一種鎘基配位聚合物的合成及其對2,4,6-三硝基苯酚的熒光識別
王高峰 孫述文 宋少飛 呂 玫
(運城學院應用化學系,運城 044000)
0 Introduction
With the increasing application of explosive materials in many areas, sensitive detection of explosive compounds has become a great challenge because of public health threats, environmental safety, and human health[1-5]. An explosive compound, namely 2,4,6-trinitrophenol (TNP), has been extensively used in many areas such as rocket fuels, matches, fireworks, dyes,and leather industries[6-7].Moreover,exposure of TNP to the environment severely affects the aquatic and soil system,causing fatal problems for humans and wildlife.Many methods have been applied to detect TNP, such as ion mobility spectrometry, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, and plasma desorption mass spectrometry[8-9]. However, these high-cost and time-consuming methods are usually performed under harsh conditions.
Recently, coordination polymers (CPs) have attracted tremendous research interests as functional materials owing to their potential applications in magnetism, gas storage and separation, and sensing[10-16].The crystalline materials of luminescent CPs provide advantages over other sensor materials because of their simplicity,high sensitivity,and instantaneous response.CPs withπ-conjugated polytopic ligands may exhibit strong emission and free coordination sites, which play vital roles in improving their sensitivity and selectivity as sensor materials[17].
As part of our research on the design of CPs with interesting properties[18-19], a unique carbazole-based ligand 3,6-di(pyridin-4-yl)-9-(4-(pyridin-4-yl)phenyl)-9H-carbazole (dppc), was selected to construct novel CPs because of itsπ-conjugated skeleton and multiple coordination sites. A new stable CP, namely {[Cd(adc)(dppc)(H2O)]·2H2O}n(1),where H2adc=adamantane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid, was synthesized and structural characterized. It can sensitively detect TNP in DMF solution with a very large quenching coefficient.
1 Experimental
1.1 Materials and methods
All reagents,e.g. TNP, 1,4-dinitrobenzene (1,4-DNB), 1,2-dinitrobenzene (1,2-DNB), 1,3-dinitrobenzene (1,3-DNB), 4-nitrotoluene (4-NT), andN,Ndimethylacetamide (DMA) were commercially available as analytical grade and used without further purification. 3,6-Dibromo-9-(4′-bromophenyl)carbazole was prepared according to the literature[20].Elemental analysis (C, H, N) was performed on an Elementar Vario ELⅢelemental analyzer. The IR spectra were recorded on a Bruker Vector 22 spectrophotometer in a range of 4 000-400 cm-1using KBr pellets. The Luminescence spectra were measured on a Hitachi F-4600 fluorescence spectrometer.
1.2 Synthesis of ligand dppc
Potassium carbonate (7.6 g, mmol) was suspended in a degassed solution of 1,4-dioxane (120 mL) and water (80 mL). 3,6-Dibromo-9-(4′-bromophenyl)carbazole (4.80 g, 10 mmol), 4-pyridyl boronic acid (6.76 g,55 mmol), and Pd(PPh3)4(500 mg, 0.434 mmol) were then added and the reaction mixture was heated at 90 ℃under nitrogen for 4 d. The solvent was evaporated until the volume was approximately 120 mL,precipitating a white compound. The precipitate was filtered after cooling to r.t., washed with EtOH, and then with water. Yield: 67.5%. Anal. Calcd. for C33H22N4(%): C,83.52;H,4.67;N,11.81.Found(%):C,83.41;H,4.59;N, 11.95.1H NMR (CDCl3, 500 MHz): δ 8.00 (s, 1H),7.99-7.57 (m, 4H), 7.29 (s, 1H). IR (KBr, cm-1): 3 240(m), 3 015(w), 1 645(m), 1 591(w), 1 524(m), 1 473(s),1 403(m),1 369(w),1 285(m),1 228(m),1 172(w),1 145(w), 1 030(w), 996(w), 909(w), 796(s), 758(w), 725(w),619(m),578(w),527(w),494(w),421(w).
1.3 Synthesis of complex 1
A mixture of Cd(NO3)2·6H2O (0.016 mmol, 4.8 mg), H2adc(0.016 mmol, 3.6 mg), dppc (0.016 mmol,7.6 mg) in DMA/H2O (7.0 mL, 5∶2,V/V) was sealed in a 15 mL reactor, heated to 95 ℃for two weeks, and then cooled to room temperature. Yellow block crystals were obtained by being washed with EtOH, filtrated,and dried in air (Yield: 53% based on dppc). Anal.Calcd. for C45H42CdN4O7(% ): C, 62.61; H, 4.90; N,6.49. Found(%): C, 62.52; H, 4.82; N, 6.56. IR (KBr,cm-1): 3 452(s), 3 382(s), 3 134(s), 2 919(m), 2 852(w),2 449(w),2 358(w),1 708(w),1 635(m),1 602(m),1 521(w), 1 475(w), 1 394(w), 1 280(w), 1 263(m), 1 220(w),1 132(s),1 066(s),993(m),950(s),864(m),817(m),761(w),705(w),619(m),561(m),538(s),514(s).
1.4 Crystal structure determination
X-ray structural data for complex 1 were recorded on a Bruker Smart-1000 CCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromatic MoKαradiation (λ=0.071 073 nm) by using anφ-ωscans mode at 293(2)K. Absorption corrections were applied using the program SADABS[21]. The structure was solved using the direct method and refined onF2with the full-matrix least-squares techniques of the SHELXTL program[22-23].All non-hydrogen atoms were refined anisotropically and the hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms were generated geometrically. The water hydrogen atoms(H5A,H5B,H6A,H6B,H7A,H7B,H7A′,H7B′)were located in difference Fourier maps and refined with O—H bond length of 0.085(2) nm and H…H distance of 0.135(2) nm as restraints. The disordered atoms O2,O7, and the aryl atoms (C23-C28, C30, C31, N3, C32,C33)were split over two sites,with a total occupancy of 1. SIMU, SADI, and DELU commands in SHEXTL(version 6.10)[22]were used to restrict theirUeq. The details of crystal data and refinement for 1 are given in Table 1. Selected bond lengths and angles for 1 are listed in Table 2.
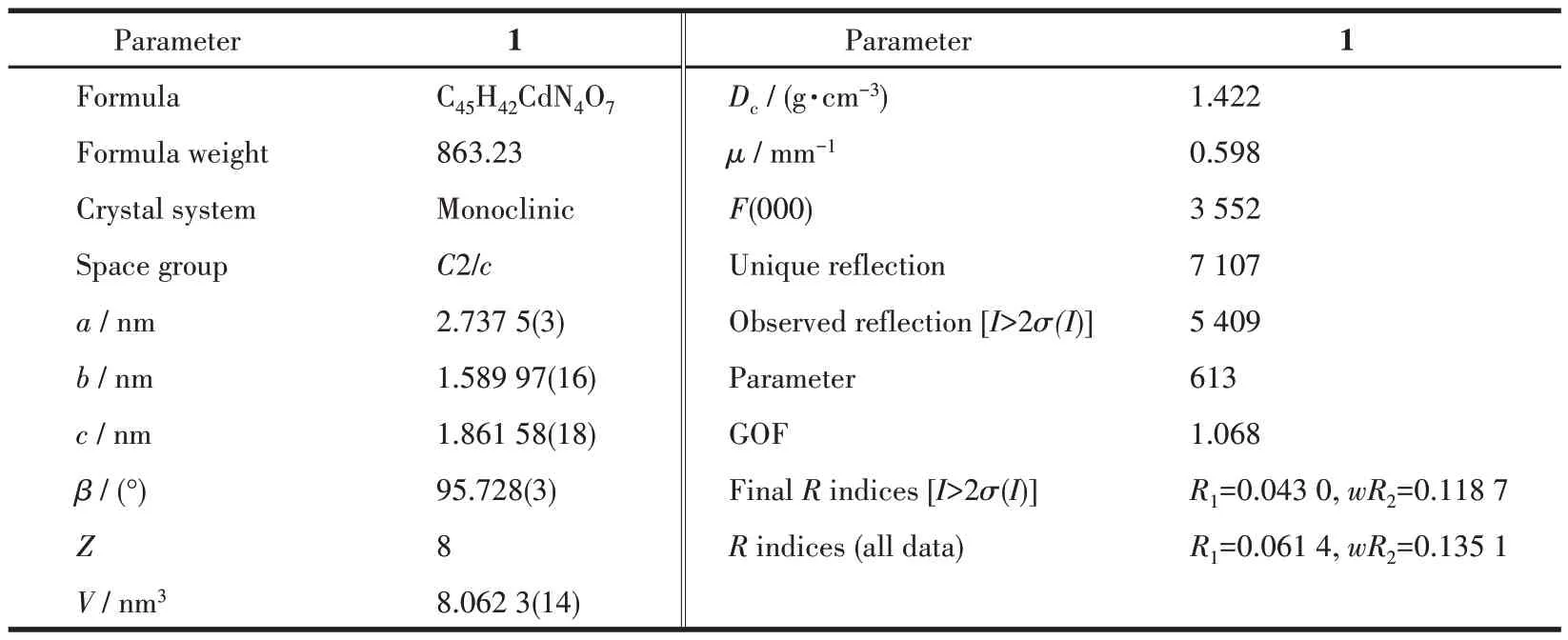
Table 1 Crystal data and refined parameters of complex 1
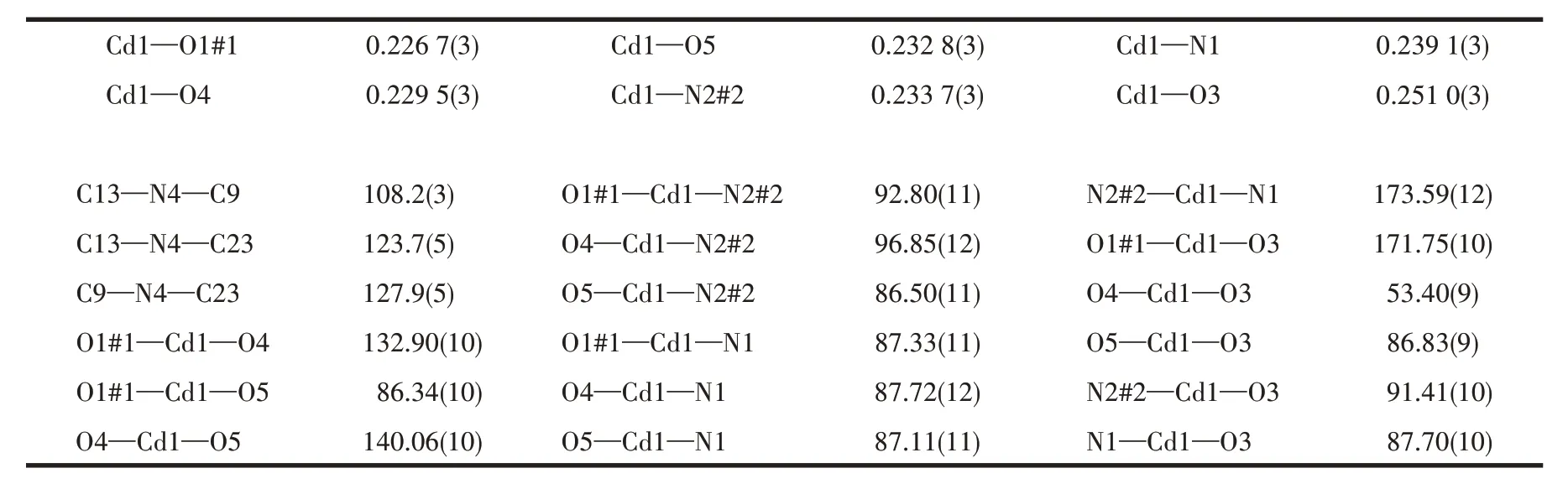
Table 2 Selected bond lengths(nm)and bond angles(°)for complex 1
CCDC:2233682.
2 Results and discussion
2.1 Crystal structure of complex 1
Complex 1 crystallizes in the monoclinicC2/cspace group. Its asymmetric unit consists of one Cd(Ⅱ)ion,one adc2-anion,one dppc molecule,one coordinated water molecule, and two lattice water molecules. As shown in Fig.1a, each Cd(Ⅱ)ion is in a slightly distorted octahedral geometry coordinated by two nitrogen atoms from two individual dppc molecules, three oxygen atoms from two individual adc2-ligands, and one oxygen atom from one coordinated water molecule. The Cd—N distances are 0.233 7(3) and 0.239 1(3) nm,and the Cd—O bonds range between 0.226 7(3) and 0.251 0(3) nm. In addition, the bond angles around each Cd(Ⅱ)range from 53.40(9)° to 173.59(12)° (Table 2).The bond lengths and bond angles are all within the normal range for reported Cd-based complexes[17,24-26].The carboxylate groups ligate to the metal ions in aμ2-η0∶η1∶η1∶η1coordination mode (Fig.1a).In 1,each adjoining pair of Cd(Ⅱ)ions is connected by adc2-ligands to form a [Cd(adc)]nchain along the b-axis (Fig.1b).The adjacent [Cd(adc)]nchains are linked by dppc to give rise to a stair-shaped network of [Cd(adc)(dppc)]nextending in the bc plane(Fig.1c).
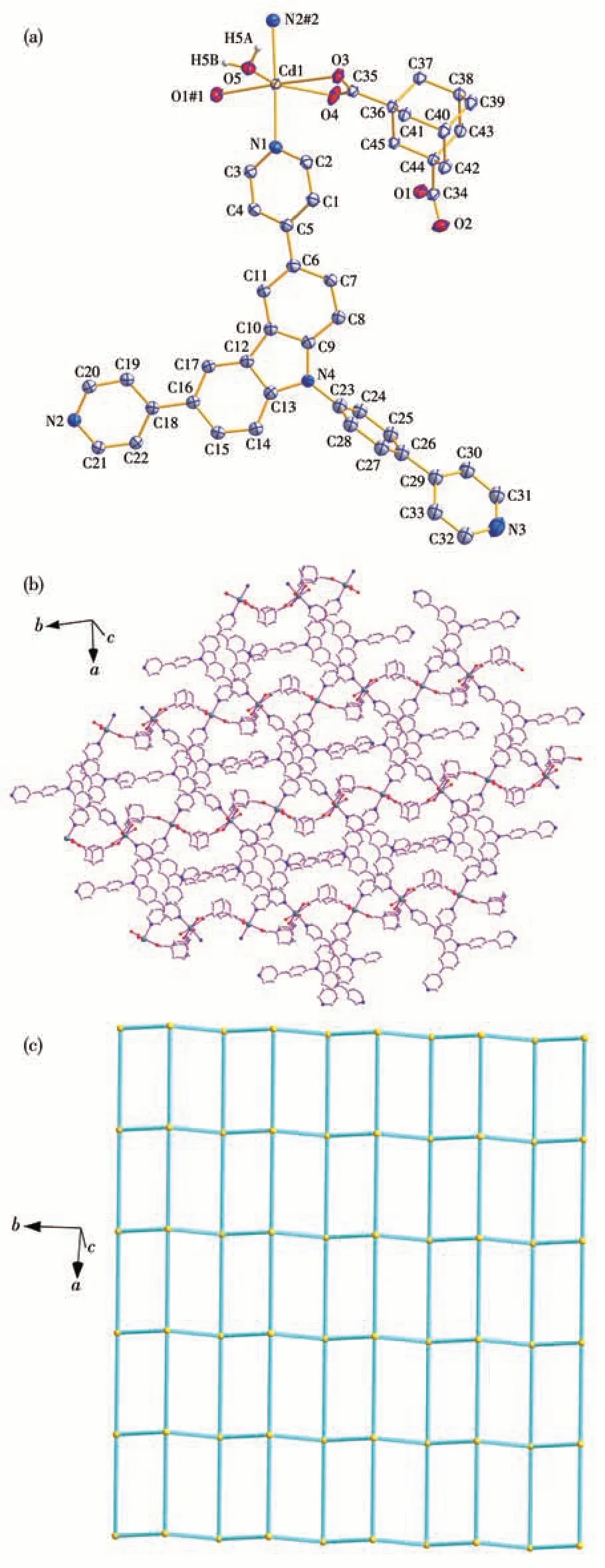
Fig.1 Crystal structure of complex 1:(a)Coordination environment,where another part of the disordered atoms,hydrogen atoms bonded to carbon atoms,and lattice water molecules are omitted for clarity;(b)View of the layer structure;(c)Simplified structure with the(44·62)topology
Based on the simplification principle[27], the Cd(Ⅱ)center is simplified to a 4-connected node, the adc2-and dppc ligands act as 2-connected linkers, the whole network can be simplified as uninodal {44.62} topology,as shown in Fig.1c,S1,and Table S1(Supporting information). In addition, some C—H…O and O—H…O hydrogen bonds were observed between adjacent layers(Fig S1 and Table S1), which are assembled into a 3D supramolecular structure.
2.2 Luminescence properties
CPs based ond10metal ions along with the electron-richπ-conjugated ligands often show interesting luminescent properties, which are applied as chemical sensors[28-29]. The solid-state luminescence spectra of complex 1 and ligand dppc were investigated under the same experimental conditions. As shown in Fig.2, the strong emission of dppc was observed at 423 nm (λex=363 nm), while the emission of 1 was observed at 433 nm (λex=381 nm). A red-shifted 10 nm as compared with pure dppc ligand was observed, which can be attributed to charge-transfer transitions between ligands and metal ion centers[17,24]. The strong coordination bonds between the metal ions and the dppc ligand will enhance the rigidity of the dppc ligand in complex 1,and thus decrease the loss of energy upon excitation,which results in the stronger emission of 1 compared to the free dppc ligand[17].
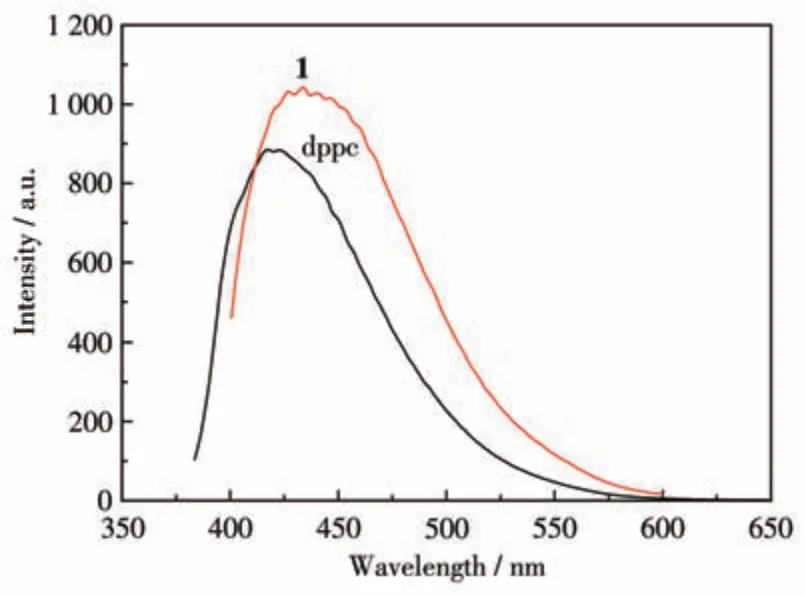
Fig.2 Solid-state luminescence spectra of complex 1 and ligand dppc
2.3 Luminescence detecting TNP
The strong solid-state luminescence of complex 1 encourages us to investigate its potential applications in detecting nitroaromatic compounds. As shown in Fig.3,the luminescence properties of 1 as a suspension in different solvents such as DMF, DMA, THF, and EtOH are displayed. The emission peaks of 1 were found at 427 nm upon excited at 351 nm and the emission intensities were strongly dependent on the dispersants, with the strongest emission found in the DMF solution. Therefore, luminescence titration experiments were carried out in DMF suspension of 1 by the addition of different nitroaromatic compound solutions(TNP, 1,4-DNB, 1,2-DNB, 1,3-DNB, and 4-NT). Upon the addition of 100 μL TNP solution, the emission intensity of 1 was quenched by nearly 99.59%. In contrast, it was much higher than those for 1 on the addition of 100 μL other different nitroaromatic compound solutions(39.78%,29.51%,24.44%,and 17.26% for 1,4-DNB, 1,2-DNB, 1,3-DNB, and 4-NT, respectively)(Fig.4). The results demonstrate that 1 can be used as chemical sensors with high sensitivity for detecting TNP.
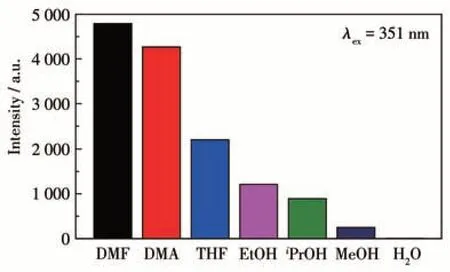
Fig.3 Comparisons of the luminescence intensities of complex 1 in different dispersants

Fig.4 Comparison of the quenching efficiency of 1 for different nitroaromatic compounds(5 mmol·L-1,100 μL)
The luminescence quenching efficiency of TNP can be quantitatively investigated using the Stern-Volmer (SV) equation[17]:I0/I=1+KsvcM, wherecMis the molar concentration of analyte,I0andIare the maximum luminescent intensity of complex 1 before and after addition of the analyte, andKsvis the quenching constant. At low concentrations, the SV plots for nitroaromatic compounds were nearly linear. It could be an energy transfer mechanism occurring between the complex and the analyte since the emission band is red shift(85 nm)upon increasing addition of TNP solution (Fig.5a). The quenching constant of 1 was found to be 7.6×104L·mol-1for TNP from the linear fitting of the plot at low concentration (Fig.5b). In addition, the detection limit of the assay calculated with 3σ/|k| (k:slope,σ: standard deviation) at the low concentration(0-25 μmol·L-1) was about 0.638 μmol·L-1for sensing TNP (Fig.6). The largeKsvand small detection limit values indicate complex 1 were better than those of reported MOFs for detecting TNP(Table 3).
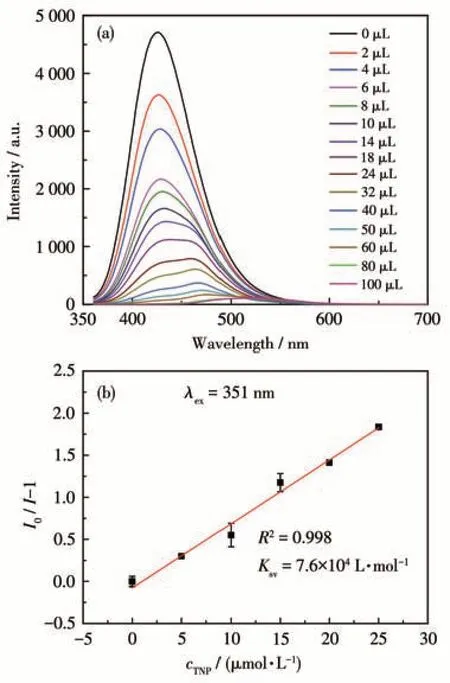
Fig.5 (a)Emission spectra of complex 1 dispersed in DMF upon addition of TNP solution(5 mmol·L-1);(b)SV plot for sensing TNP of 1 in DMF suspension at the low concentration(0-25 μmol·L-1)
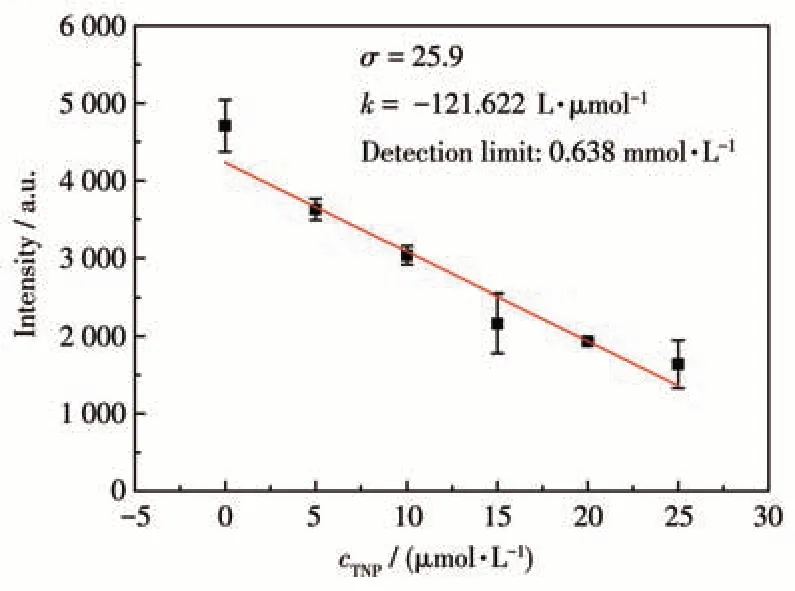
Fig.6 Detection limit for sensing TNP of complex 1 in DMF suspension calculated with 3σ/|k|(k:slope,σ:standard deviation)at the low concentration(0-25 μmol·L-1)
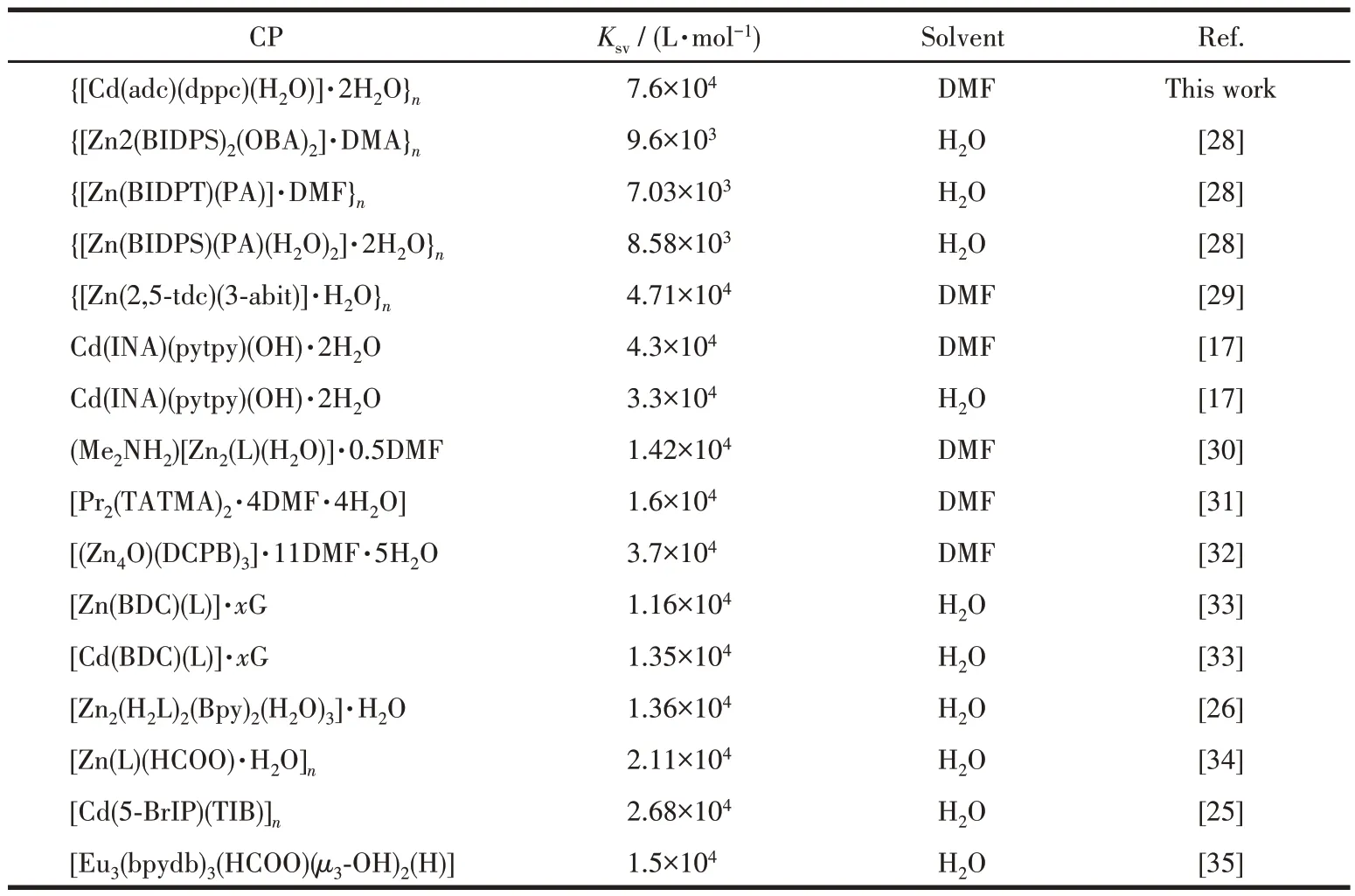
Table 3 Quenching constants of the reported CPs for detecting TNP in DMF or H2O suspension
The TNP selective detection capability of complex 1 was investigated through an anti-interference experiment conducted in the presence of other nitroaromatic compounds[17]. Initially, the emission intensity of 1 was monitored. Subsequently, two equal portions of a 10 μL solution of 1,4-DNB (5 mmol·L-1) were added to the suspension, resulting in a negligible decrease in emission intensity. However, a significant decrease in emission intensity was observed upon adding an equal amount of a 5 mmol·L-1TNP solution (Fig.7). This trend persisted in subsequent cycles of analyte addition. Furthermore, similar results were obtained when evaluating the detecting selectivity between other nitroaromatic compounds and TNP. Based on these findings, it can be concluded that complex 1 exhibits a robust anti-interference ability towards TNP.
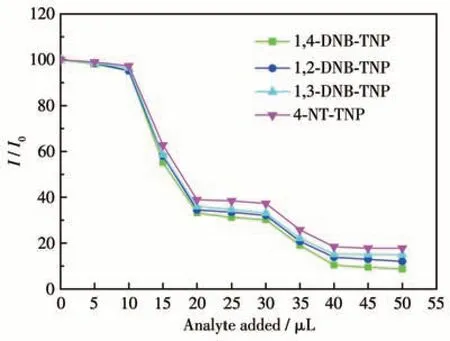
Fig.7 Competitive luminescence quenching of complex 1 upon addition of other nitroaromatic compounds followed by TNP
More importantly,complex 1 can be recycled after the luminescence titration experiment. The suspension containing 1 and TNP were centrifuged to separate the solids and washed with DMF, then dried. As illustrated in Fig.8, the luminescence intensity can be regained and the sensing ability of 1 exhibited little changes after five cycles. These results indicated that 1 is an excellent TNP sensor.
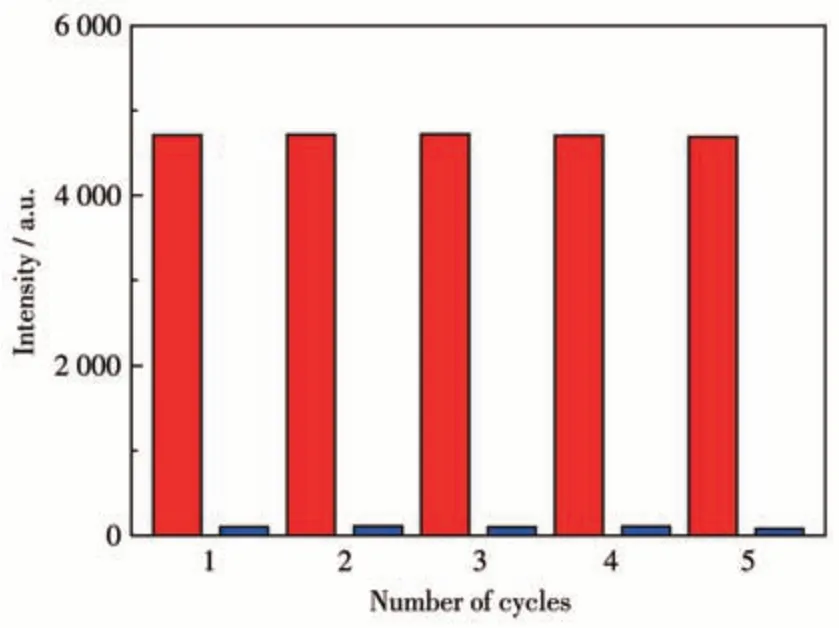
Fig.8 Recyclability of complex 1 for TNP detection in DMF
3 Conclusions
In summary, a carbazole-based Cd(Ⅱ)CP (1) was successfully synthesized and characterized. Complex 1 exhibits a uninodal net with {44·62}topology,constructed by Cd(Ⅱ)ions, dppc and adc2-“bridges”. The luminescent investigations suggest that 1 can sensitively detect TNP in DMF solution by luminescent quenching effect. The mechanisms of 1 for detecting TNP have been preliminarily elucidated. The results show that 1 can be used as a stable and recyclable chemical sensor for the detection of TNP.
Supporting information is available at http://www.wjhxxb.cn

