聯合檢測CRP、D-二聚體和CEA在診斷胸腔積液性質中的意義
張衛東
聯合檢測CRP、D-二聚體和CEA在診斷胸腔積液性質中的意義
張衛東
目的 探討聯合檢測C反應蛋白(CRP)、D-二聚體和癌胚抗原(CEA)在診斷胸腔積液性質中的意義。方法 收集76例惡性胸腔積液患者(試驗組)和58例結核性胸腔積液患者(對照組)的胸腔積液標本, 檢測胸腔積液中CRP、D-二聚體和CEA的數值, 并進行統計學分析。結果 試驗組D-二聚體和CEA的陽性率顯著高于對照組, 差異有統計學意義(P<0.05或P<0.01), 而CRP含量卻顯著低于對照組, 差異有統計學意義(P<0.01)。結論 CRP、D-二聚體和CEA的聯合檢測可提高對胸腔積液性質診斷的準確性。
C反應蛋白 ;D-二聚體;癌胚抗原 ;胸腔積液
胸腔積液是呼吸內科常見的疾病表現, 主要包括結核性與惡性腫瘤性胸腔積液, 惡性胸腔積液多由肺癌引起, 但是臨床上缺乏敏感性和特異性較高的檢查手段, 以致于影響到二者之間的診斷與鑒別診斷, 部分病例難以獲得快速明確的診斷, 以致延誤病情, 甚至影響患者生存。近年來有許多檢測指標被用于兩者的鑒別診斷, 但單一指標難以確診, 且費用高、實驗條件難以達到等無法普及。本文聯合檢測CRP、D-二聚體和CEA在胸腔積液中的含量來判斷胸腔積液的性質,現將研究結果報告如下。
1 資料與方法
1.1 一般資料 選擇本院2011年6月~2014年9月期間住院的76例惡性胸腔積液患者(試驗組)和58例結核性胸腔積液患者(對照組), 其中試驗組男52例, 女 24例, 年齡38~75歲, 平均年齡59歲, 均經纖維支氣管鏡、脫落細胞、淋巴結活檢及病理細胞學檢查確診。對照組男33例, 女25例, 年齡27~72歲, 平均年齡53歲, 均經結核菌素試驗(PPD)、結核菌培養、影像學及常規檢查確診, 抗結核治療有效。兩組一般資料比較, 差異無統計學意義(P>0.05), 具有可比性。
1.2 檢測方法 所有患者均行胸腔穿刺, 取胸腔積液5 ml,離心后取上清液, 采用免疫散射比濁法檢測CRP, 正常范圍0~10 mg/L;采用酶聯免疫吸附法測定D-二聚體, 正常范圍0~0.5 mg/L, 采用放射免疫吸附法測定CEA水平, 正常范圍0~10 μg/ml。
1.3 統計學方法 采用SPSS17.0統計學軟件進行統計分析。計量資料以均數±標準差表示, 采用t檢驗;計數資料以率(%)表示, 采用χ2檢驗。P<0.05表示差異具有統計學意義。
2 結果
CRP、D-二聚體和CEA在試驗組中的陽性率分別為28.9%、64.5%、73.7%, 在對照組中的陽性率分別為77.6%、36.2%、5.2%。試驗組D-二聚體陽性率顯著高于對照組(χ2=10.53, P<0.05);試驗組CEA陽性率顯著高于對照組(χ2=62.06, P<0.01);試驗組CRP含量顯著低于對照組(χ2=31.13, P<0.01)。見表1~3。
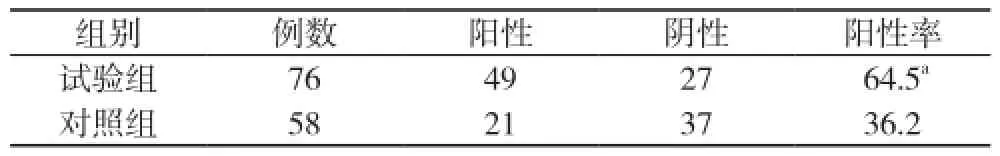
表1 D-二聚體在兩組中的陽性率比較(n, %)
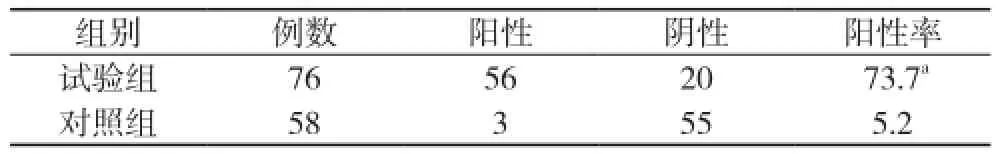
表2 CEA在兩組中的陽性率比較(n, %)
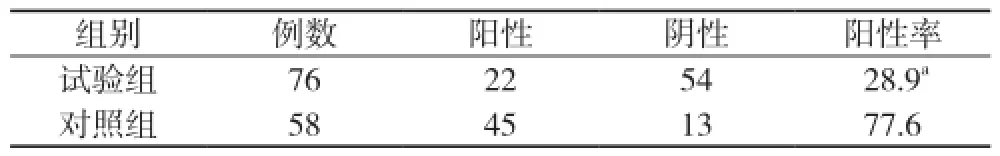
表3 CRP在兩組中的陽性率比較 (n, %)
3 討論
胸腔積液是呼吸內科常見的臨床癥狀, 病因非常復雜,常見的原因主要有結核性胸膜炎和惡性腫瘤, 目前確診主要根據胸膜活檢、胸腔積液脫落細胞學檢查, 陽性率和敏感性都不高, 且難以在大規模篩查惡性胸腔積液患者中發揮作用,難以在臨床普及[1,2], 常常造成診斷延誤, 使惡性腫瘤的治療錯過了最佳時機。
D-二聚體是纖維蛋白降解形成的特異性產物, 是體內高凝狀態和纖溶亢進的分子標記物之一。惡性胸腔積液可能因為腫瘤刺激機體啟動內、外源性凝血系統, 常伴隨著高凝狀態, 有研究發現在惡性胸腔積液患者的胸膜組織中存在局部的炎癥反應[3], D-二聚體作為高凝狀態后繼發纖溶活動增強的標志物在胸腔積液中的表達明顯增加, 有望用于惡性胸腔積液的鑒別診斷。
CEA是一種糖蛋白, 主要存在于妊娠6個月前胎兒的腸道、肝臟、胰腺中, 也是臨床上常規使用的腫瘤標志物,常用于結腸、肺、乳腺等組織的惡性腫瘤的檢測[4]。由于CEA的分子量大, 被腫瘤細胞釋放入胸腔積液后不易進入血液循環, 且未經肝臟代謝, 因此惡性胸腔積液中CEA的水平較高, 出現也早, 對良惡性胸腔積液的鑒別有一定價值[5]。有研究表明, CEA診斷惡性胸腔積液的合并敏感度為54%,特異度為94%[6]。
CRP是一種急性時相反應蛋白, 由肝臟合成, 在各種感染、外傷急性期、炎癥、自身免疫性疾病及惡性腫瘤等疾病中明顯升高, 具有調理免疫細胞、促進細胞吞噬等作用, 可以抵御外來病原體的侵入, 抵抗外界細菌感染[7]。由于結核分枝桿菌的侵入產生炎性反應使CRP升高, 國外亦有文獻報道, 胸水CRP可用于鑒別結核性胸腔積液與惡性胸腔積液[8]。
由于單一檢測指標敏感性及特異性都不高, 因此目前臨床上對于聯合檢測多種標志物來提高對惡性胸腔積液的診斷準確性已達成共識[9]。本次研究發現D-二聚體和CEA在惡性胸腔積液中的水平明顯高于結核性胸腔積液, CRP在結核性胸腔積液中的水平又明顯高于惡性胸腔積液, 聯合檢測CRP、D-二聚體和CEA在胸腔積液中的含量有助于提高診斷惡性胸腔積液的敏感度和準確度, 有較高的臨床價值。
[1] Pereira TC, Saad RS, Liu Y, et al.The diagnosis of malignancy in effusion cytology: a pattern recognition approach.Adv Anat Pathol, 2006, 13(4):174-184.
[2] Sriram KB, Relan V, Clarke BE, et al.Diagnostic molecular biomarkers for malignant pleural effusions.Future Oncol, 2011, 7(6):737-752.
[3] Vaz MA, Vargas FS, Marinho FC, et al.Does the evaluation of coagulation factors contribute to etiological diagnosis of pleural effusions.Clinics (Sao Paulo), 2009, 64(9):891-895.
[4] Alatas F, Alatas O, Metintas M, et al.Diagnostic value of CEA, CA 15-3, CA 19-9, CYFRA 21-1 and TSA assay in pleural effusions.Lung Cancer, 2001, 31(1):9-16.
[5] Gu P, Huang C, Chen Y, et al.Diagnostic utility of pleural fluid carcinomambryonic antigen and CYFRA 21-1 in patients with pleural effusion: a sytematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Lab Anal, 2007, 21(6): 398-405.
[6] Shi HZ, Liang QL, Jiang J, et al.Diagnostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen in malignant pleural effusion: a metaanalysis.Respirology, 2008, 13(4):518-527.
[7] 陳金濤.結核性胸腔積液CRP與LDH表達的臨床研究.中國現代醫生, 2012, 50(19):139-140.
[8] Yilmaz Turay U, Yildirim Z, Turkoz Y, et al.Use of pleural fluid Creactive protein in diagnosis of pleural effusions.Respir Med, 2000, 94(5):432-435.
[9] Heffner JE.Diagnosis and management of malignant pleural effusions.Respirology, 2008, 13(1):5-20.
Significance of combined detection of CRP, D-dimer and CEA in diagnosis of pleural effusion quality
ZHANG Wei-dong.Department of Respiration Medicine, Henan Pingdingshan City the Third People’s Hospital, Pingdingshan 467000, China
Objective To explore the significance of combined detection of C-reactive protein (CRP), D-dimer and Carcino embryonie antigen (CEA) in diagnosis of pleural effusion quality.Methods Pleural effusion samples of 76 malignant pleural effusion patients (experimental group) and 58 tuberculous pleural effusion patients (control group) were collected.CRP, D-dimer and CEA were tested, and the results were statistically analyzed.Results Positive rates of D-dimer and CEA were higher in the experimental group than the control group, and the difference had statistical significance (P<0.05 or P<0.01).Content of CRP was lower in the experimental group than the control group, and the difference had statistical significance (P<0.01).Conclusion The combined detection of CRP, D-dimer and CEA can improve the accuracy of diagnosis of pleural effusion quality.
C-reactive protein; D-dimer; Carcino embryonie antigen; Pleural effusion
10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2015.02.004
2014-10-15]
467000 河南省平頂山市第三人民醫院呼吸內科

