HSCCC-ELSD法分離純化青葙子中的皂苷
武清斌,王 燕,郭美麗
第二軍醫大學藥學院,上海200433
Introduction
Celosia argentea L.(Amaranthaceae)is widely distributed in southern China,Asia and torrid zones of Africa[1].Semen celosiae,the dried ripe seeds of C.argentea,has long been used in folk practices for the treatment of hepatitis,caligo corneae,hypertension and sarcoptidosis[2].The crude EtOH extract of Semen celosiae possesses antipyretic,antispasmodic,anticancer,diuretic,anti-inflammatory and antibacterial activities[3].
A phytochemical investigation of Semen celosiae mainly focused on the isolation of alkaloids[4],cyclic peptides[5-8],palmitic,and oleanolic acids[9,10].However,for the time being,few researches about the triterpenoid saponins of Semen celosiae were reported.In our continuing search for bioactive compounds from this plant,four hepatoprotective saponins celosins A,B,C and D were isolated from the ethanol extract of Semen celosiae[11,12].The conventional method of purifying celosins A and B was utilizing column chromatography[11],which required multiple steps and was time-consuming,often with low recovery yields and purity.For determining the content of Semen celosiae from various origins,the purity of celosins A and B needs to be at least 98%.This article describes our successful preparative separation and purification of celosins A and B from the extract of Semen celosiae by high-speed counter-current chromatography(HSCCC)combined with ELSD for the first time.
Experiment
Apparatus
The preparative HSCCC instrument(Model TBE-300B,Tauto Biological Company,Shanghai,China) was equipped with three preparative coils connected in series(diameter of the polyte-tra?uoroethylene(PTFE)tube,2.6 mm;total volume,280 mL)and a 20 mL sample loop.The revolution speed of the instrument was regulated with a speed controller in the range between 0 and 1000 rpm.The constant-flow pump(Model TBP5002,Tauto Biological Company,Shanghai,China) pumped the two-phase solvent into the column at a flow rate of up to 50 mL/min and pressure up to 2.0 MPa.The vessel was retained at 25℃ by a Model HX-1050 constant-temperature controller(Beijing Detianyou Technology,Beijing,China).An optimum speed of 2.0 mL/min was used in the experiment.The effluent was monitored continuously with an evaporative light scattering detector(SEDEX 85 ELSD,France).
Materials

Fig.1 The chemical structures of celosins A and B
The seeds(Semen celosiae)were collected in Bozhou,Anhui province of China in October 2004,and identified by the author.A voucher specimen(SMMU 04063)was deposited at the herbarium of the Second Military Medical University(Shanghai,China).Column chromatographic separation was performed on D101 MR(Chemical Factory of Nankai University,Tianjin,PR.China)and ODS(50 mesh,AA12S50,YMC).The solvents used for HSCCC and preparation of the total saponins were of analytical grade from China National Medicine Group Shanghai Chemical Reagent Company(Shanghai,China).Methanol(Merck),acetonitrile(Honeywell)and pure distilled water were used for high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).The standard substances of celosins A and B (Fig.1)were offered by Xue Qian[11].
Preparation of the major saponins
The dried seeds(Semen celosiae,10 kg)were ground to a coarse powder and extracted with 50%ethanol at room temperature after 24 h maceration.The extracted liquid was concentrated under reduced pressure to give an ethanol extract(3.6 kg).A portion of the ethanol extract(3.0 kg)was subjected to chromatographic separation over D101 MR(10 kg)eluted sequentially four times with a gradient of H2O,30%,60%,and 95%EtOH to give four fractions with the yields of 45.3,50.7,90.1 and 18.9 g,respectively.The 30% EtOH fraction(2.0 g)was chromatographed through ODS silica gel(3.5×40 cm),eluted with a gradient of MeOH-H2O(5∶95→30∶70→50∶50,v/v,1000 mL,1200 mL,1500 mL)to afford three fractions.The third fraction(790 mg)was called the major saponins.Celosins A and B were isolated from the major saponins.
Selection of a two-phase solvent system
Selection of a two-phase solvent system for the target compounds is the most important step in HSCCC,accounting for 90%of the total work in HSCCC[13].Two principles are generally followed.First,it is important to find a system with K value of the target compounds in a proper range:the suitable K value for HSCCC is 0.5<K<1.0.K is the ratio of the solute distributing between the mutually equilibrated two solvent phases.Second,higher retention of the stationary phase normally results in better peak resolution.Successful separation in HSCCC largely depends on the amount of the stationary phase retaining in the column.The setting time of the two-phase solvent system is less than 20 s.A two-phase solvent system containing dichloromethane-methanol-n-butanol-water(4∶3∶0.3∶2,v/v/v/v) with addition of 0.5%glacial acetic acid was chosen for the separation and purification of the major saponins.
HSCCC separation procedures
Preparative HSCCC separation was performed as follows.First of all,the multilayer coiled column was entirely filled with the upper phase(solid phase)at a flow rate of 50 mL/min.Then,the lower phase(mobile phase)was pumped into the head end of the column at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min when the instrument was rotated at a revolution speed of 850 rpm at constant temperature 25℃.After hydrodynamic equilibrium was reached,120 mL solid phase eluted at the tail outlet,so the retention rate was 75%.The most ideal retention is 50%,but 75%retention may also give a satisfactory outcome of separation.20 mL sample solution(5 mg/ mL)was injected using an injection valve.The effluent from the tail end of the column was continuously monitored with an ELSD.Peak fractions were individually collected according to the chromatogram.After the separation work was completed,the column contents were forced out of the column with pressurized atmosphere.
HPLC analyses and identification of HSCCC peak fractions
HPLC analysis was performed with an Agilent/HP 1100 series(Agilent,USA)equipped with an SEDEX 85 ELSD(SEDEX,France).The Agilent/HP 1100 series HPLC consisted of a vacuum degasser,a quandary pump,a thermostated column compartment,a diode array detector and an injection valve.The semi-purified extract of Semen celosiae and each purified peak fraction from the preparative HSCCC separation were analyzed by HPLC(Agilent Exlipse XBD C18column,5 μm,4.6 mm ×250 mm)with acetonitrile-0.1%glacial acetic acid gradient elution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min,and column temperature was 30℃.ELSD data were as follows:drift tube temperature 40℃ and pressure 0.3 Mpa.The purified fractions of celosins A and B obtained from the preparative HSCCC separation were analyzed by13C NMR(Bruker DMX-600 NMR) and EI-MS(Varian MAT-212 MS).
Results and Discussion
Selection of a solvent system
To achieve a successful separation in the HSCCC experiment,a good solvent system must be found with an ideal partition coefflcient(K) for the target compounds.The most suitable K value of the target compounds is close to 1.In our experiment,the two compounds must have different K-values if they want to be separated by one solvent system.According to the solubility of celosins A and B,a dichloromethane system was used.The procedures of finding the suitable K-value are shown in Table 1.After comparison of different ratios,the system of dichloromethane-methanol-n-butanol-water(4∶3∶0.3∶2,v/v/v)with addition of 0.5% glacial acetic acid was used.The purpose of adding 0.5%glacial acetic acid was to prevent the target compounds from being ionized,simultaneously augmenting their organo-phobicity.This measure made the saponins more easily dissolve in the solid phase,thus enlarged the K value.

Table 1 K-value of celosins A and B in different two-phase solvent systems

Fig.1 HSCCC chromatogram of the main saponins prepared from Semen celosiae.Solvent system:
To find the most suitable experiment condition,other factors including the revolution speed of the separation column,the flow rate of the mobile phase and the separation temperature were also investigated.It was found ultimately that the best separation was achieved at a 2.0 mL/min flow rate,an 850 rpm revolution speed and 25℃ separation temperature.Fig.2 shows the preparative HSCCC separation chromatogram.30.5 mg celosin A and 10.7 mg celosin B were obtained from 100 mg major saponins.
HPLC analysis
The HPLC analysis method was referenced in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia(2005).The crude samples and peak fractions separated by HSCCC were analyzed by HPLC(Fig.3)under the analytical conditions as shown in Table 2.Addition of 0.1%glacial acetic acid was aimed at a better peak separation and a more beautiful presentation of the figure.The purified samples of celosins A and B were made by comparison of the retention time with the standard.The results showed that peak 1 corresponded to celosin B,and peak 2 to celosin A.Their purity was 98.1%and 98.9%,respectively.In addition,using water as the blank space contrast excluded the interference of the solvent peak.

Table 2 The gradient elution using acetonitrile-0.1%glacial acetic acid
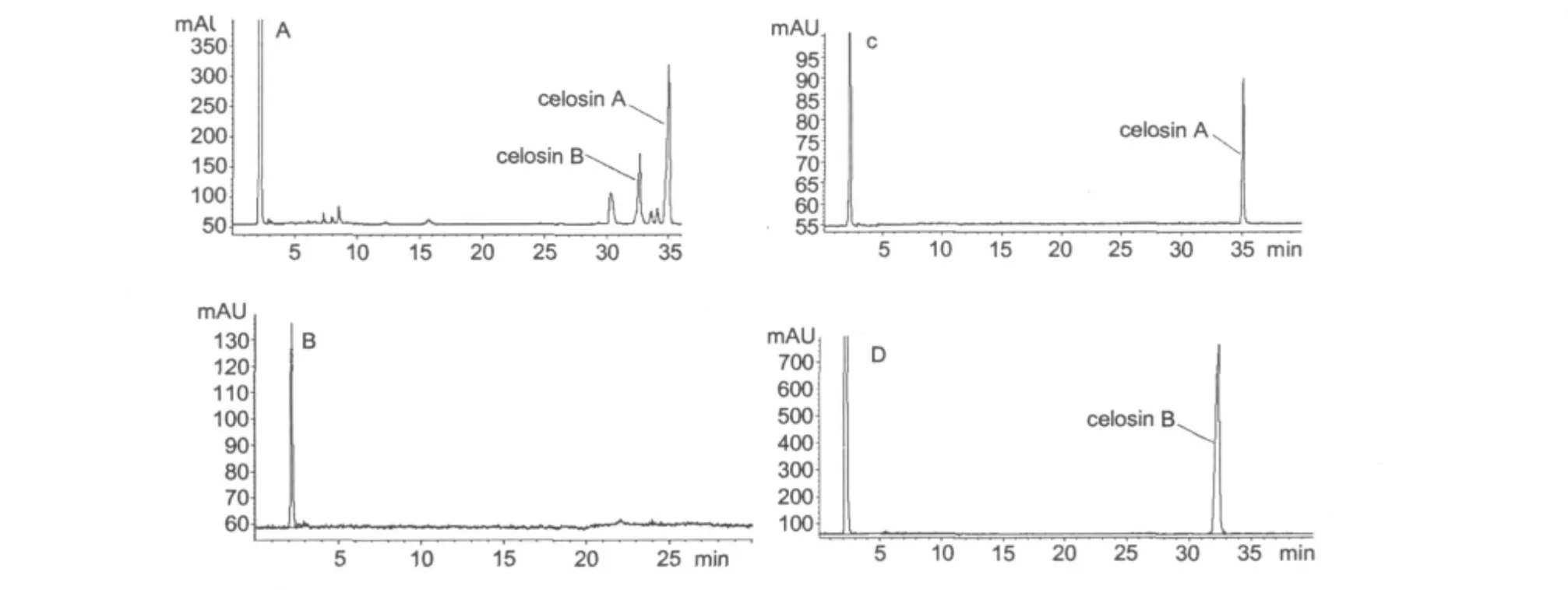
Fig.1 HPLC chromatogram of major saponins from Semen celosiae(A),the blank space contrast using water as the (B),peak 1 from preparative HSCCC(C),and peak 2 from preparative HSCCC(D).solvent
Structural identication
The two compounds were both obtained as yellow amorphous powder,with a positive reaction when they were dealt with the Liebermann-Burchard and Molish regents[11].Their structures were identified and confirmed by EI-MS and13C NMR(Table 3).Celosin A:HR-FABMS(m/z):817.6762[M+Na]+(Calcd.for C41H62O15Na,817.6755);celosin B:HR-FAB-MS(m/z):863.6412[M+Na]+(Calcd.for C42H64O17Na,863.6418).

Table 3 13C NMR(100 MHz)spectral data of two compounds in C5D5N+D2O(δ,ppm).

46.9 47.2 GlcA-3' 75.9 75.8 10 35.1 34.9 GlcA-4' 72.7 72.5 11 22.4 21.6 GlcA-5' 74.6 75.1 12 121.4 120.1 GlcA-6' 174.5 174.3 13 143.8 144.7 Ara-1? 103.7 14 41.2 40.9 Ara-2? 70.2 15 26.8 26.8 Ara-3? 73.6 16 22.7 22.5 Ara-4? 67.8 17 45.8 46.2 Ara-5? 65.5 18 40.9 41.2 Gal-1?' 102.3 19 45.4 45.9 Gal-2?' 72.8 20 29.7 29.5 Gal-3?' 73.7 21 33.1 33.2 Gal-4?' 68.9 22 31.3 31.4 Gal-5?' 74.8 23 207.4 184.2 Gal-6?' 60.2 9 24 10.4 13.2
Conclusions
The results of our present studies demonstrated that separation and purification of celosins A and B by HSCCC and ELSD were successful and effective with a high purity(98.9%and 98.1%respectively).The successful separation of the two saponins could be a valuable reference to the isolation of other saponins from Semencelosiae.HSCCC coupledwithELSD proved to be a feasible method for separating components without UV absorption from natural products.
1 Fujian Science and Technology Committee and Writing Group of Flora of Fujian,Flora of Fujian.Fuzhou:Fujian Science and Technology Press,1982.553-554.
2 Institute of Materia Medica Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences,Chin Tradit Chin Med,Beijing:People’s Health Publishing House,1984.441-444.
3 Hase K,Kadota S,Basnet P,et al.Immunostimulating activity of celosian,an antihepatotoxic polysaccharide isolated from Celosia argentea.Planta Med,1997,63:216-219.
4 Degenkolb T,Cai Y,Schmidt J,et al.Betalains of Celosia argentea.Phytochemistry,2001,58:159-165.
5 Kobayashi J,Suzuki H,Shimbo K,et al.Celogentins A-C,new antimitotic bicyclic peptides from the seeds of Celosia argentea.J Org Chem,2001,66:6626-6633.
6 Morita H,Suzuki H,Kobayashi J.Celogenamide A,a new cyclic peptide from the seeds of Celosia argentea.J Nat Prod.2004,67:1628-1630.
7 Suzuki H,Morita H,Iwasaki S,et al.New antimitotic bicyclic peptides,celogentins D-H,and J from the seeds of Celosia argentea.Tetrahedron,2003,59:5307-5315.
8 Suzuki H,Morita H,Shiro M,et al.Celogentin K,a new cyclic peptide from the seeds of Celosia argentea and X-ray structure of moroidin.Tetrahedron,2004,60:2489-2495.
9 Fu HZ,Meng XS,Li SS,et al.Study of chemical constituents of Semen celosiae.Chin Tradit Herb Drugs,1992,23:344-345.
10 Xue Q,Guo ML,Zhang G.Study of chemical constituents of Semen celosiae.Pharm Care&Res,2006,6:345-347.
11 Xue Q,Guo ML,Sun ZL,et al.Two new compounds from Semen celosiae and the protective effects against CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity.Nat Prod Res,2009,doi:10.1080/ 14786410902833948.
12 Sun ZL,Wang Y,Li YX,et al.Two new hepatoprotective saponins from Semen celosiae.Fitoterapia,2010,81:375-380.
13 Ito Y.Golden rules and pitfalls in selecting optimum conditions for high-speed counter-current chromatography.J Chromatogr A,2005,1065:145-168.

