress[J]. Front Mol Neurosci, 2020, 13:2.
[20] Mancini M, Machamer CE, Roy S, et al. Caspase-2 is localized at the Golgi complex and cleaves golgin-160 during apoptosis[J]. J Cell Biol, 2000, 149(3):603-612.
[21] Nozawa K, Casiano CA, Hamel JC, et al. Fragmentation of Golgi complex and Golgi autoantigens during apoptosis and necrosis[J]. Arthritis Res, 2002, 4(4):R3.
[22] Passemard S, Perez F, Gressens P, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stress in microcephaly[J]. Cell Stress, 2019, 3 (12):369-384.
[23] Guiney SJ, Adlard PA, Bush AI, et al. Ferroptosis and cell death mechanisms in Parkinson's disease[J]. Neurochem Int, 2017, 104:34-48.
[24] Li XY, Yu JB, Gong LR, et al. Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) regulates Golgi stress and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury through hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2021, 165:243-253.
[25] Li HB, Zhang XZ, Sun Y, et al. HO-1/PINK1 regulated mitochondrial fusion/fission to inhibit pyroptosis and attenuate septic acute kidney injury[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020, 2020:2148706.
[26] Chen XX, Wu SS, Tang L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing heme oxygenase-1 ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5):7301-7319.
[27] 程梅, 董曉筠, 朱彬. 利多卡因對膿毒癥大鼠心肌損傷及Nrf2/HO-1通路的影響[J]. 中國病理生理雜志, 2021, 37(4):634-639.
Chen M, Dong XY, Zhu B. Effects of lidocaine on myocardial injury and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in sepsis rats[J]. Chin J Pathophysiol, 2021, 37(4):634-639.
[28] Shi J, Yu JB, Zhang Y, et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-mediated HO-1/CO represses Fis1 levels and alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative injury in alveolar macrophages[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(3):2735-2742.
[29] Shi J, Yu JB, Zhang Y, et al. PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated HO-1 induction regulates mitochondrial quality control and attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury[J]. Lab Invest, 2019, 99(12):1795-1809.
Role of HO-1 on Golgi stress in LPS-stimulated rat alveolar macrophages
LI Yu-ting, LI Xiang-yun, SHI Jia, LI Cui, YU Jian-bo△
(,,,,300100,)
To evaluate the role of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) on Golgi stress in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated rat alveolar macrophages.The injury model of rat alveolar macrophages was established by LPS stimulation. CCK-8 assay was applied to measure cell viability, and the DCFH-DA probing was used to detect the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). In addition, the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) were assayed by SOD and MDA kits, and apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL assay and caspase-3/7 activity determination. The mRNA expression levels of HO-1 and Golgi phosphoprotein 3 (GOLPH3) were detected by RT-qPCR, and the protein expression levels of HO-1, GOLPH3 and Golgi structure-related proteins (GM130, golgin-97 and mannosidase II) were detected by Western blot.small interfering RNA (siRNA) was applied to reduce the expression ofin rat alveolar macrophages.Stimulation with LPS reduced cell viability and SOD activity, increased the levels of ROS and MDA, up-regulated the expression of HO-1 and GOLPH3, impaired the expression of GM130, golgin-97 and mannosidase II, and further increased TUNEL positive rate and caspase-3/7 activityin rat alveolar macrophages (<0.05). Knockdown ofsignificantly inhibited cell viability and SOD activity, increased ROS and MDA levels, decreased the expression of HO-1, GM130, golgin-97 and mannosidase II, increased the expression of GOLPH3, and further increased TUNEL positive rate and caspase-3/7 activity (<0.05).The HO-1 attenuates oxidative stress and Golgi stress response, and prevents apoptosis in LPS-stimulated alveolar macrophages.
Golgi stress; Heme oxygenase-1; Lipopolysaccharides; Alveolar macrophages; Oxidative stress
R329.2+5; R363
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-4718.2022.03.016
1000-4718(2022)03-0509-08
2021-07-05
2022-01-13
[基金項目]國家自然科學基金資助項目(No.81772106)
Tel: 022-27435873; Email: jianboyu99@sina.com
(責任編輯:林白霜,羅森)

